
Internal Medicine MD
Writing about science worth applying to your life
📩 BrandonLuuMD@proton.me
11 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App

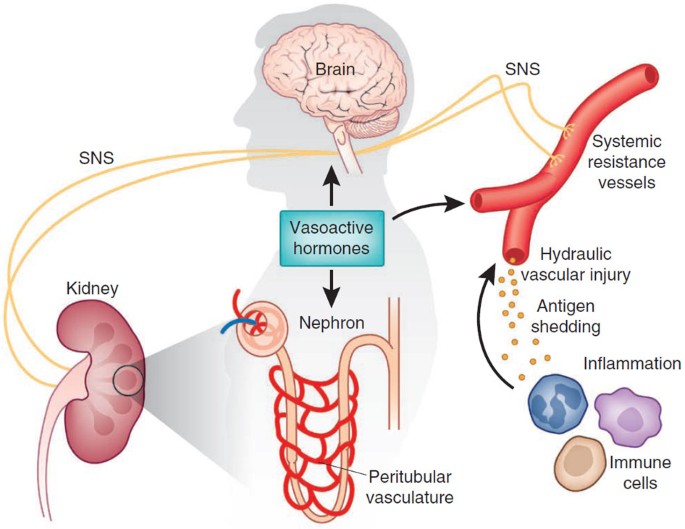
 High blood pressure often causes zero symptoms for years while quietly damaging the heart, brain, kidneys, eyes, and more.
High blood pressure often causes zero symptoms for years while quietly damaging the heart, brain, kidneys, eyes, and more.

 Delayed circadian rhythms are linked to impaired concentration, mood disturbances, increased metabolic and cardiovascular risk, and weakened immune function.
Delayed circadian rhythms are linked to impaired concentration, mood disturbances, increased metabolic and cardiovascular risk, and weakened immune function.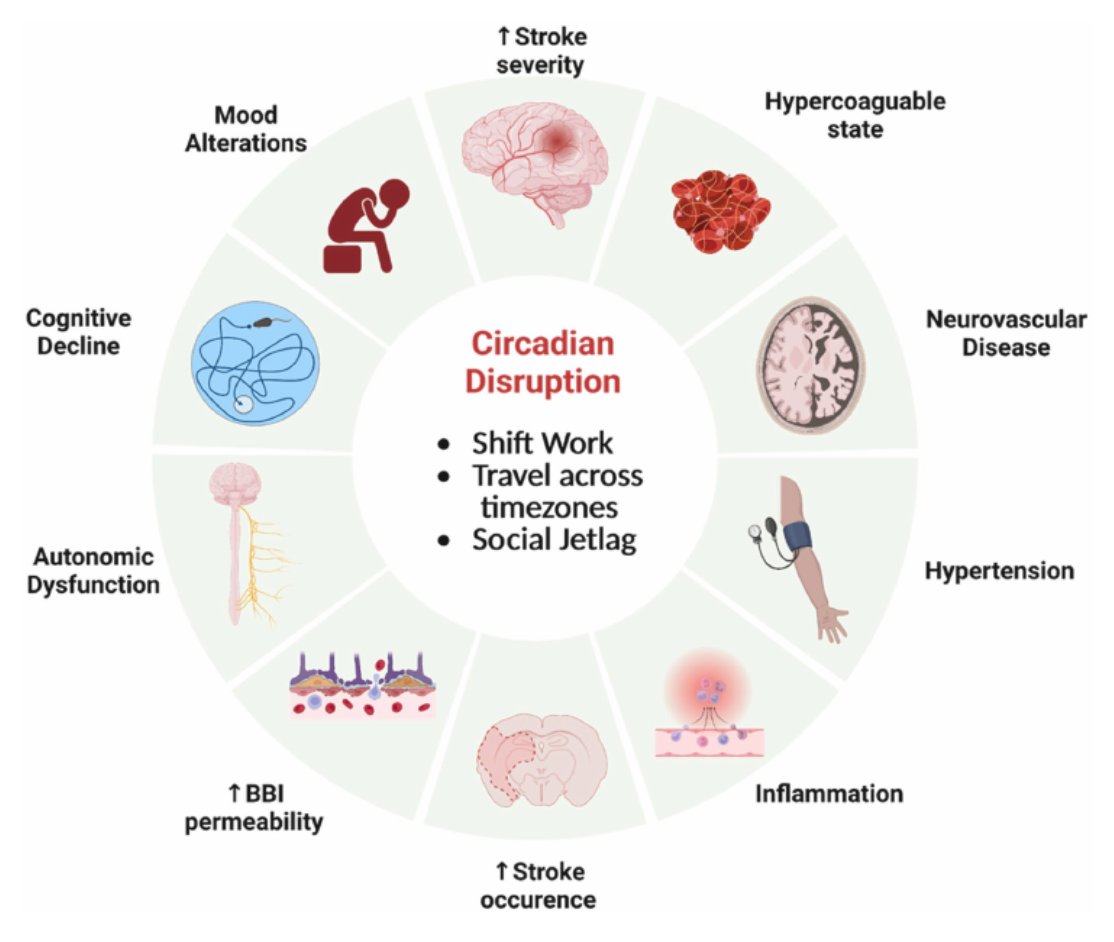
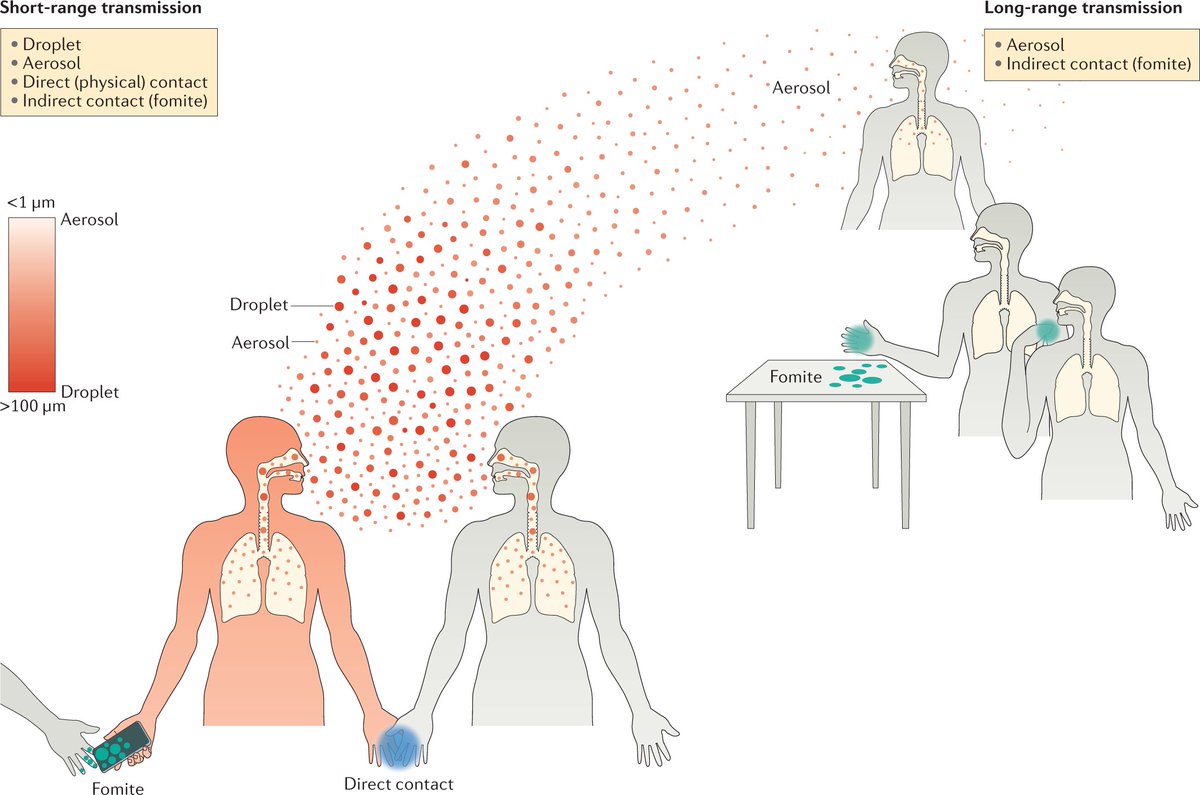
 The sooner you act the better. Respiratory viruses attach to cells and begin replicating within hours of exposure. Most interventions work best when started immediately and continued for 3-5 days (the typical incubation period) /2
The sooner you act the better. Respiratory viruses attach to cells and begin replicating within hours of exposure. Most interventions work best when started immediately and continued for 3-5 days (the typical incubation period) /2
 The circadian system is fundamentally disrupted in many with ADHD:
The circadian system is fundamentally disrupted in many with ADHD: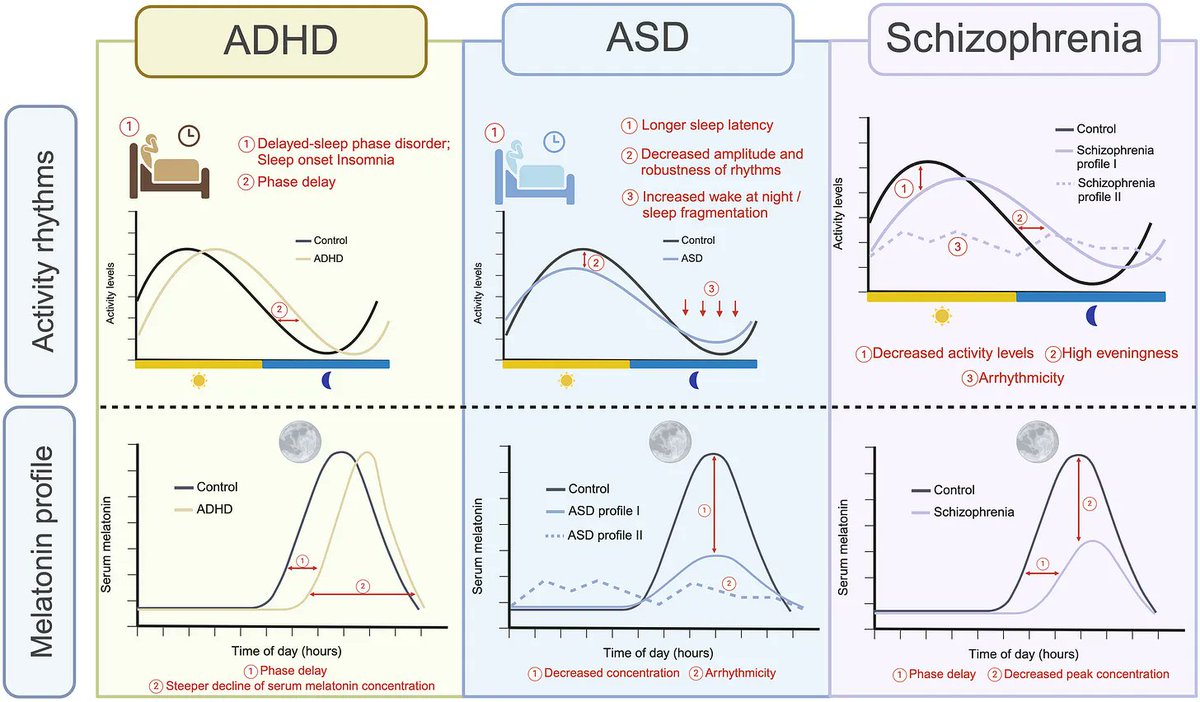

 For the full deep dive with all the studies and protocols, listen to a full podcast I recently joined and read the full protocols here:
For the full deep dive with all the studies and protocols, listen to a full podcast I recently joined and read the full protocols here: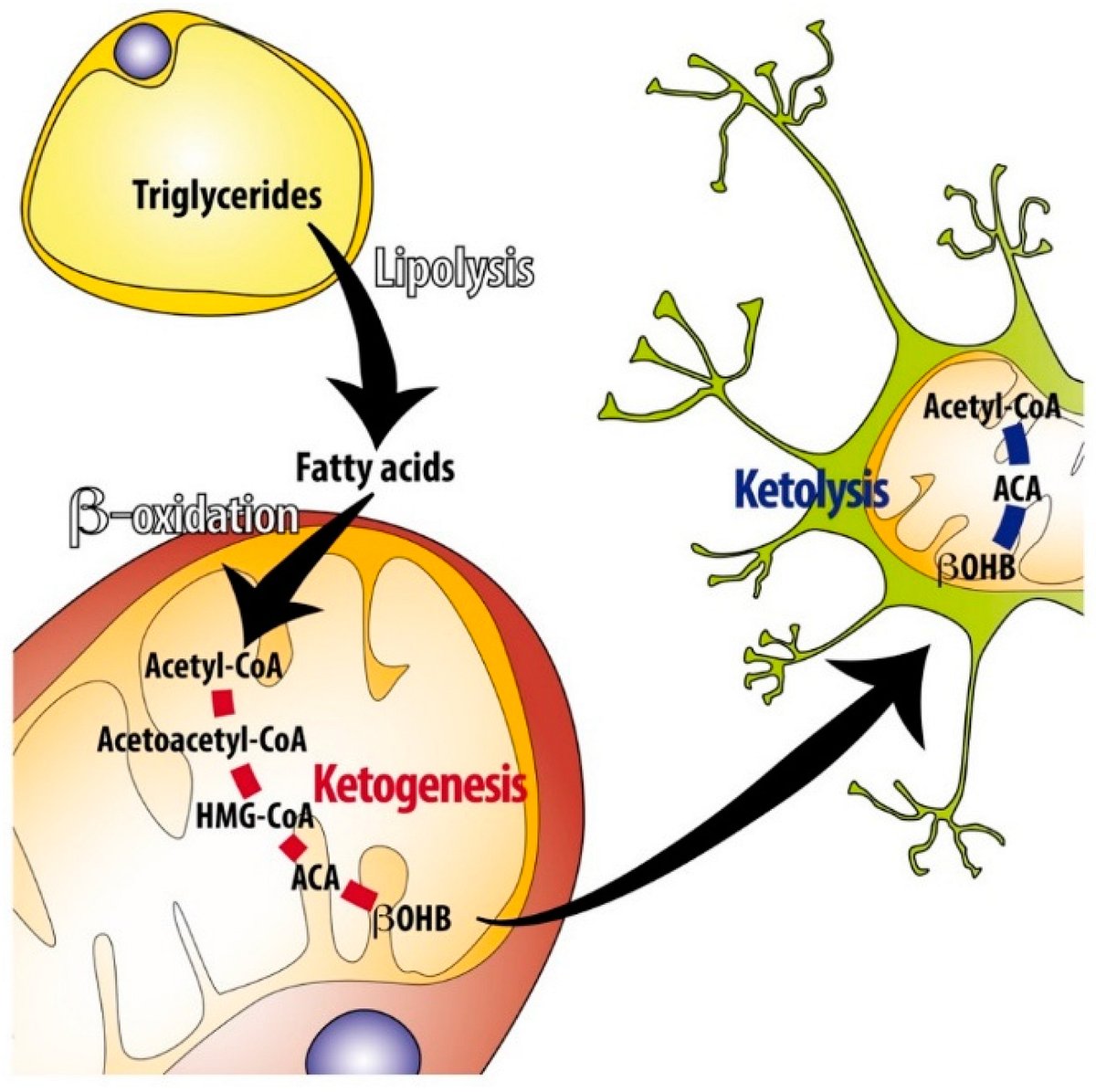
 Intermittent fasting and keto promise similar metabolic benefits: enhanced fat burning, weight loss, better blood lipids (in some cases)
Intermittent fasting and keto promise similar metabolic benefits: enhanced fat burning, weight loss, better blood lipids (in some cases)

 Stop rereading your notes. Start testing yourself.
Stop rereading your notes. Start testing yourself.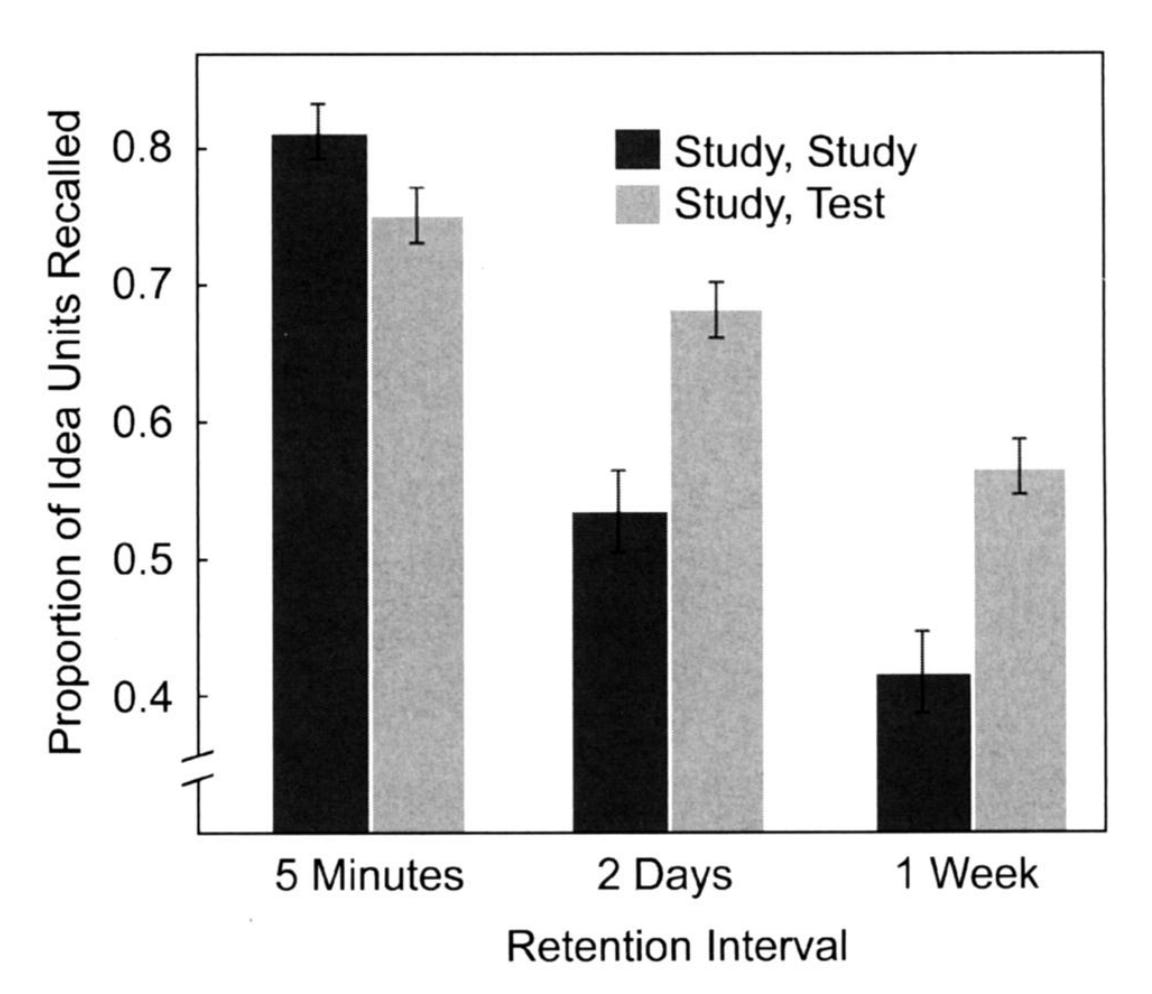
 Morning eating amplifies your natural temperature rise through diet-induced thermogenesis. Evening fasting lets it drop naturally. Plus, timing glucose spikes when baseline glucose is already high (daytime) helps keep your immune cell clocks aligned /2
Morning eating amplifies your natural temperature rise through diet-induced thermogenesis. Evening fasting lets it drop naturally. Plus, timing glucose spikes when baseline glucose is already high (daytime) helps keep your immune cell clocks aligned /2 

 The MOTAR trial setup: 45 patients took escitalopram 10-20mg daily, 96 chose supervised running (45min outdoor sessions 2-3x/week)
The MOTAR trial setup: 45 patients took escitalopram 10-20mg daily, 96 chose supervised running (45min outdoor sessions 2-3x/week) 

 1/3 of adults get <7 hours of sleep while spending billions on diet programs. This University of Chicago trial on people sleeping less than 6.5h/night changed how I think about weight loss in people with sleep deprivation. No diets, no exercise, just sleep /2
1/3 of adults get <7 hours of sleep while spending billions on diet programs. This University of Chicago trial on people sleeping less than 6.5h/night changed how I think about weight loss in people with sleep deprivation. No diets, no exercise, just sleep /2 
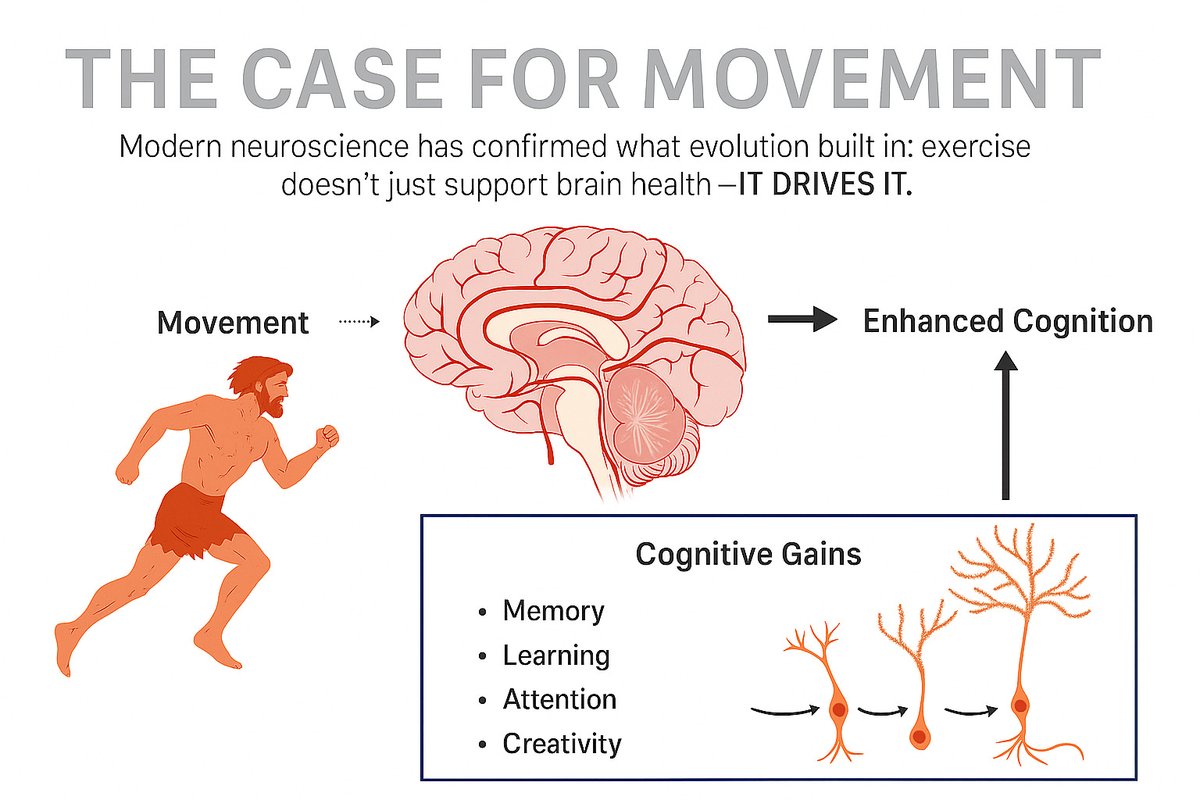
 Exercise reshapes your brain through key mechanisms:
Exercise reshapes your brain through key mechanisms:

 Creatine isn't just for the gym. Under stress, it boosts brain energy by regenerating ATP.
Creatine isn't just for the gym. Under stress, it boosts brain energy by regenerating ATP.


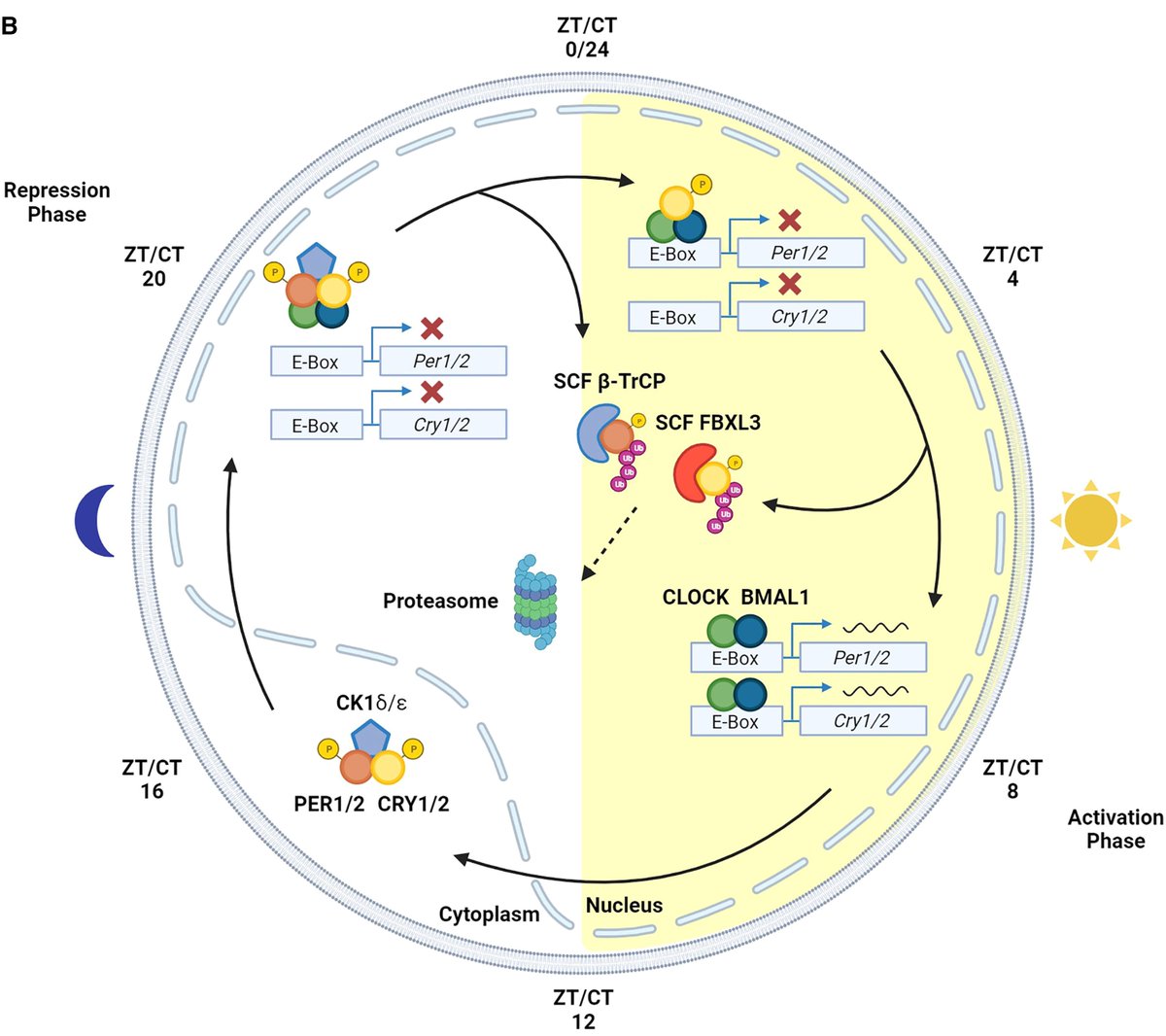
 Your body runs on a clock.
Your body runs on a clock.

 Why warmth if your body prefers cooler temperatures for sleep?
Why warmth if your body prefers cooler temperatures for sleep?

 Psyllium significantly improves blood sugar control and weight in diabetics. In a randomized trial, type 2 diabetes patients taking ~10g/day for 8 weeks saw:
Psyllium significantly improves blood sugar control and weight in diabetics. In a randomized trial, type 2 diabetes patients taking ~10g/day for 8 weeks saw:

 In a Japanese study, 3 days of forest bathing increased Natural Killer cell activity by ~50% and enhanced potential anti-cancer proteins like perforin and granulysin. Benefits lasted a full week after returning to city life /2
In a Japanese study, 3 days of forest bathing increased Natural Killer cell activity by ~50% and enhanced potential anti-cancer proteins like perforin and granulysin. Benefits lasted a full week after returning to city life /2 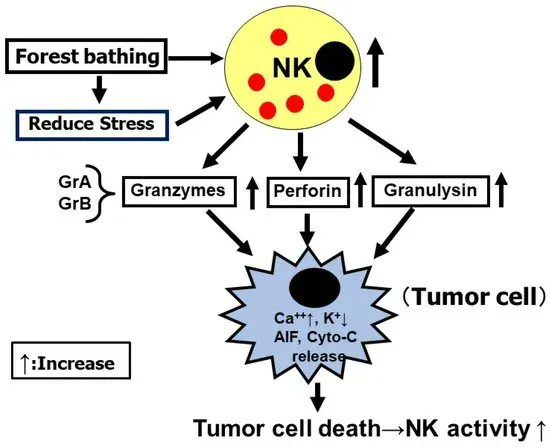

 Big breakfast vs. big dinner matters. Identical 1400 kcal diets for 12 wks, different timing:
Big breakfast vs. big dinner matters. Identical 1400 kcal diets for 12 wks, different timing:https://x.com/BrandonLuuMD/status/1887119301682860356

 FYI for the full article, data, protocols, and research, I share free weekly deep dives here:
FYI for the full article, data, protocols, and research, I share free weekly deep dives here:
 Curious about the full data, dosing protocols, and research? I share free weekly deep dives here:
Curious about the full data, dosing protocols, and research? I share free weekly deep dives here:
 Want the full breakdown + step-by-step protocol?
Want the full breakdown + step-by-step protocol?
 Researchers wanted to know:
Researchers wanted to know: