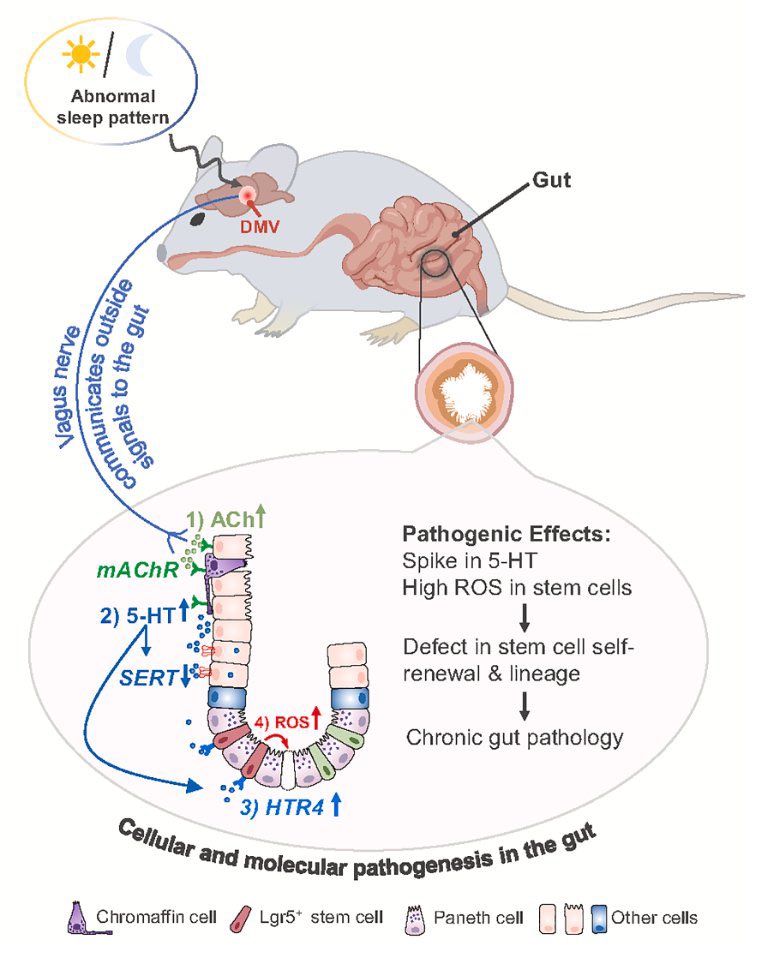
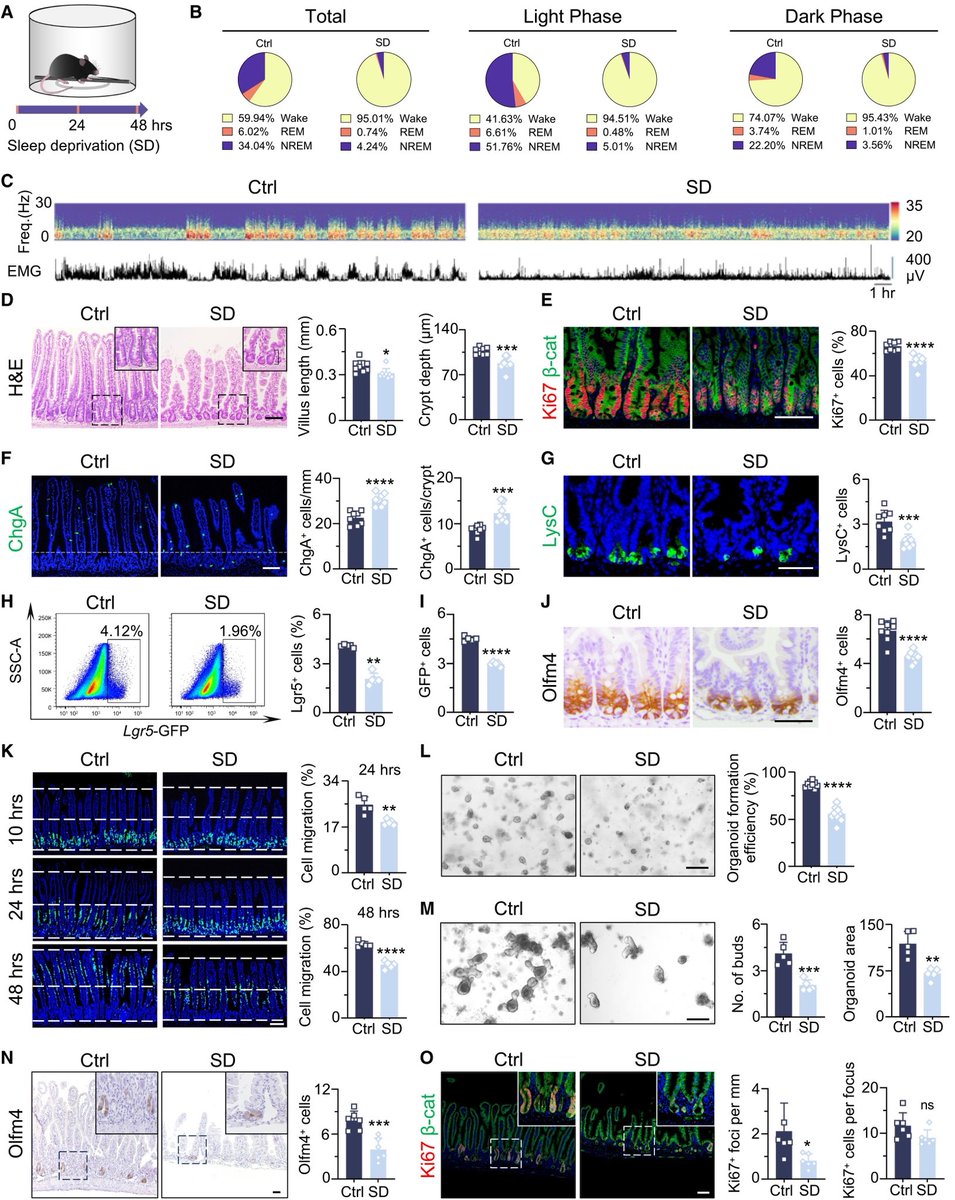
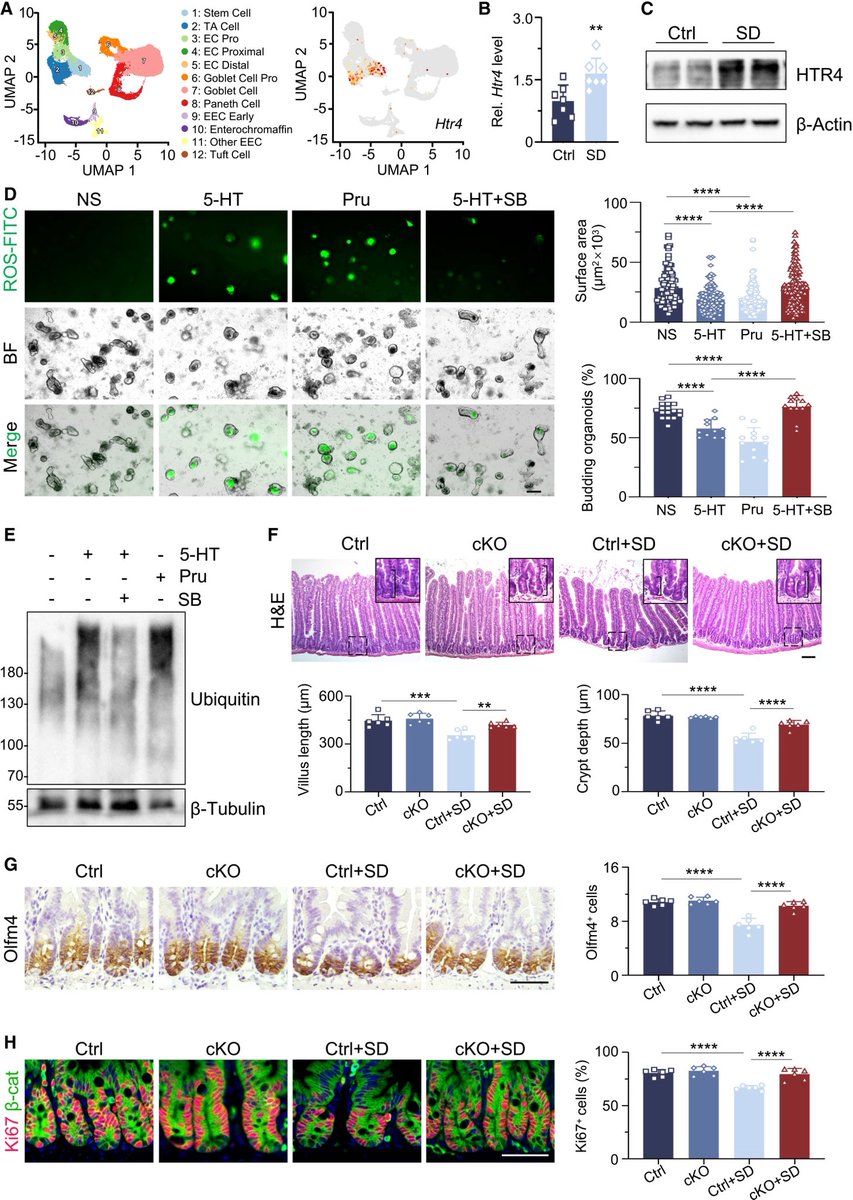
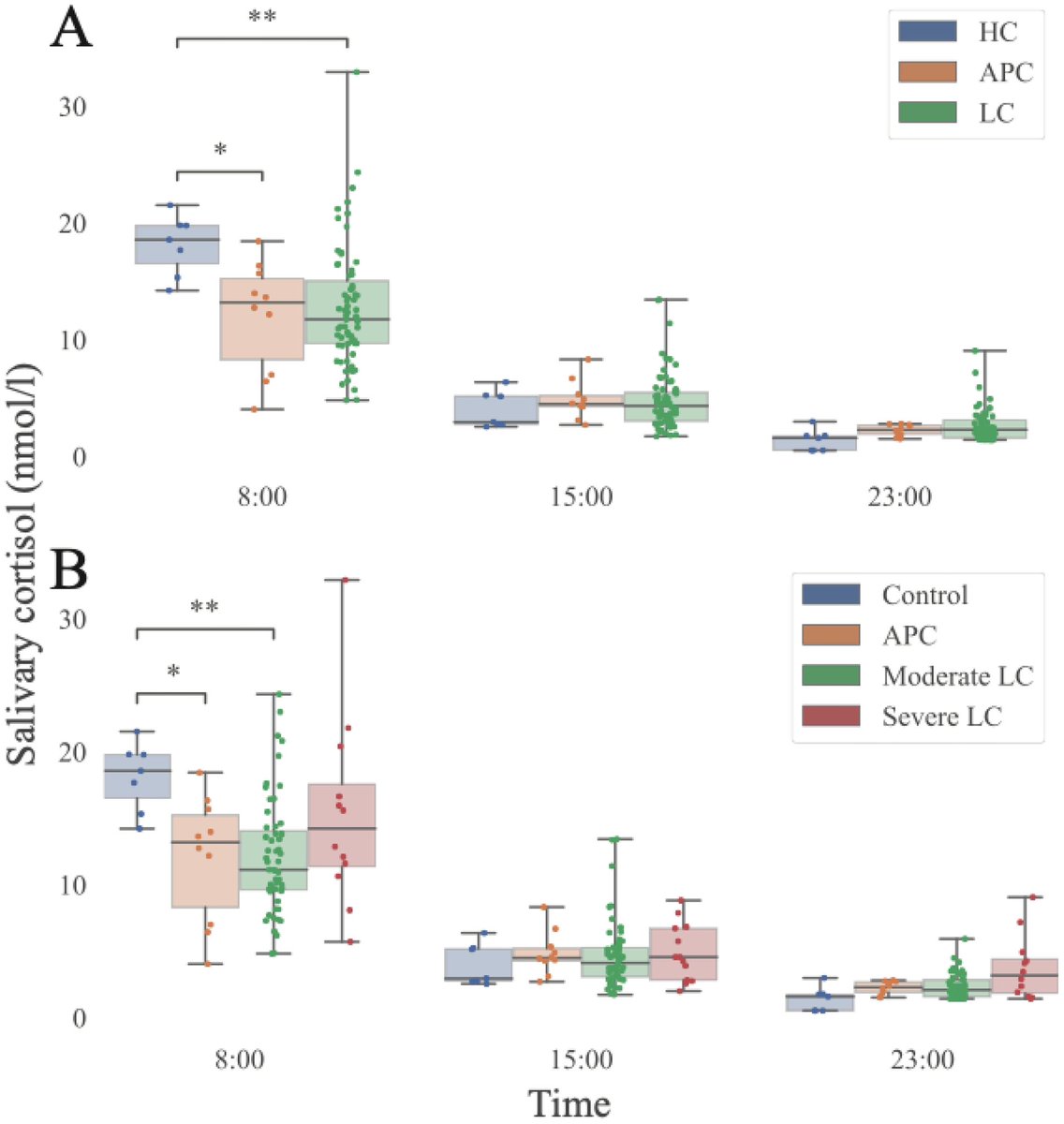
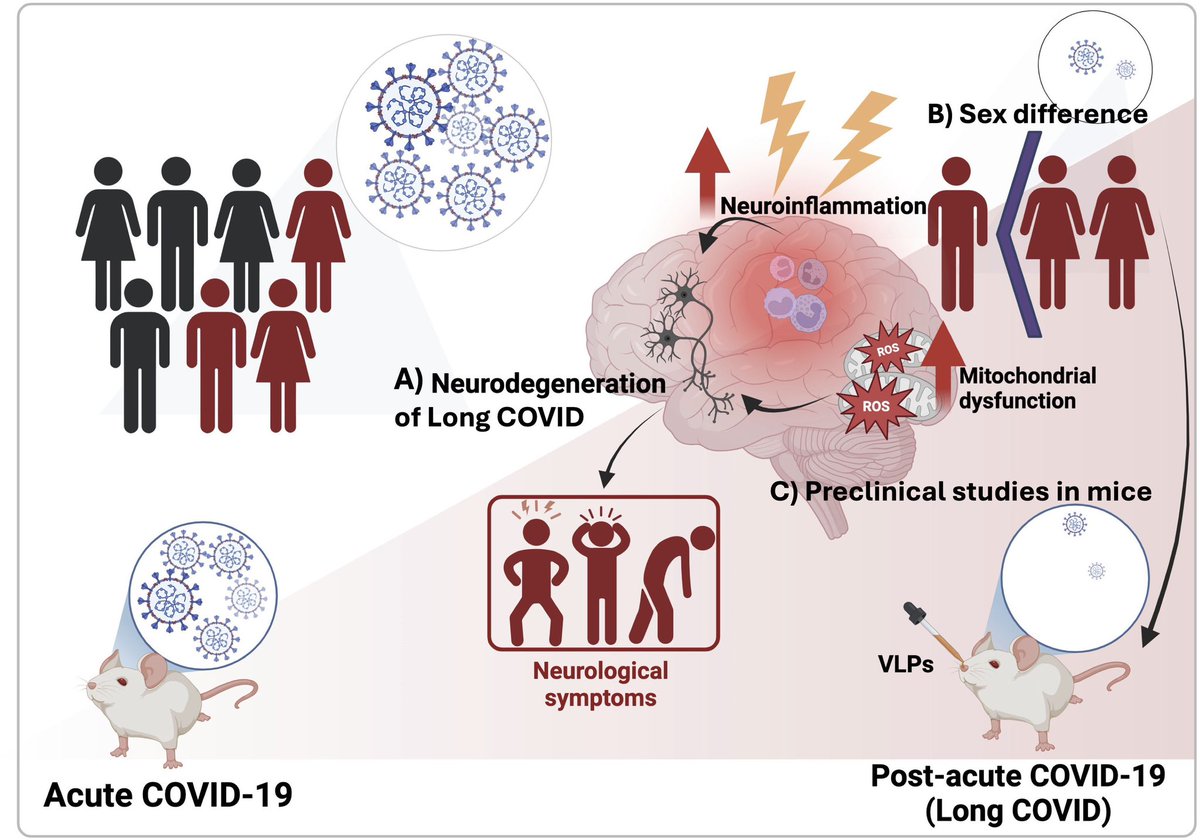
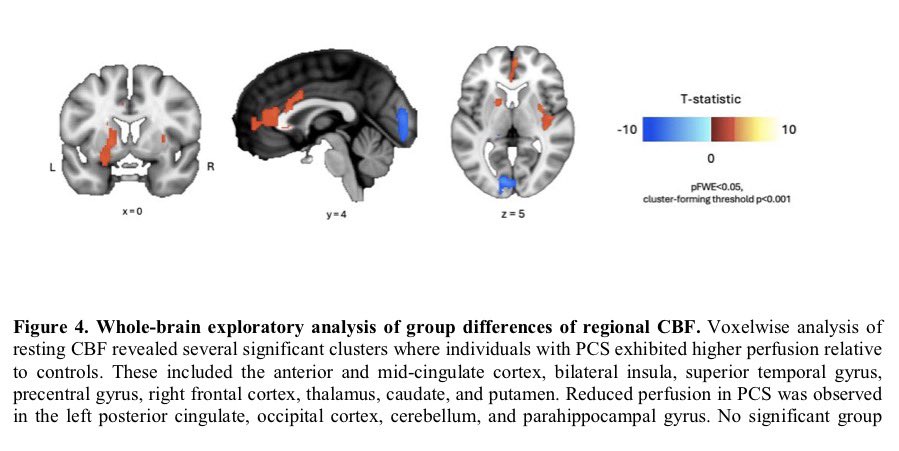
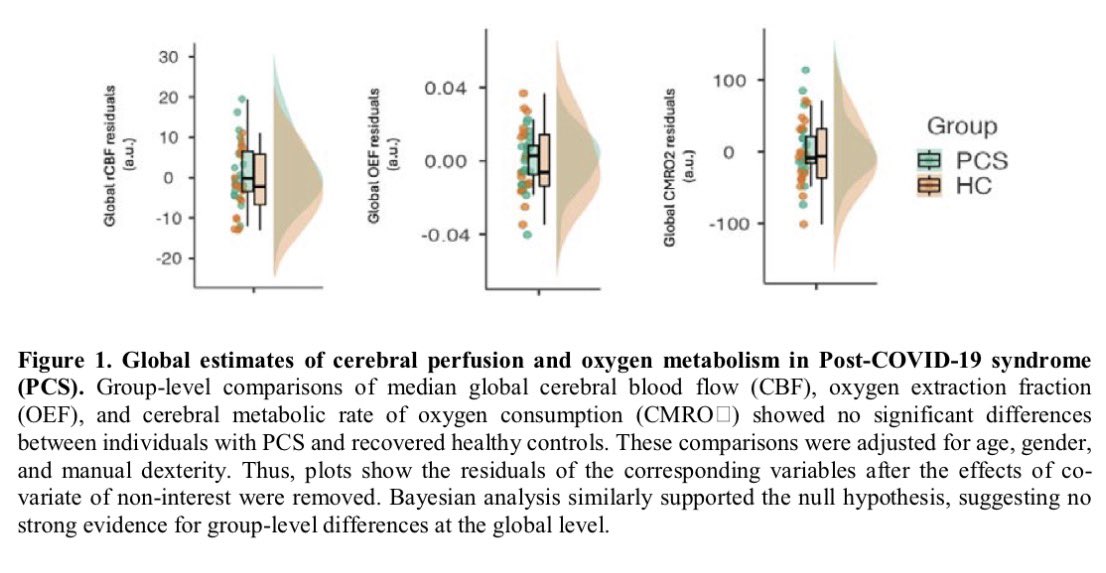
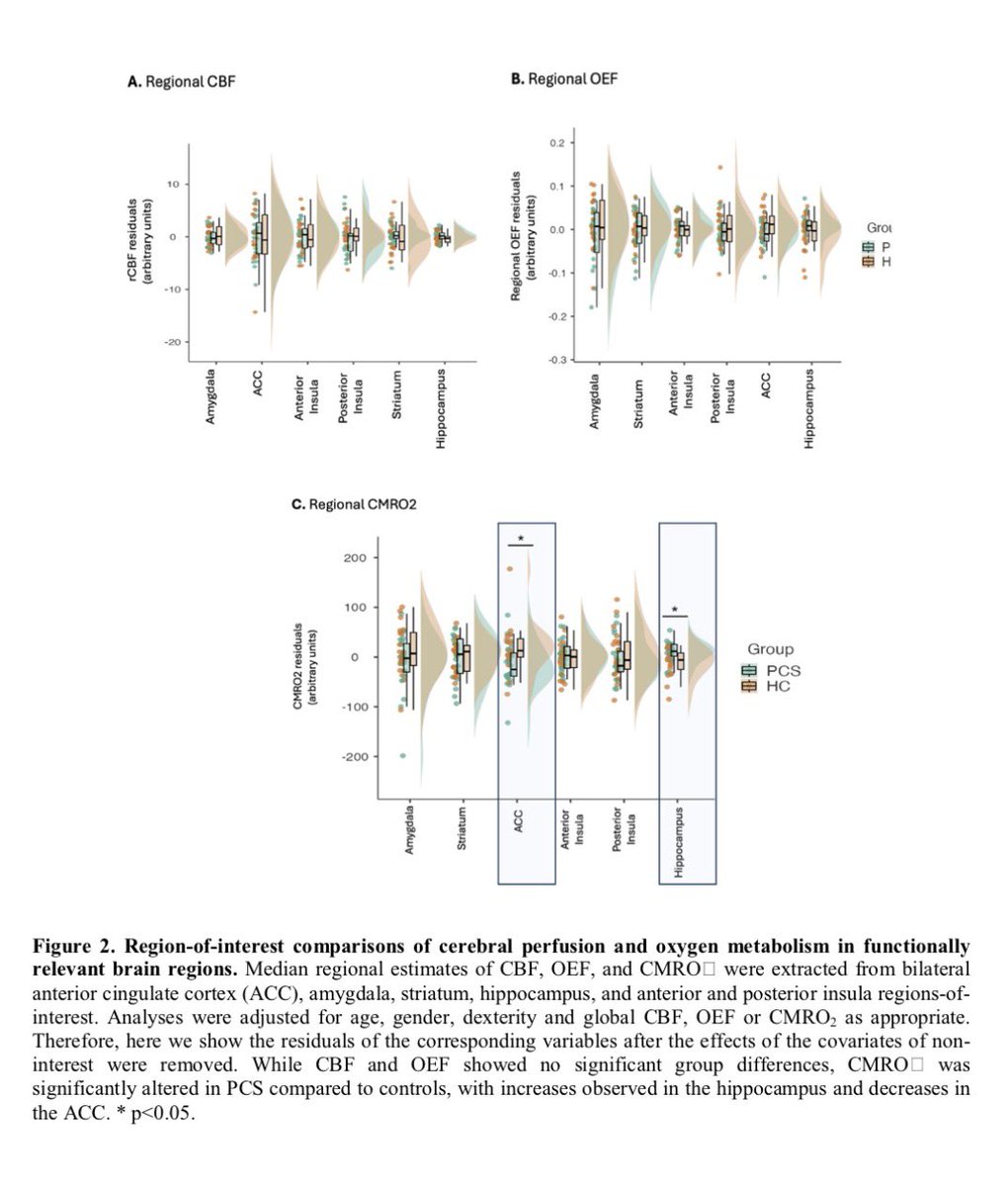
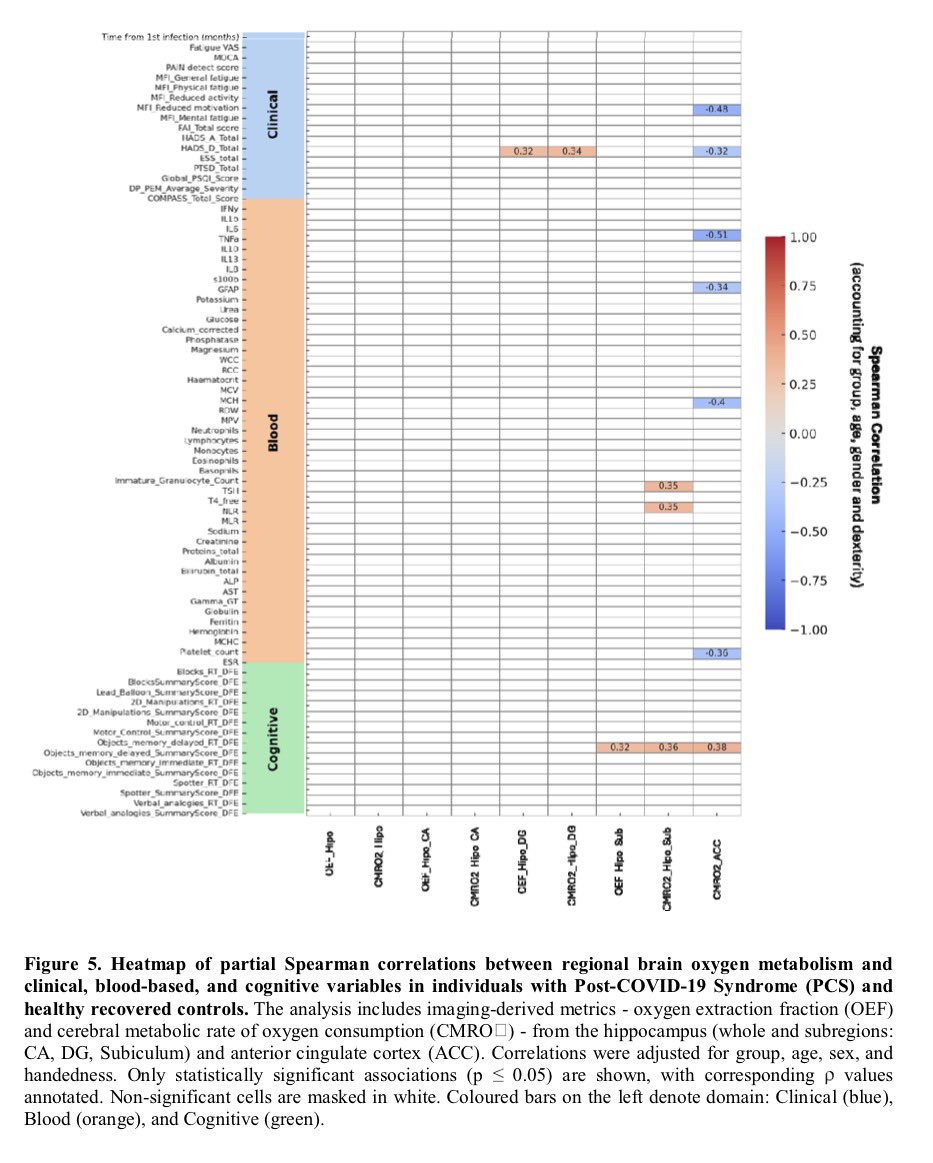
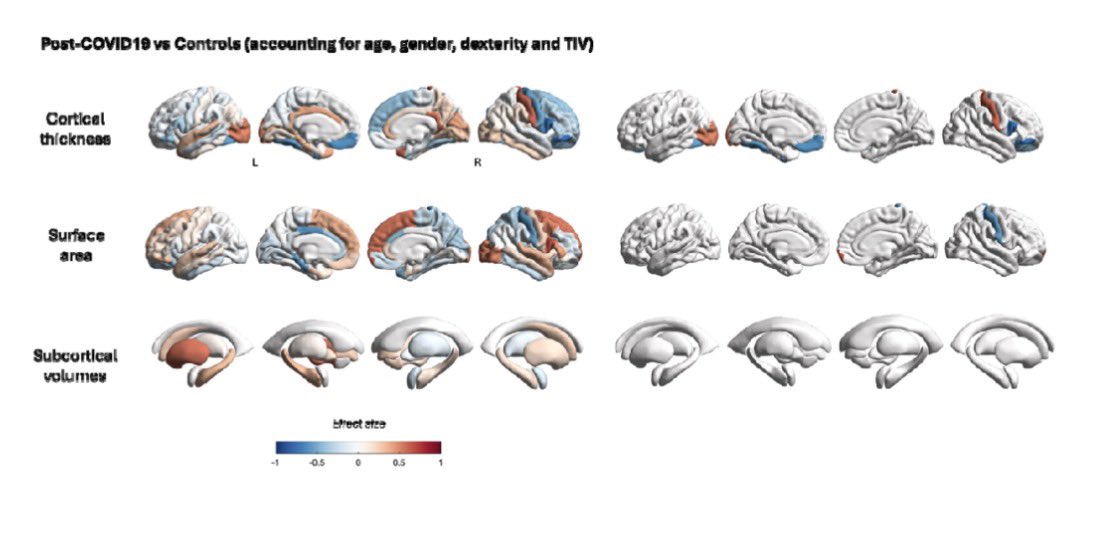
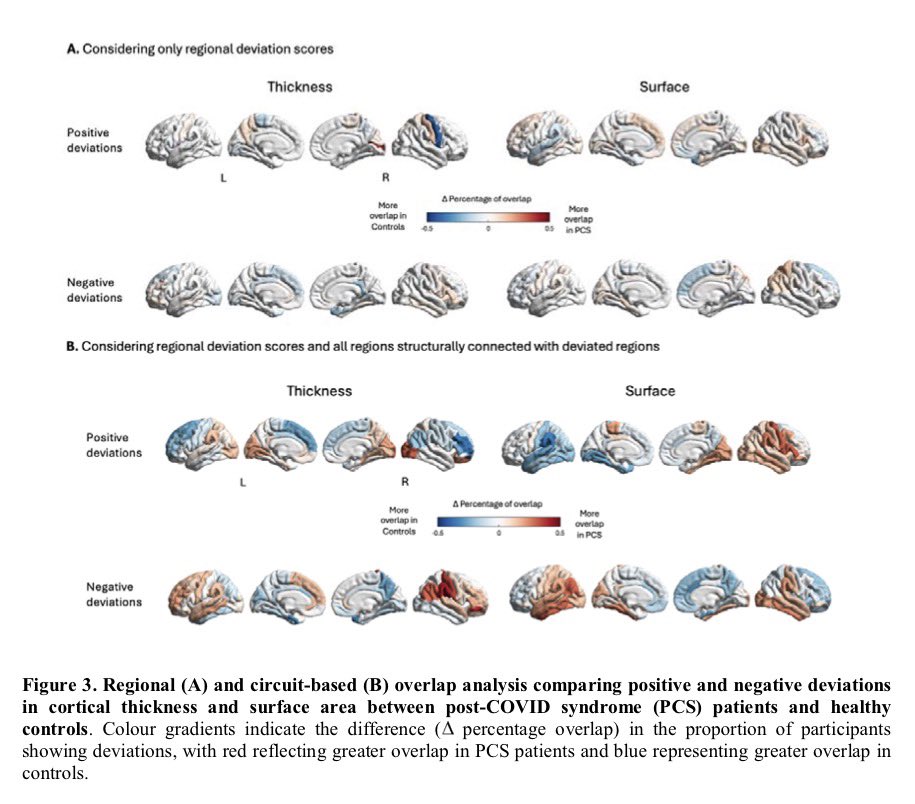
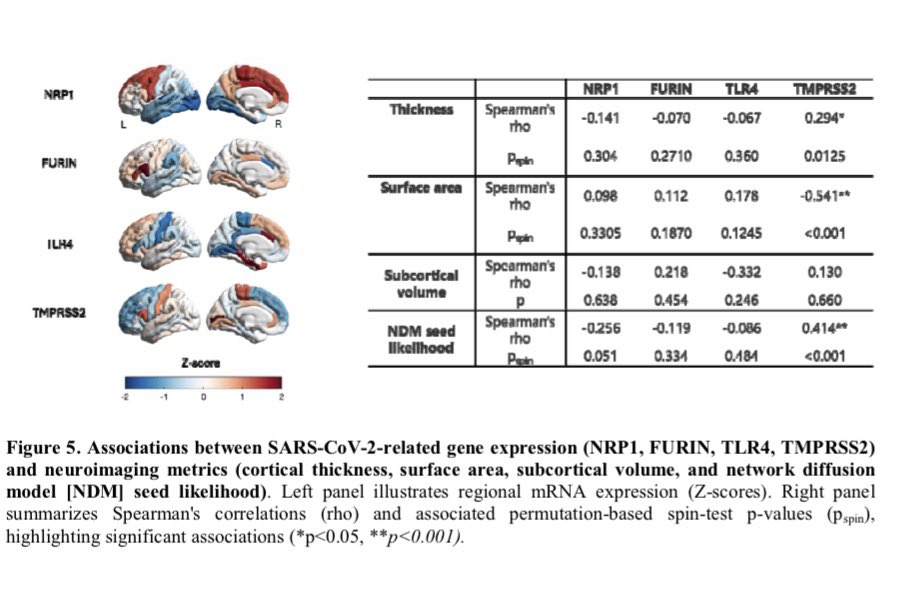
COVID pregnancies may have boosted autism risk!
A NEW study shows the onset of autism in COVID exposed babies at 28 months. Researchers found 23 of 211 children (11%), screened positive for autism spectrum disorder, compared with an expected prevalence of 1-2% at that age 1/
A NEW study shows the onset of autism in COVID exposed babies at 28 months. Researchers found 23 of 211 children (11%), screened positive for autism spectrum disorder, compared with an expected prevalence of 1-2% at that age 1/

When researchers analyzed videos of children lying on their backs in what’s called General Movement Assessment, 14% of infants showed signs of developmental problems. The test evaluates early motor functions & is often used to assess the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders 2/ 

Later, the findings proved equally troubling. At 6-8 months old, 13 of 109 infants born to infected mothers — almost 12% — had failed to reach developmental milestones. In stark contrast, all infants in a control group born before the pandemic showed normal development. 3/
Around 11.6% of toddlers born to mothers with lab-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy showed cognitive, motor or language problems indicative of neurodevelopmental delays. By comparison, only two of 128 unexposed controls — 1.6% — showed such issues. 4/ 

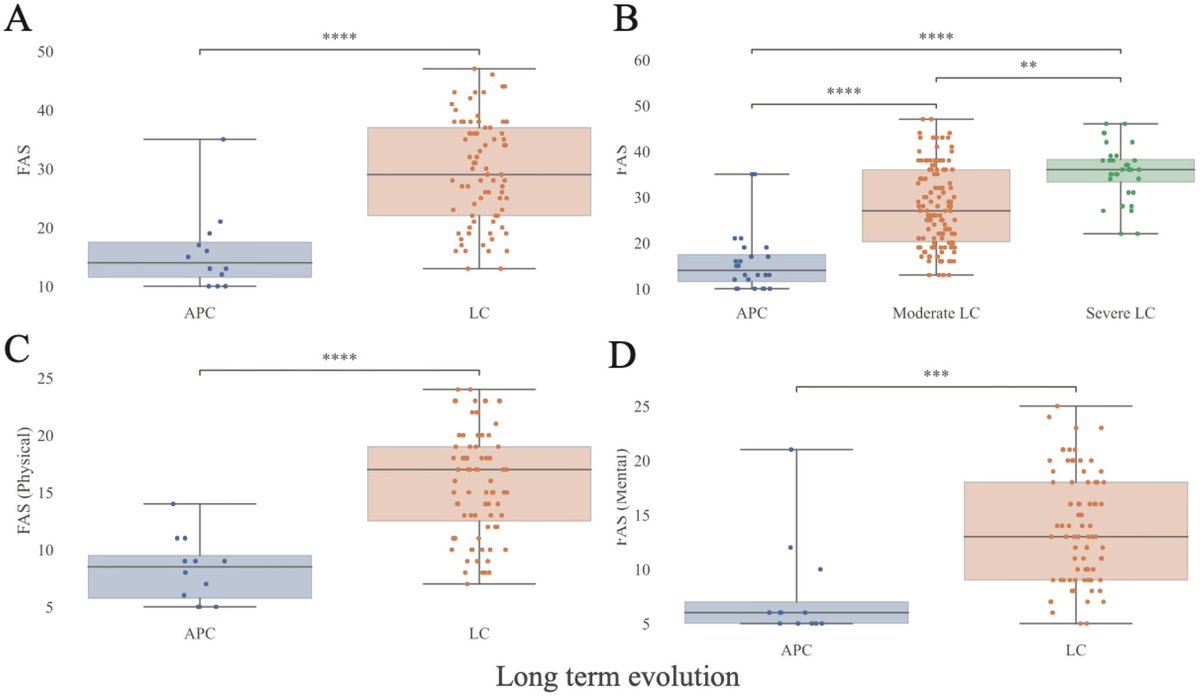
When the eldest of the COVID-exposed babies reached 28 months, the study found another concerning pattern: 23 of 211 children — almost 11% — screened positive for autism spectrum disorder. 5/
The later findings, currently undergoing peer review ahead of publication, are a reminder that COVID’s long-term consequences, including higher risks for dementia and heart disease, continue to unravel almost five years after the pandemic began. 6/. 

While the virus is generally known to cause more severe symptoms in adults than in children, emerging data suggest that babies exposed to COVID in utero face elevated risks for preterm birth, congenital heart abnormalities & rare conditions, such as situs inversus. 7/ 

Children born during the Covid era are now reaching the average age for autism diagnoses. Identifying developmental issues early can open the door to speech and behavioral therapies, which are proven to support a child’s development. 8/ 

Scientists say the full consequences of in utero exposure to the SARs-CoV-2 may take decades to uncover and understand. Even if a link is established, genetics are likely to play a crucial role. 9/ 

The researchers continue to analyze stored blood & other specimens from the babies in their study. “It’s a new pathogen. We don’t know how it behaves. Things might appear down the road that we were not expecting.” 10/10
bloomberg.com/news/articles/…
bloomberg.com/news/articles/…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh