Machine Learning is the secret ingredient in my algorithmic trading.
Here are 5 steps to get started (with Python code):
Here are 5 steps to get started (with Python code):

1. Define the Problem and Gather Data
Start by deciding what you want to predict (e.g., stock price direction, volatility) and collect relevant data (e.g., historical prices, volume, economic indicators). Use APIs like yfinance or Alpha Vantage for financial data.
Start by deciding what you want to predict (e.g., stock price direction, volatility) and collect relevant data (e.g., historical prices, volume, economic indicators). Use APIs like yfinance or Alpha Vantage for financial data.

2. Preprocess and Feature Engineering
Clean the data (handle missing values and incorrect prices) and create features like moving averages, RSI, or lagged returns to give the model predictive power.
Clean the data (handle missing values and incorrect prices) and create features like moving averages, RSI, or lagged returns to give the model predictive power.

3. Choose and Train a Model
Pick an ML model for trading (e.g., regression for price prediction, classification for buy/sell signals). Split data into training and testing sets, then train the model.
Pick an ML model for trading (e.g., regression for price prediction, classification for buy/sell signals). Split data into training and testing sets, then train the model.
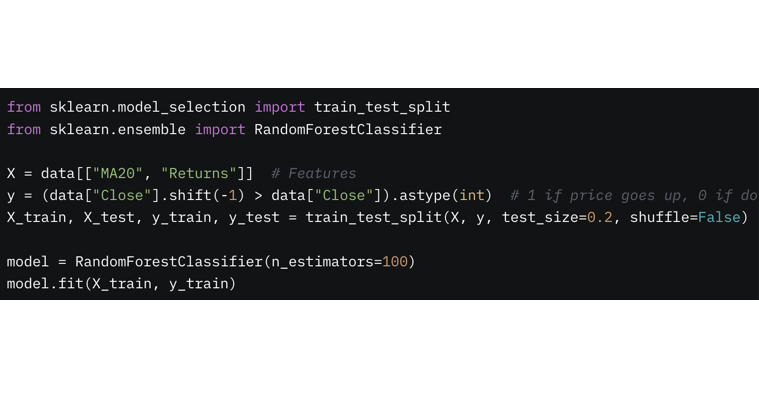
4. Evaluate and Optimize
Test the model’s performance using metrics like accuracy, precision, or annualized returns. Tune hyperparameters to improve results and avoid overfitting.
Test the model’s performance using metrics like accuracy, precision, or annualized returns. Tune hyperparameters to improve results and avoid overfitting.
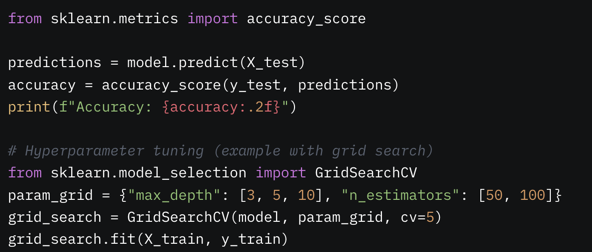
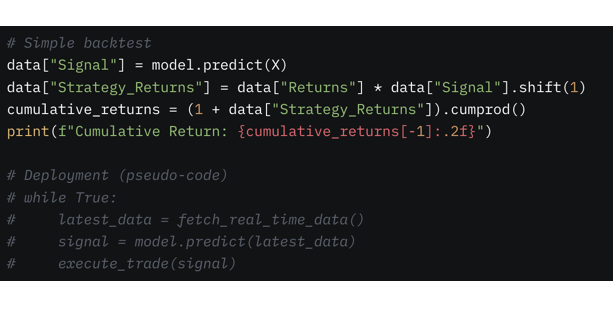
5. Backtest and Deploy
Simulate the model’s performance on historical data to estimate profitability and risk. If successful, integrate it into a trading system with proper risk management.
Simulate the model’s performance on historical data to estimate profitability and risk. If successful, integrate it into a trading system with proper risk management.
Want to learn how to get started with algorithmic trading with Python?
Then join us on March 5th for a live webinar, how to Build Algorithmic Trading Strategies (that actually get results)
Register here (780+ registered): learn.quantscience.io/qs-register
Then join us on March 5th for a live webinar, how to Build Algorithmic Trading Strategies (that actually get results)
Register here (780+ registered): learn.quantscience.io/qs-register
P.S. - Want Algorithmic Trading with Python tutorials every Sunday?
Register here to join our Sunday Quant Scientist Newsletter (it's free): learn.quantscience.io/quant-scientis…
Register here to join our Sunday Quant Scientist Newsletter (it's free): learn.quantscience.io/quant-scientis…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh