How SARS-COV-2 spreads (Re) and why there are differences between countries ?
An explanation for kids based on the astonishing new study of @firefoxx66 @richardneher and colleagues
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40233303/
An explanation for kids based on the astonishing new study of @firefoxx66 @richardneher and colleagues
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40233303/

2) With a really fast-spreading virus going around, like the one that causes COVID-19, when someone gets sick, they can pass the virus to other people. But some sick people end up spreading it to a lot more people than others. 

2) The scientists in this study wanted to figure out how the virus is spreading and how much it's spreading from person to person. To do this, they looked at the genetic code, or the "DNA", of the virus.
Whenever the virus infects someone new, it can change a little bit.
Whenever the virus infects someone new, it can change a little bit.
3) So if two people have the exact same virus DNA, it means the virus must have spread directly from one person to the other, without changing much.
The scientists grouped all the virus DNA samples into clusters of identical ones.
The scientists grouped all the virus DNA samples into clusters of identical ones.
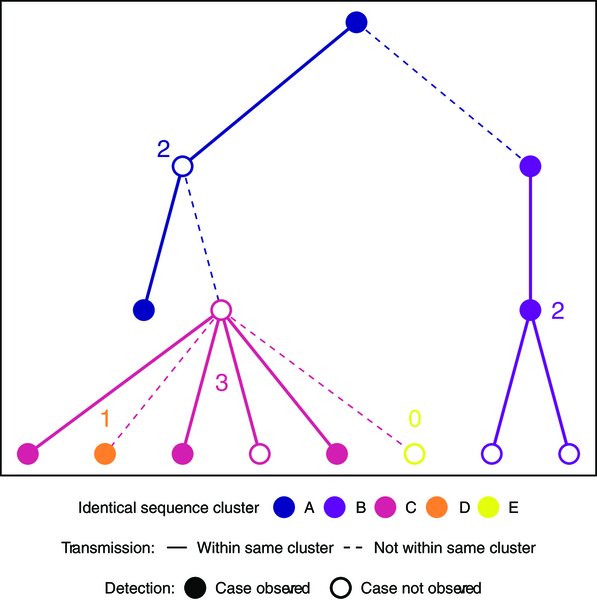
4) The size of these clusters tells them how the virus is spreading. If there are a lot of big clusters, it means the virus is spreading a lot from person to person. But if there are mostly small clusters, it means the virus isn't spreading as much. 

5) By looking at these virus DNA clusters, the scientists were able to estimate two important numbers:
1. The average number of people each sick person infects (called R)
2. How much the virus spreads differently between people (called k)
1. The average number of people each sick person infects (called R)
2. How much the virus spreads differently between people (called k)

6) The scientists found that in some countries, the virus wasn't spreading as much between people, while in other countries, it was spreading more unevenly, with some people infecting a lot more people than others.
Thanks for reading 🙏
Thanks for reading 🙏

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh


















