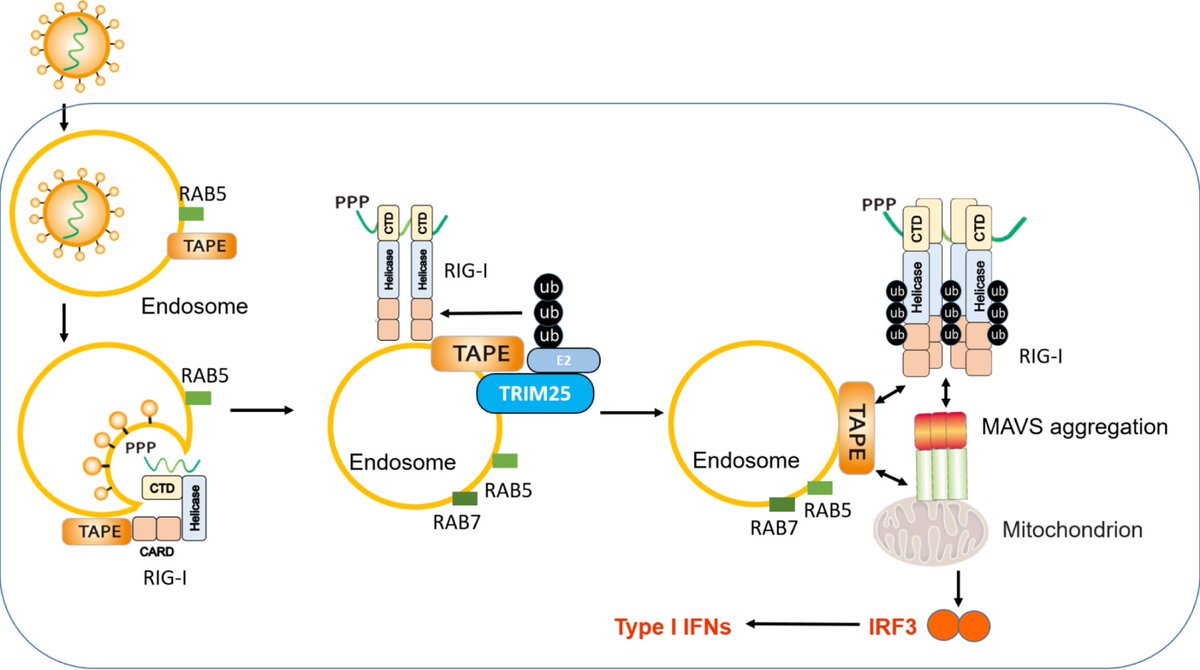
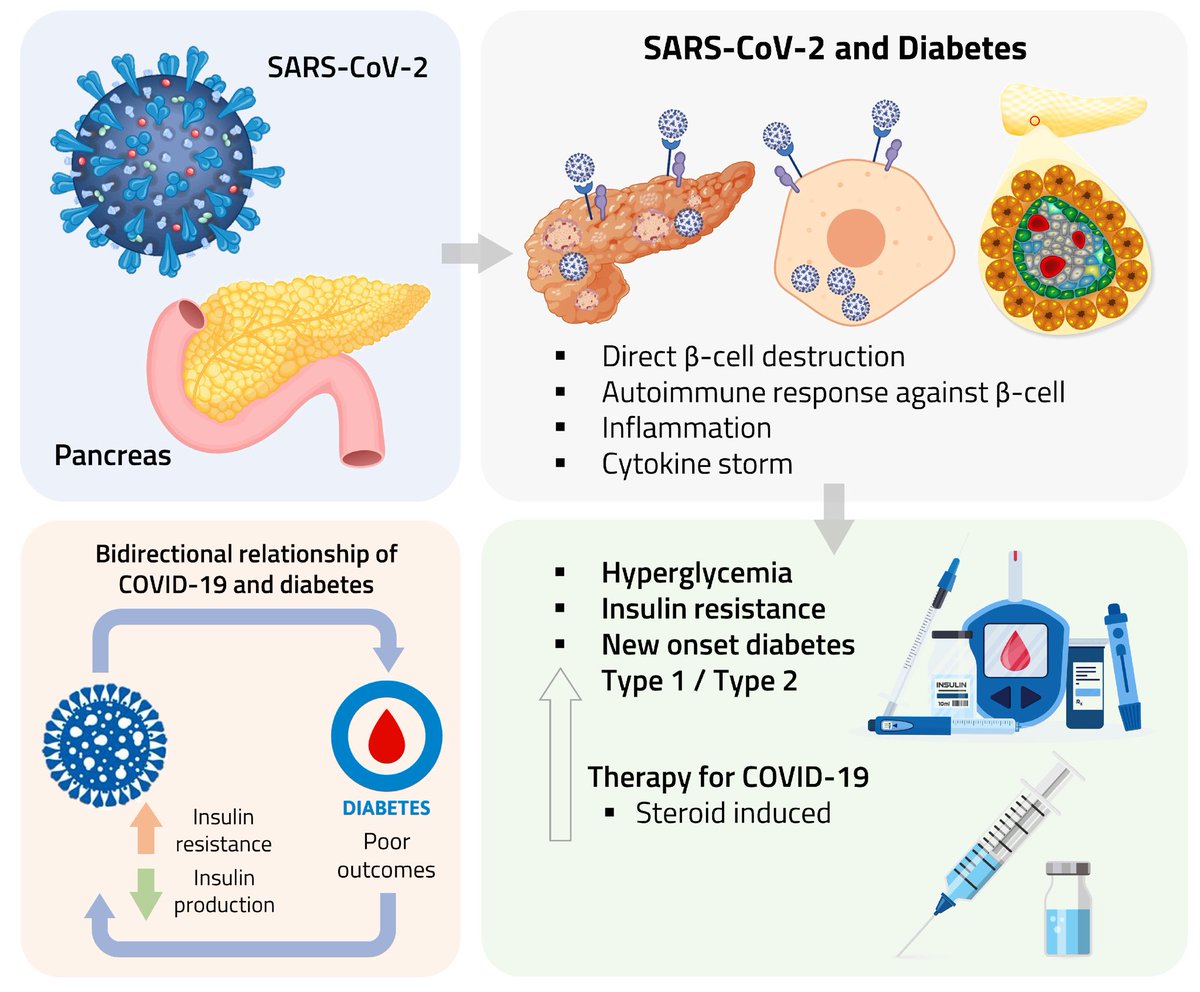
Clinical evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 directly disrupts vascular homeostasis, with perfusion abnormalities observed in various tissues. The pancreatic islet, a key endocrine mini-organ reliant on its microvasculature for optimal function, may be particularly vulnerable. 1/ 

Studies have proposed a link between SARS-CoV-2 infection and islet dysfunction, but the mechanisms remain unclear.
Here, researchers investigated how SARS-CoV-2 spike S1 protein affects human islet microvascular function. 2/
Here, researchers investigated how SARS-CoV-2 spike S1 protein affects human islet microvascular function. 2/

Using confocal microscopy and living pancreas slices from non-diabetic organ donors, they show that a SARS-CoV-2 spike S1 recombinant protein activates pericytes — key regulators of islet capillary diameter and beta cell function—and induces capillary constriction. 3/ 

These effects are driven by a loss of ACE2 from pericytes’ plasma membrane, impairing ACE2 activity and increasing local angiotensin II levels. 4/ 
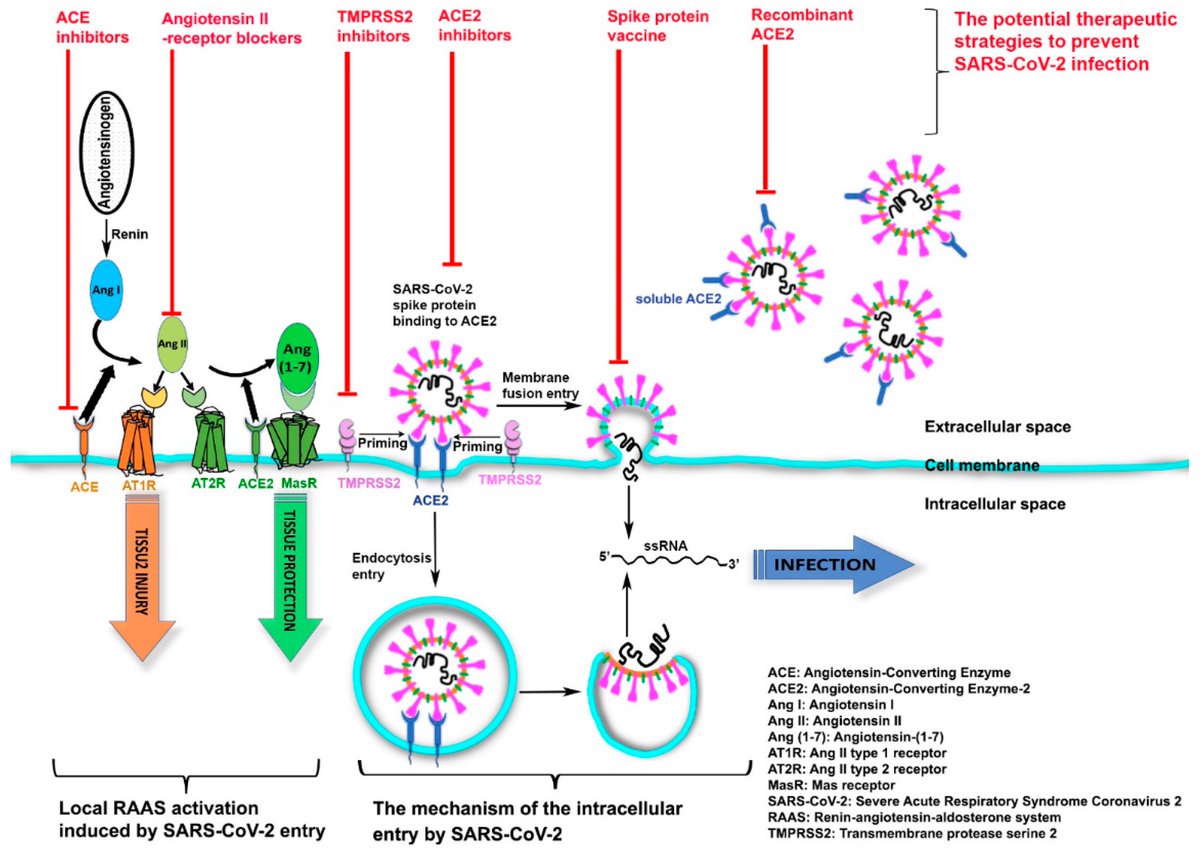
These findings highlight islet pericyte dysfunction as a potential contributor to the diabetogenic effects of SARS-CoV-2 and offer new insights into the mechanisms linking COVID-19, vascular dysfunction and diabetes. 5/5
diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/artic…
diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/artic…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh