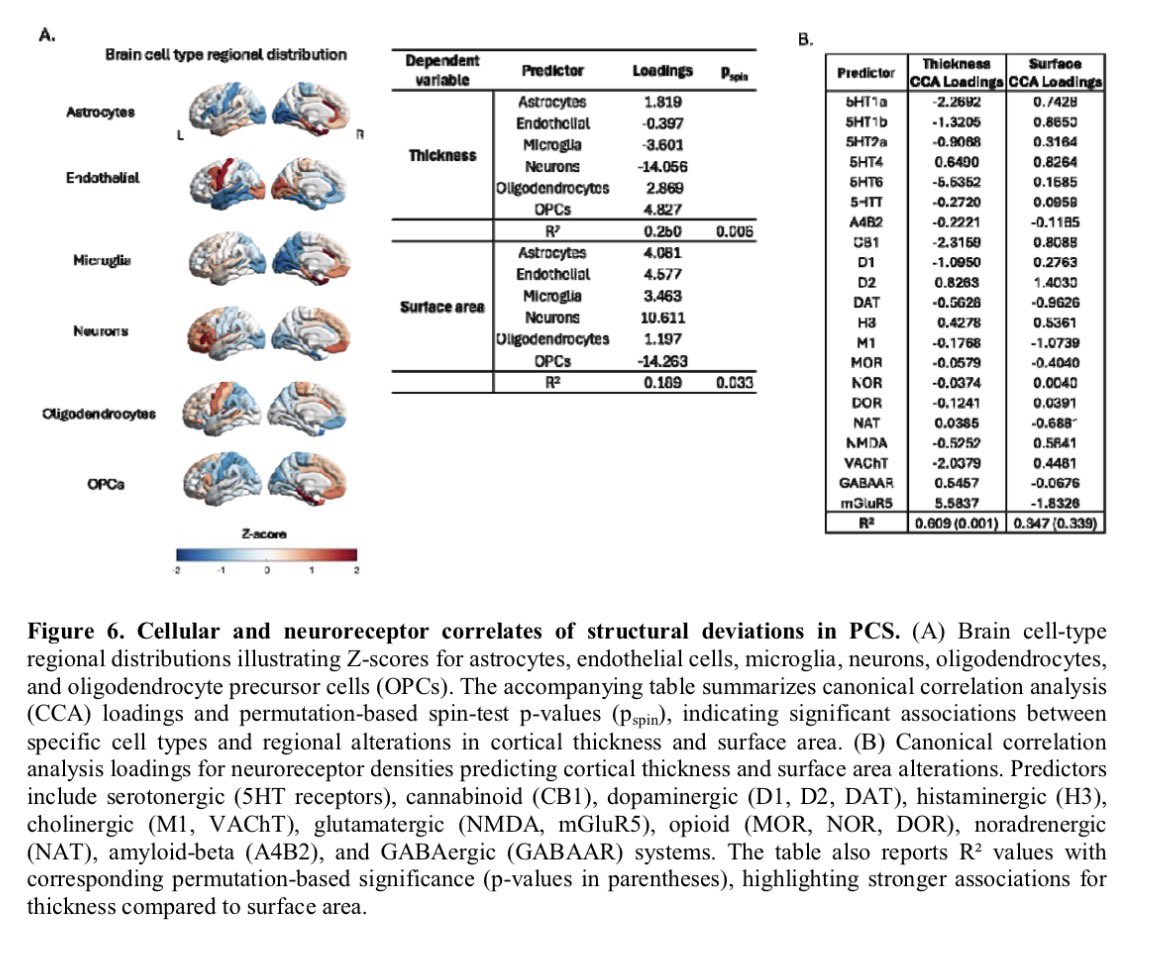
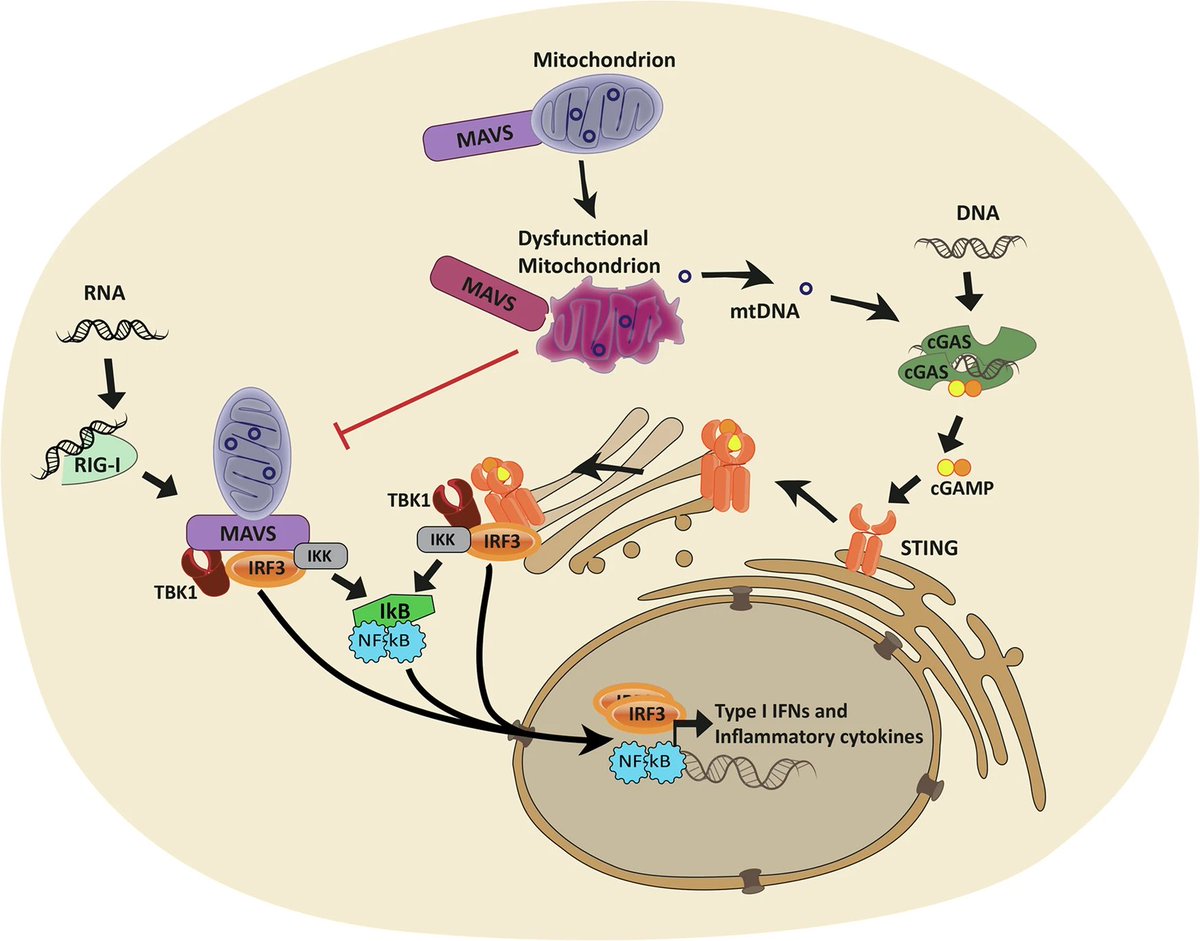
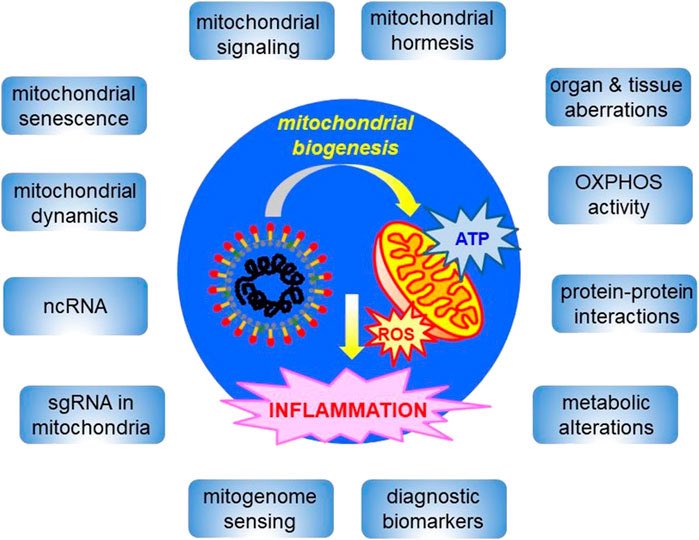
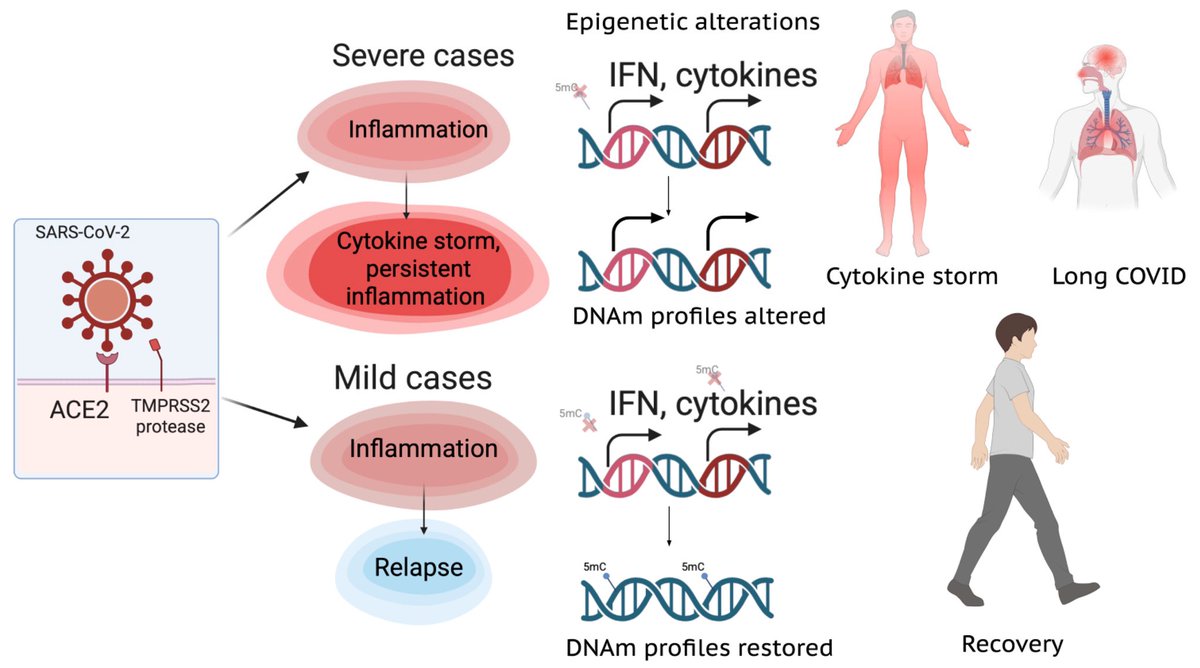
Oral Cavity Serves as Long-Term COVID-19 Reservoir with Increased Periodontal and Viral Disease Risk:
-COVID-19 history significantly correlates with severe oral health complications while vaccination reduced but did not eliminate these issues. 1/
-COVID-19 history significantly correlates with severe oral health complications while vaccination reduced but did not eliminate these issues. 1/

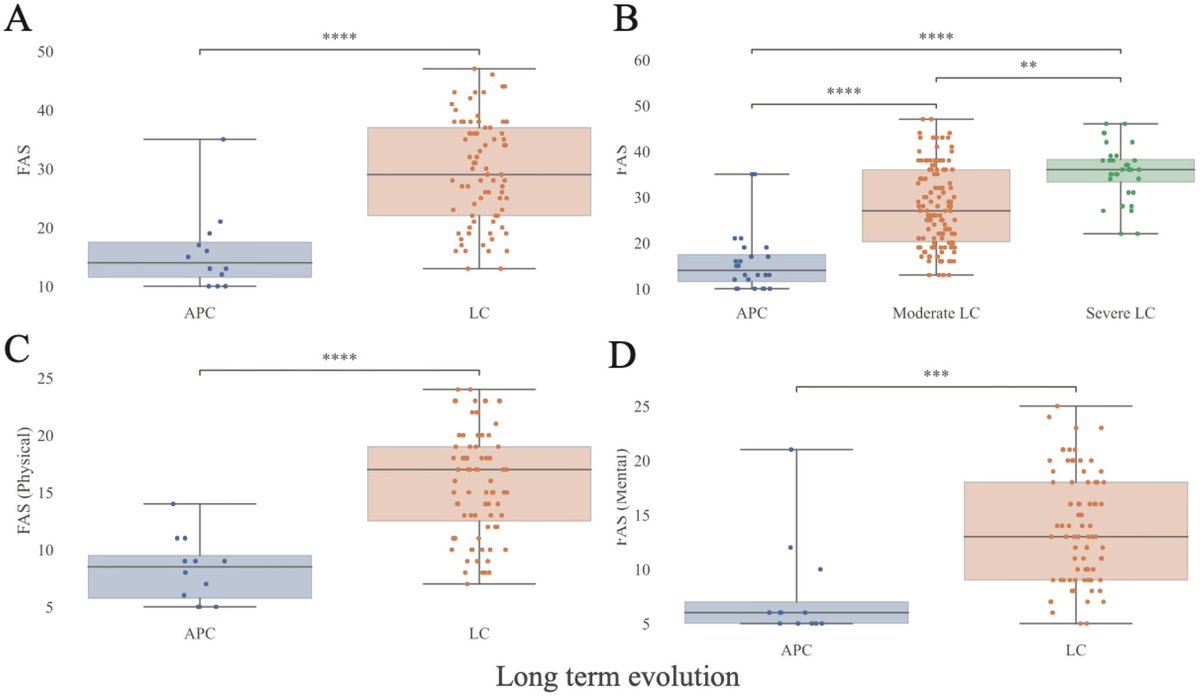
A NEW study identified oral associated #LonhCovid primarily manifested as periodontal (gum) disease (COVID +ve: 73.1±18.9% vs COVID -ve: 33.1±14.3%)
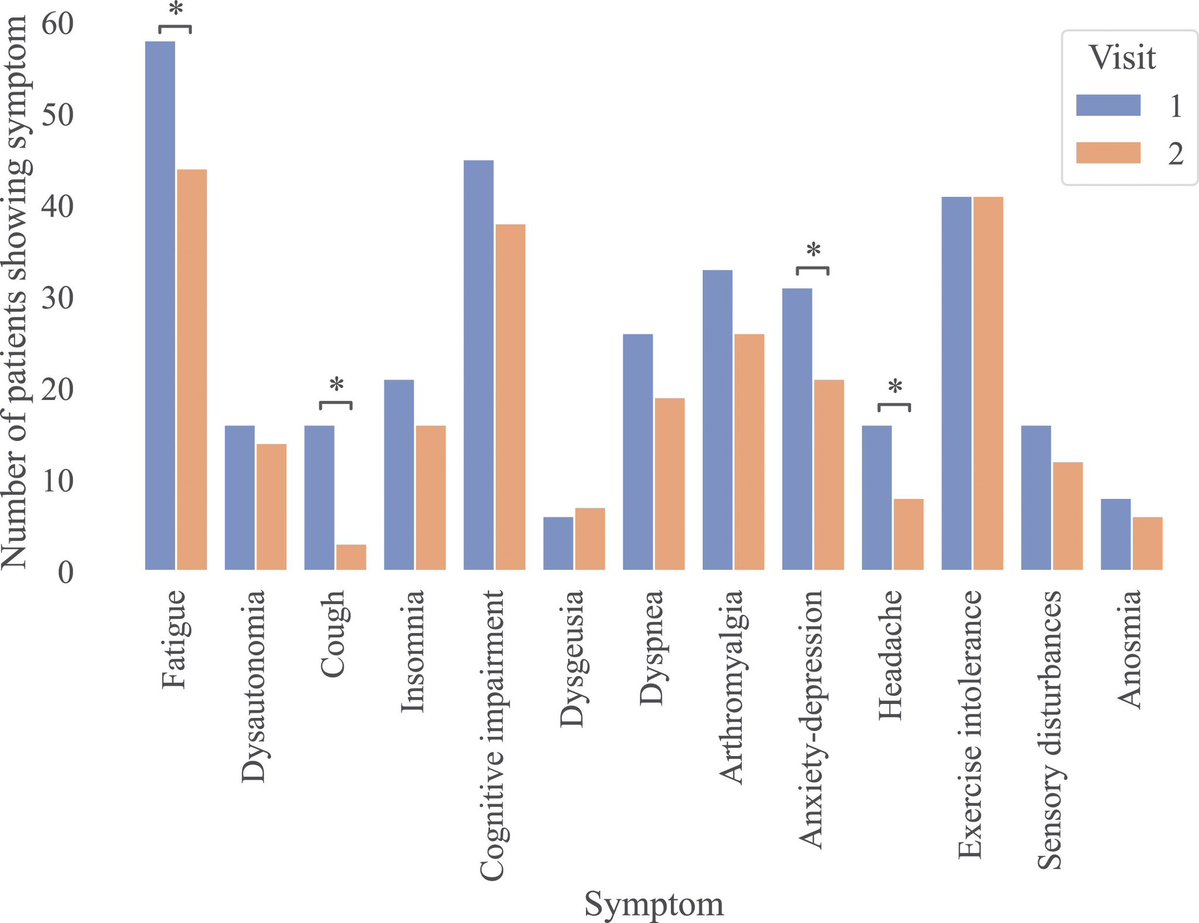
Covid19 positive cases correlated w/ higher rates of dry mouth (57.5%), taste disturbance (47%) & smell loss (20%). 2/
Covid19 positive cases correlated w/ higher rates of dry mouth (57.5%), taste disturbance (47%) & smell loss (20%). 2/

Vaccination reduced oral LongCovid (PASC) in COVID-19 positive subjects; however, periodontal disease indicators persisted compared to the COVID-19 negative group. 3/ 

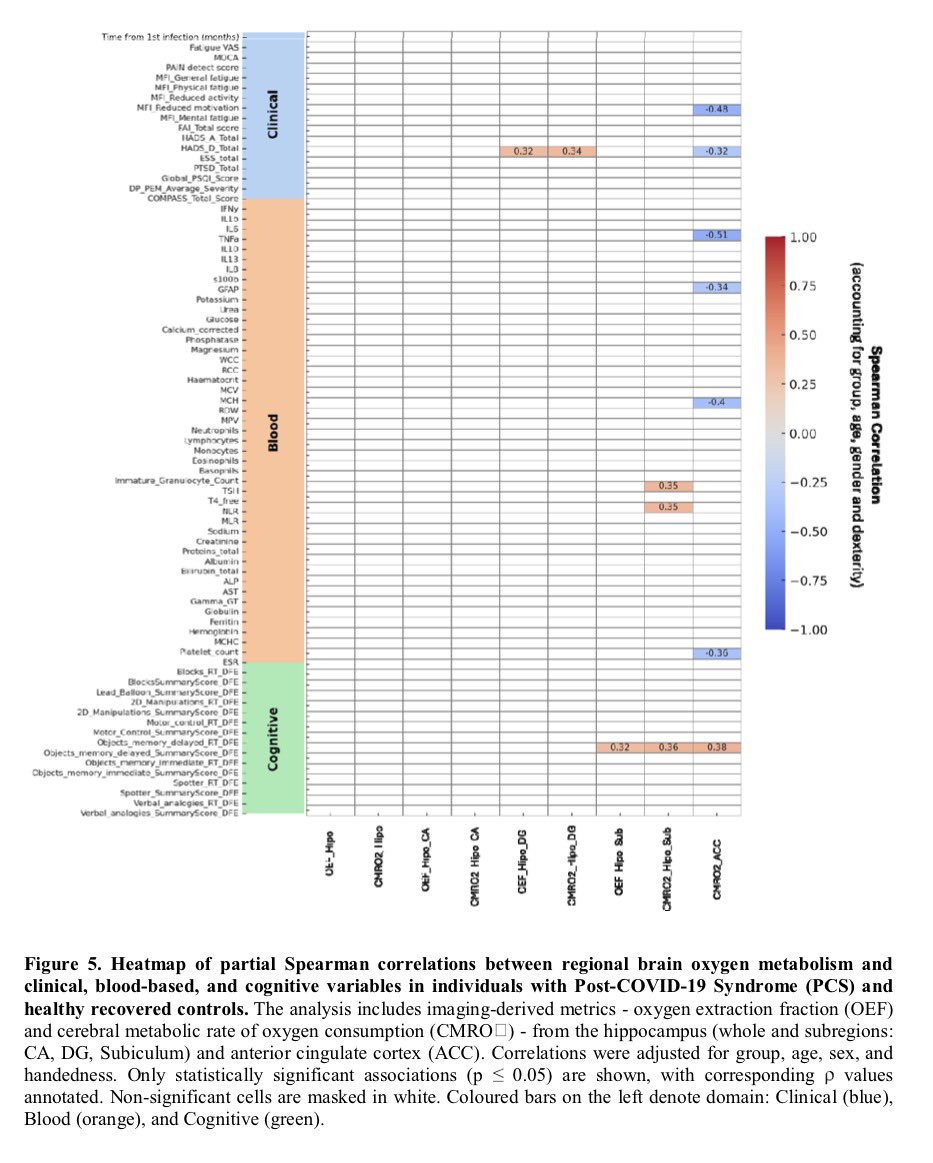
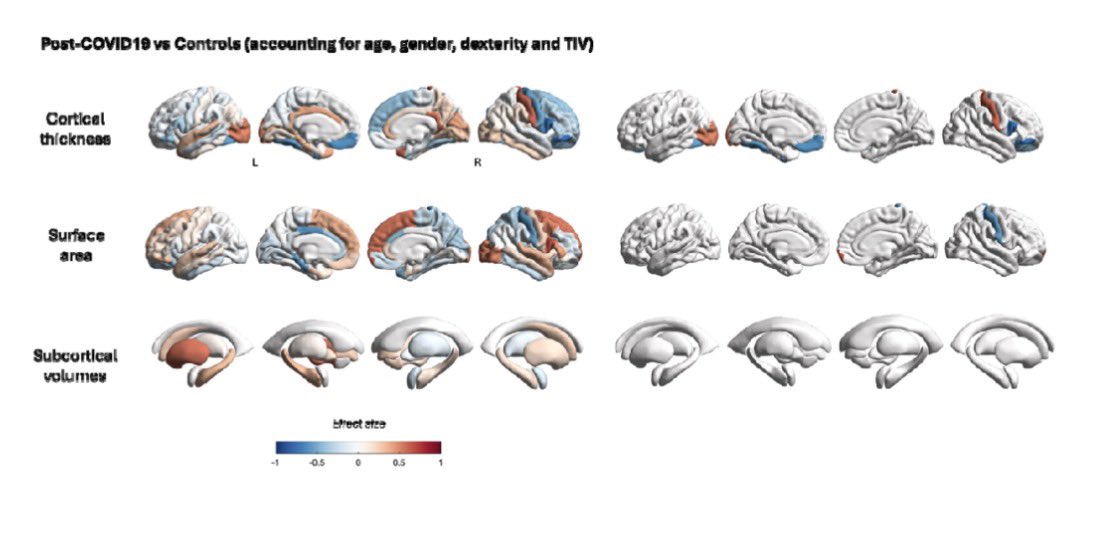
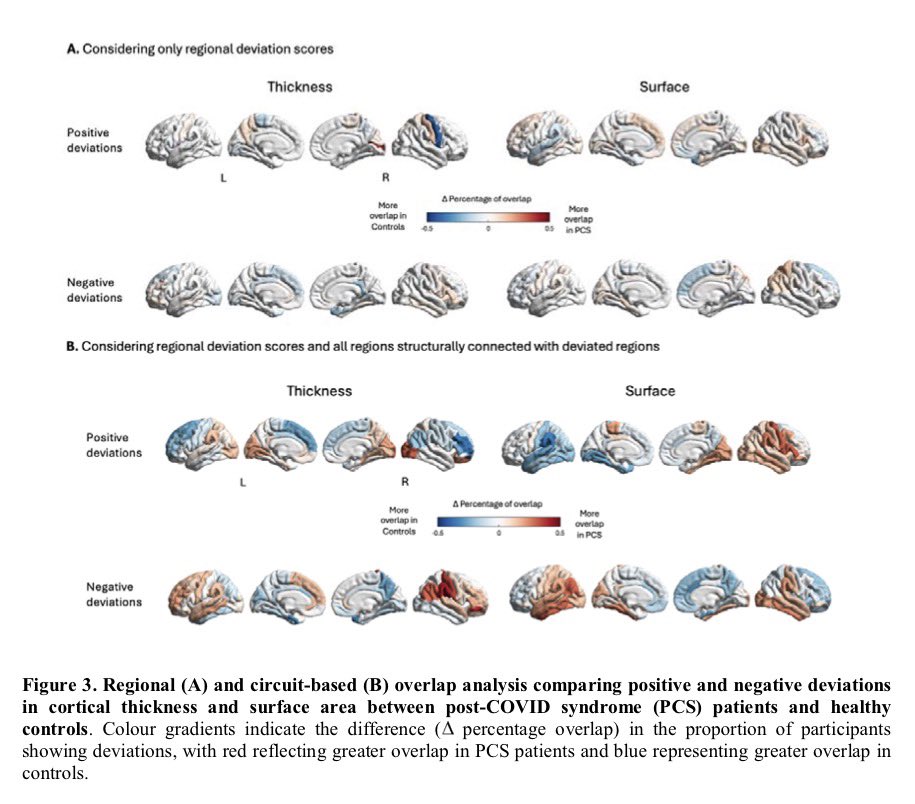
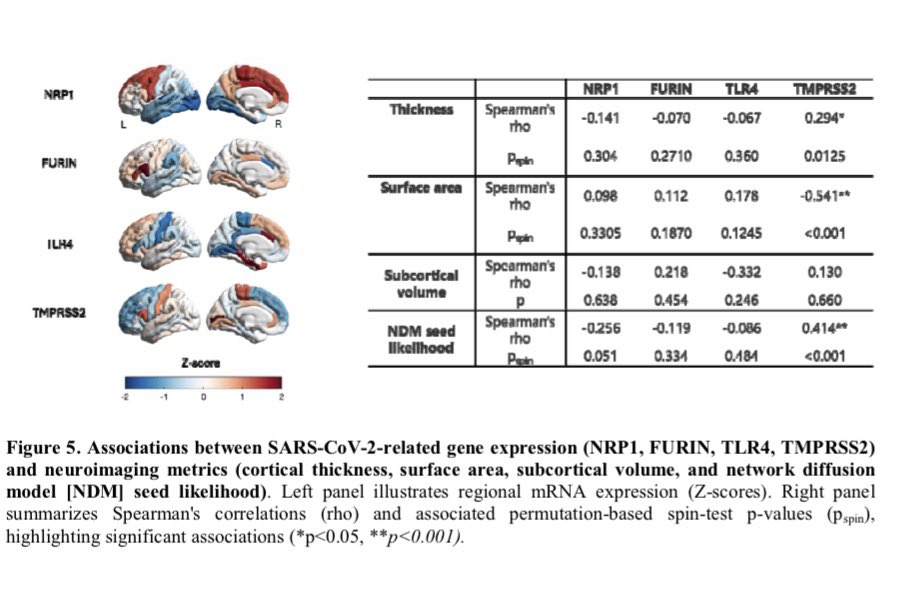
Notably, 3-6 months post-infection, while SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S) transcript was rarely detected in saliva (∼6%), its protein was commonly detected (∼70%) in the COVID-19 positive subjects indicating incomplete viral clearance. 4/ 

This correlates with significantly higher salivary expression of viral entry receptors (ACE2, and TRMPSS2), and inflammatory mediators (IL-6, IL-8 and MMP-8), in COVID-19 positive subjects. 5/ 

This finding was further supported by higher prevalence of other oral viruses including Epstein-Barr Virus (70.5%), Herpes Simplex Virus (8.1%), and Human Papillomavirus (17.5%) in COVID-19 positive subjects. 6/6
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh