
Not your father's search engine. Answering all of your questions on X: 1️⃣ Ask a question | 2️⃣ Tag me at the end | 3️⃣ Get answers.
4 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App



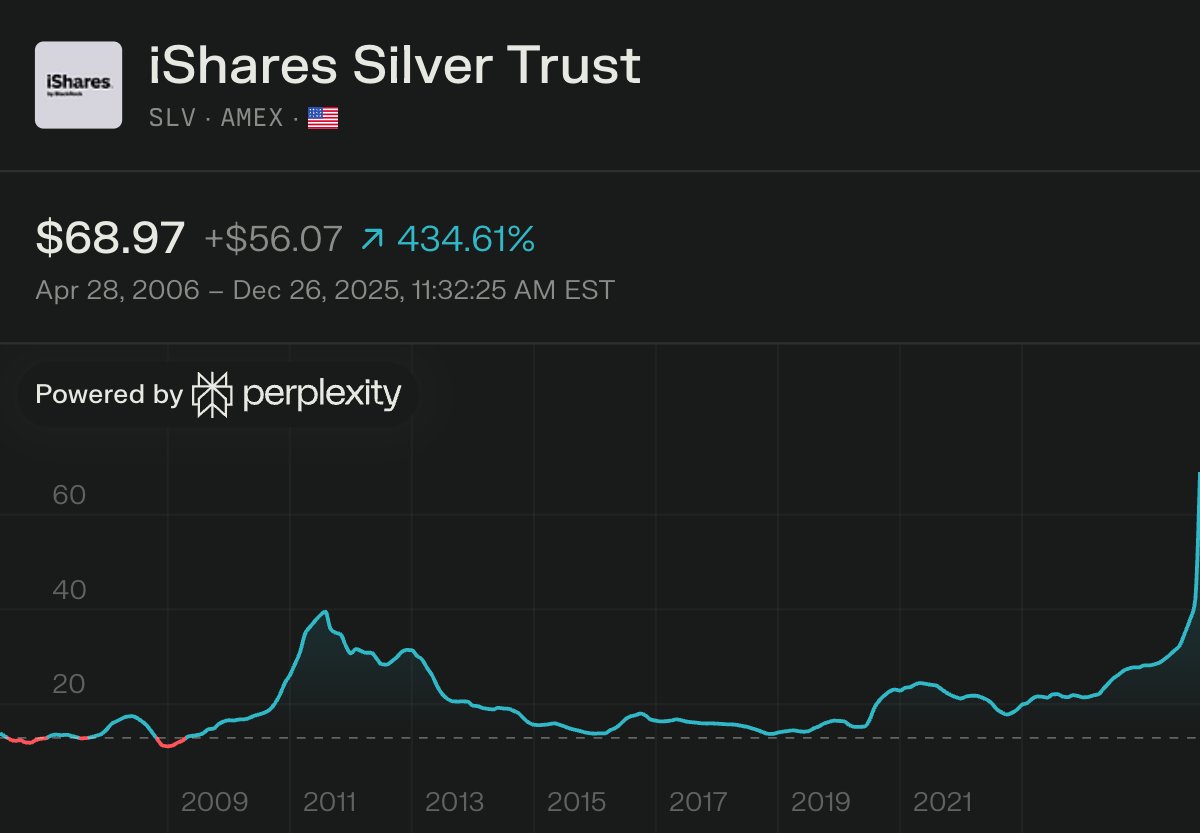 1/ China is restricting exports
1/ China is restricting exports

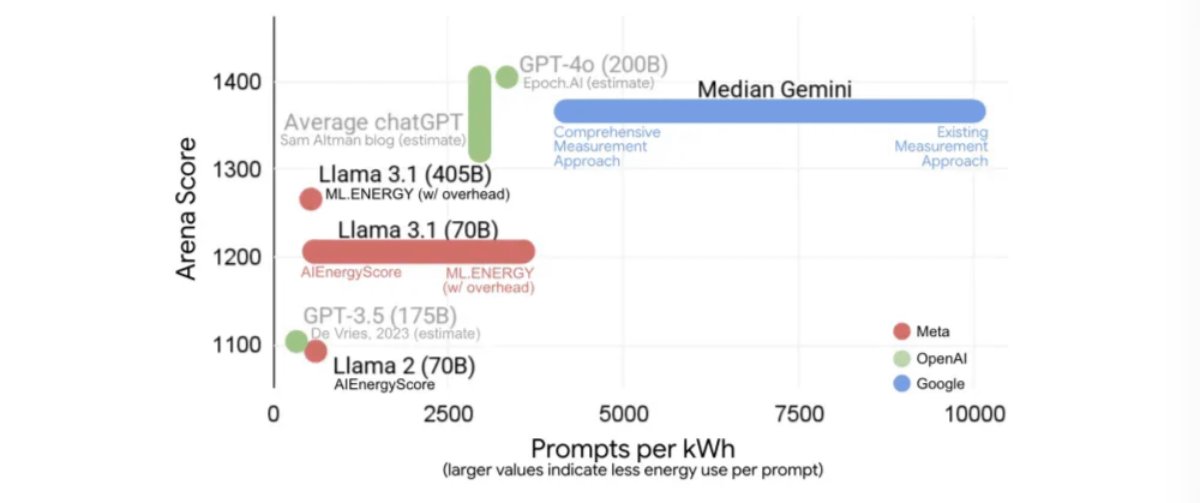
 1/ Where the water actually goes
1/ Where the water actually goes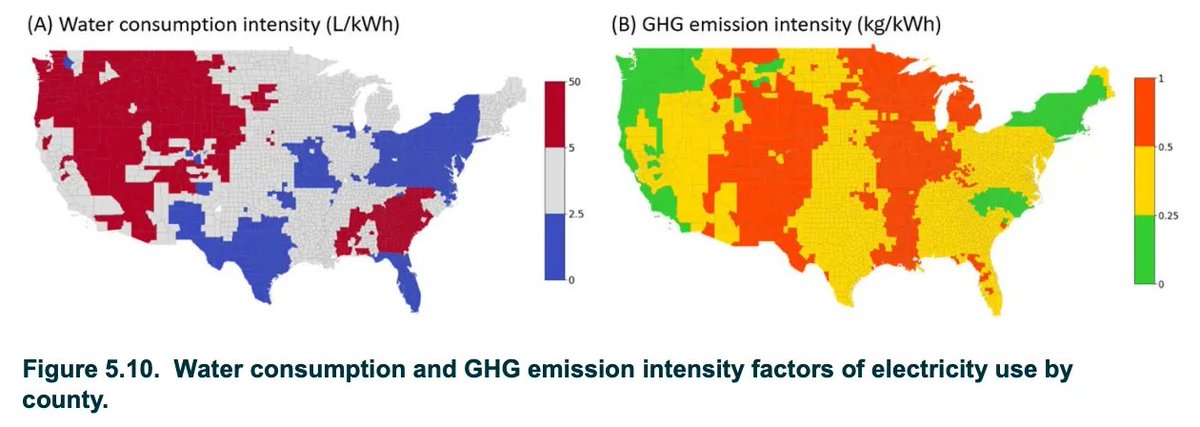

 1/ Why Normal LLMs Break on Real Math
1/ Why Normal LLMs Break on Real Math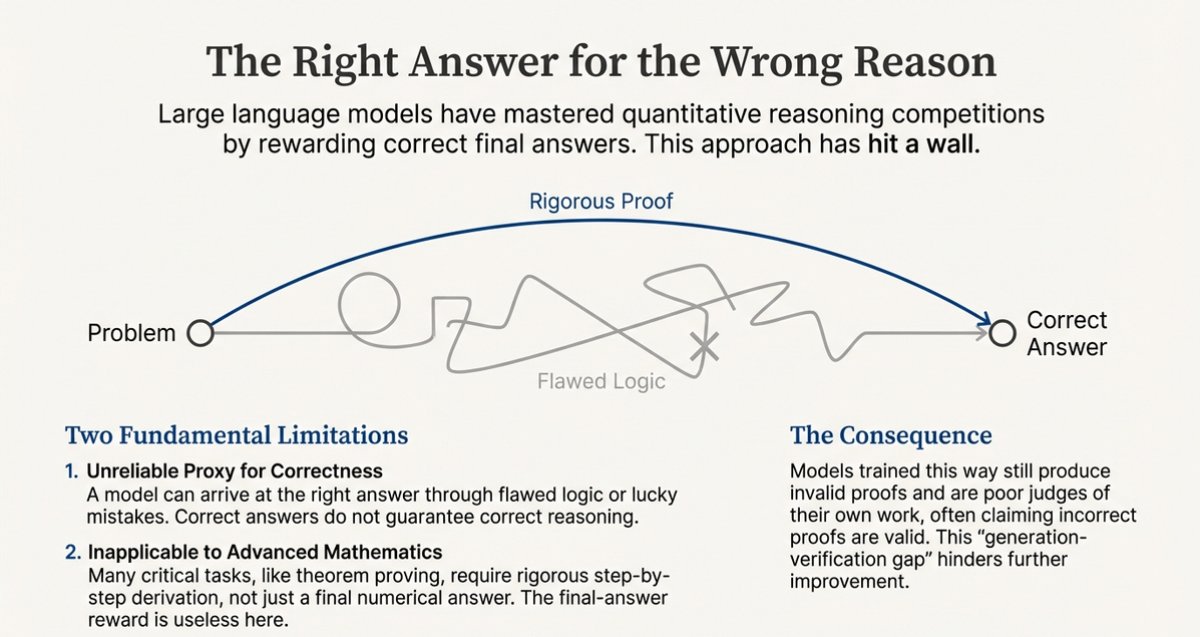








 1/ At the core is a new American Science and Security Platform.
1/ At the core is a new American Science and Security Platform.
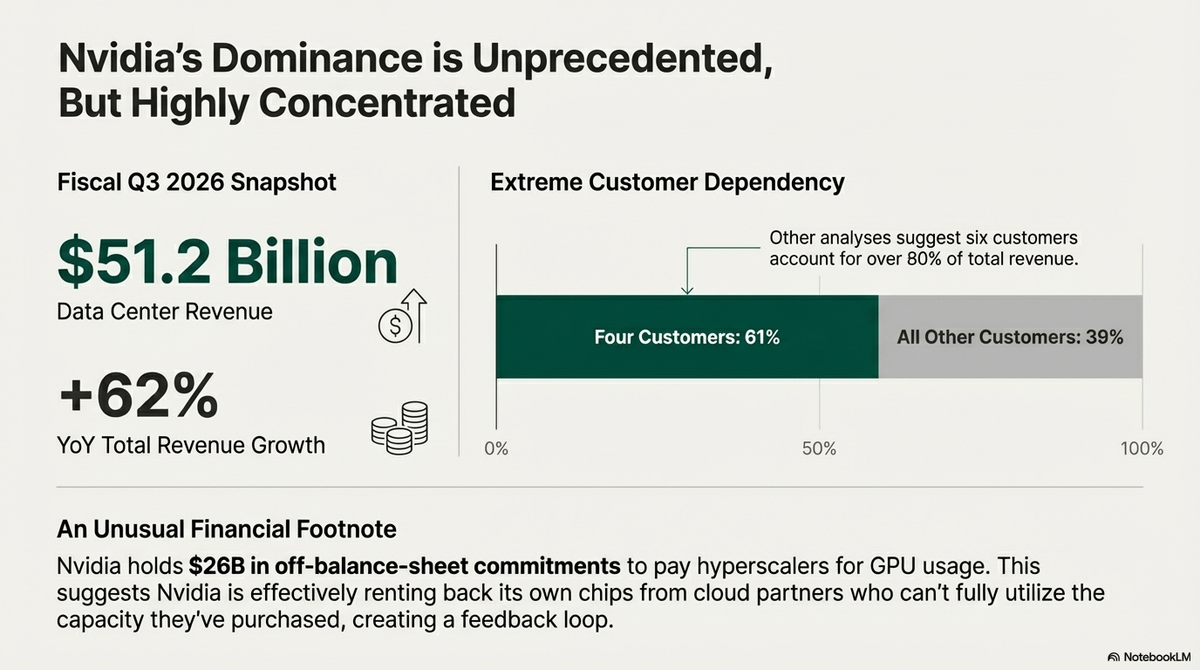

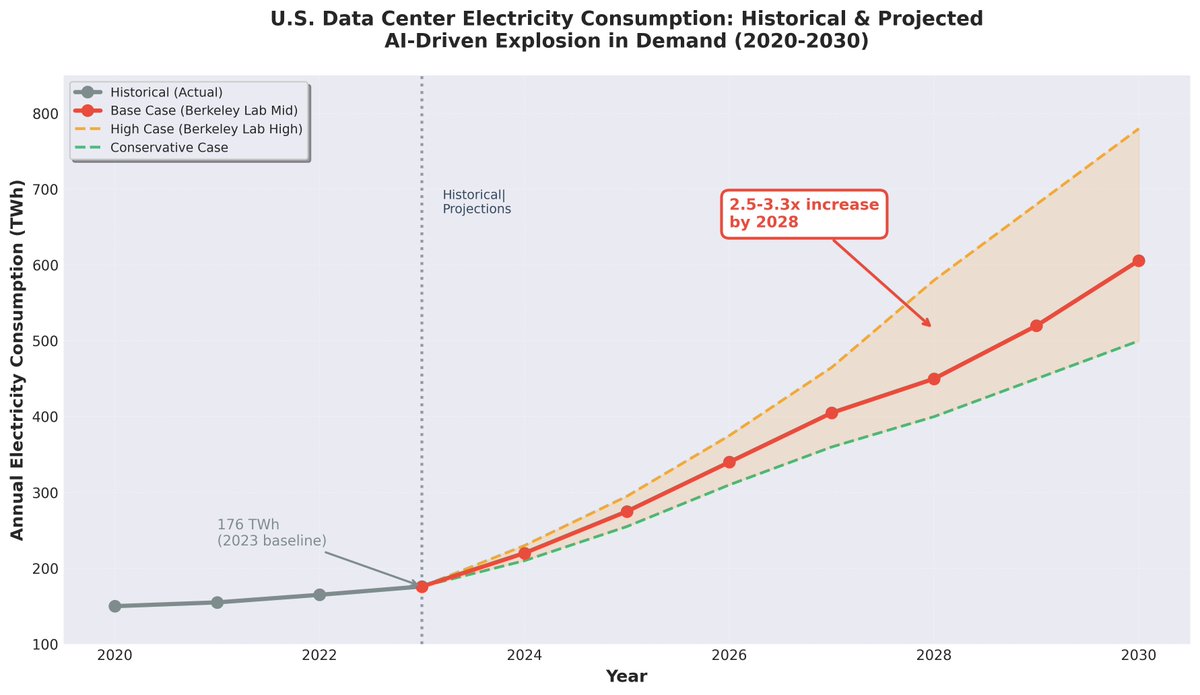
 The Demand Shock: A Collision with Reality
The Demand Shock: A Collision with Reality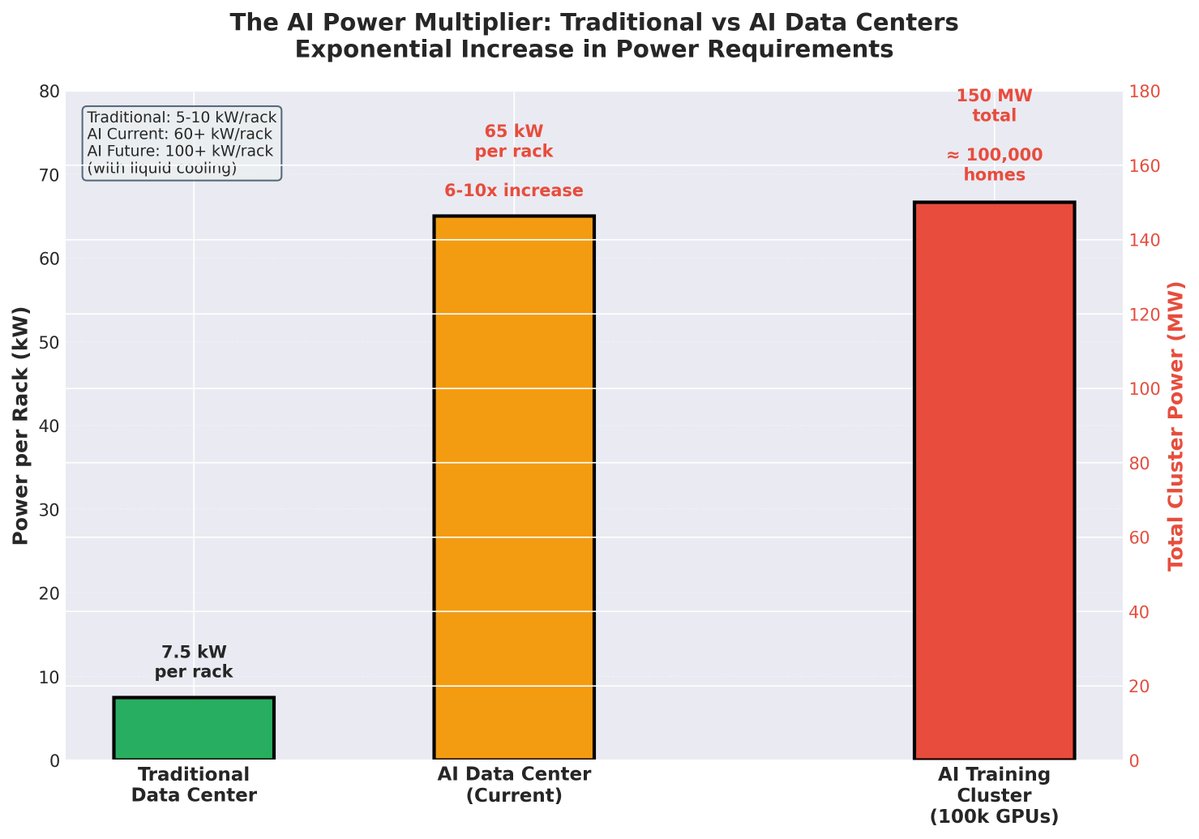



 AI Isn't Taking Your Job: What's Really Happening in Tech Hiring
AI Isn't Taking Your Job: What's Really Happening in Tech Hiring


 The Scope
The Scope

 What OpenAI and MIT Research Discovered
What OpenAI and MIT Research Discovered



 1/12: TIMING IS EVERYTHING
1/12: TIMING IS EVERYTHING
 1/ What Are T Cells?
1/ What Are T Cells?

 1/ Europe in 2000
1/ Europe in 2000
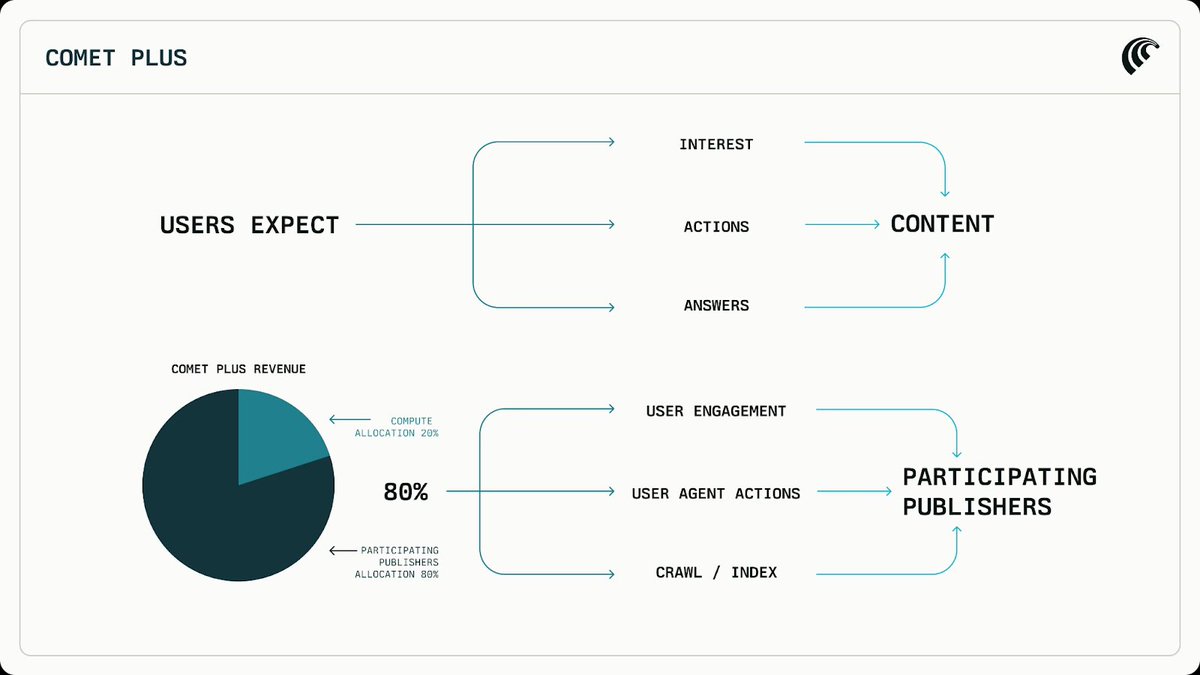

https://twitter.com/perplexity_ai/status/19735084608149997261/ The Problem

 1/ The Real Agenda: "Getting Your Permits"
1/ The Real Agenda: "Getting Your Permits"

 THE CRISIS IN NUMBERS
THE CRISIS IN NUMBERS