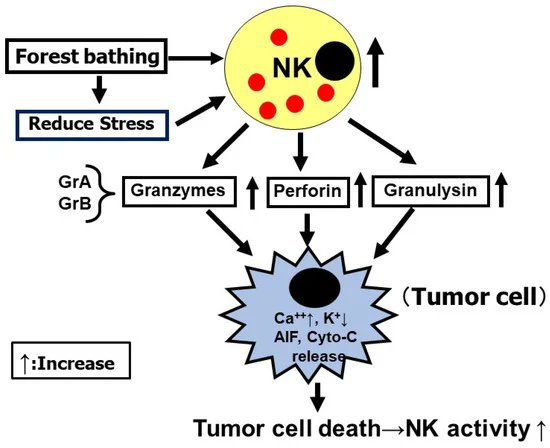
Mitochondrial transplantation could revolutionize aging and disease treatment.
In older rodents, transplantation enhances:
🏃♂️ Speed by 45% & endurance by 48%
⚡ATP by 51%
🏋️♂️Mitochondrial enzyme activity by up to 65%
Human trials are already underway 🧵1/12
In older rodents, transplantation enhances:
🏃♂️ Speed by 45% & endurance by 48%
⚡ATP by 51%
🏋️♂️Mitochondrial enzyme activity by up to 65%
Human trials are already underway 🧵1/12
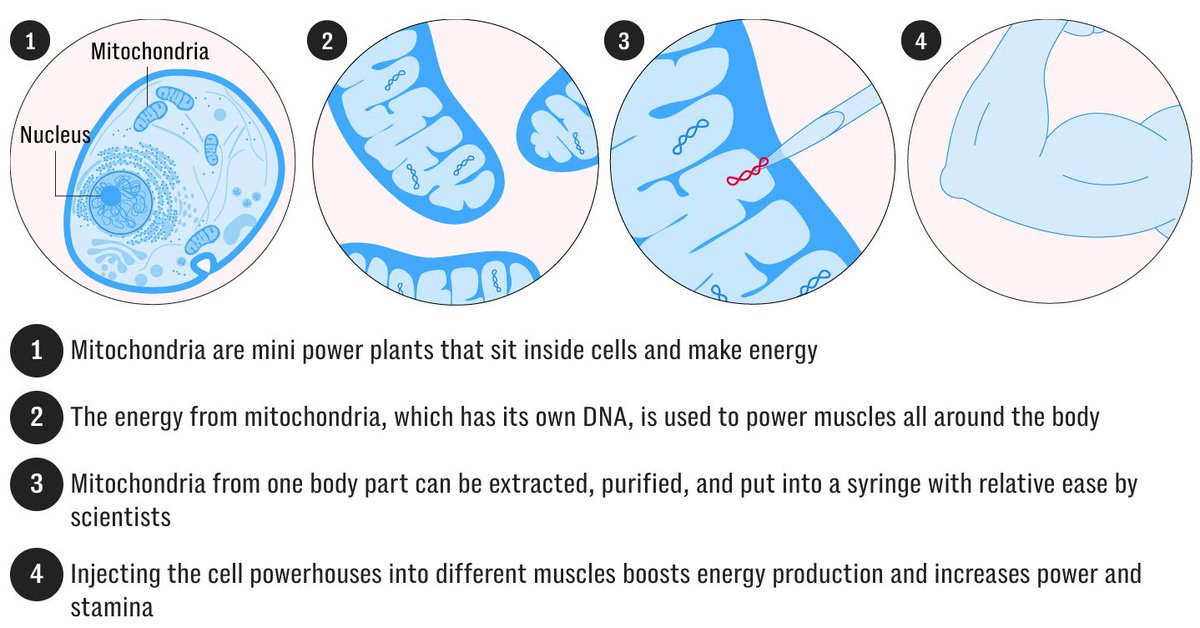
As we age, our muscle mitochondria decline in function, leading to fatigue and reduced mobility. The question: Could injecting mitochondria directly into muscle offset these aging-driven deficits? A study tested that idea specifically in older rodents. /2 
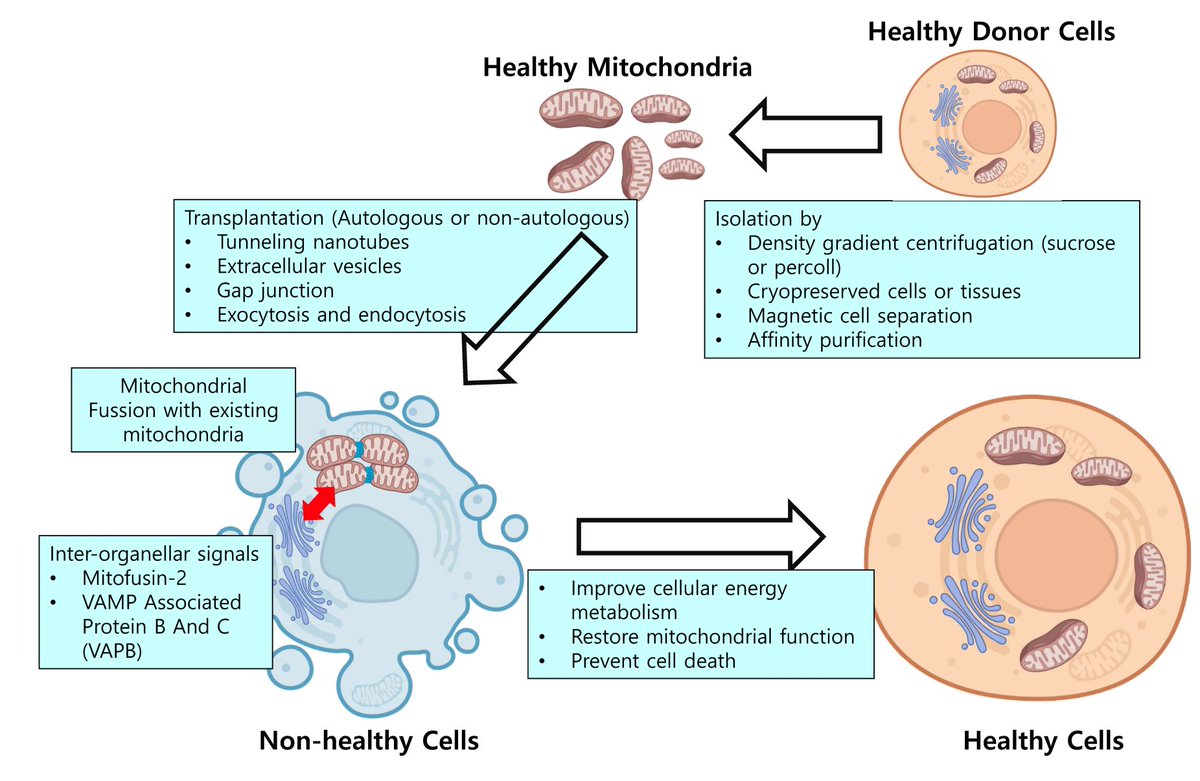
Researchers used 15 female mice (24 months old, equivalent to 70yo humans). They isolated mitochondria from two donor mice of the same age and strain, then injected these mitochondria into key hindlimb muscles (quadriceps, tibialis anterior, gastrocnemius). A separate group got a placebo injection. /3
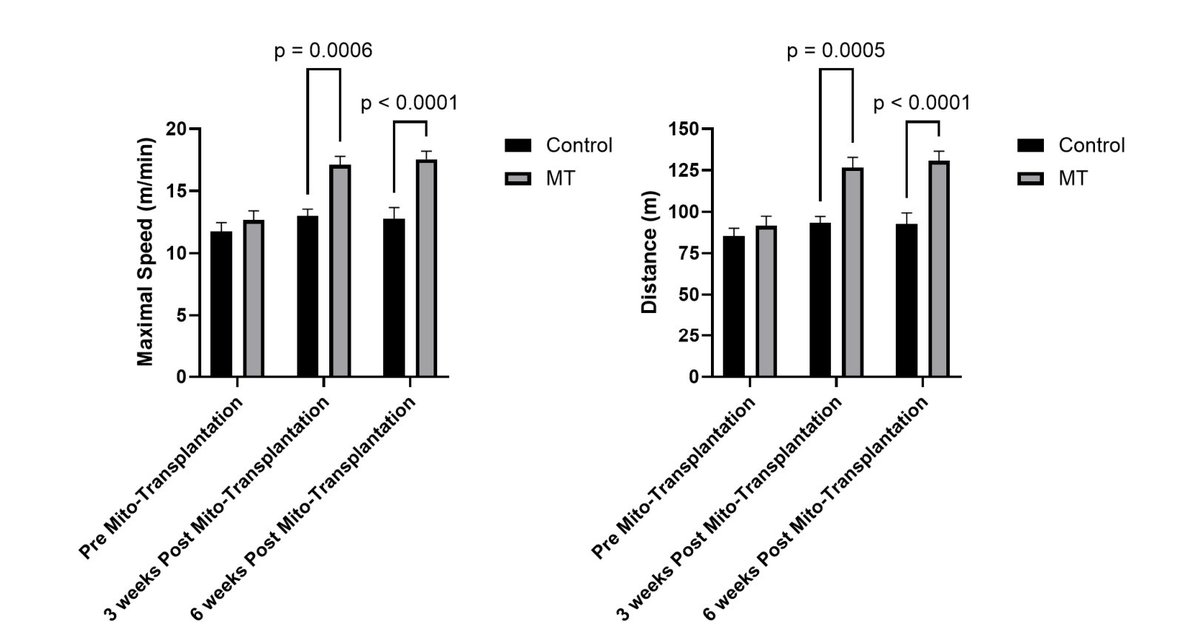
They tested endurance on a treadmill at baseline, 3 weeks, and 6 weeks post-injection. By 3 weeks, mice receiving mitochondrial transplants ran ~48% farther and ~45% faster than placebo controls. These gains persisted at the 6-week mark. /4 
Cytochrome c oxidase (CcO) activity rose up to ~65% in transplanted muscles (vs. placebo). CcO is crucial for the final steps of energy production.
ATP levels were ~51% higher in transplanted muscles—directly reflecting better energy output. /5
ATP levels were ~51% higher in transplanted muscles—directly reflecting better energy output. /5
They also found a ~37% boost in citrate synthase activity, an important enzyme in the mitochondrial energy pathway. Plus, markers of mitochondrial quality control (Parkin, TFAM, BNIP3, Drp1) increased up to two-fold, indicating enhanced turnover and maintenance of healthy mitochondria. /6
Interestingly, donor mitochondria came from mice of the same age. You might think younger donors would help more, but this study suggests that even “age-matched” mitochondria can significantly bolster muscle bioenergetics—at least in this rodent model. /7
How long do the benefits last? This study only tracked improvements through week 6, and the performance gains remained. Whether these enhancements persist beyond 6 weeks—or whether booster injections help—remains to be determined. /8
Though promising, there are important limitations:
These results are in rodents, not humans.
No significant epigenetic changes were seen at 6 weeks.
The best donor age, optimal doses, safety, or frequencies for human therapy are still unknown. Yet the concept of mitochondrial transplantation is an intriguing new frontier, especially for those with mitochondrial disorders. /9
These results are in rodents, not humans.
No significant epigenetic changes were seen at 6 weeks.
The best donor age, optimal doses, safety, or frequencies for human therapy are still unknown. Yet the concept of mitochondrial transplantation is an intriguing new frontier, especially for those with mitochondrial disorders. /9
Concerns are growing over the potential use of this technology to gain an unfair edge in sports. Reports state that “human trials have already been conducted in Iran, China, and other countries worldwide”. /10
telegraph.co.uk/news/2025/02/1…
telegraph.co.uk/news/2025/02/1…

If successfully translated, mitochondrial transplantation could revolutionize disease treatment and enhance strength and endurance—especially for older adults. But it also raises ethical concerns about its use for enhancing already healthy individuals. /11 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh