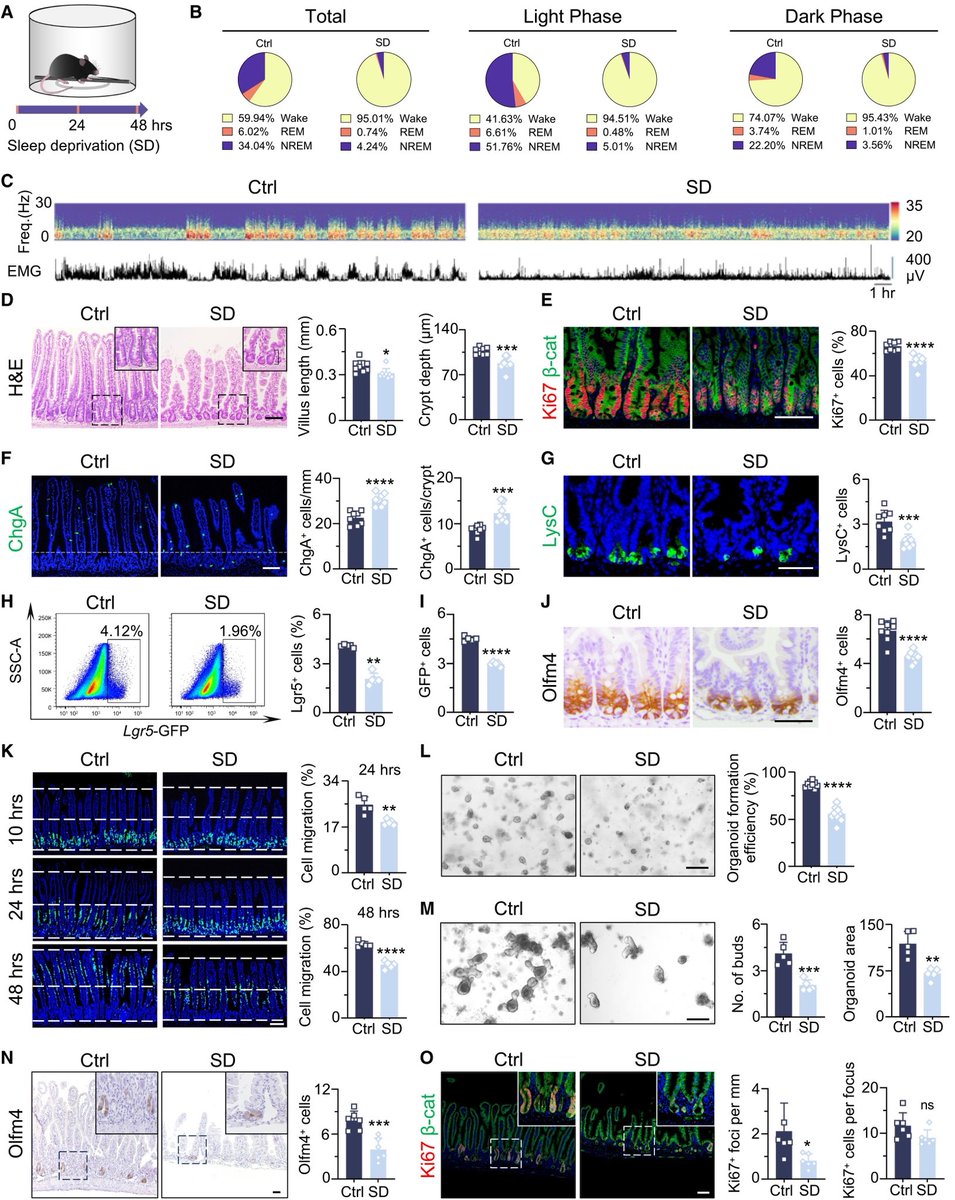
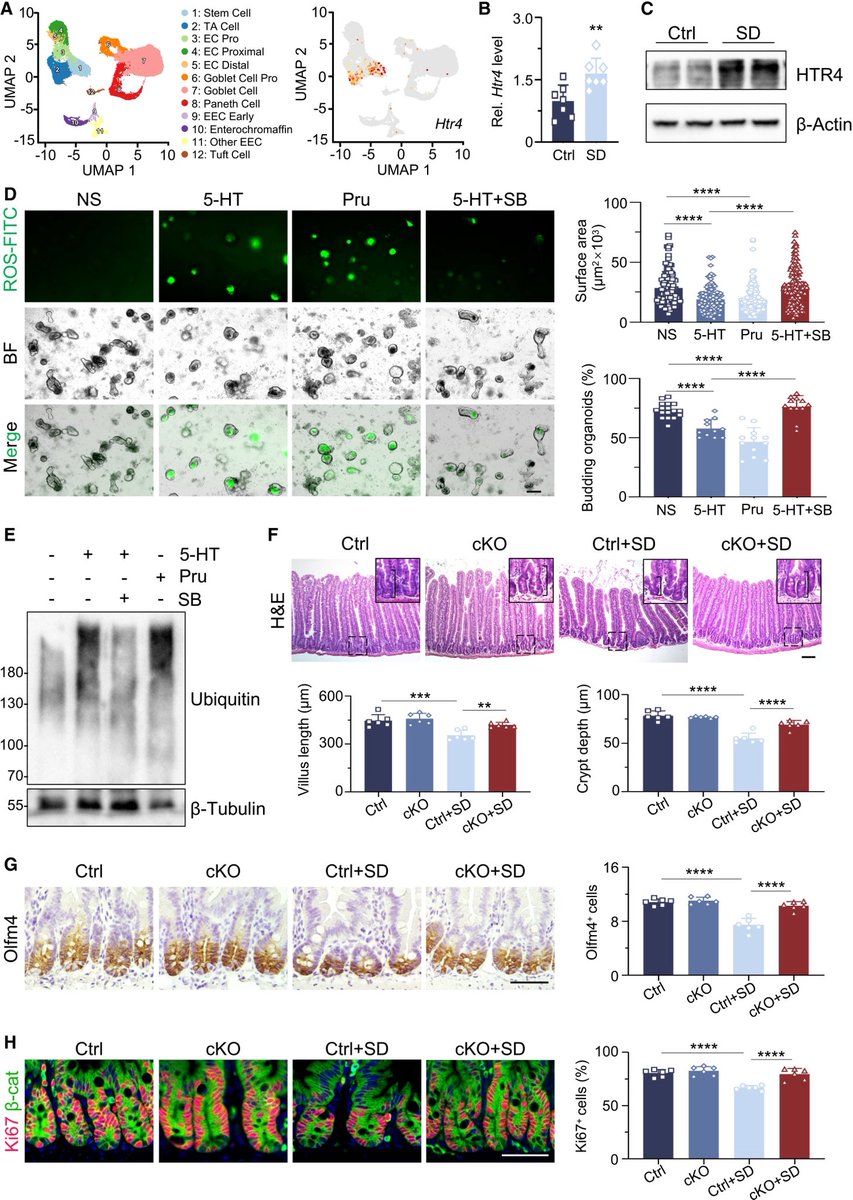
Researchers have developed an oral antiviral drug candidate for COVID-19 that could overcome major limitations of Paxlovid, currently the most prescribed oral treatment. 1/ 

As with its predecessor, the new drug candidate, Jun13296, targets a different viral protein than Paxlovid does and works alone rather than in combination with another drug called ritonavir. 2/ 

This new compound, #Jun3296 is more potent than the 1st generation candidate. In animal studies, this 2nd-generation inhibitor still provides 90% protection at just one-third dose of the initial compound and significantly outperforms it in reducing viral loads in the lungs. 3/ 

#Jun13296 also addresses Paxlovid's major limitation: drug interaction-induced side effects. Efficacy at lower doses helps patients because it reduces the chance that a drug will have serious side effects 4/
The researchers designed this new compound to target a structure in the virus called its papain-like protease (PLpro) rather than the main protease targeted by Paxlovid. In laboratory testing, Jun13296 remained effective against Paxlovid-resistant strains of the virus. 5/ 

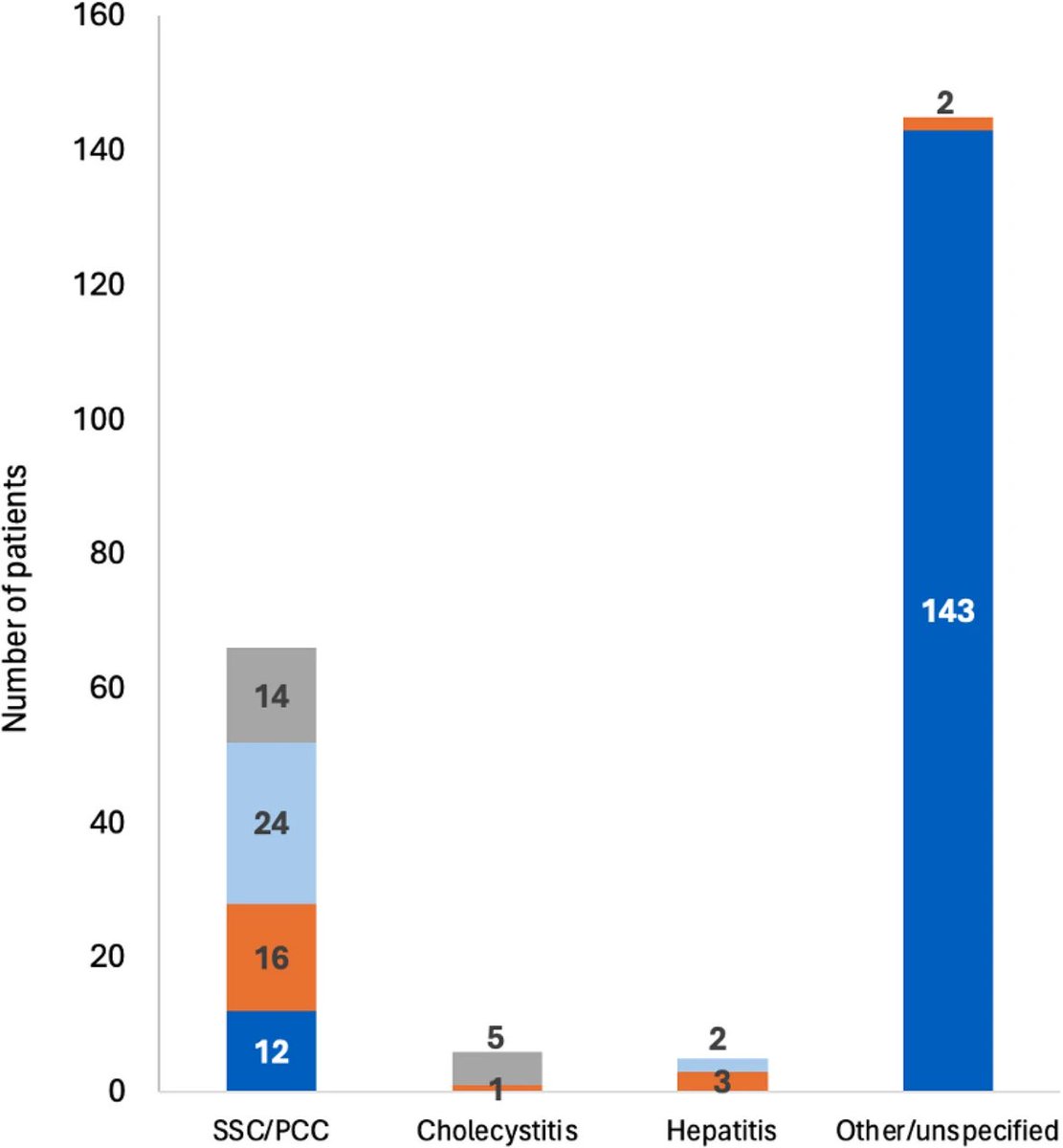
Each version evaluated by researchers shows significant inhibition by this PLpro inhibitor. The drug also considerably lowered pulmonary inflammation & virus levels. #Jun13296 protected inflammation well at 75 milligrams per kilogram, while Jun12682 just moderately did. 6/
Unlike Paxlovid, Jun13296 shows no inhibition of major drug-metabolizing CYP450 enzymes in lab tests, suggesting it would not interfere with other medications & does not need to co-administer w/ ritonavir, thereby circumventing the drug interaction-induced side effects 7/ 
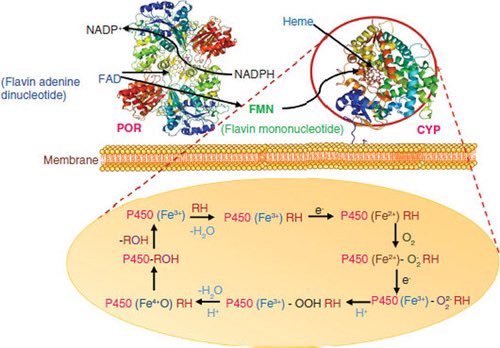
The development comes as COVID-19 evolves, including treatment-resistant strains. The researchers say pandemic preparedness requires different treatment options. Early-stage clinical studies would speed up therapy approval if SARS-CoV-2 evolves and causes another pandemic. 8/
The study team's methods apply to infectious disorders beyond COVID-19 such as multiple respiratory viruses, including influenza & enteroviruses. 9/9
nature.com/articles/s4146…
nature.com/articles/s4146…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh