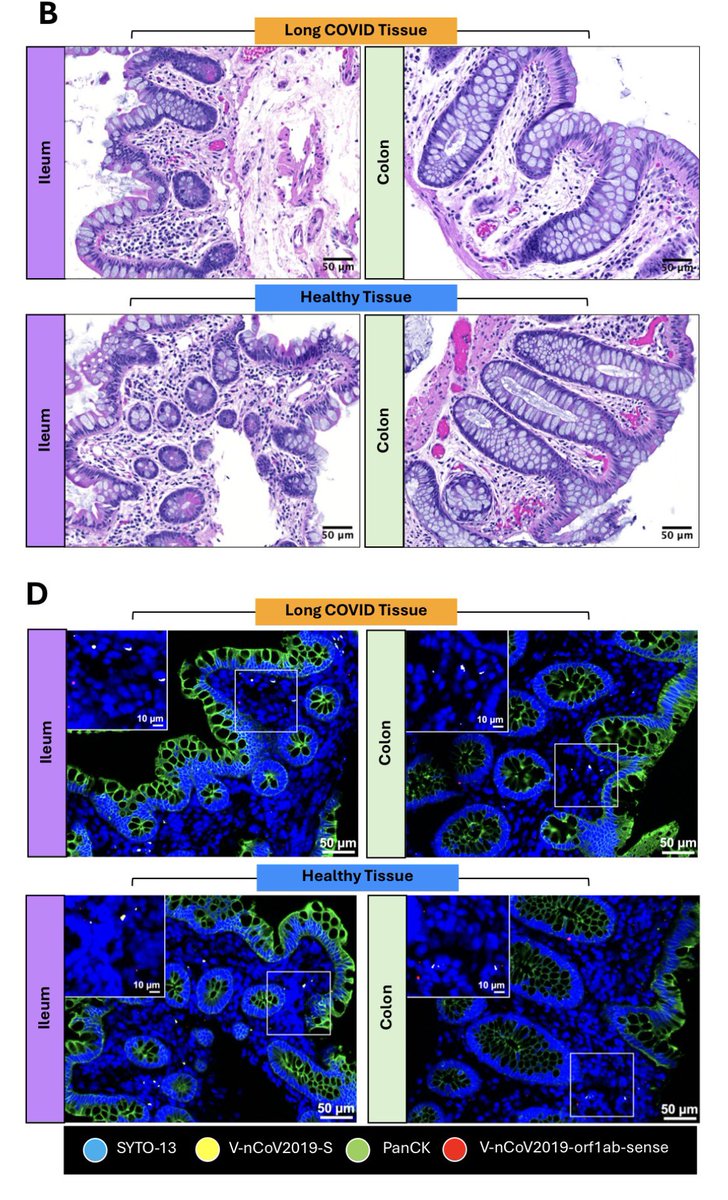
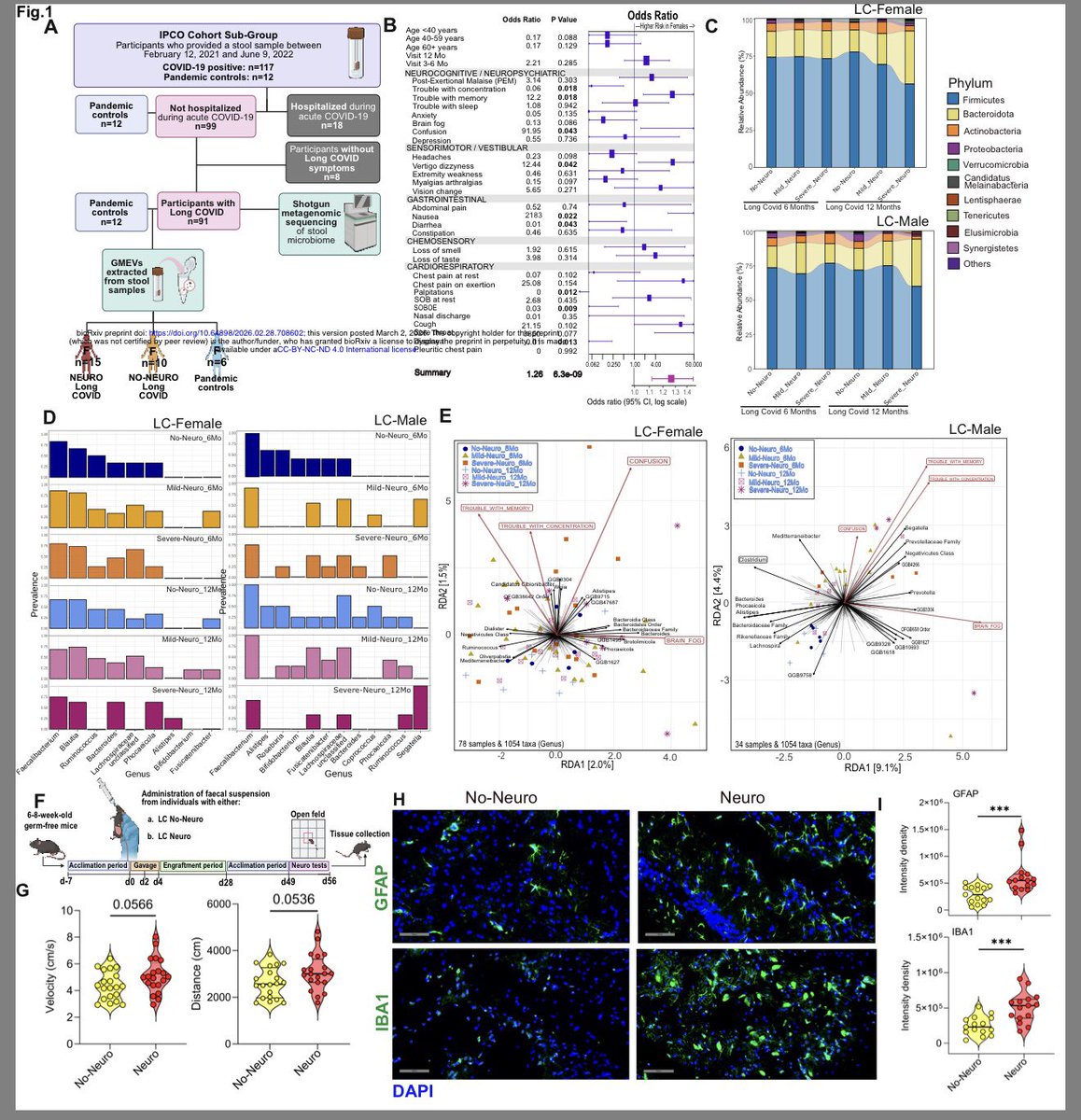
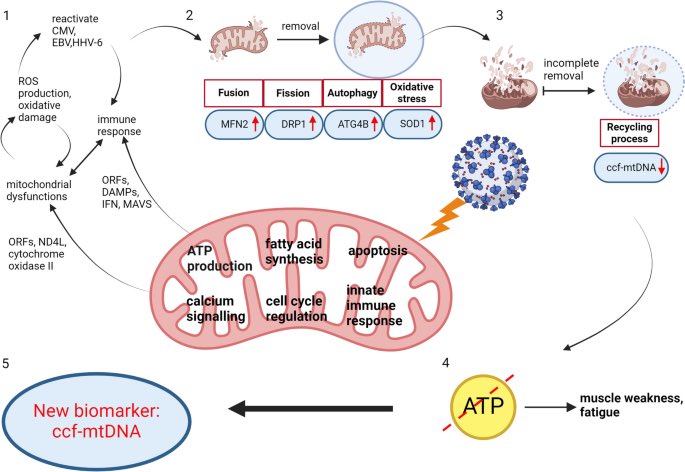
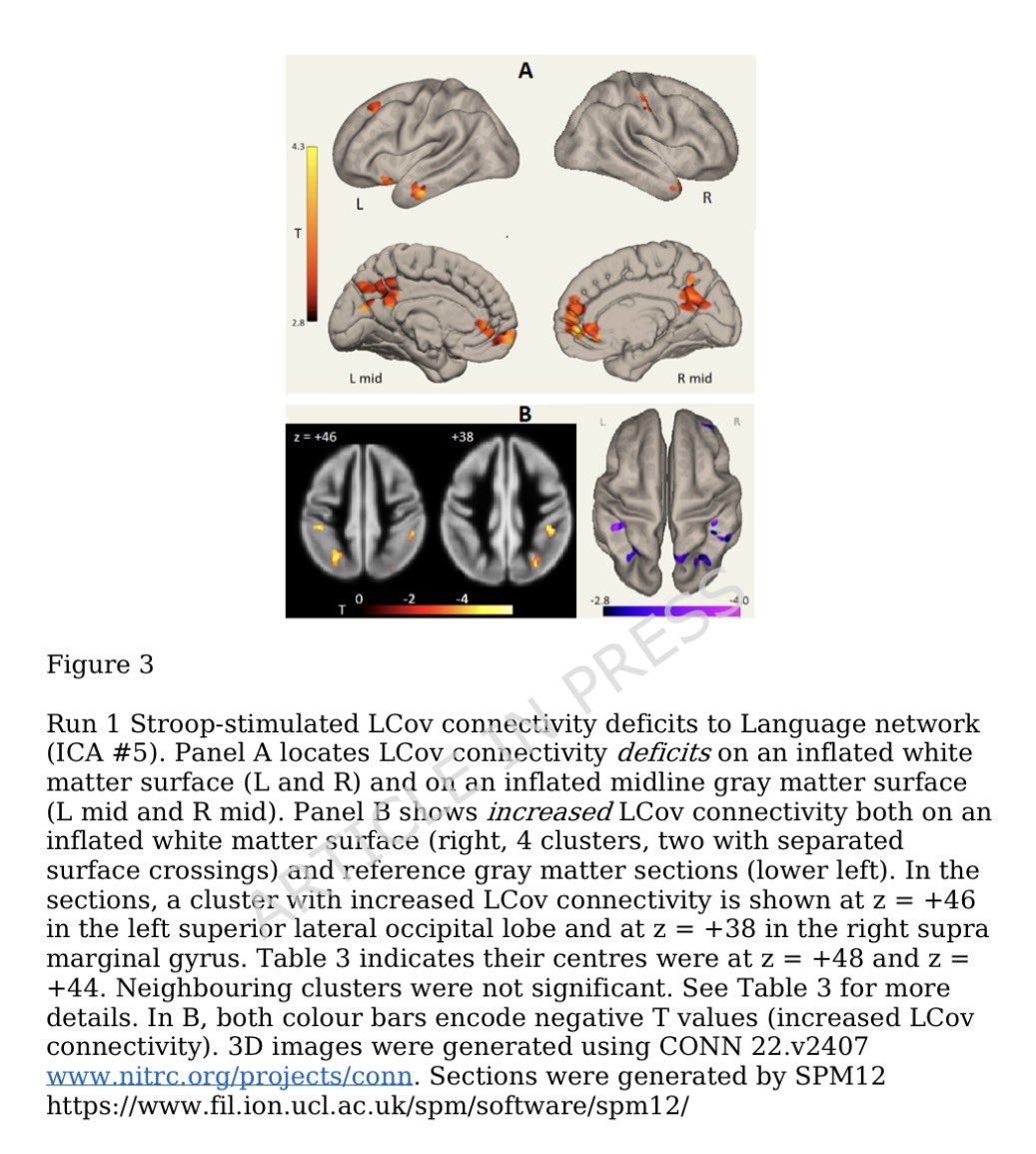
A NEW study finds that H5N1 influenza viral lineages are beginning to evade human immunological defenses. This indicates current and future H5N1 viral lineages pose a greater risk to human health—including the possibility of increased transmission in humans. 1/ 

This new computational modeling of avian influenza variants' immunoprotein interactions reveals the H5N1 influenza virus is evolving to escape immunological defenses raised by previous infection or vaccination in mammals. 2/ 

This rapid adaptation means that if one makes an H5N1 vaccine with a previous vaccine candidate virus, the vaccine will have less efficacy, based on the measurements of how much the virus has evolved in recent years. 3/ 

The continuous transmission of H5N1 from birds to mammals and the increase in strains with immuno-evasive HA in mammals sampled over time suggest that antigenic drift is a source of zoonotic risk. 4/ 

Using high-performance computational modeling, the researchers documented a trend of weakening binding affinity of a wide variety of existing antibodies, collected from vaccinated and or infected hosts, against H5 viral isolates over time. 5/ 

In assessing the possible pandemic risk spurred by H5 bird flu spread and mutation, global researchers agree that the avian virus remains high on lists of potential pandemic agents. 6/ 

As of today, no human-to-human transmission has been reported. However, cattle in at least 17 states have tested positive for H5N1 in addition to millions of cases among wild birds, small mammals, commercial chickens, and other flocks. 7/ 

Between January 2022 and March 2025, the CDC reported:
-12,510 outbreaks among wild birds in U.S.
-51 jurisdictions w/ bird flu among wild birds.
-166,417,923 poultry affected
-70 human cases of H5N1, one fatal, in the U.S. 8/
cdc.gov/bird-flu/situa…
-12,510 outbreaks among wild birds in U.S.
-51 jurisdictions w/ bird flu among wild birds.
-166,417,923 poultry affected
-70 human cases of H5N1, one fatal, in the U.S. 8/
cdc.gov/bird-flu/situa…
The H5N1 virus, according to the World Health Organization, has killed 466 people worldwide since January 2003. 9/ 

Speed important to respond to fast-evolving viral threat!
Vaccines will likely be a crucial tool in controlling a bird flu pandemic, as mutations of viral lineages adapt to new mammal hosts. 10/10
thelancet.com/journals/ebiom…
Vaccines will likely be a crucial tool in controlling a bird flu pandemic, as mutations of viral lineages adapt to new mammal hosts. 10/10
thelancet.com/journals/ebiom…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh