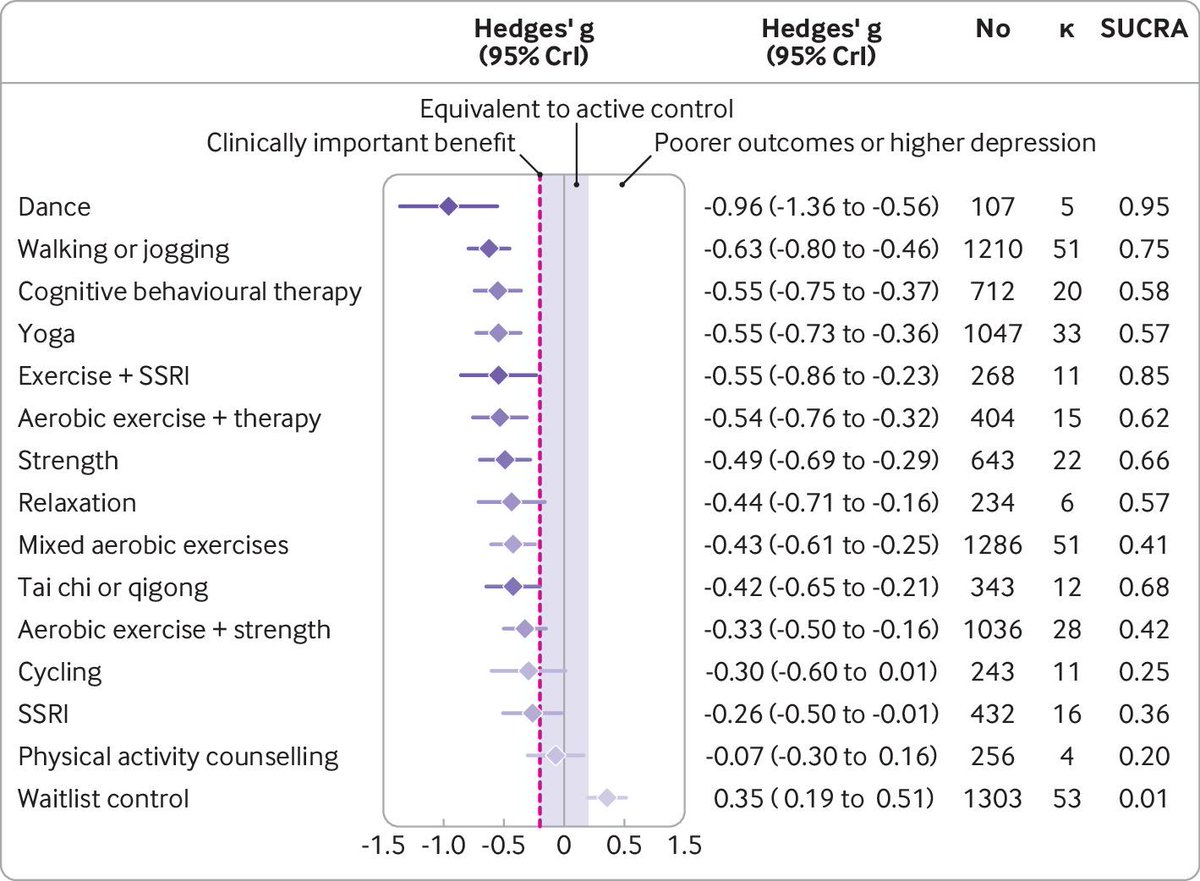
These findings are from a study in @ScienceAdvances which explored how viruses alter the function of the nervous system. 2/9 science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…

Numerous viruses use specialized surface molecules called fusogens to enter host cells. 3/9
Many of these viruses, including the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), can infect the brain and are associated with severe neurological symptoms through poorly understood mechanisms. 4/9
In this study, it was demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 infection induces fusion between neurons and between neurons and glia in mouse and human brain organoids. 5/9 

This was caused by the viral fusogen, as it is fully mimicked by the expression of the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein or the unrelated fusogen p15 from the baboon orthoreovirus. 6/9 

It was demonstrated that neuronal fusion is a progressive event, leading to the formation of multicellular syncytia, and causing the spread of large molecules and organelles. 7/9 

Overall, these results provide mechanistic insights into how SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses affect the nervous system, alter its function, and cause neuropathology. 9/9
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh