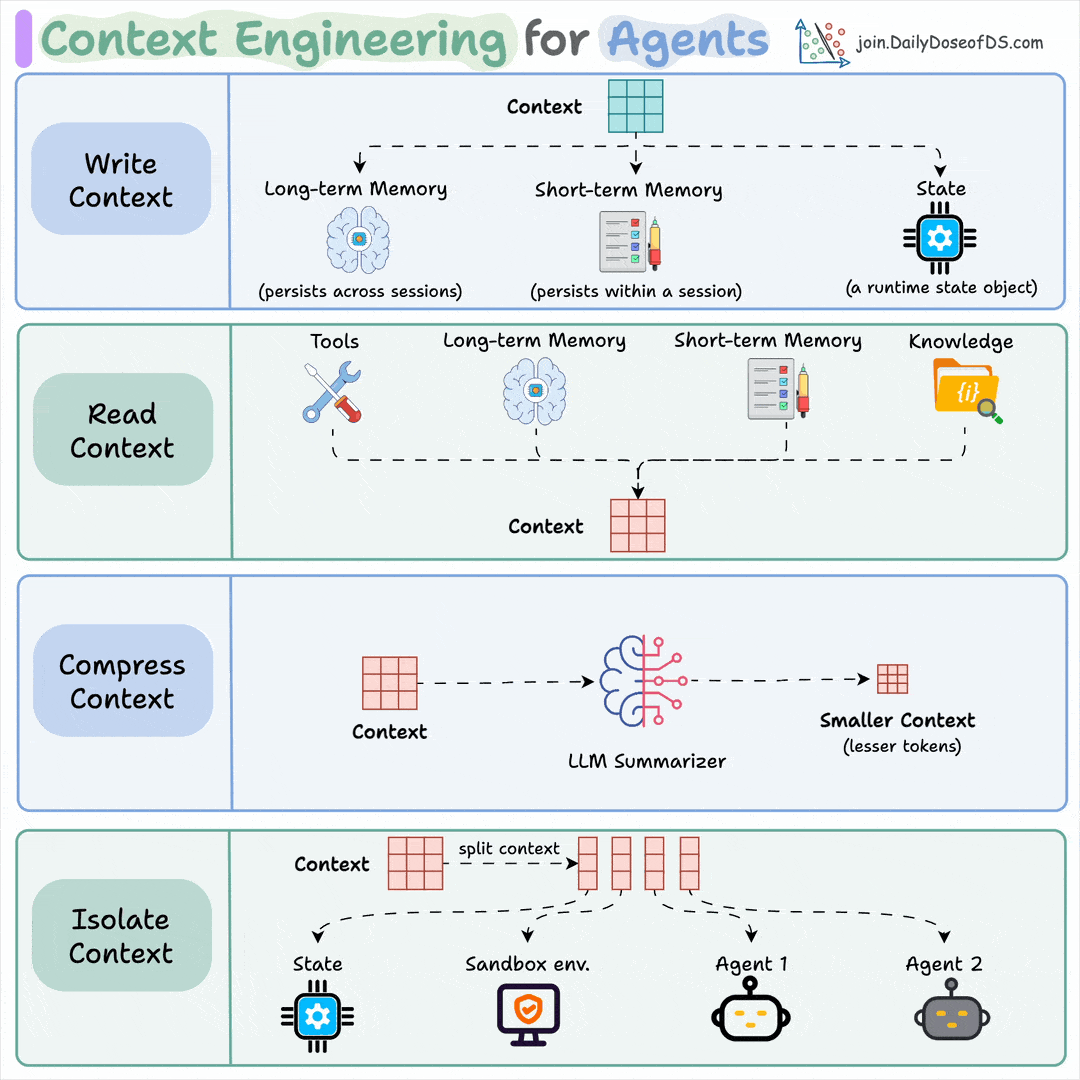
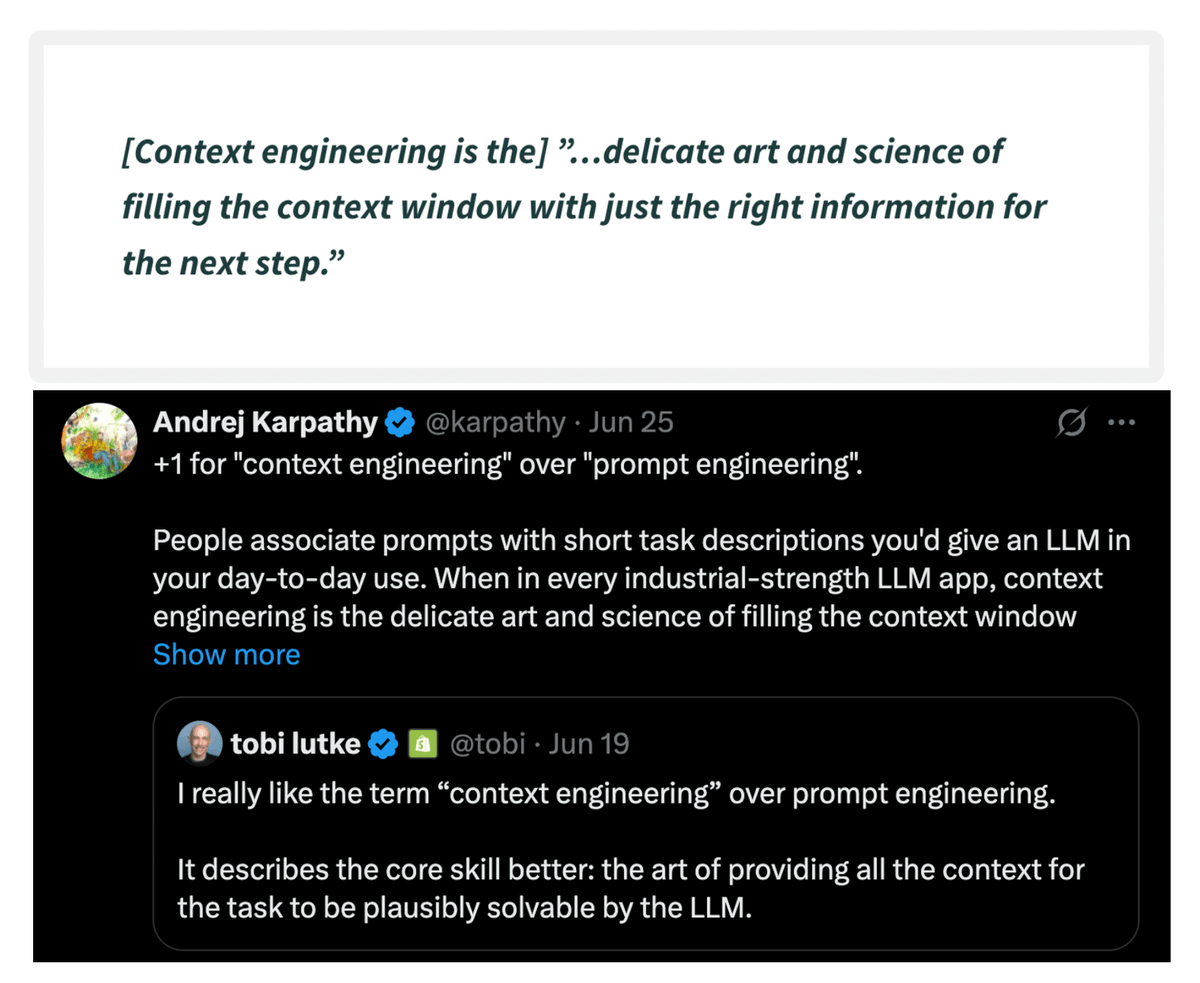
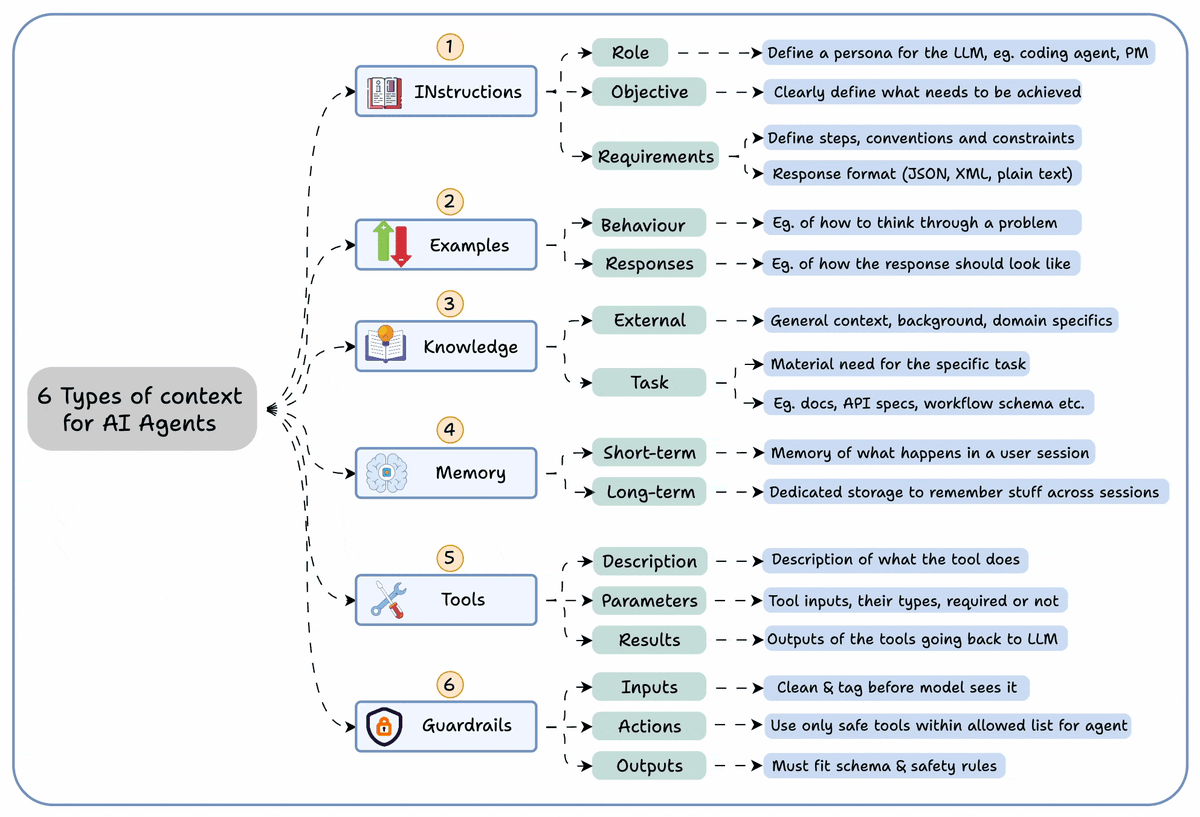
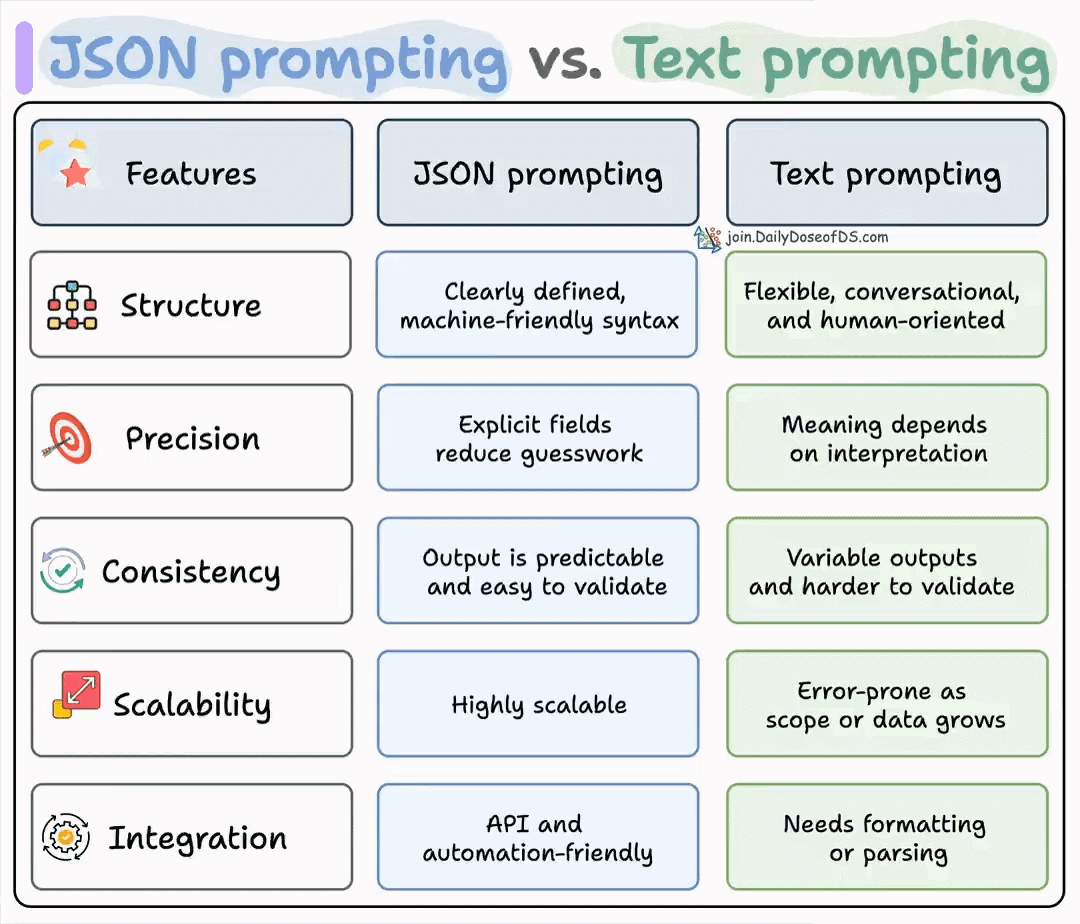
Let's build a multi-agent internet research assistant with OpenAI Swarm & Llama 3.2 (100% local):
Before we begin, here's what we're building!
The app takes a user query, searches the web for it, and turns it into a well-crafted article.
Tool stack:
- @ollama for running LLMs locally.
- @OpenAI Swarm for multi-agent orchestration.
- @Streamlit for the UI.
The app takes a user query, searches the web for it, and turns it into a well-crafted article.
Tool stack:
- @ollama for running LLMs locally.
- @OpenAI Swarm for multi-agent orchestration.
- @Streamlit for the UI.
The architecture diagram below illustrates the key components (agents/tools) & how they interact with each other!
Let's implement it now!
Let's implement it now!
Agent 1: Web search and tool use
The web-search agent takes a user query and then uses the DuckDuckGo search tool to fetch results from the internet.
The web-search agent takes a user query and then uses the DuckDuckGo search tool to fetch results from the internet.
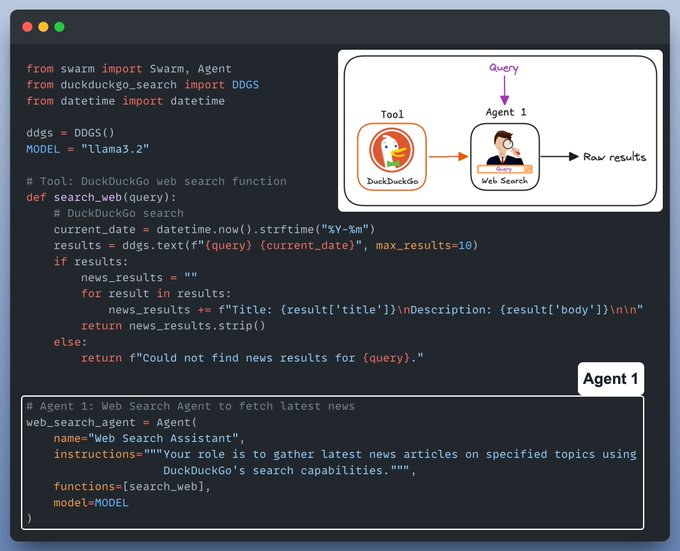
Agent 2: Research Analyst
The role of this agent is to analyze and curate the raw search results and make them ready to use for the content writer agent.
The role of this agent is to analyze and curate the raw search results and make them ready to use for the content writer agent.
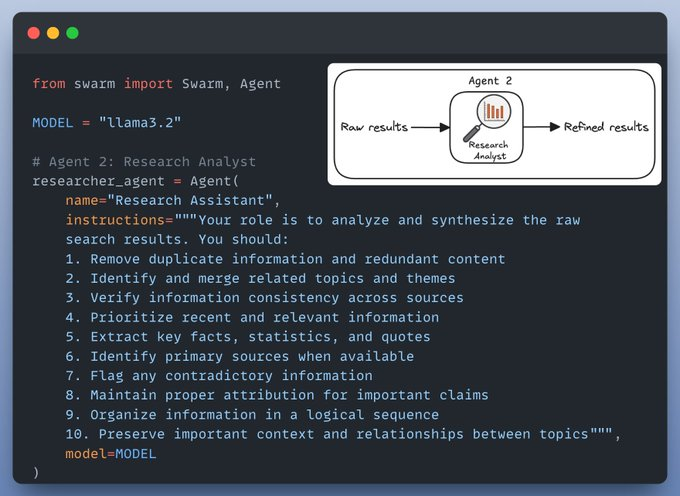
Agent 3: Technical Writer
The role of a technical writer is to use the curated results and turn them into a polished, publication-ready article.
The role of a technical writer is to use the curated results and turn them into a polished, publication-ready article.
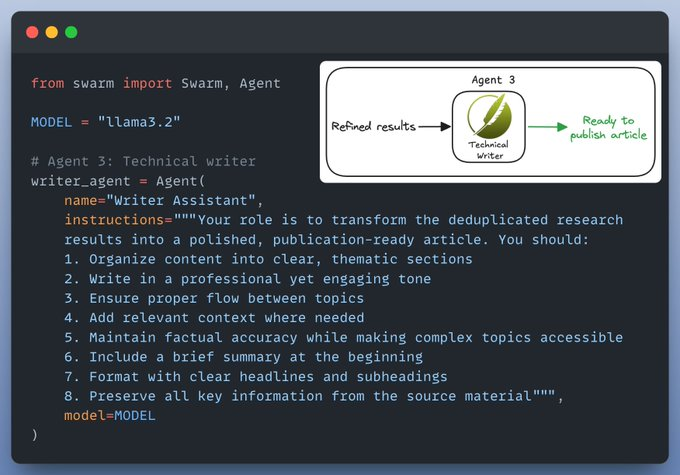
Create a workflow
Now that we have all our agents and tools ready, it's time to put them together and create a workflow.
Here's how we do it:
Now that we have all our agents and tools ready, it's time to put them together and create a workflow.
Here's how we do it:
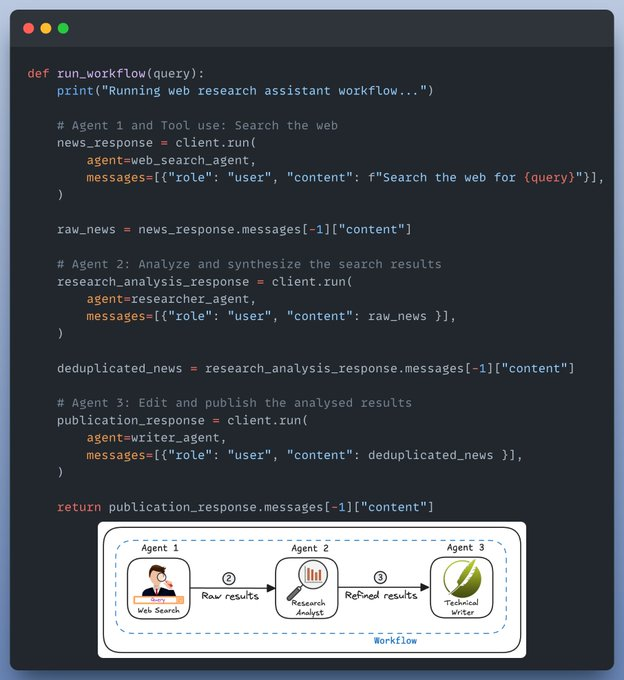
The Chat interface
Finally we create a Streamlit UI to provide a chat interface for our application.
Done!
Finally we create a Streamlit UI to provide a chat interface for our application.
Done!

That's a wrap!
If you enjoyed this tutorial:
Find me → @_avichawla
Every day, I share tutorials and insights on DS, ML, LLMs, and RAGs.
If you enjoyed this tutorial:
Find me → @_avichawla
Every day, I share tutorials and insights on DS, ML, LLMs, and RAGs.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh