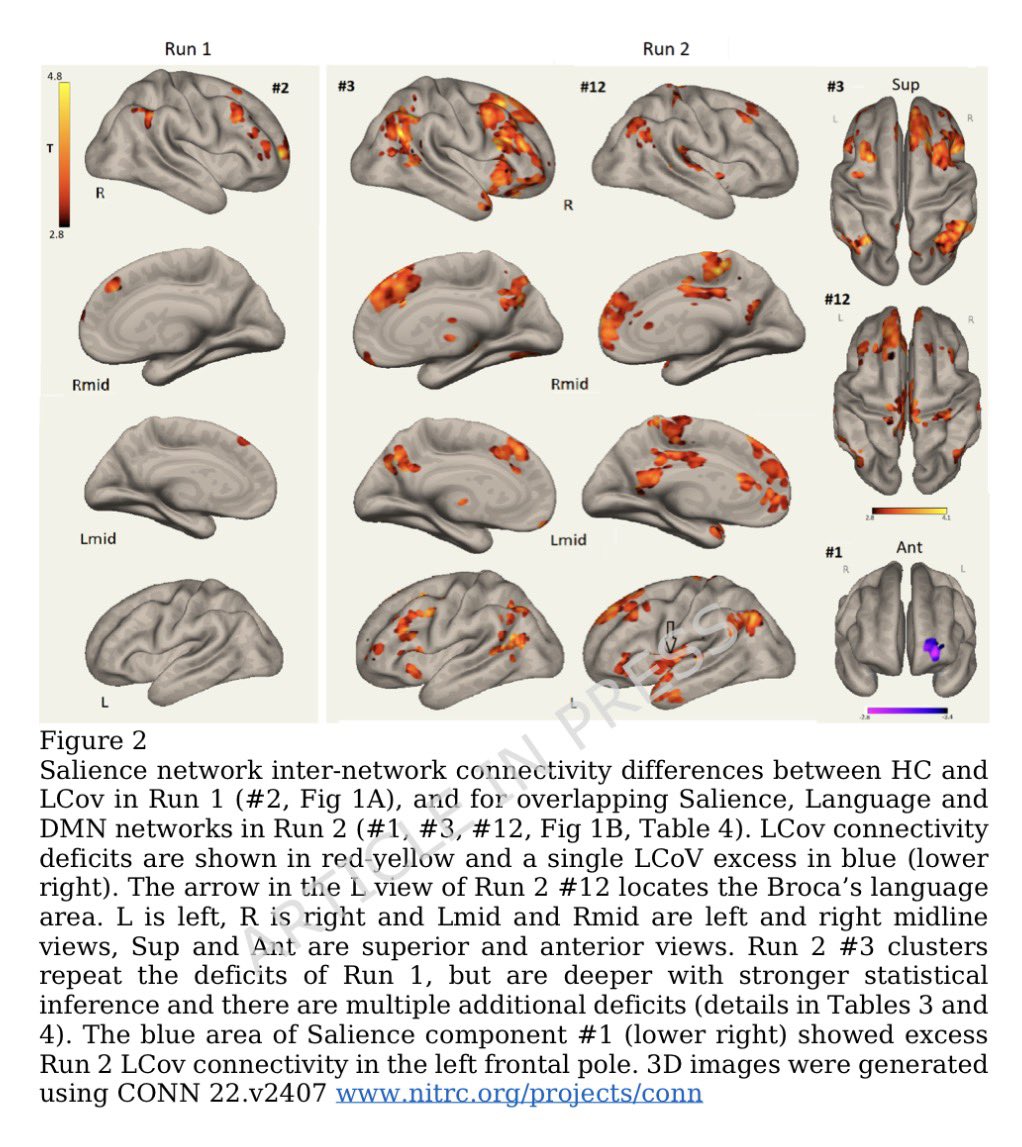
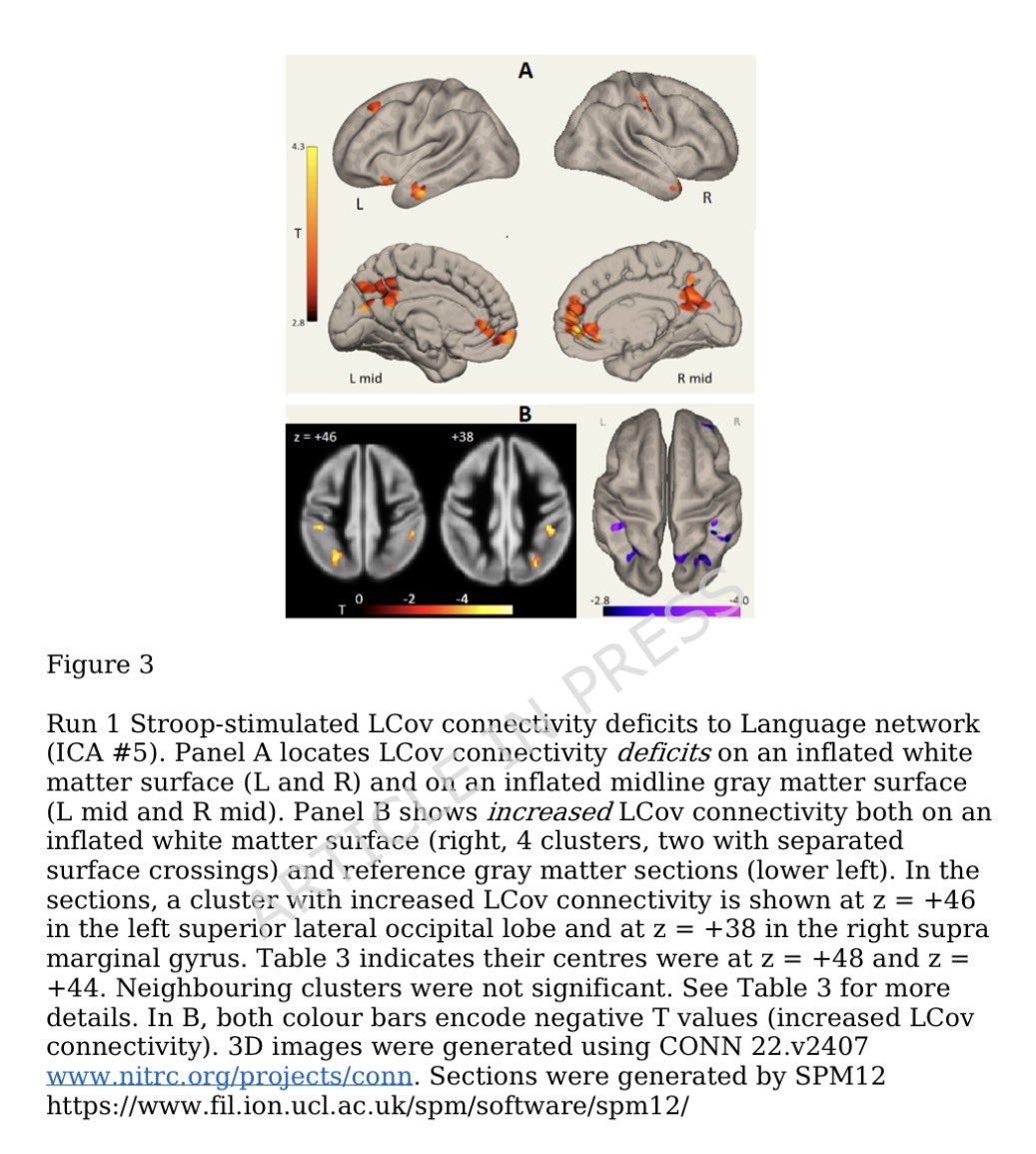
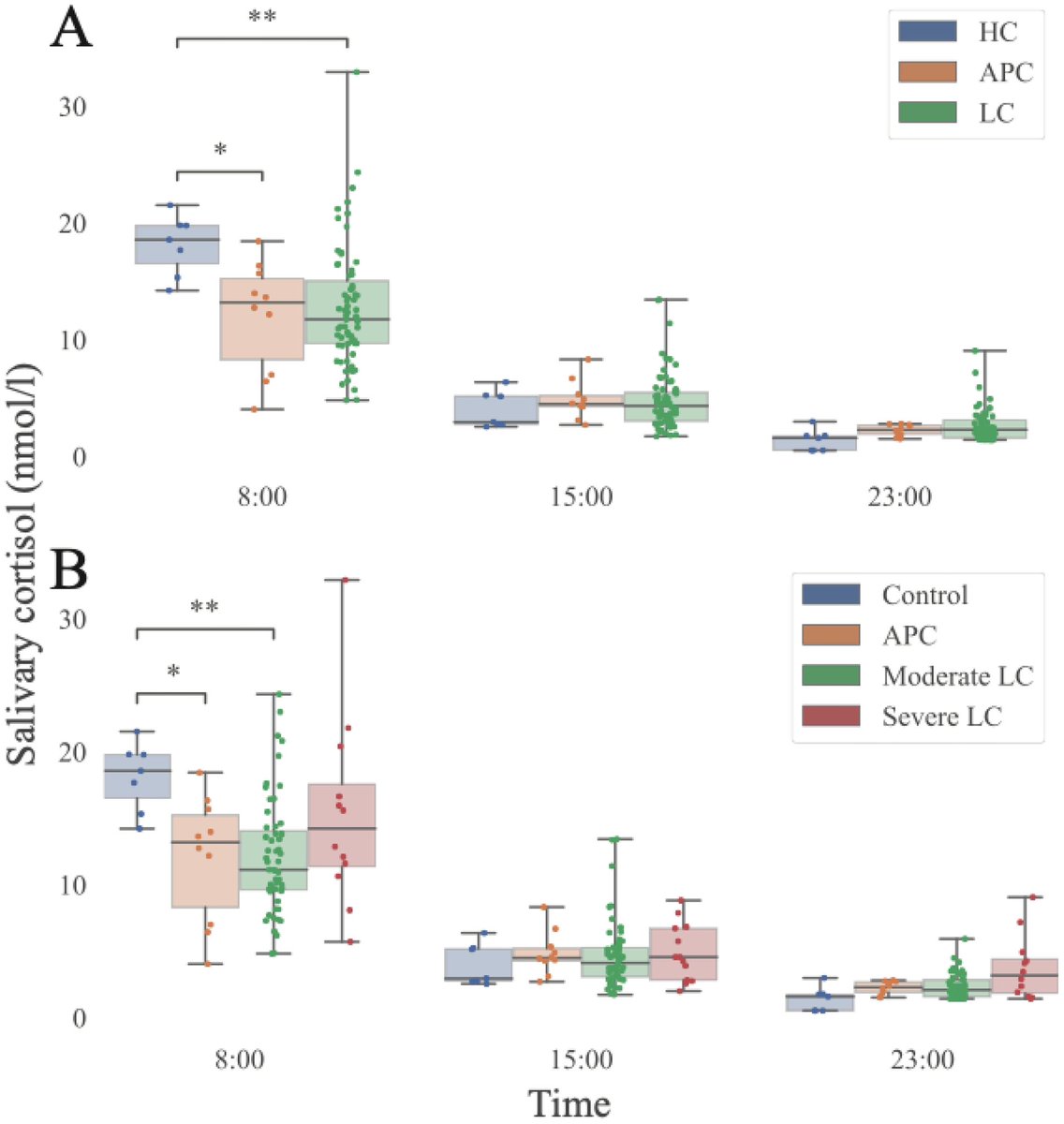
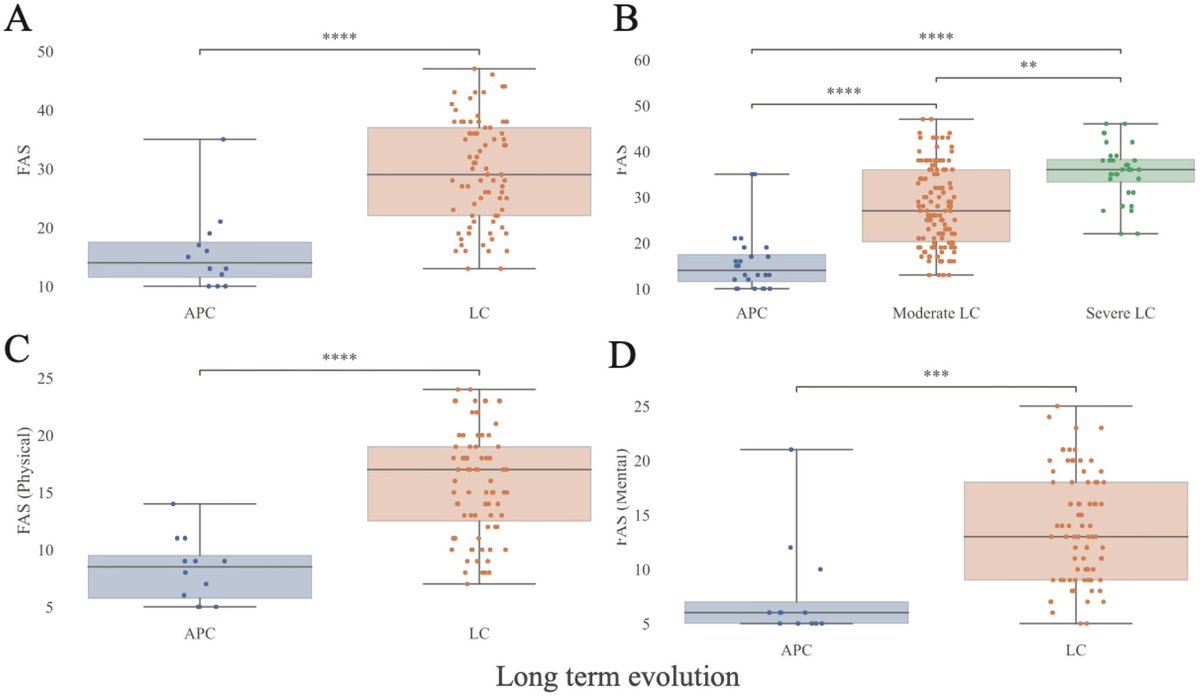
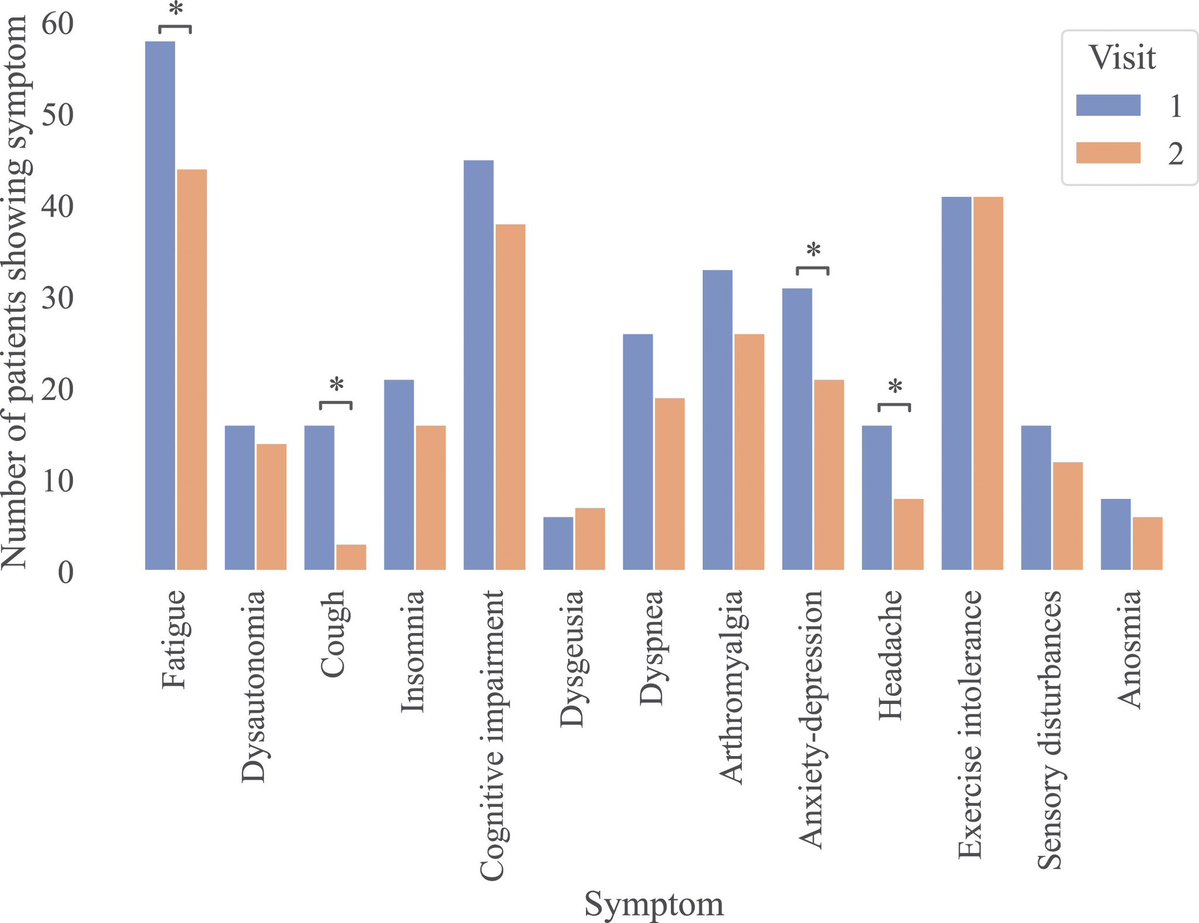
Researchers found a link between COVID-19 & blood markers linked to faulty proteins in the brain. They found people who had previously had COVID-19 were more likely to have increased levels of biomarkers linked to faulty amyloid proteins—a hallmark for Alzheimer's disease. 1/ 

On average, the effects were comparable to 4 years of aging with the greatest effects seen in those hospitalized with severe COVID-19 or with underlying risk factors for dementia such as smoking or high blood pressure. 2/ 

The findings suggest that mild or moderate COVID may accelerate biological processes that contribute to buildup of disease-promoting amyloid in brain. This raises possibility that COVID-19 might contribute to an increase in later risks of developing Alzheimer's disease. 3/ 

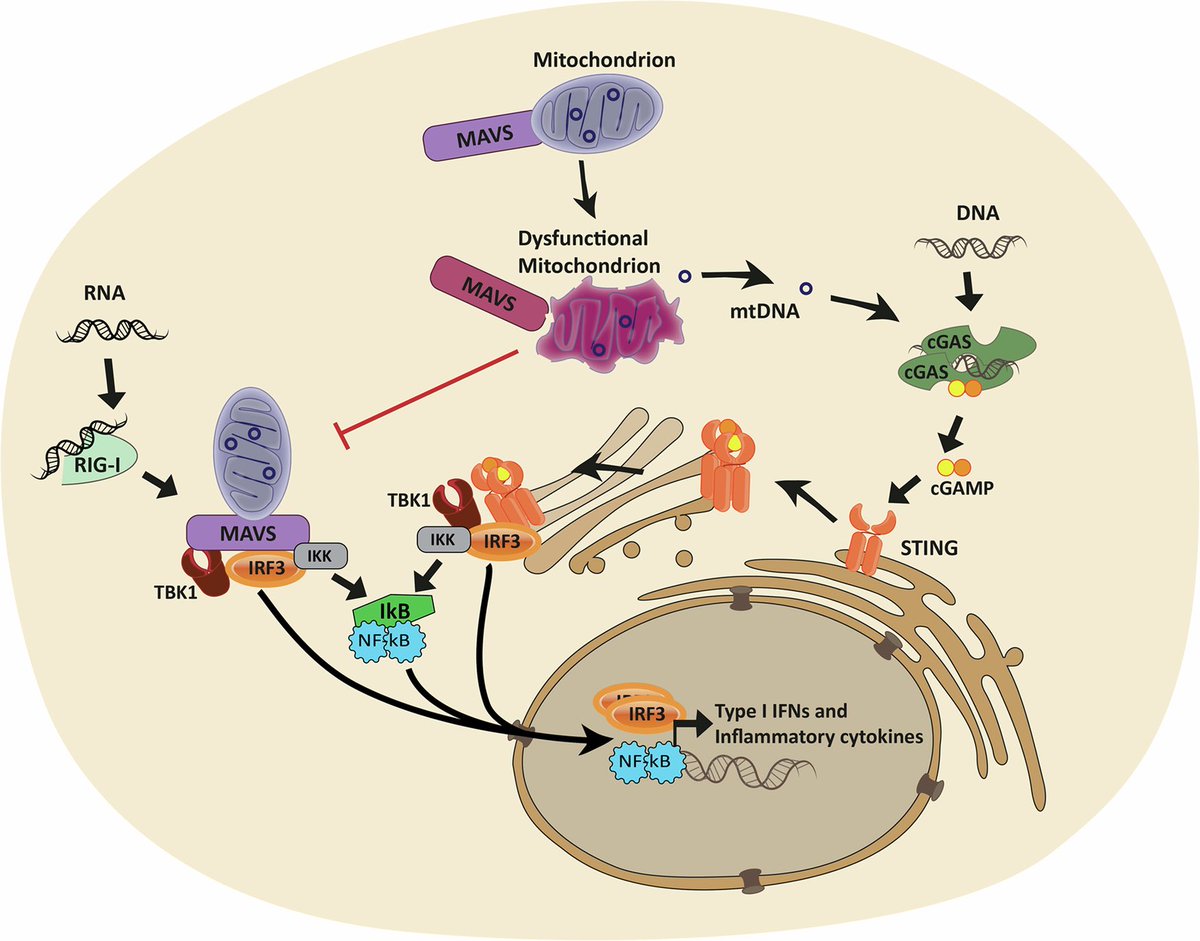
These findings suggest COVID-19 may drive changes which contribute to neurodegenerative disease. This may be due to the inflammation triggered by the disease, although how this inflammation might impact the brain and changes to amyloid is not yet fully clear. 4/ 
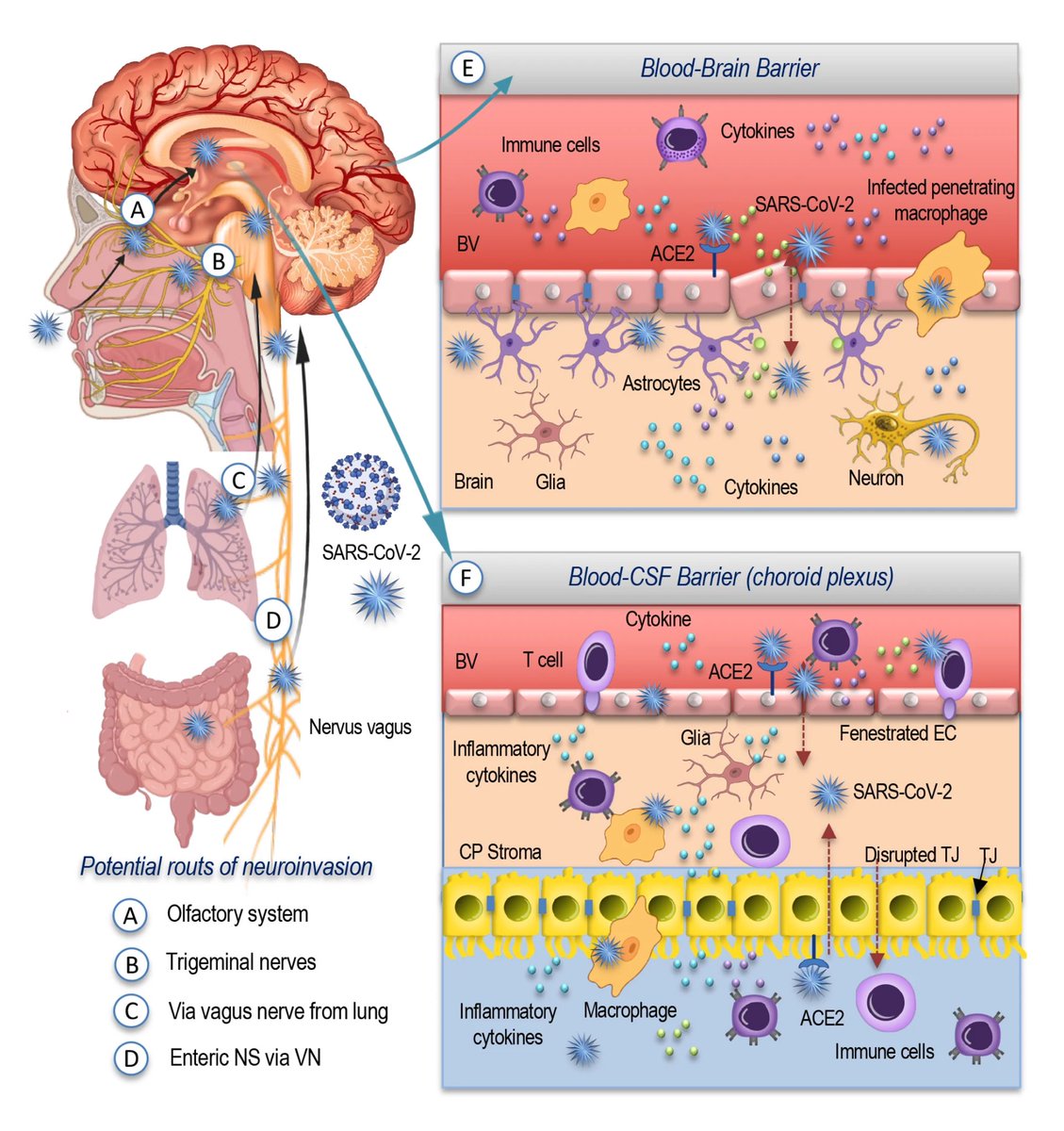
However, the researchers can’t say that catching the SARS-CoV-2 virus directly causes these changes, or if it does, by how much a single episode of infection increases someone's risk. 5/
But these findings do suggest that COVID-19 may increase the risk of Alzheimer's in the future—as has been suggested in the past for other kinds of infections—especially among people with pre-existing risk factors. 6/ 

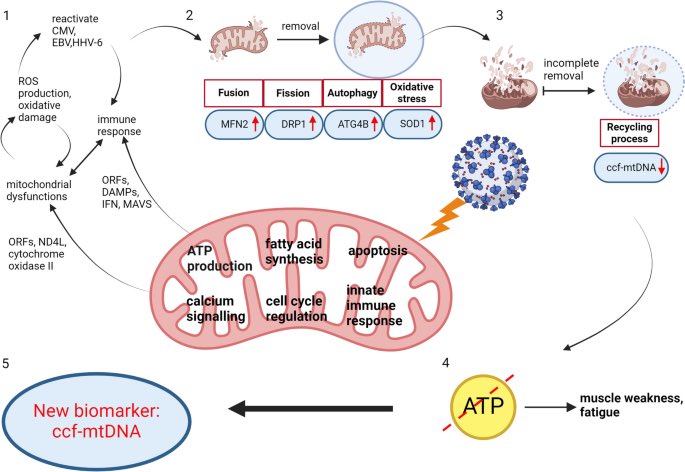
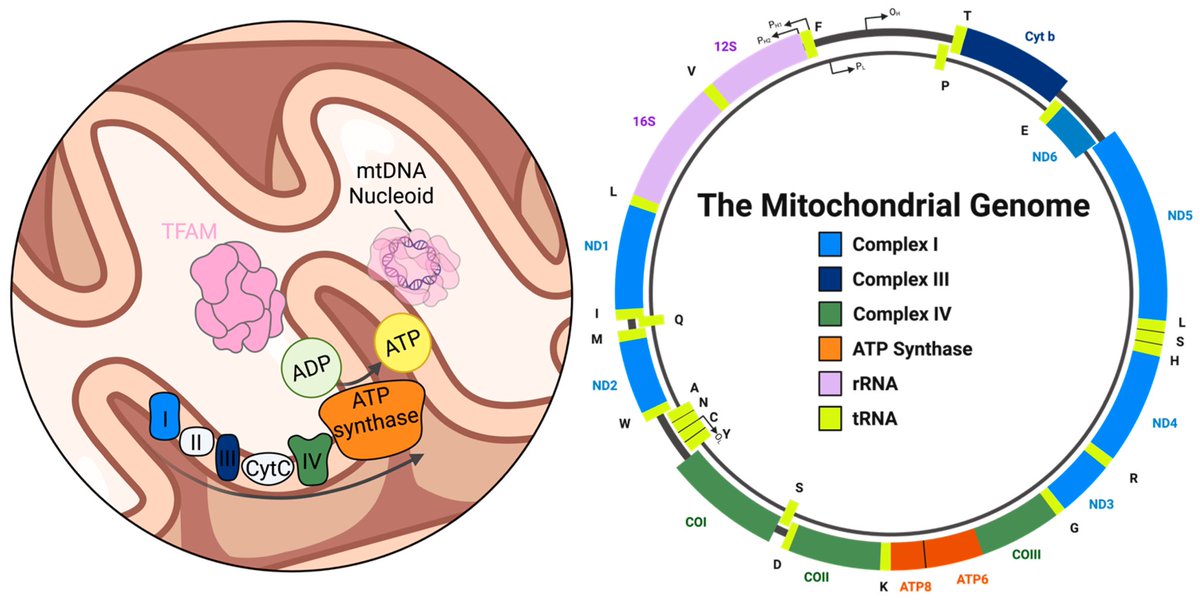
Amyloid is a common protein with a range of functions in the body. But the buildup of an abnormal form of the protein, called beta amyloid (Aβ), is a key component of many diseases. 7/ 

Aβ forms the characteristic clumps seen in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease, which are thought to cause damage to the neurons in the brain, leading to changes in cognition and behavior. 8/ 

In this study, the researchers found SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated w/ changes in several blood proteins previously linked to brain Aβ pathology. The magnitude of changes was similar to that associated w/ a well-known genetic risk factor for AD, a genetic variant: APOE4 9/ 

Greater changes found in older participants & those hospitalized with COVID-19-19 or had a history of hypertension. These correlated with poorer cognitive test scores & measures of overall health as well as changes in brain imaging patterns associated w/neurodegeneration 10/ 

More studies now are needed to prove any causal links. Ultimately, the more we know about factors that contribute to dementia risk—whether they are directly under our control, like lifestyle or diet, or modifiable by vaccines or early treatment for infectious diseases. 11/11 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh