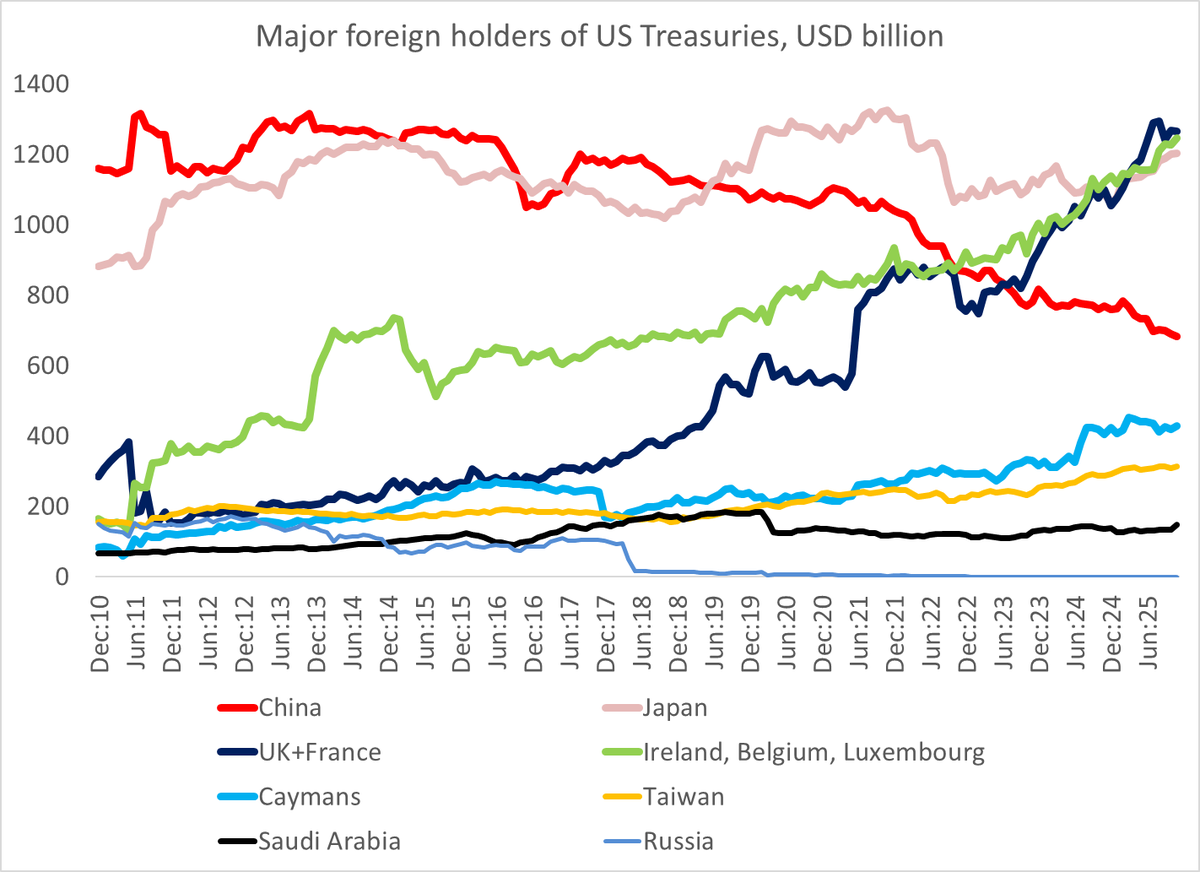
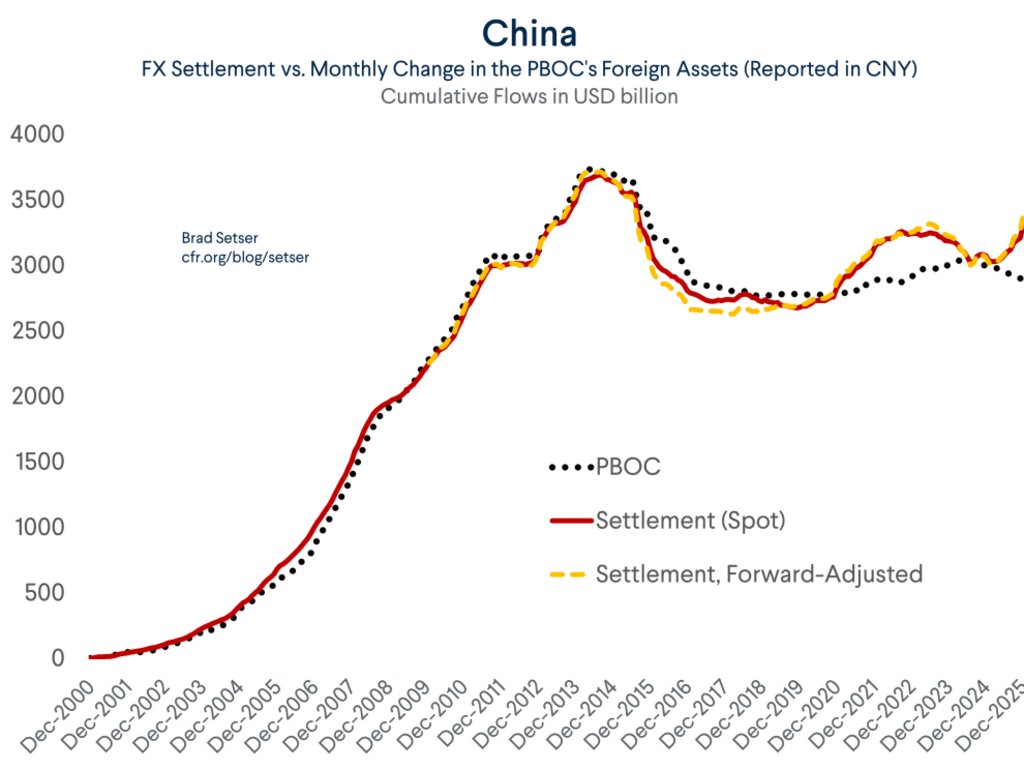
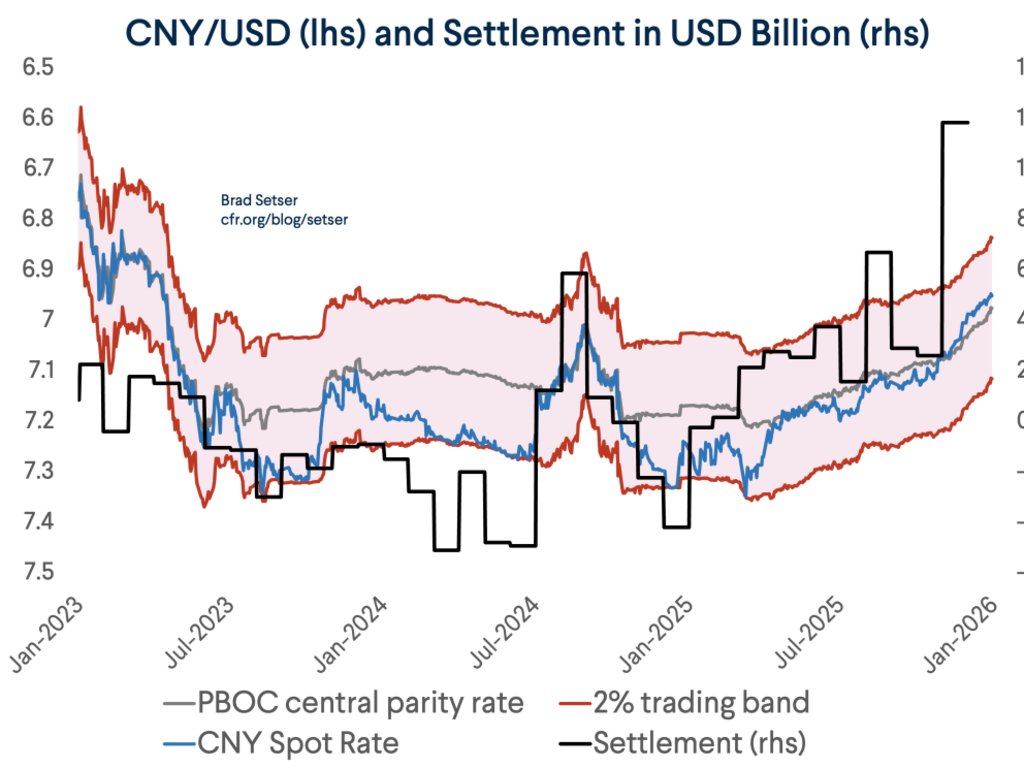
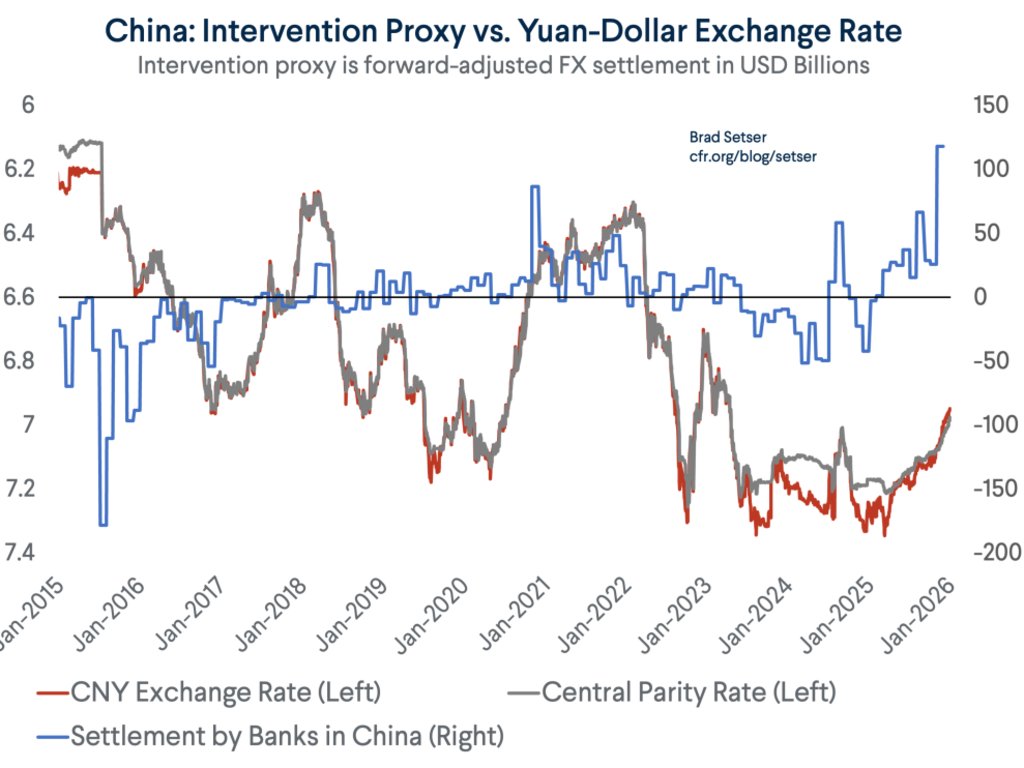
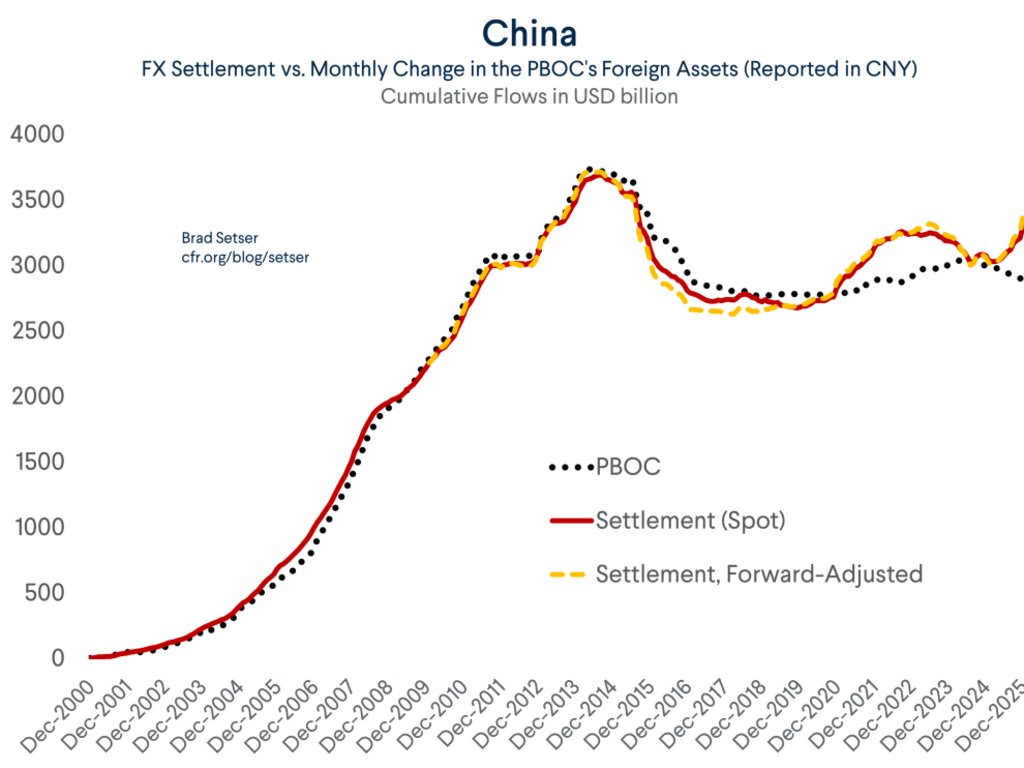
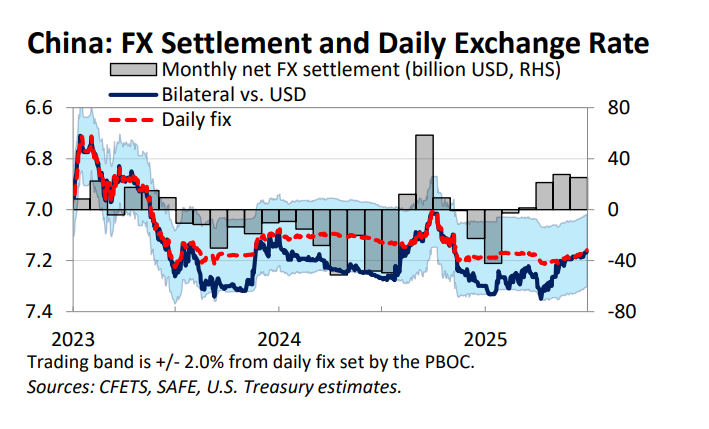
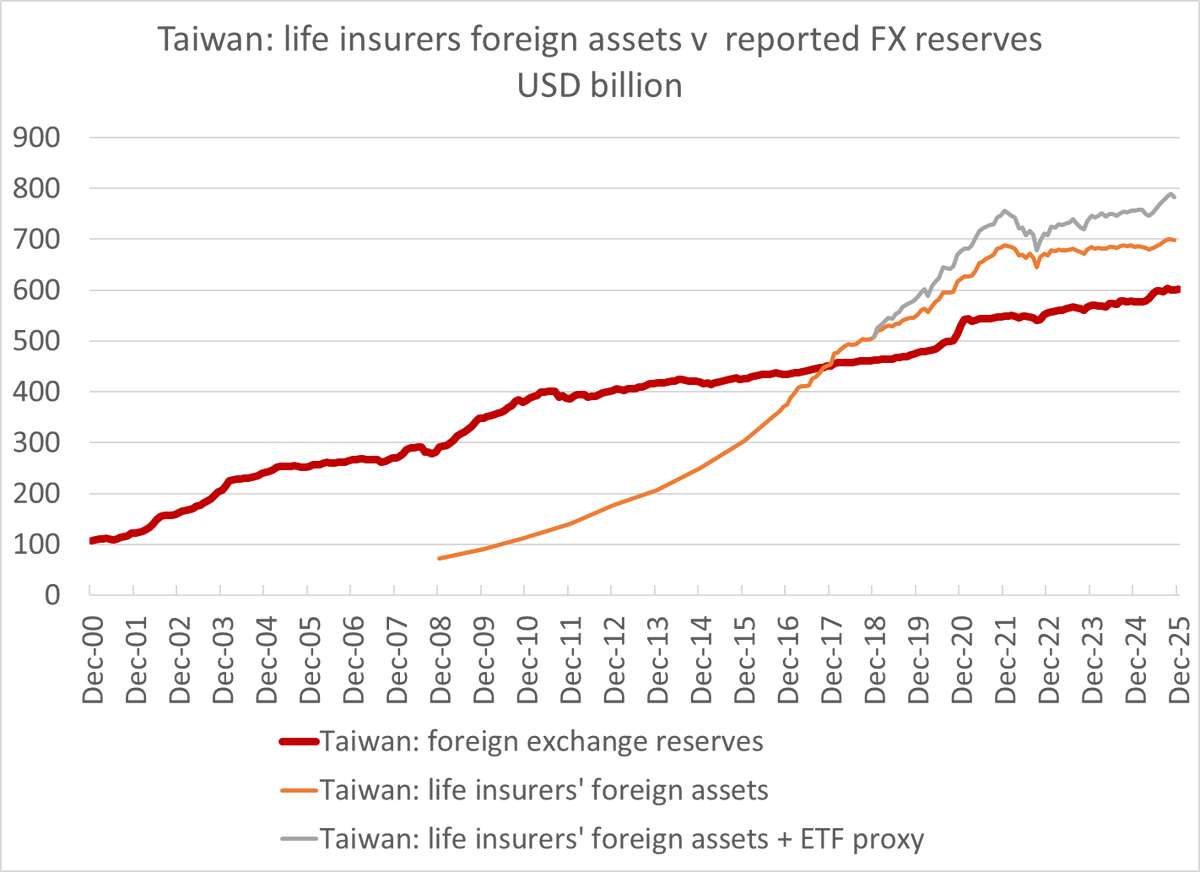
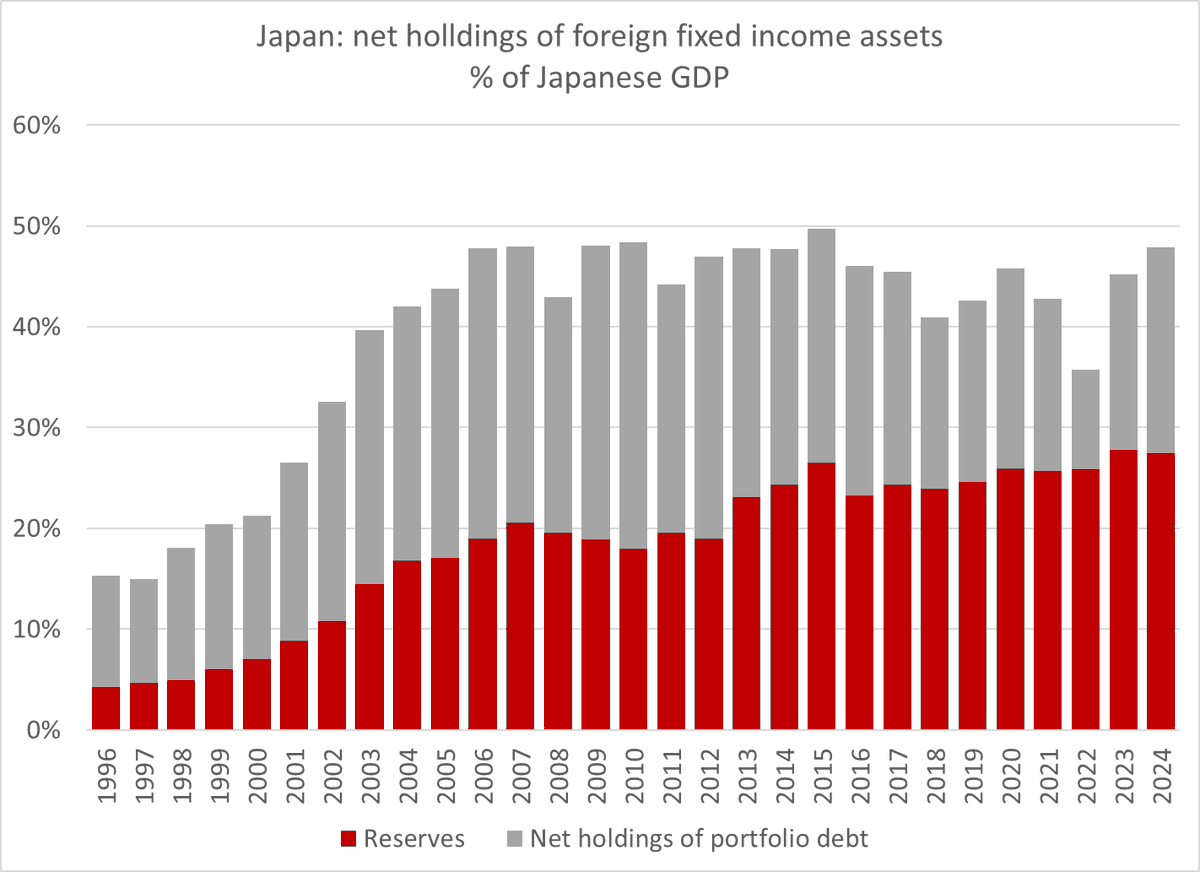
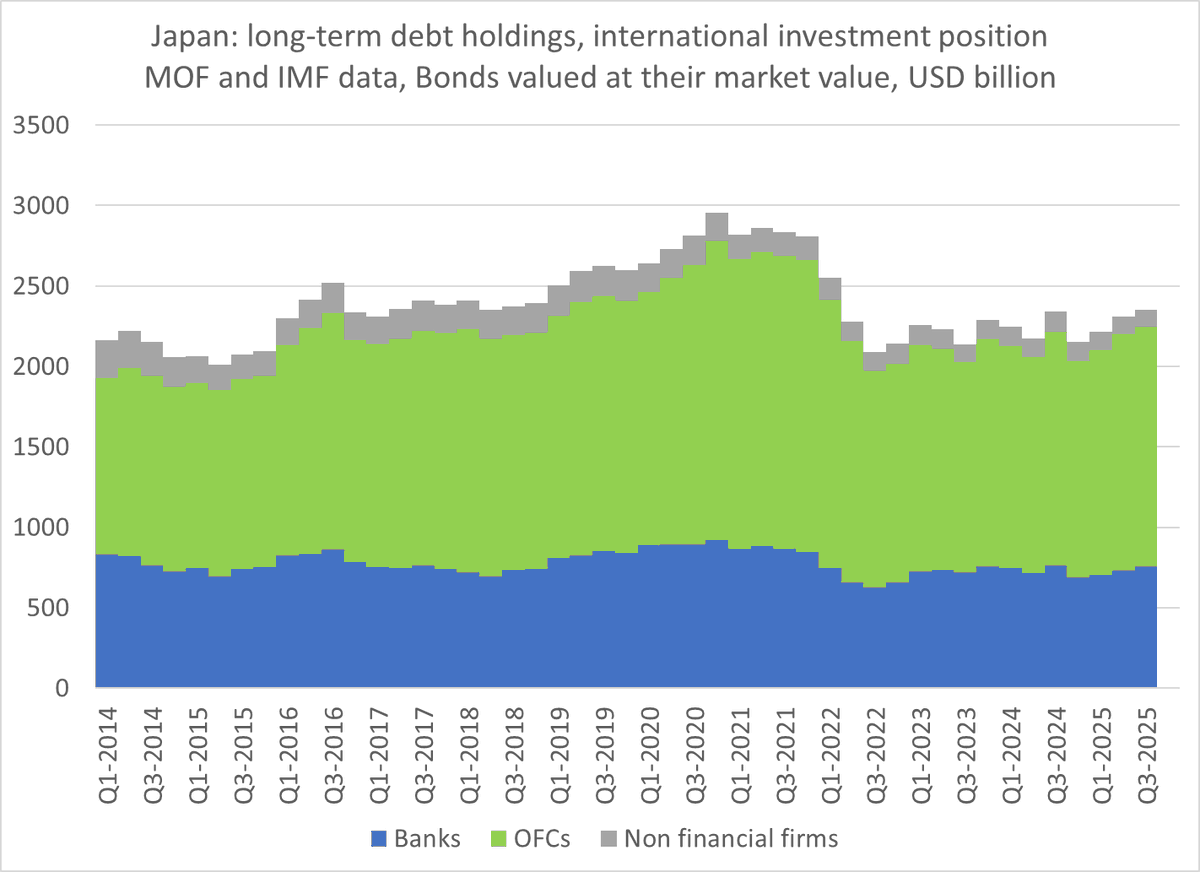
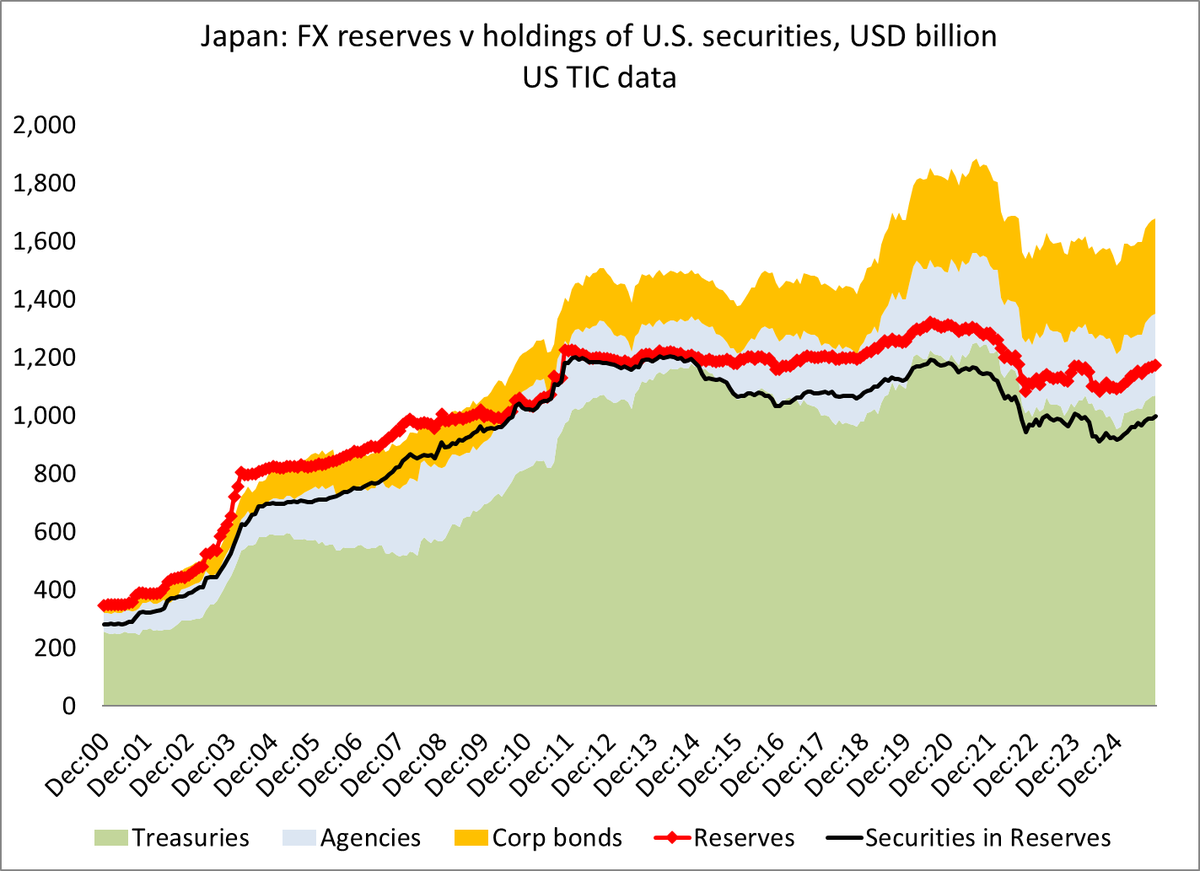
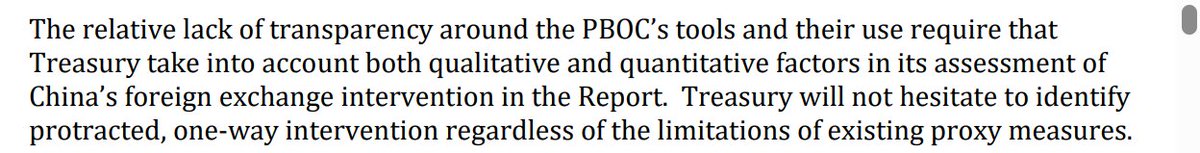One fact about the global economy should not be subject to debate any more -- the US is more than meeting global demand for reserve assets (a significant change from 2002 to 2014 ... )
1/ many
1/ many

And since China has had a policy of limiting its Treasury holdings (and shifting fx reserves over to the SCBs and policy banks) since around 2010, China's share of the Treasury market has shrunk radically ...
2/
2/

The split is imprecise (Treasuries held by central banks in offshore custodians count as "private") but there is no real doubt that the role of official investors in the market has shrunk -- and there has been a big increase in private US holdings ...
3/
3/

The stock in private domestic hands still is absolutely huge (it is around 50% of GDP) but it is up ~ 20 pp of GDP compared to the pre-COVID era, and a lot of that increase has been funded by US money market funds, either directly or indirectly (via repo)
4/
4/

These structural shifts help explain why the Treasury issued a lot of bills in 2022 and 2023 -- that was where the demand was ...
Note issuance actually picked up significantly over the course of 2024 ...
5/
Note issuance actually picked up significantly over the course of 2024 ...
5/

Note issuance is now running at just under 5% of US GDP -- a level consistent with a stable bill share if the fiscal deficit is around 6% of GDP. Counting QT, the market absorbed note supply equal to the fiscal deficit last year ...
6/
6/

Foreign demand for notes has been stable at around 1.5 pp of GDP/ $450b -- a decent number absolutely and relative to history, but modest v total supply.
7/
7/
Increased note (coupon paying Treasuries, bills are sold at a discount to pay) issuance has been facilitated by gigantic fall off in mortgage issuance (Fed tightening clearly impacted the secondary market in housing)
8/
8/

And shifting from the flow of funds data to the Bertaut Judson monthly flow data, the bulk of foreign demand for Treasury coupons does look to be from true private holders. b/c China shifted to bills at the margins, my estimates imply its note holdings fell modestly in 2024
9/
9/

Bottom line -- the increase in the stock of Treasuries in the market since the start of the pandemic has largely been absorbed domestically ... a point that is well known among actual market participants (who like to point that there are more price sensitive buyers)
10/
10/

& absent a very elastic definition of reserve demand that includes private holdings abroad, it no longer is really accurate to say the US external deficit reflects excess global demand for reserve assets. That was the case imo from 03 to 13 -- but the world has changed
/end
/end
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh