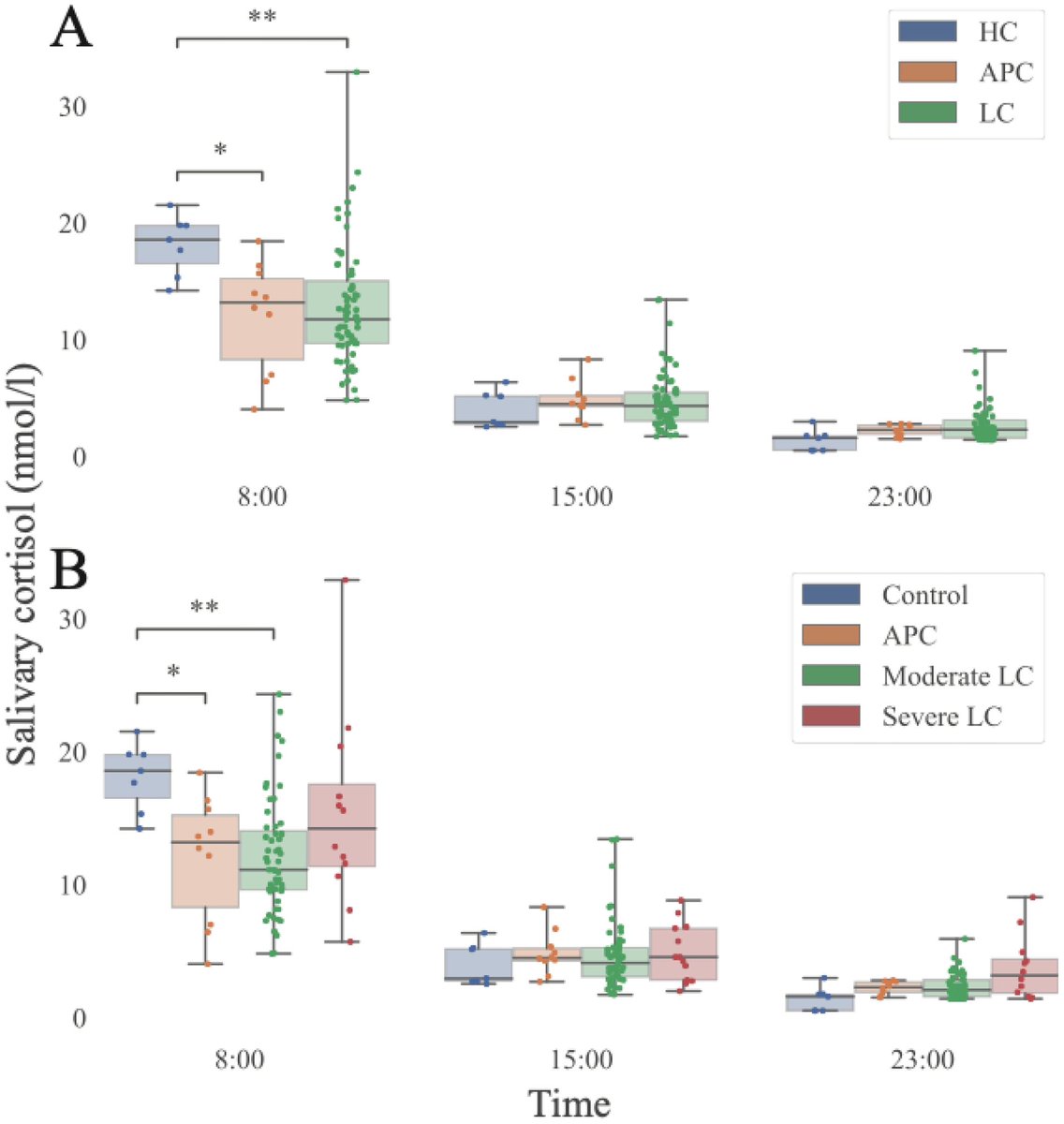
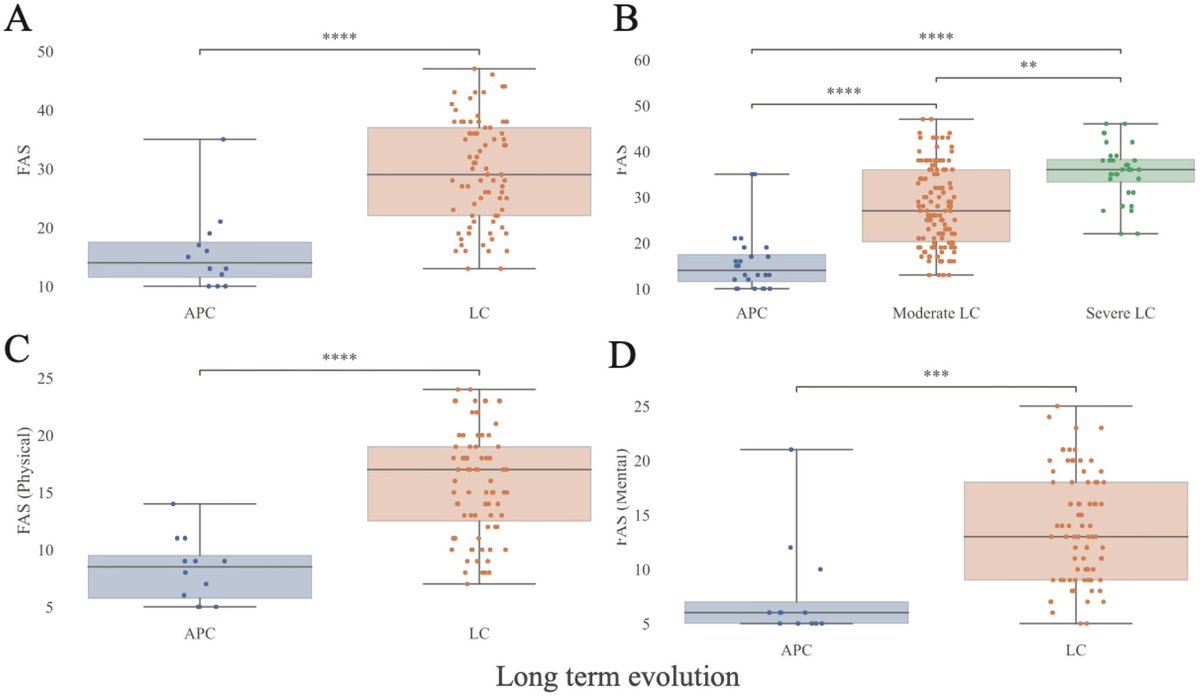
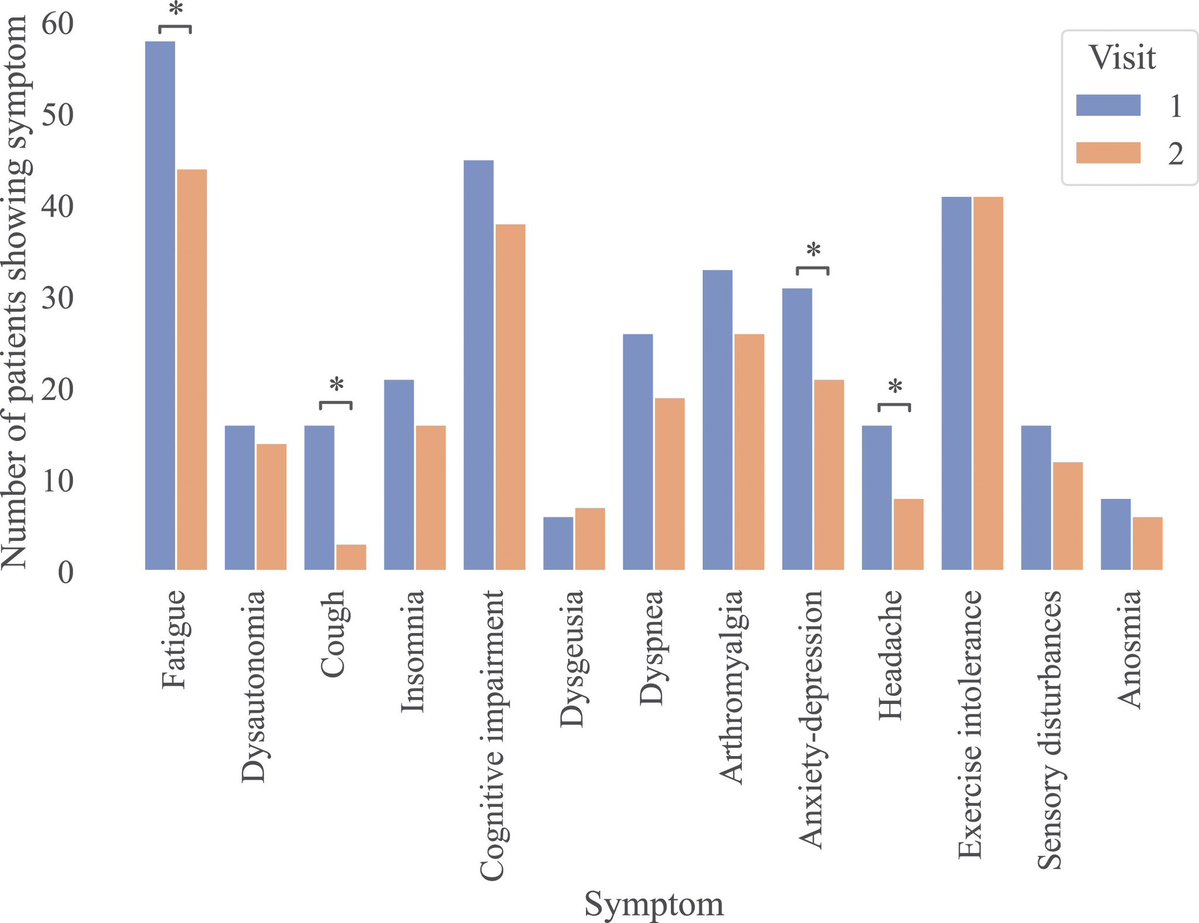
Air pollution causing brain damage of young kids!
Tissues from the brains of kids living in Mexico City show features linked to Alzheimer's disease: amyloid-ß plaques, neuronal phosphorylated tau protein tangles & frontal pyramidal immunoreactivity of DNA-binding protein 1/
Tissues from the brains of kids living in Mexico City show features linked to Alzheimer's disease: amyloid-ß plaques, neuronal phosphorylated tau protein tangles & frontal pyramidal immunoreactivity of DNA-binding protein 1/

Furthermore, the city children, with no other risk factors for brain disorders, performed comparatively poorly on cognitive tasks. 2/
It’s well established that air pollution, in the form of particulate matter, ozone or other toxic gases, contributes to asthma, lung cancer and other respiratory illnesses, and that particulate matter especially contributes to heart disease. 3/ 

Studies have shown that higher levels of air pollution are correlated with increased risks of dementia, as well as higher rates of depression, anxiety & psychosis. Researchers found links to neurodevelopmental conditions, such as autism & cognitive deficits in children. 4/ 

Neuroimaging revealed that many more children living in the highly polluted city had lesions in the white-matter tracts that connect brain regions than did children in less-polluted areas, with the prefrontal cortex seeming particularly vulnerable. 5/ 

A recent 16-year study of >200,000 residents in Scotland found that higher cumulative nitrogen dioxide exposure was associated with increased hospital admissions for mental-health and behavioural disorders 6/ 

Meanwhile, studies in France, the United States and China have documented that in regions where air quality has improved, there are decreased rates of dementia, cognitive decline and depression in older populations. 7/
Few studies have also linked air pollution to structural changes in the brain, such as reduced hippocampal volume, that are consistent with heightened dementia risk in older adults. 8/ 

Mice exposed to ultrafine particles during development — including in the womb, from their mothers’ breathing — have enlarged white-matter tracts and brain ventricles. Mice exposed during development went on to exhibit greater impulsivity and short-term memory deficits. 9/ 

In older animals, air pollution seems to accelerate the deposition of the amyloid and tau proteins associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Other animal studies have found damage at the anatomical, cellular and molecular levels. 10/ 

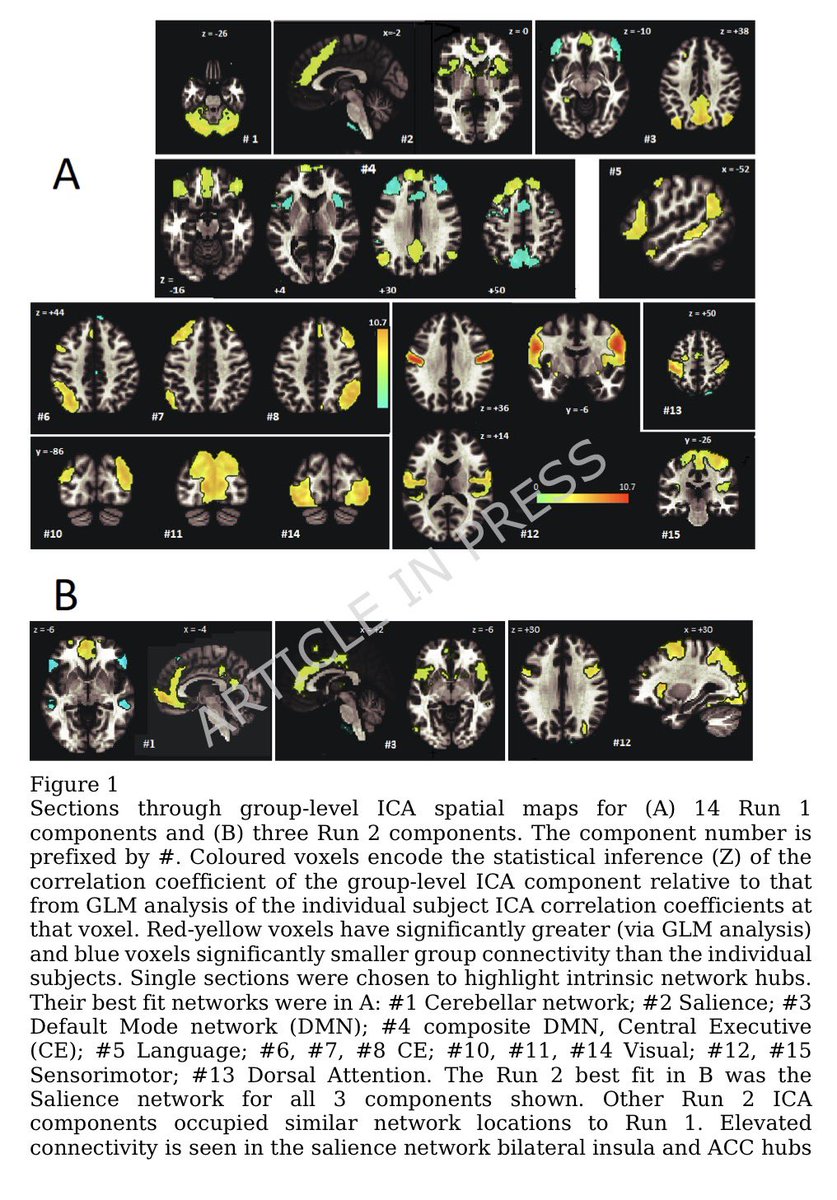
Brain scans show areas of reduced cortical thickness (coloured regions) in children exposed to higher levels of traffic pollution during their first year of life. 11/ 

Although signs of damage vary from study to study, Caleb Finch, who researches ageing at the University of Southern California, says that there is one shared facet: “It’s an inflammatory response”. 12/ 

Studies show that the genes that mediate inflammatory responses are switched on;
messengers associated with inflammation become more abundant; there are signs of oxidative stress & microglial cells that sense damage & protect neurons are activated 13/13
nature.com/articles/d4158…
messengers associated with inflammation become more abundant; there are signs of oxidative stress & microglial cells that sense damage & protect neurons are activated 13/13
nature.com/articles/d4158…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh