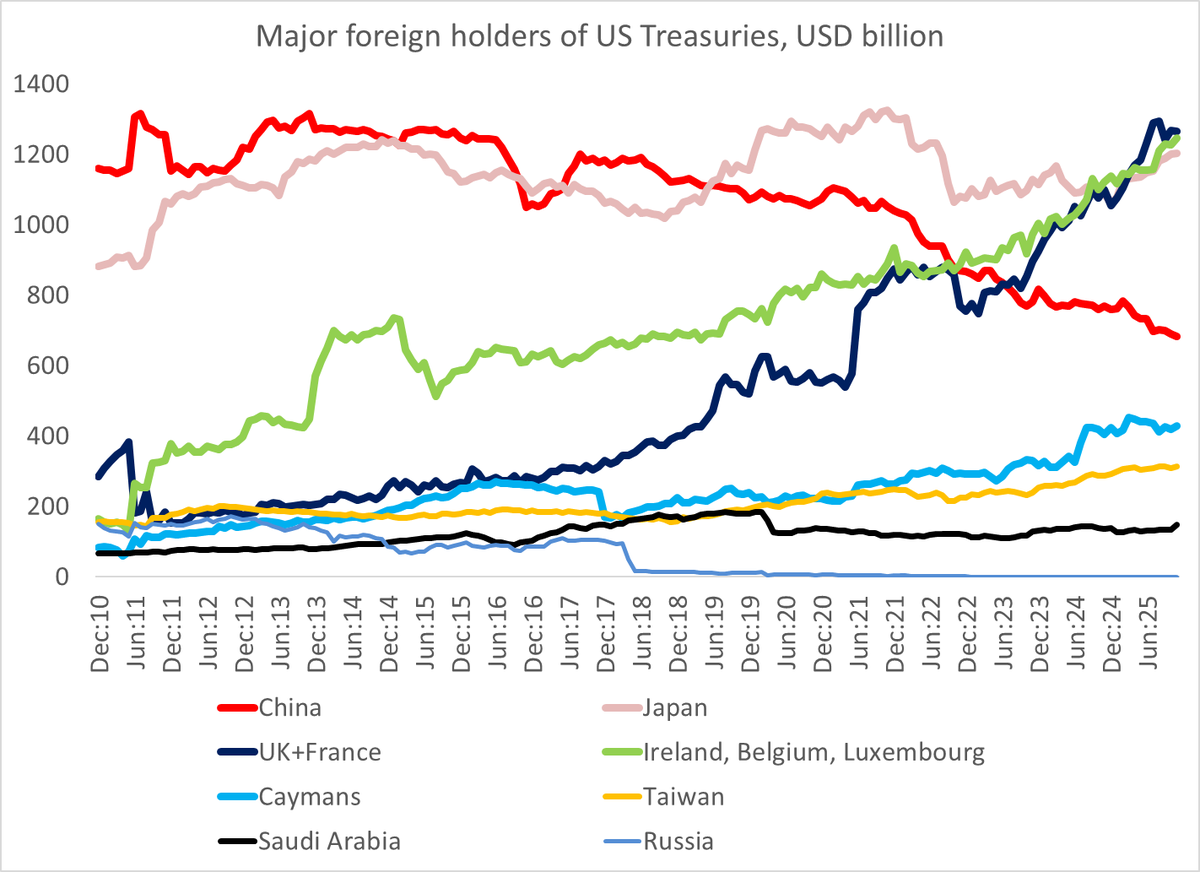
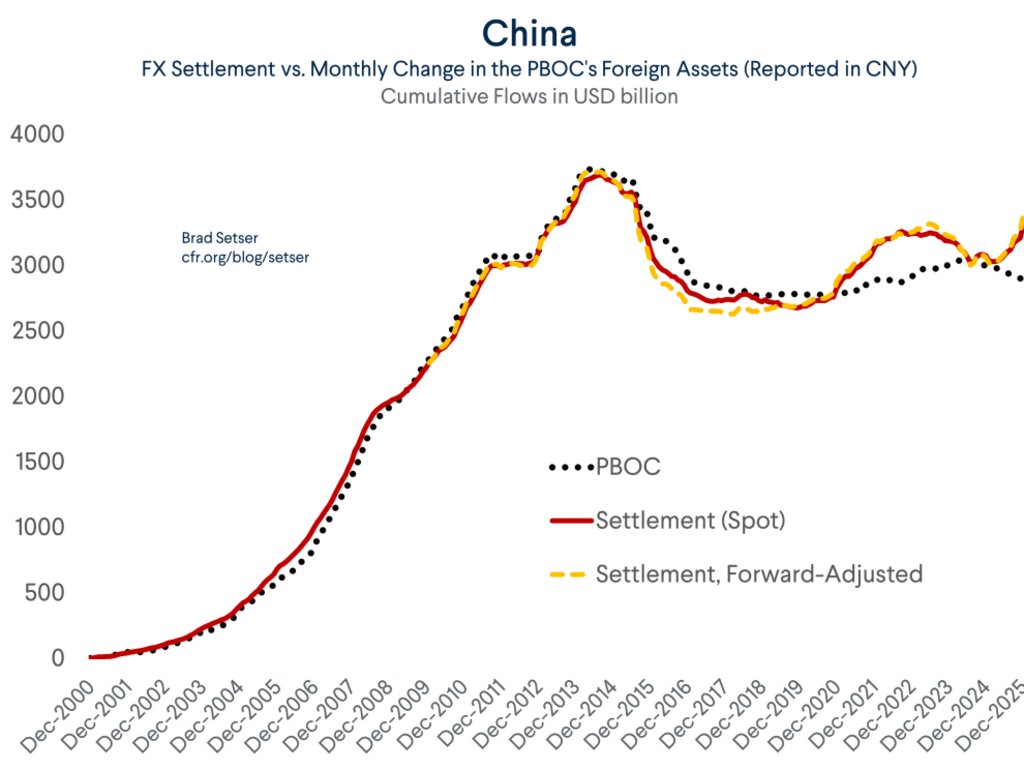
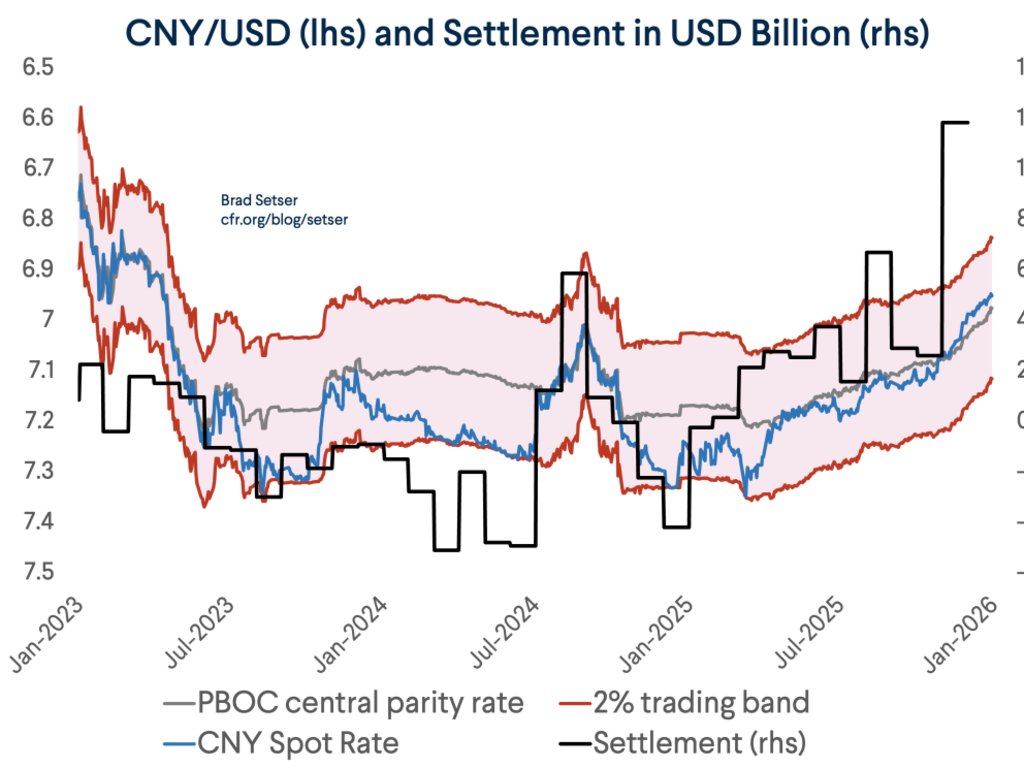
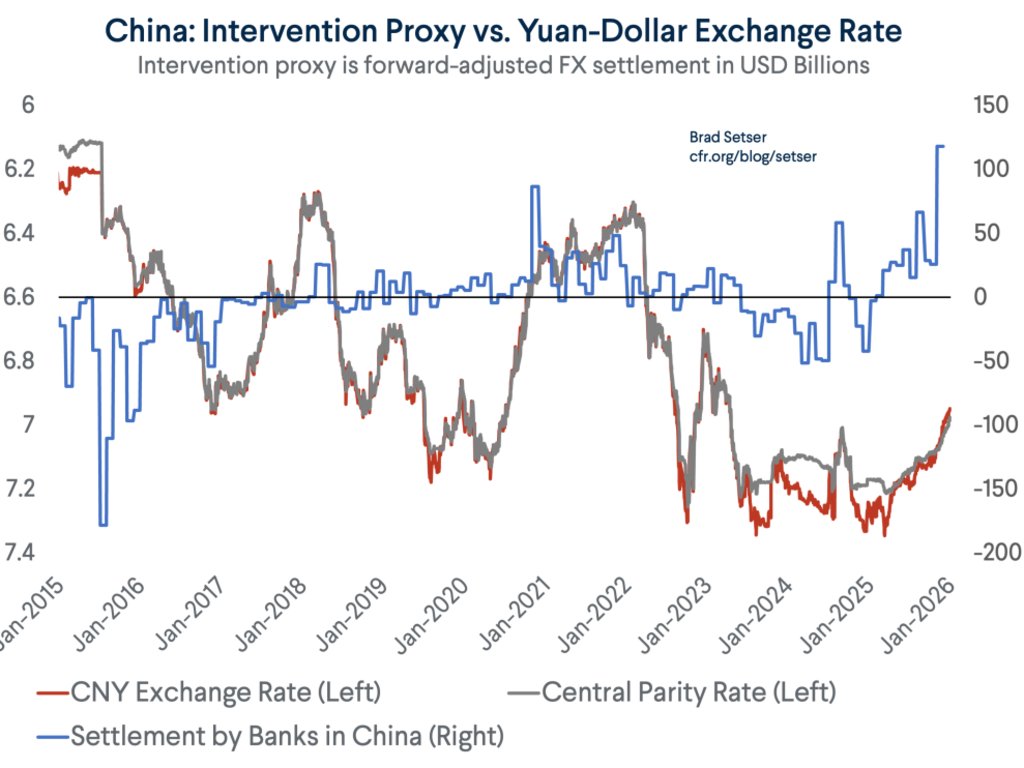
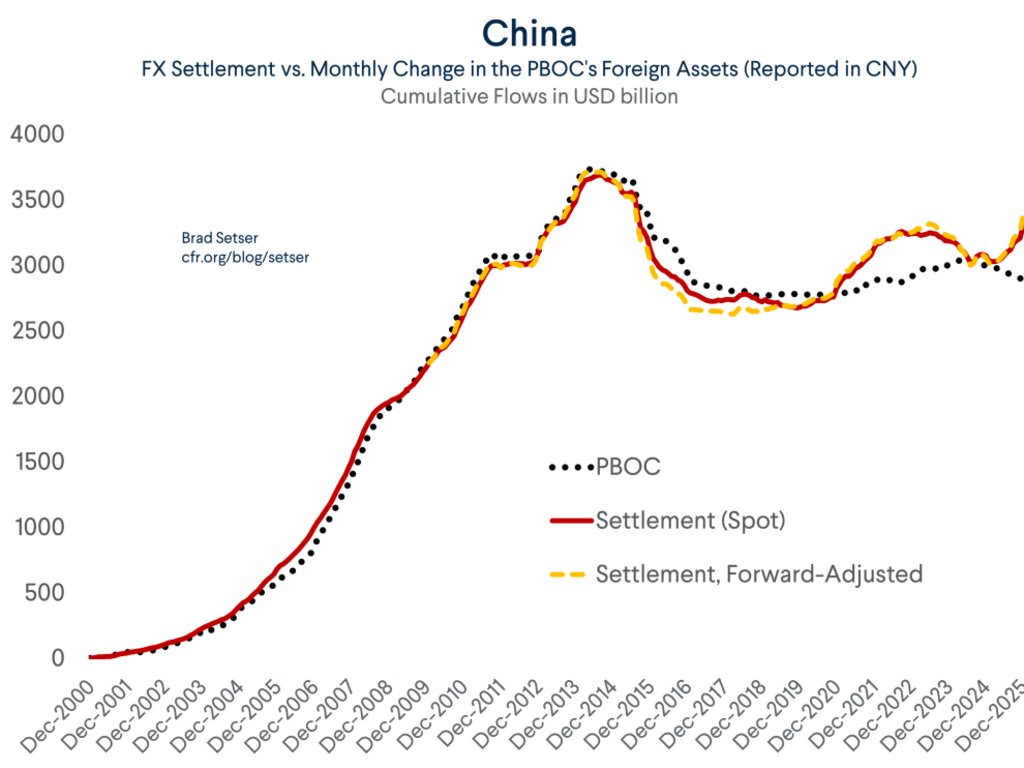
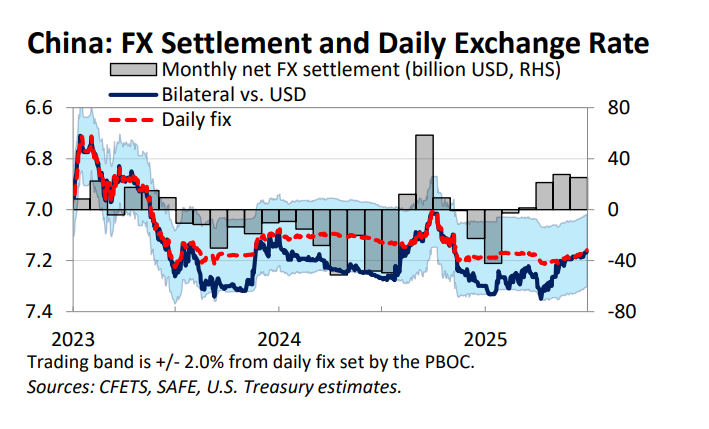
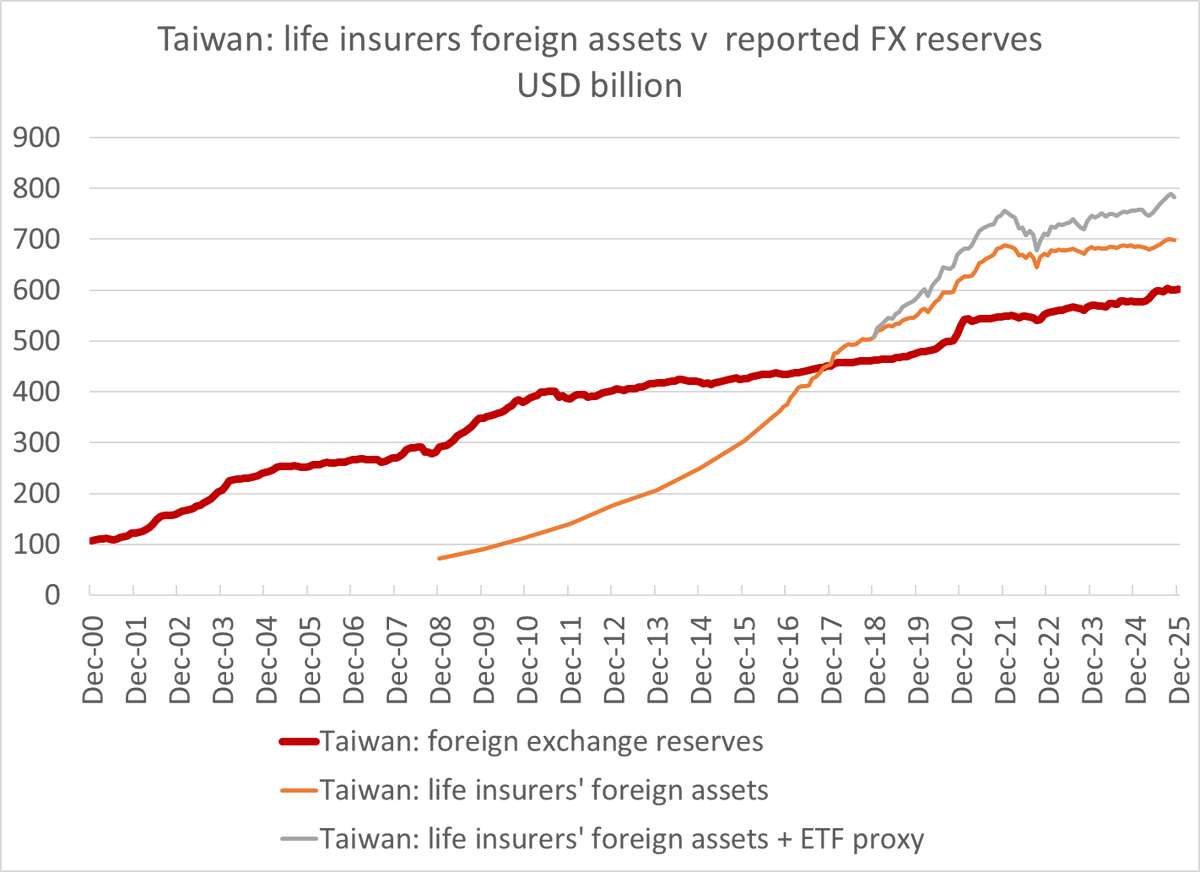
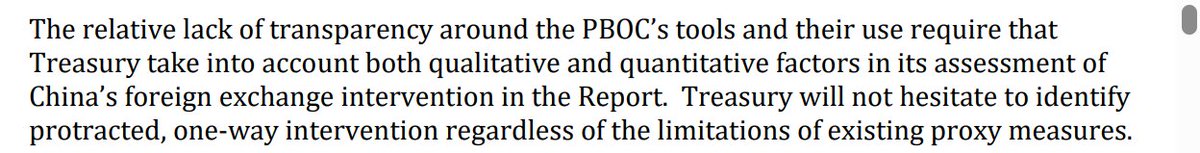A bit of background on Taiwan ahead of what may be an eventful week. Certainly there will be a lot attention on the action to Taiwan's central bank after Friday's TWD move.
Key context: the TWD is incredibly weak
1/
Key context: the TWD is incredibly weak
1/

That weakness is obvious from the 15% of GDP current account surplus or any examination of purchasing power parity. In real effective terms, the Taiwan dollar is down 25% from its pre-Asian financial crisis level (i.e. the mid 90s)
2/
2/

While the currency slid (after 1996) the current account surplus soared ... so there is a pretty link. TSMC's very real success should have pulled the currency up but it didn't, in part because Taiwan's central bank hasn't been shy about intervention
3/
3/

The main counterpart to the sustained surplus has been reserve growth and the purchase of foreign bonds by Taiwanese financial institutions -- holdings of foreign bonds are now something like 170% of Taiwan's GDP
4/
4/

And specifically a huge share of the life insurers $1.1 to $1.2 trillion in assets has been invested abroad -- and a significant amount of that investment is unhedged (more on that later)
5/
5/

Data center demand for chips made by TSMC (+ Taiwan's role as connector country that helps Chinese made parts get around the tariffs) + a very high domestic savings rate has pushed Taiwan's surplus up to $120b or so (lower oil will help in 25 ...)
6/
6/

The basic equilibrium condition for maintaining a weak TWD in the face of flow pressure from a massive current account surplus is that a set of the major players in Taiwan's economy have to add to their external assets --
7/
7/
Before COVID that was mostly the lifers -- but the lifer flow recently has been more modest (big stock position, some wounds from the rise in US rates and associated valuation losses).
8/
8/

in 2022 (after Russia invaded Ukraine, and with rising tensions across the straight) foreigners selling TSMC generated the needed outflow -- but in 23 and 24 it has mostly come from the banks (intermediating fx deposits I think) and TSMC investing abroad
9/
9/

In periods of stress (which for Taiwan comes when the Taiwan dollar appreciations, creating a mismatch between fx assts and TWD liabilities), stability has requires heavy fx accumulation by the central bank (~ 10% of GDP in the period before 2016, and again in 2020)
10/
10/

This matters for the lifers in particular, as they have an estimated open position (see my piece in the FT with Josh Younger) or around $200b/ between 15% and 20% of their asset base --
11/
ft.com/content/972c54…
11/
ft.com/content/972c54…
So a 1% move in the Taiwan dollar all else equal generates mark to market losses (tho not necessarily accounting losses) of around $2b/ a 10% move losses of more like $20b -- big sums
12/
12/
The insurers though do have "fx volatility reserves" of at least $10b (and maybe more ... tho some of that was the unrealized gain on TWD appreciation I suspect) so there are buffers ...
13/
taipeitimes.com/News/biz/archi…
13/
taipeitimes.com/News/biz/archi…
But the lifers probably do need to increase their hedge ratios in the current context, and that could put appreciation pressure on the TWD (and regional proxies)
14/
ft.com/content/88e0c3…
14/
ft.com/content/88e0c3…
So there will be a lot of attention on when and how Taiwan's central bank the (CBC) intervenes on Monday -- it allowed a bit larger move than expected last Friday, which got everyone's attention --
15/
15/

Now in the past the CBC has generally smoothed market moves (more so than on Friday) and generally started to resist appreciation more firmly as the TWD through 30 to 29 and then 28. They absolutely defended 28 with hefty intervention back in 2020 and 21
16/
16/

The other policy tool available to the CBC is to use its massive reserves to help the lifers hedge, and open up an onshore swaps facility (there aren't other sources of a $100-200b in hedges, the CBC has $600b or so in fx
17/
17/

I note that, thanks to the Fed's FIMA repo facility, the CBC could get dollar liquidity from the Fed without selling its Treasuries or Agencies. I advocated for FIMA repo with this kind of contingency in mind (I was obsessed with Asian insurer hedging needs back in 19/20)
18/
18/
The other new variable of course is the trade negotiations with the US -- if the US is serious about bringing down its bilateral deficit, undervalued Asian currencies (like the TWD) do need to appreciate and the US cannot make it too easy for the CBC to protect the lifers
19/
19/
Makes for an interesting set up -- politics, economics, finance (bond flows, lifer balance sheets), currencies all in play.
And the underlying financial exposure for Taiwan is massive
20/20
And the underlying financial exposure for Taiwan is massive
20/20

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh