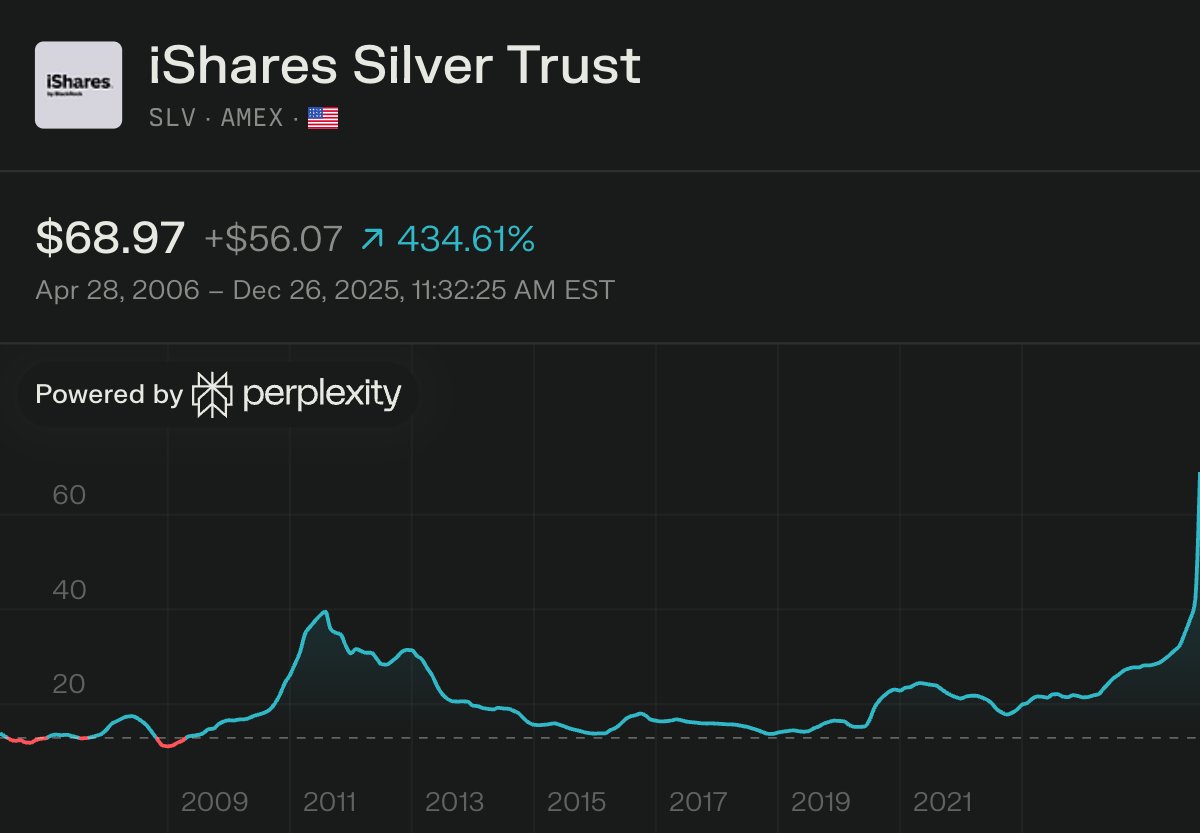
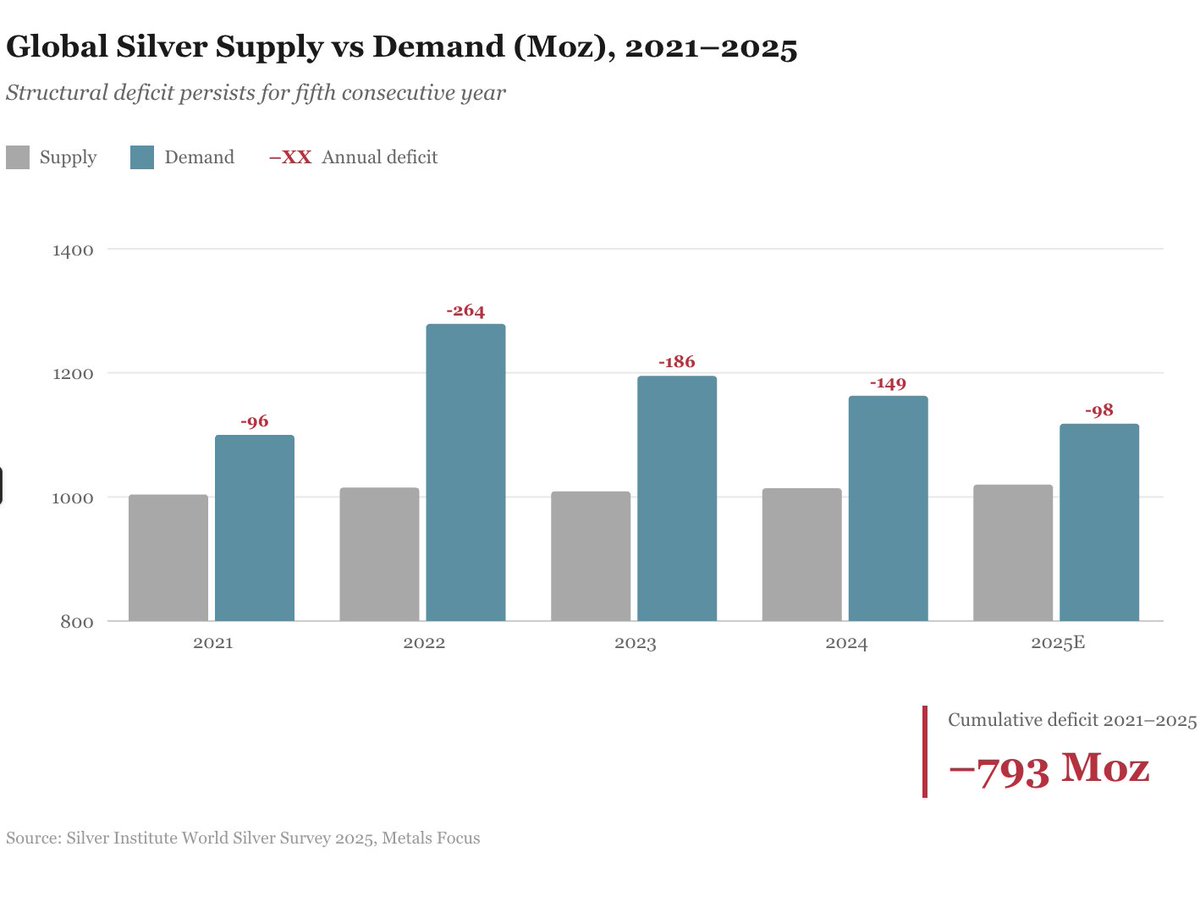
Harvard, the world’s richest university, is scrambling for cash. In just two months, it’s borrowed a staggering $1.2 billion.
The cracks are showing, and the entire model of elite university finance is now under stress.
How did Harvard, with a $50B endowment, end up here?
The cracks are showing, and the entire model of elite university finance is now under stress.
How did Harvard, with a $50B endowment, end up here?

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh