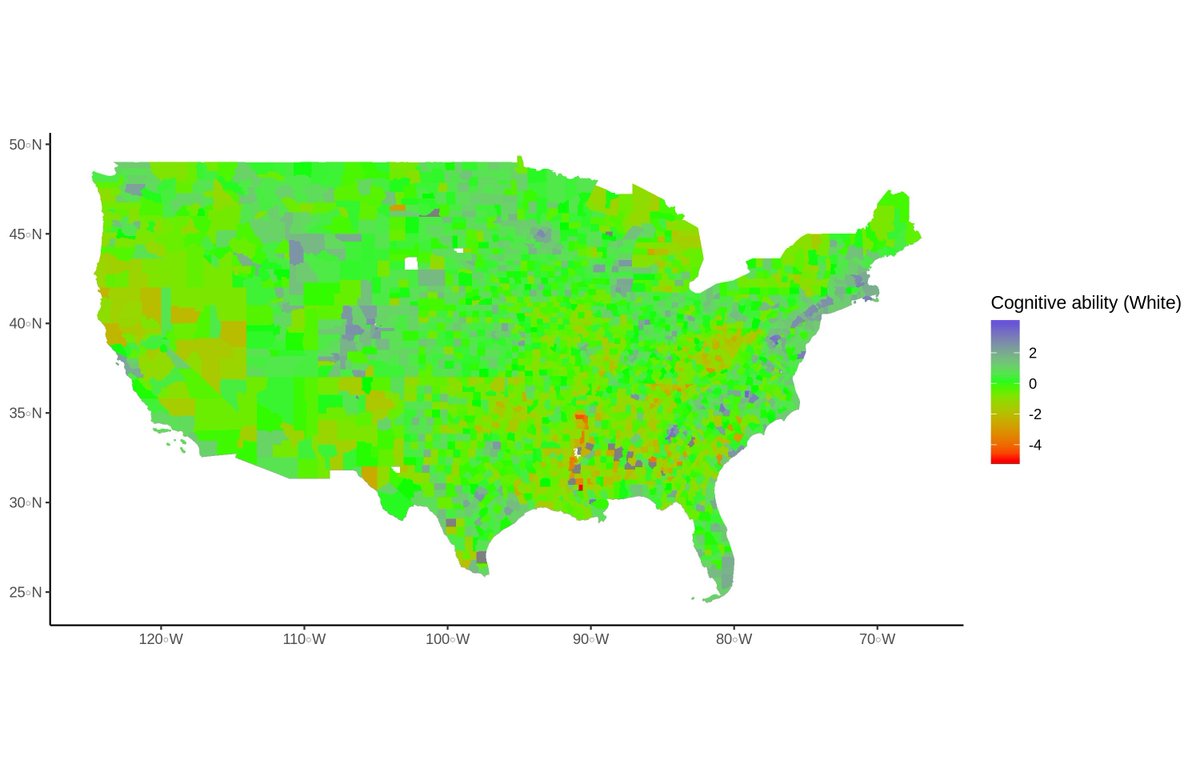
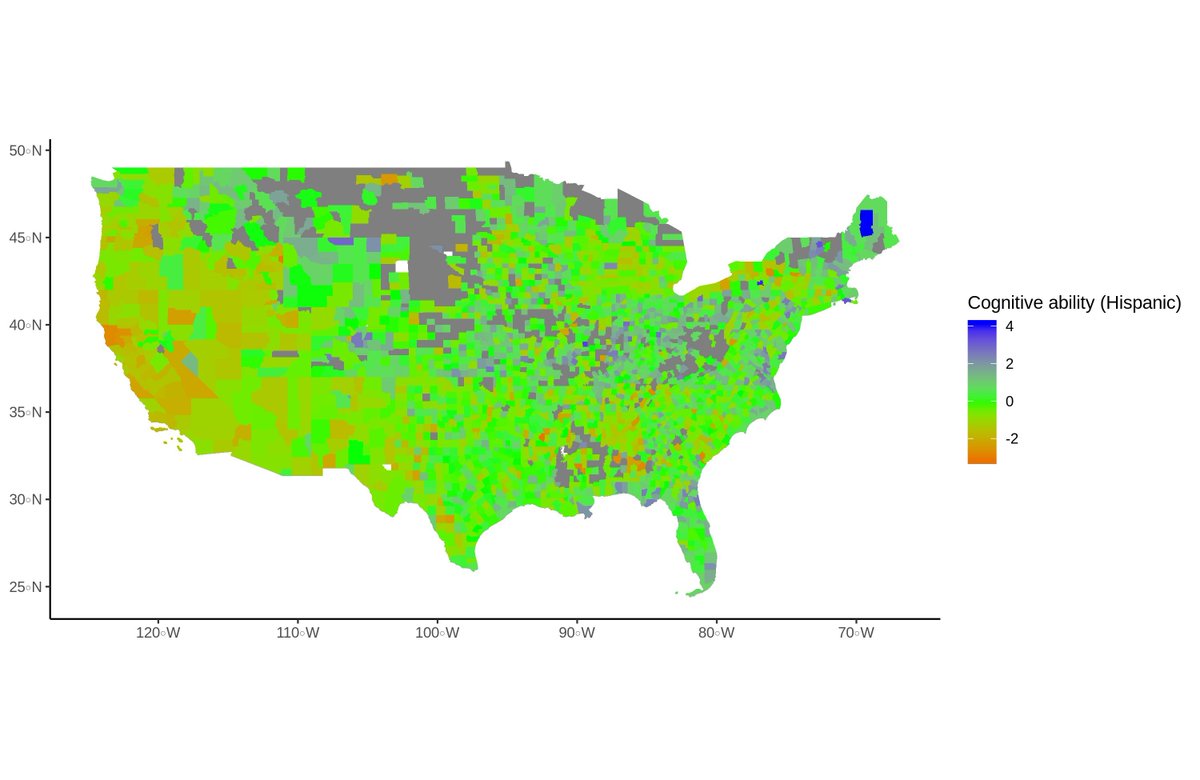
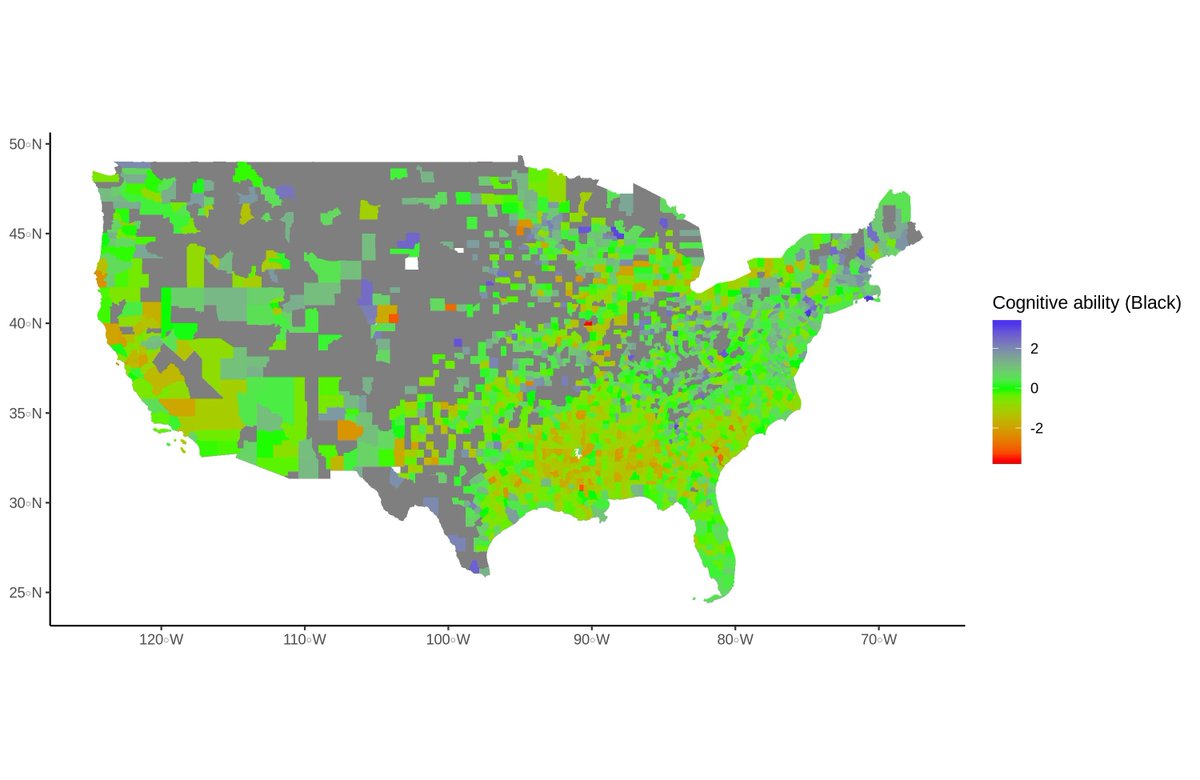
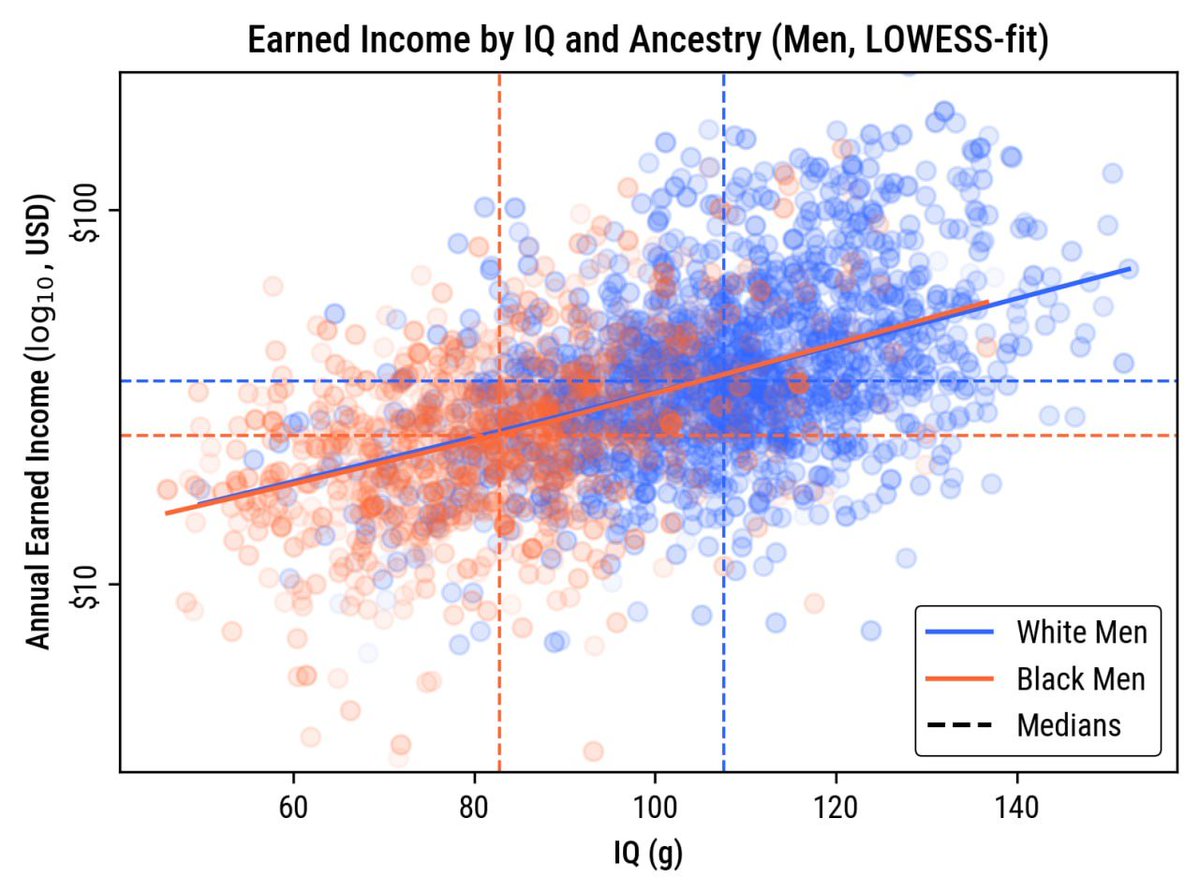
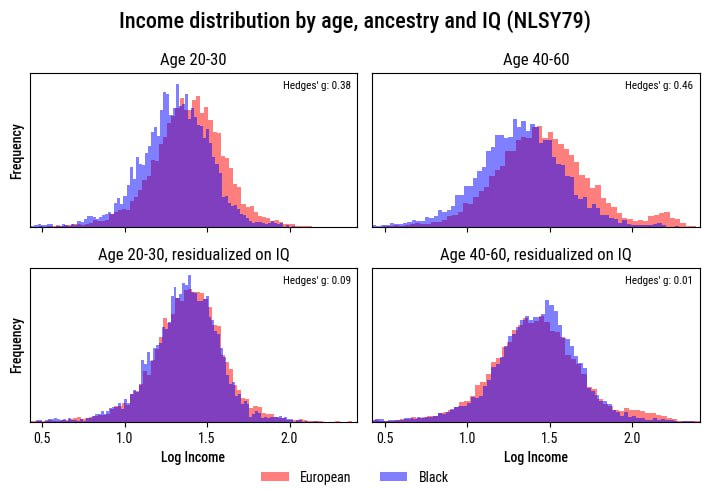
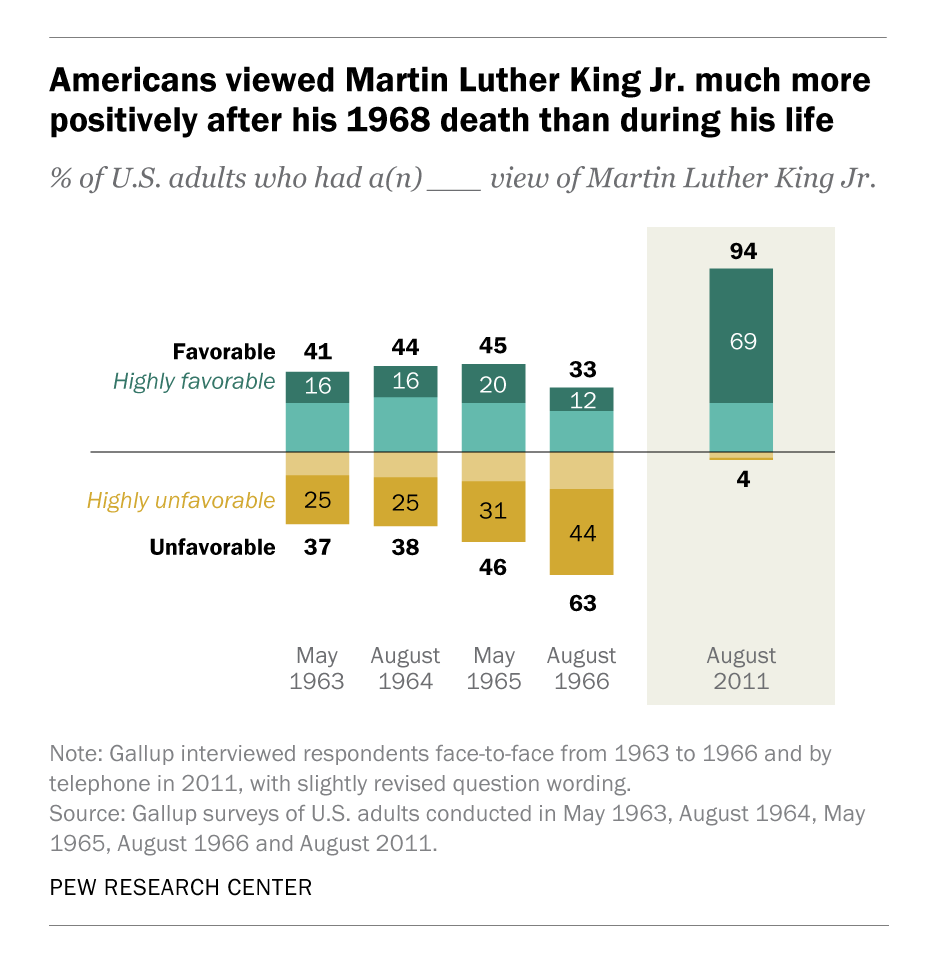
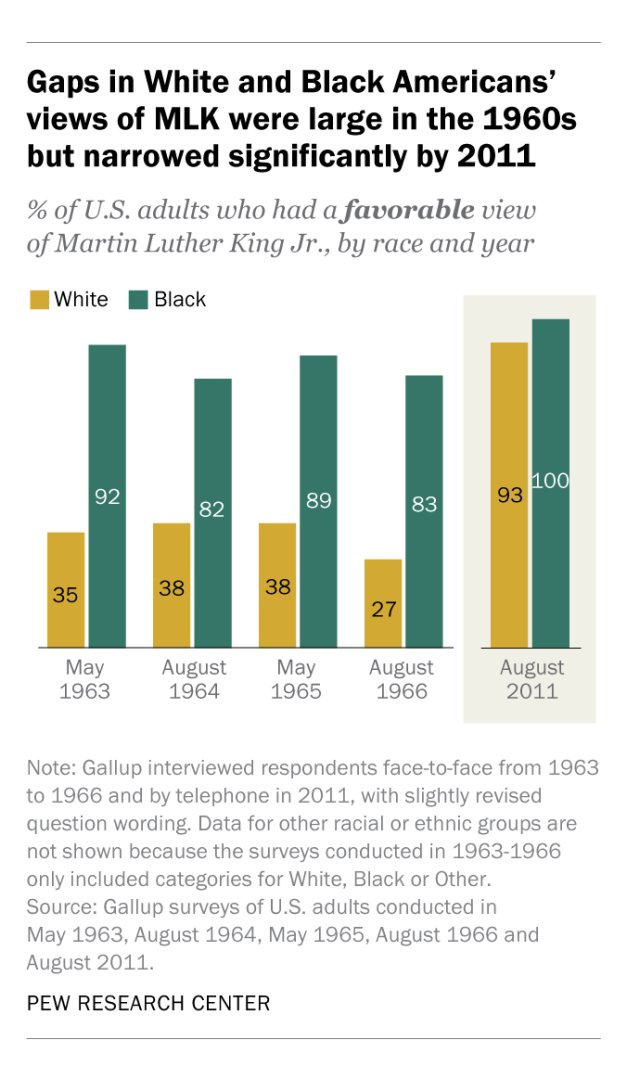
The biggest news today should probably be about one of the Executive Orders from yesterday evening.
Trust me, it's big.
The President just authorized DOGE to start cutting regulations🧵
Trust me, it's big.
The President just authorized DOGE to start cutting regulations🧵

This order starts off huge.
Remember those recently-created DOGE Team Leads going into every agency? They're going to work with agency heads and the OMB to review all of the regulations across a number of huge categories.
Which categories? Let's see.

Remember those recently-created DOGE Team Leads going into every agency? They're going to work with agency heads and the OMB to review all of the regulations across a number of huge categories.
Which categories? Let's see.
https://x.com/cremieuxrecueil/status/1889479172348629194

The first category is those rules and regulations which violate the law of the land: unlawful and unconstitutional regulations, things that agencies enacted but which they shouldn't have been able to. 

Now you might ask: Who decides what's lawful or unlawful, constitutional or unconstitutional, a good or a bad interpretation of statutes, prohibitions, and the law writ large?
Try to keep up, because the administration outlined this a few days ago:
Try to keep up, because the administration outlined this a few days ago:
https://x.com/cremieuxrecueil/status/1892111604147245158
The next category of regulations that DOGE will be purging is sizable.
DOGE was tasked with purging the federal government of socially significant regulations that Congress didn't roll out, and regulations that are costly for private entities without benefitting the public more.
DOGE was tasked with purging the federal government of socially significant regulations that Congress didn't roll out, and regulations that are costly for private entities without benefitting the public more.

This next category of regulations is where things get huge.
DOGE will be purging all regulations that impede innovation and infrastructure, make it harder to response to natural and manmade disasters, and just generally anything unnecessarily standing in the way of business.
DOGE will be purging all regulations that impede innovation and infrastructure, make it harder to response to natural and manmade disasters, and just generally anything unnecessarily standing in the way of business.

Now obviously this is a major task, but don't worry: the next section says which regulations to focus on first.
It says to focus on regulations that are particularly important. This is totally logical: get rid of the big barriers to growth first, and then move down the list.
It says to focus on regulations that are particularly important. This is totally logical: get rid of the big barriers to growth first, and then move down the list.

The next section might be my favorite part of this whole Order.
This section calls for an end to bureaucratic overreach.
It says that if a bureaucrat is doing more than they're required to, they need to stop it. This means fewer bureaucrats abusing their 'authority'.
This section calls for an end to bureaucratic overreach.
It says that if a bureaucrat is doing more than they're required to, they need to stop it. This means fewer bureaucrats abusing their 'authority'.

Additionally, if agencies are currently engaged in overreach in the enforcement of rules and regulations, they're going to stop.
This can also apply to rules and regulations that the President does not want enforced in a given way based on his valid interpretation of said rule.
This can also apply to rules and regulations that the President does not want enforced in a given way based on his valid interpretation of said rule.

And finally, the Order says what to do with new regulations:
Run them by DOGE, and if they're a barrier to business or a burden on the public, they won't go into effect.
Run them by DOGE, and if they're a barrier to business or a burden on the public, they won't go into effect.

Every new regulation will be reviewed and every existing regulation will be reviewed too, and all barriers to growth that can be extirpated from the Federal Register will be extirpated from it.
This authority is expansive and unprecedented, and the admin was building to this.
This authority is expansive and unprecedented, and the admin was building to this.
And just to be sure, there's still more to come.
DOGE is enabling the digitization of records, the installation of modern systems and tools that will enable the U.S. to be governed in a modern, rapid, and flexible way.
That's its purpose, is making a 21st-century government.
DOGE is enabling the digitization of records, the installation of modern systems and tools that will enable the U.S. to be governed in a modern, rapid, and flexible way.
That's its purpose, is making a 21st-century government.
And why?
Well obviously because regulations are burdensome, the spending has been too high, and so on, but this Order contains another clue.
Well obviously because regulations are burdensome, the spending has been too high, and so on, but this Order contains another clue.

One of Trump's goals is ending the secret fourth branch of government that persists between Presidencies and ensures Democrats are always in power.
It is an explicit goal of this Administration to end the "Administrative State."
It is an explicit goal of this Administration to end the "Administrative State."
In their Fact Sheet on this Executive Order, the Presidency stated that it is their goal to end the extreme burdens on the American people from this unconstitutional fourth branch of government, and to stop them from prying into American lives forevermore. 

It is hard to overstate how huge this Order is.
There are hundreds of thousands of federal regulations, and a very large portion of them can be stripped back with executive authority alone.
And now, DOGE has been enabled to start that process, with all that entails.
There are hundreds of thousands of federal regulations, and a very large portion of them can be stripped back with executive authority alone.
And now, DOGE has been enabled to start that process, with all that entails.
That entails a lot, but I'll cut myself off here. And keep in mind, this is just the first month of this administration.
Here's the Executive Order: whitehouse.gov/presidential-a…
Here's the Fact Sheet: whitehouse.gov/fact-sheets/20…
Here's the Executive Order: whitehouse.gov/presidential-a…
Here's the Fact Sheet: whitehouse.gov/fact-sheets/20…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh