1/Wish that your knowledge of autoimmune encephalitis was automatic?
Do you feel in limbo about limbic encephalitis?
Do you know the patterns?
Read on for what you need to know in this month's @RadioGraphics review!
@cookyscan1 @RadG_Editor doi.org/10.1148/rg.240…
Do you feel in limbo about limbic encephalitis?
Do you know the patterns?
Read on for what you need to know in this month's @RadioGraphics review!
@cookyscan1 @RadG_Editor doi.org/10.1148/rg.240…
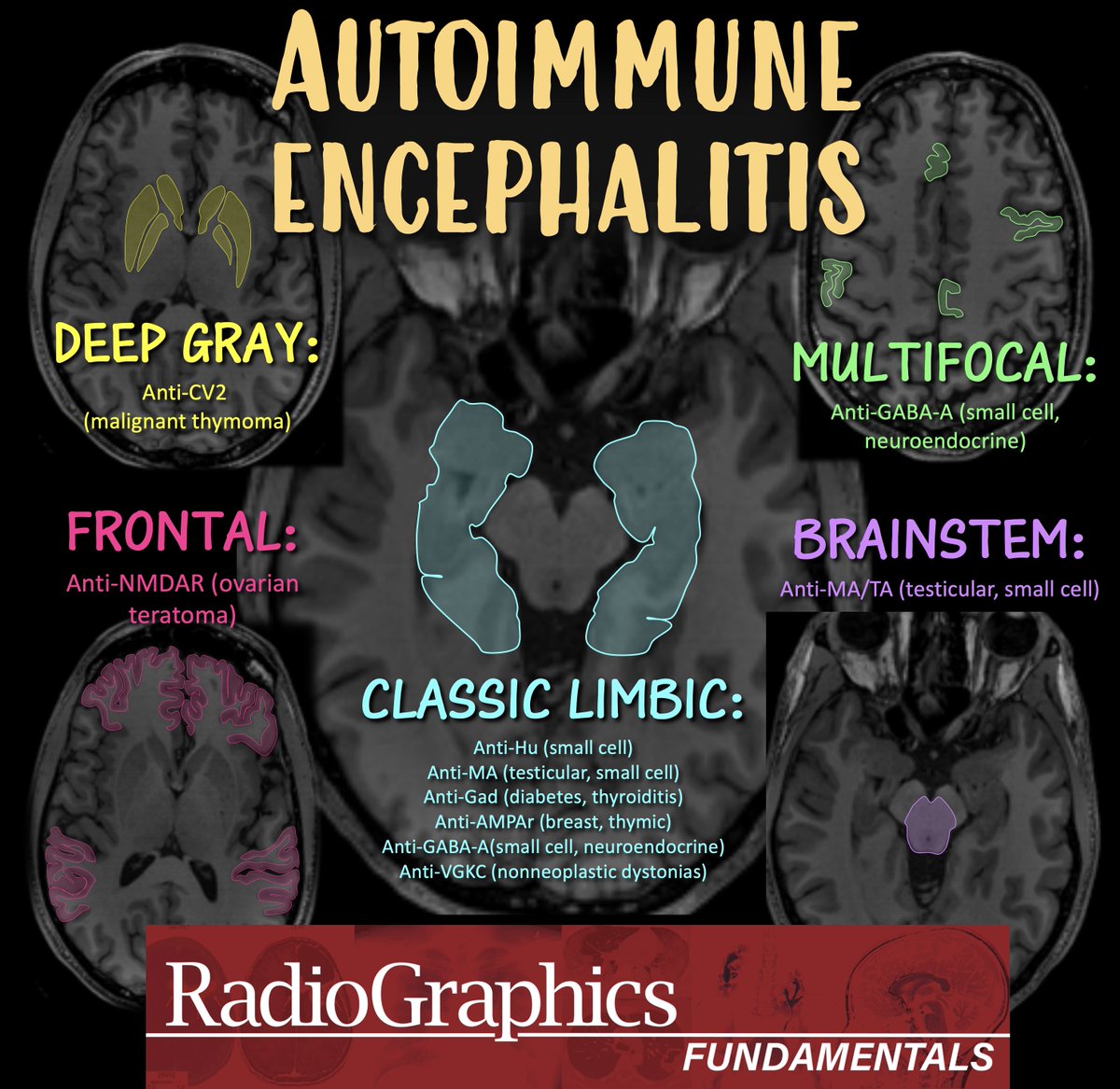
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1 @RadG_Editor 2/Two pearls:
(1) Most common pattern is limbic encephalitis
(2) Small cell can cause any autoimmune pattern.
You can remember the causes by the demographic:
Young man: testicular
Older: Small cell
Woman with psychiatric symptoms (limbic): breast
(1) Most common pattern is limbic encephalitis
(2) Small cell can cause any autoimmune pattern.
You can remember the causes by the demographic:
Young man: testicular
Older: Small cell
Woman with psychiatric symptoms (limbic): breast

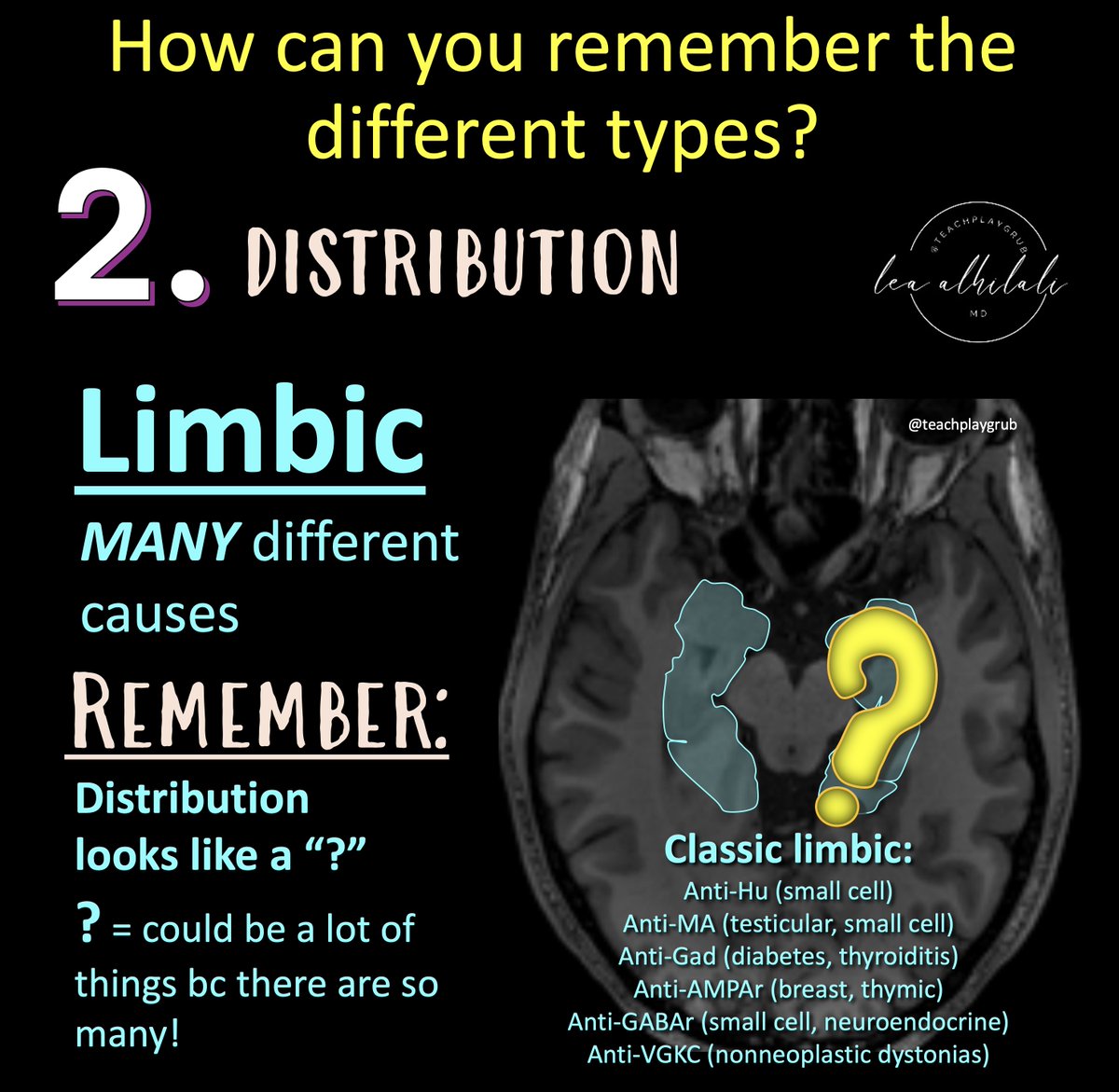
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1 @RadG_Editor 3/Limbic encephalitis is the most common pattern
But it has many, many different causes
Remember--limbic involvement is shaped like a question mark!
So for limbic encephalitis, the cause remains a question bc differential is so broad
Must question & clinically correlate!
But it has many, many different causes
Remember--limbic involvement is shaped like a question mark!
So for limbic encephalitis, the cause remains a question bc differential is so broad
Must question & clinically correlate!
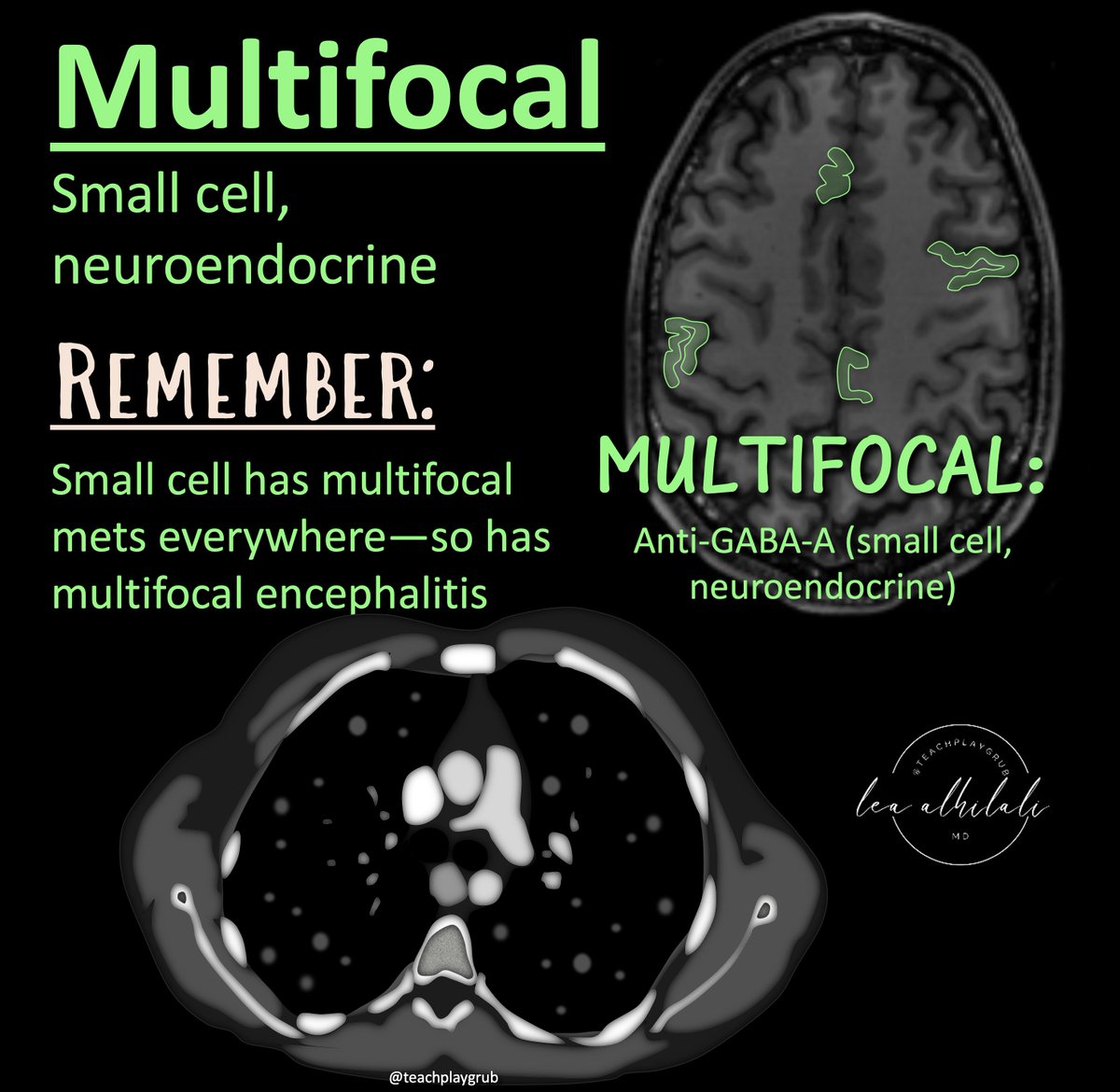
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1 @RadG_Editor 4/Some other patterns to remember:
Multifocal = small cell and neuroendocrine
Remember:
Small cell gives you mets everywhere = small encephalitis everywhere
Neuroendocrine can arise from different places all over your body = encephalitis different places all over your brain
Multifocal = small cell and neuroendocrine
Remember:
Small cell gives you mets everywhere = small encephalitis everywhere
Neuroendocrine can arise from different places all over your body = encephalitis different places all over your brain
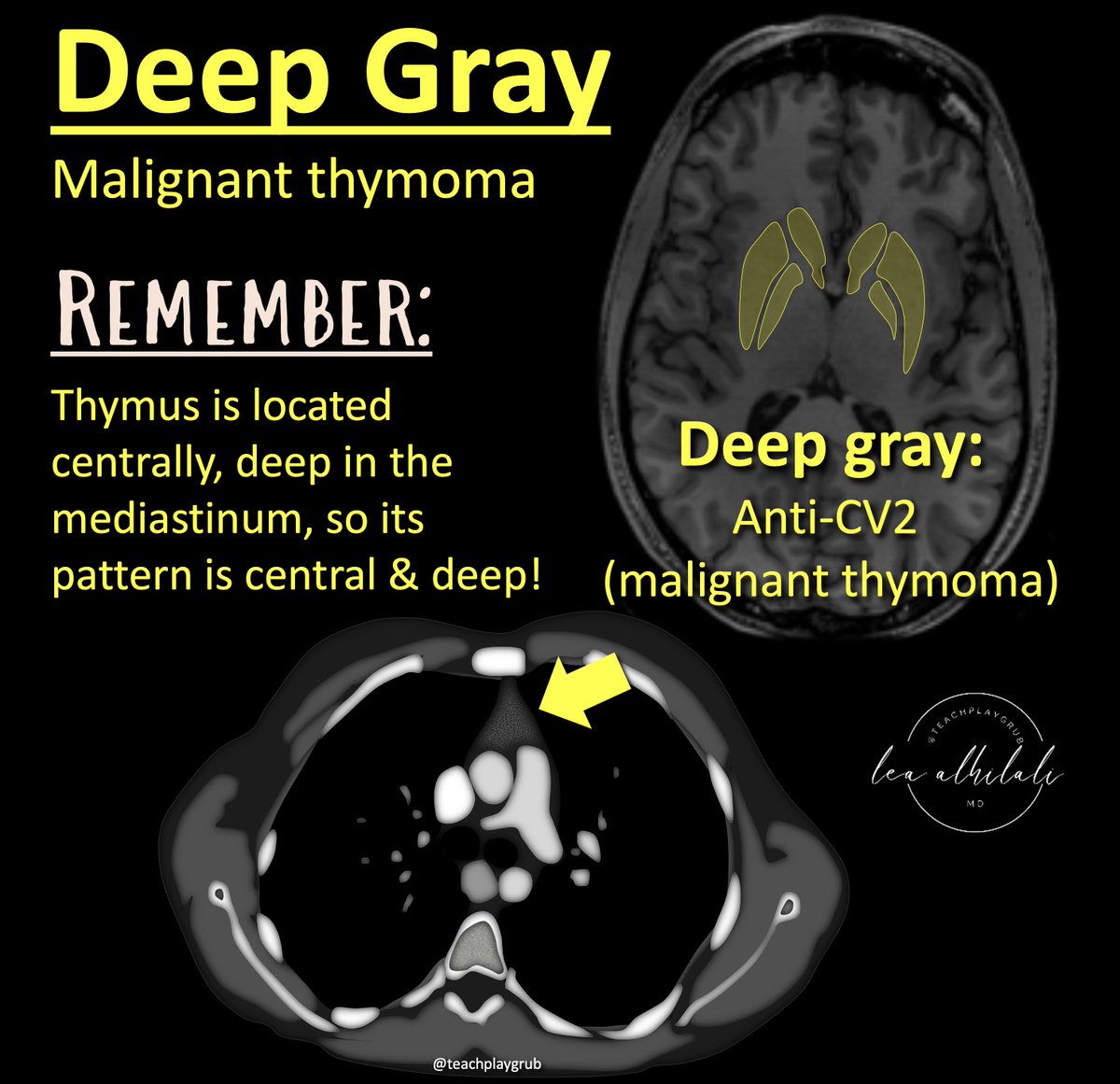
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1 @RadG_Editor 5/Central/Deep gray = malignant thymoma
Remember: thymus is located central and deep in your chest, so its pattern is central and deep!
Remember: thymus is located central and deep in your chest, so its pattern is central and deep!
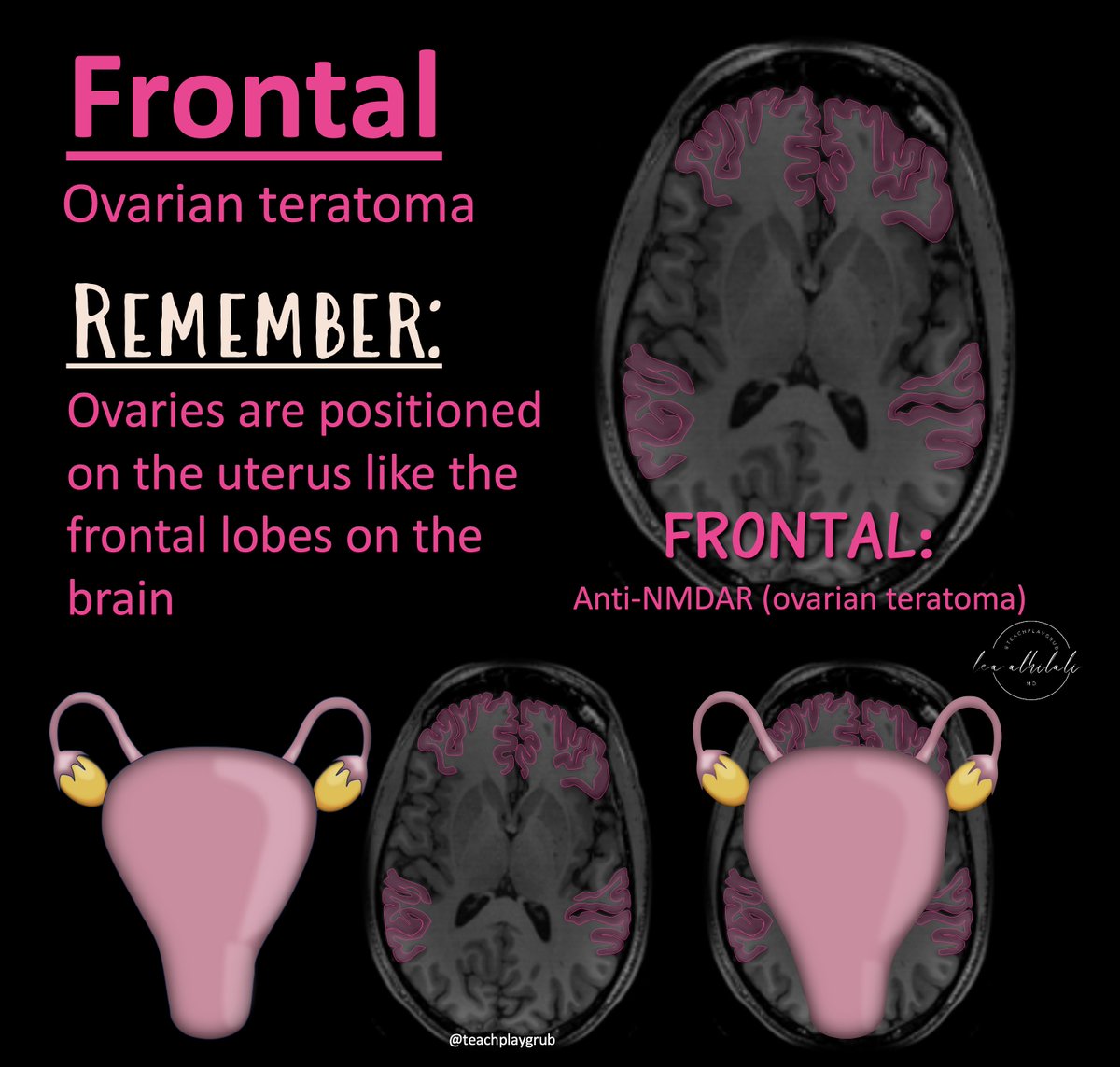
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1 @RadG_Editor 6/Frontal = ovarian teratoma
Remember: ovaries are situated on the uterus right where the frontal lobes are situated on the brain!
Remember: ovaries are situated on the uterus right where the frontal lobes are situated on the brain!
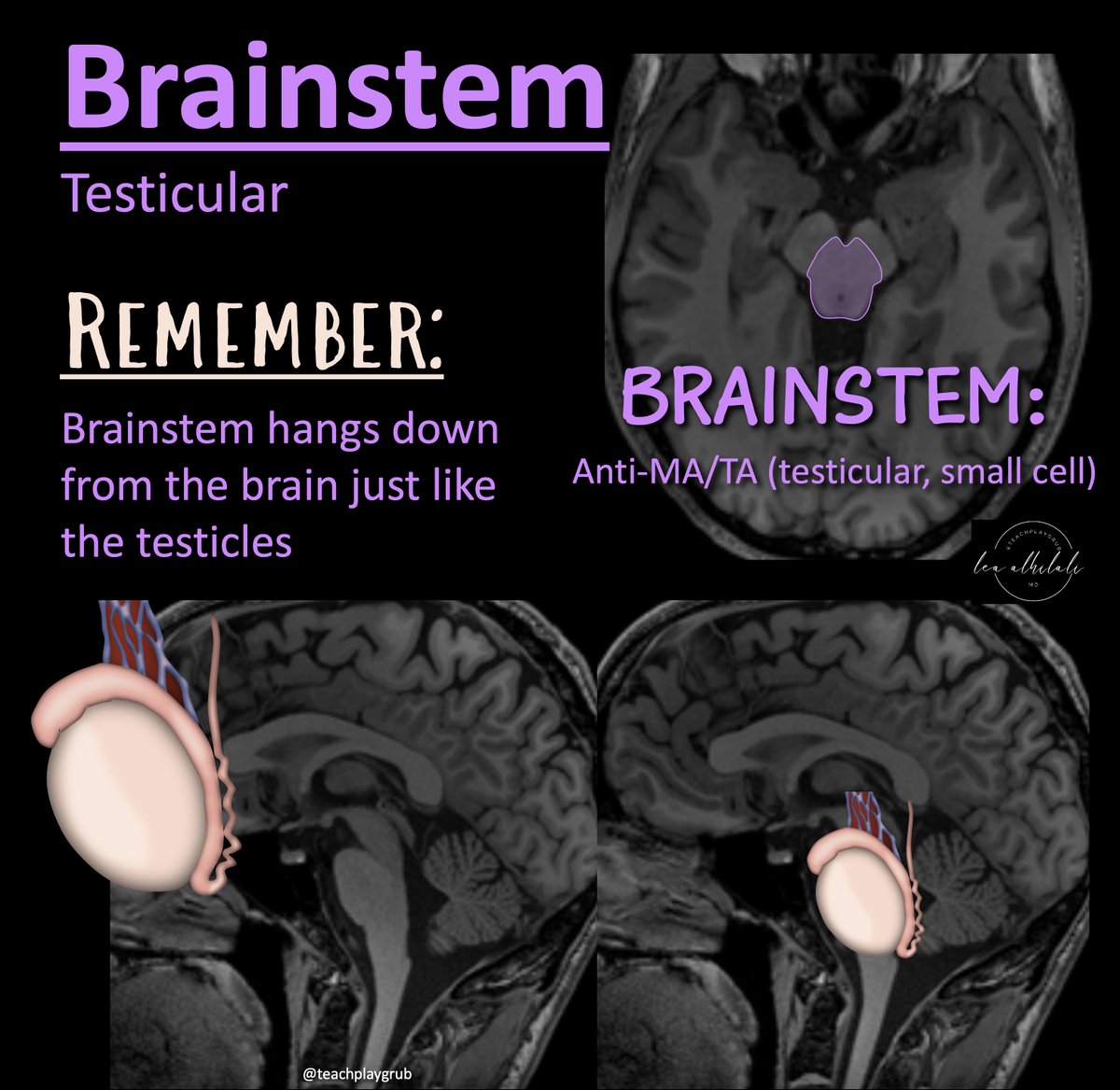
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1 @RadG_Editor 7/Brainstem = testicular
Remember: brainstem hangs down from the cerebrum like the testicles
Remember: brainstem hangs down from the cerebrum like the testicles
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1 @RadG_Editor This is NOT comprehensive, but a starting point, to point the direction to further workup!
Remember these patterns to get a bigger work up started
Check it out yourself:
Hopefully, the next time you see autoimmune encephalitis, you'll be on autopilot! doi.org/10.1148/rg.240…
Remember these patterns to get a bigger work up started
Check it out yourself:
Hopefully, the next time you see autoimmune encephalitis, you'll be on autopilot! doi.org/10.1148/rg.240…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















