There is no limit to our electricity bills as new spending on renewables has diminishing impact on emissions intensity. Our bills are going to infinity and beyond. A thread (1/n) 

First up, we need to acknowledge that measuring the emissions intensity of electricity generation is an imprecise science. Three different datasets from Ember, DUKES and NESO give different results although have a similar shape. (2/n) 

The numbers are also a bit of a con, because they ignore the CO2 emissions from burning trees at places like Drax. If these are added back, assuming similar emissions as for coal, the the picture is less impressive (3/n) 

Going back to the NESO data, it is clear that the main driver of reduced emissions intensity (solid orange line) has been the removal of coal from the system (grey area) (4/n) 

From a peak in 2012, emissions intensity fell from 519g/kWh in 2012 to 195g/kWh in 2019 as coal generation fell from 137TWh to single digits. Each extra GW of wind and solar capacity led to a reduction in emissions intensity of 11.9g/kWh (5/n)
Since 2019, extra emissions reductions have been hard to come by, with emissions intensity falling to 151g/kWh after an addition of a further 9.2GW of wind and solar capacity. A reduction of just 4.8g/kWh per GW of added capacity (6/n)
This is hardly a surprising result because despite big increases in wind capacity, the minimum generation has hardly changed since 2015. 1 x 0 =0, 10 x 0 = 0 and 100 x 0 = 0 (7/n) 

Looking at the dotted lines out to 2030, we first have to make an adjustment to the forecast emissions intensity. NESO and the Government decided to ignore the emissions from waste incineration and combined heat & power plants, another con. (8/n)
Adding that back means that emissions intensity falls from 151g/kWh in 2023 to 51g/kWh in 2030 after an addition of a further 81.8GW of wind and solar. This gives a measly reduction of just 0.8g/kWh per GW of extra capacity (9/n) 

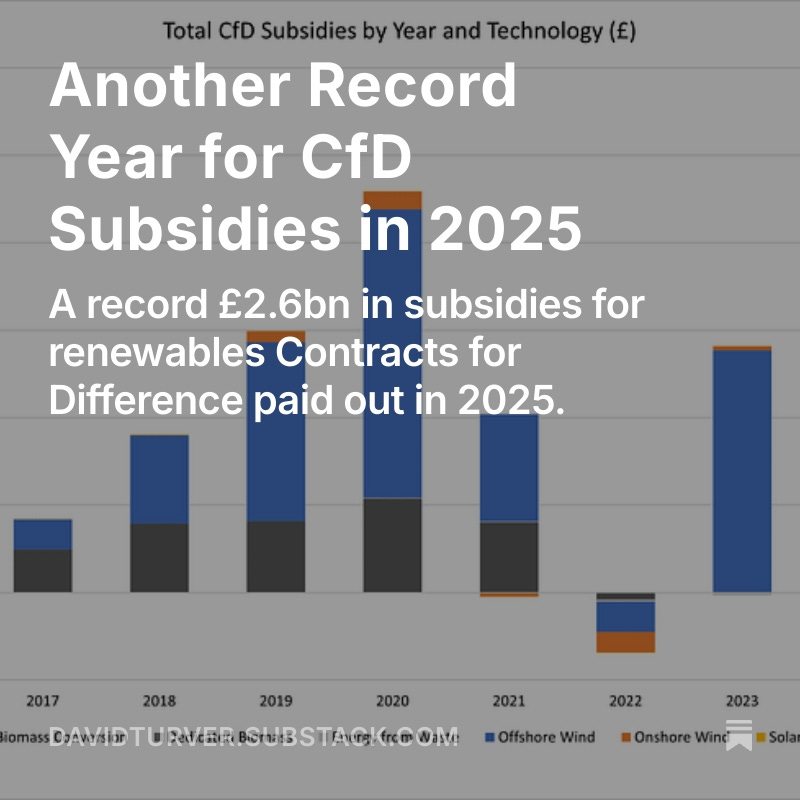
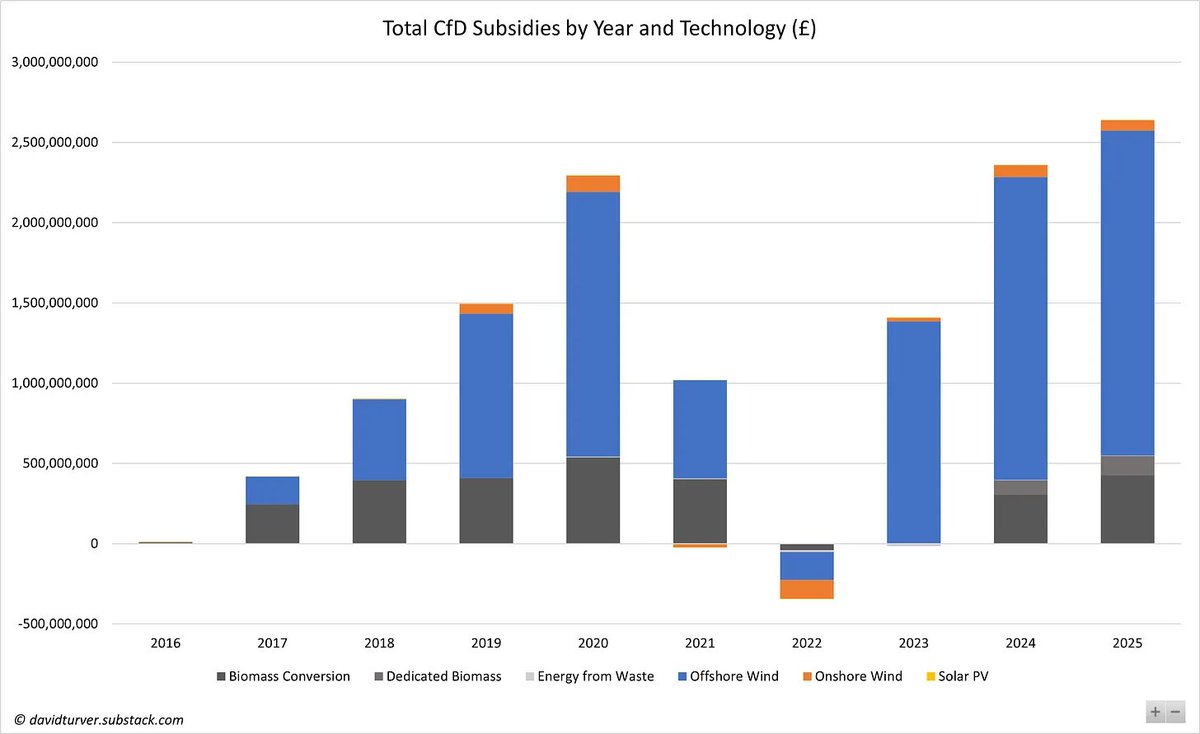
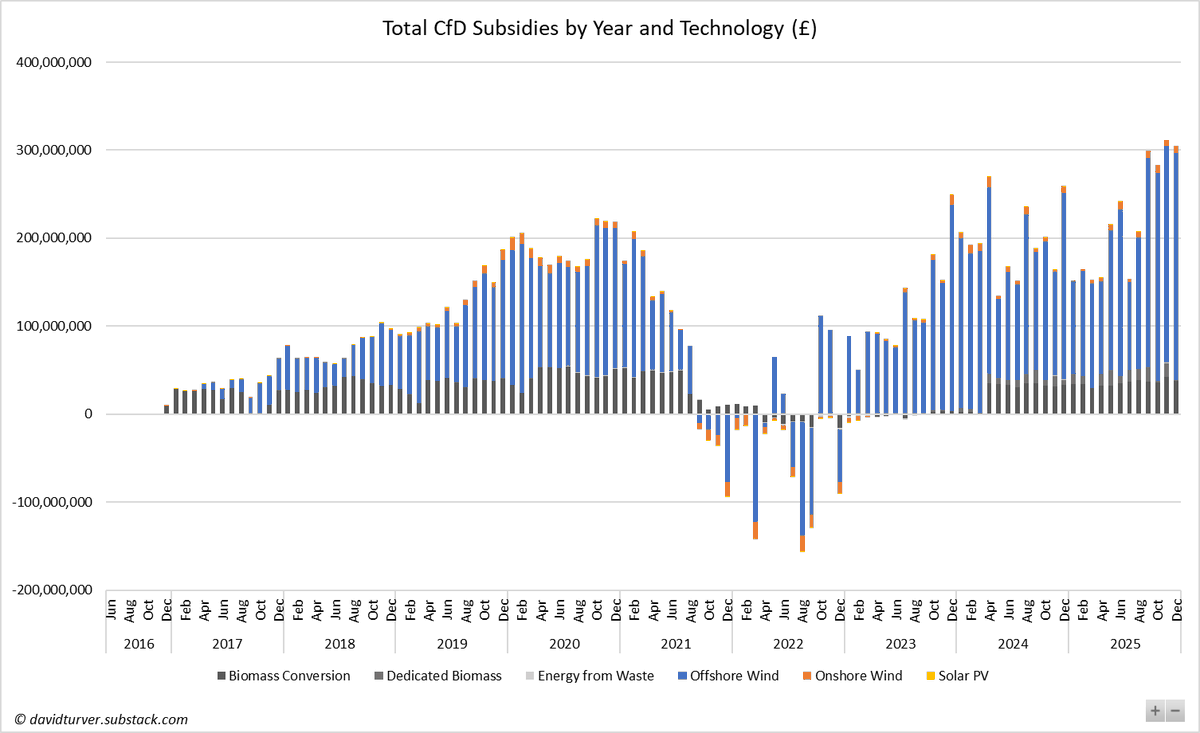
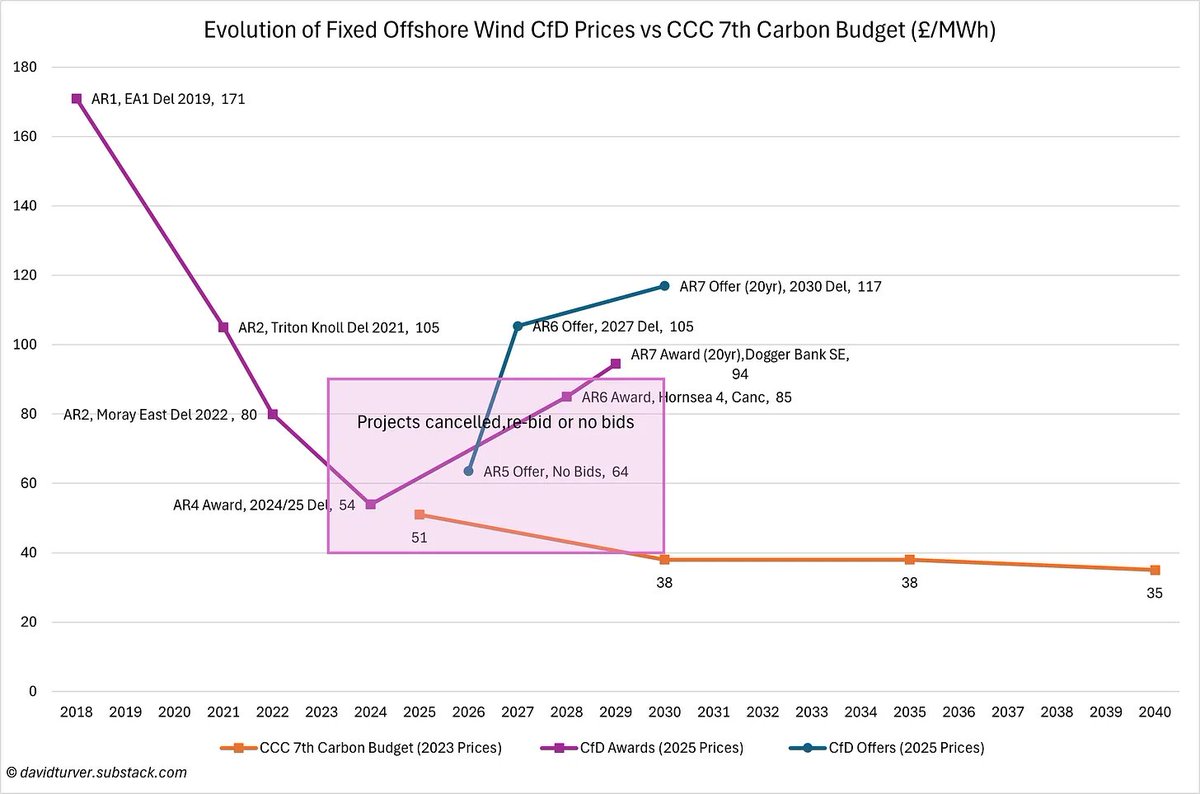
If we believe the Government can achieve the big acceleration of wind and solar deployment, NESO estimate it will cost £260-290bn. Assuming 8% cost of capital & 2% operations costs, we can expect our bills to rise by £26-29bn per annum or about £1,000 per household (10/n)
The diminishing returns on extra wind and solar capacity means that to achieve the truly "zero-carbon electricity" promised in their manifesto, Labour will send our electricity bills to infinity and beyond. (11/n)
If you enjoyed this thread please like and share. You can sign up for free to read the full article here (12/12):
davidturver.substack.com/p/to-infinity-…
davidturver.substack.com/p/to-infinity-…

Hi @threadreaderapp unroll please.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh