NEW: Sure Start generated widespread, long-lasting benefits for children in education, health, absences, and SEND.
Every £1 of up-front spending on Sure Start could generate around £2 in total benefits over the long run.
THREAD on our new @NuffieldFound-funded report:
[1/11]
Every £1 of up-front spending on Sure Start could generate around £2 in total benefits over the long run.
THREAD on our new @NuffieldFound-funded report:
[1/11]

@NuffieldFound This new report summarises our 10-year body of work on the effects of Sure Start, a network of ‘one-stop shops’ integrating services for families with children under 5. And the report provides a detailed cost-benefit analysis cutting across a range of child outcomes.
[2/11]
[2/11]
@NuffieldFound We find that access to a Sure Start centre from birth significantly improved the children’s educational attainment, with benefits lasting at least until GCSEs (age 16).
[3/11]
[3/11]

@NuffieldFound Access to Sure Start also substantially reduced hospitalisations of children and teenagers.
Increases in infancy are driven by increases in “preventable” hospitalisations and in hospitalisations for infections and illnesses, both of which then fell later in childhood.
[4/11]
Increases in infancy are driven by increases in “preventable” hospitalisations and in hospitalisations for infections and illnesses, both of which then fell later in childhood.
[4/11]

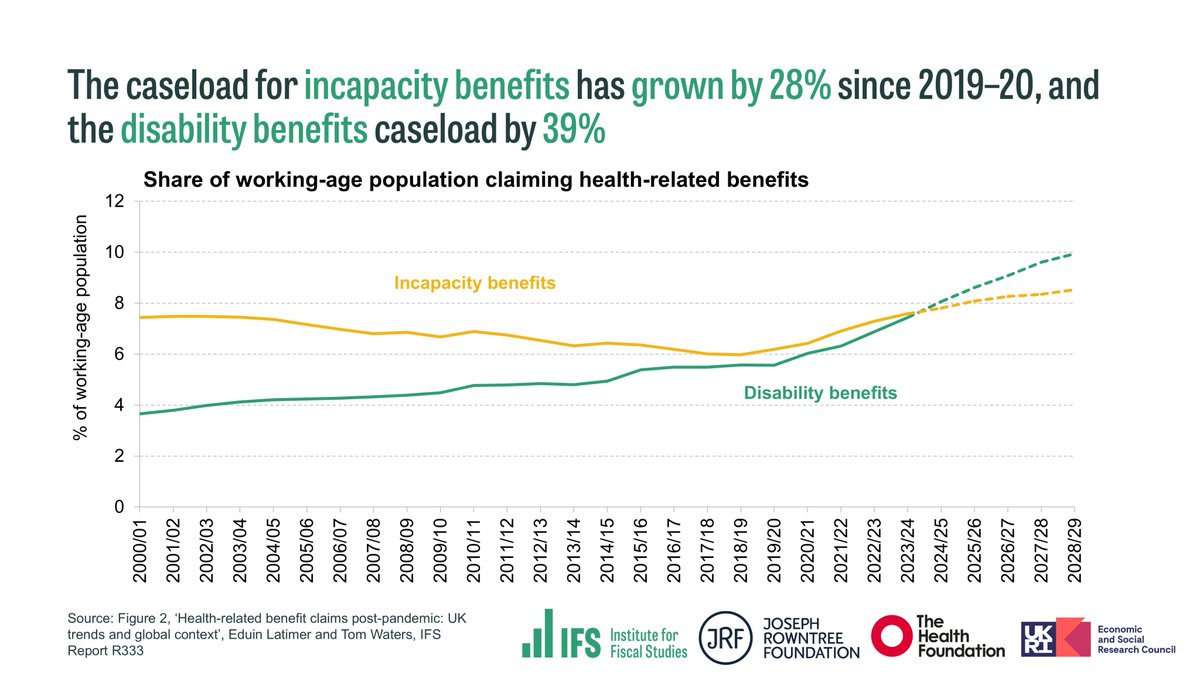
@NuffieldFound Sure Start also reduced the number of children with SEN support plans from age 7 onwards.
This followed an increase in rates of SEN support at age 5, likely driven by an increase in detection or increased interaction with services.
[5/11]
This followed an increase in rates of SEN support at age 5, likely driven by an increase in detection or increased interaction with services.
[5/11]
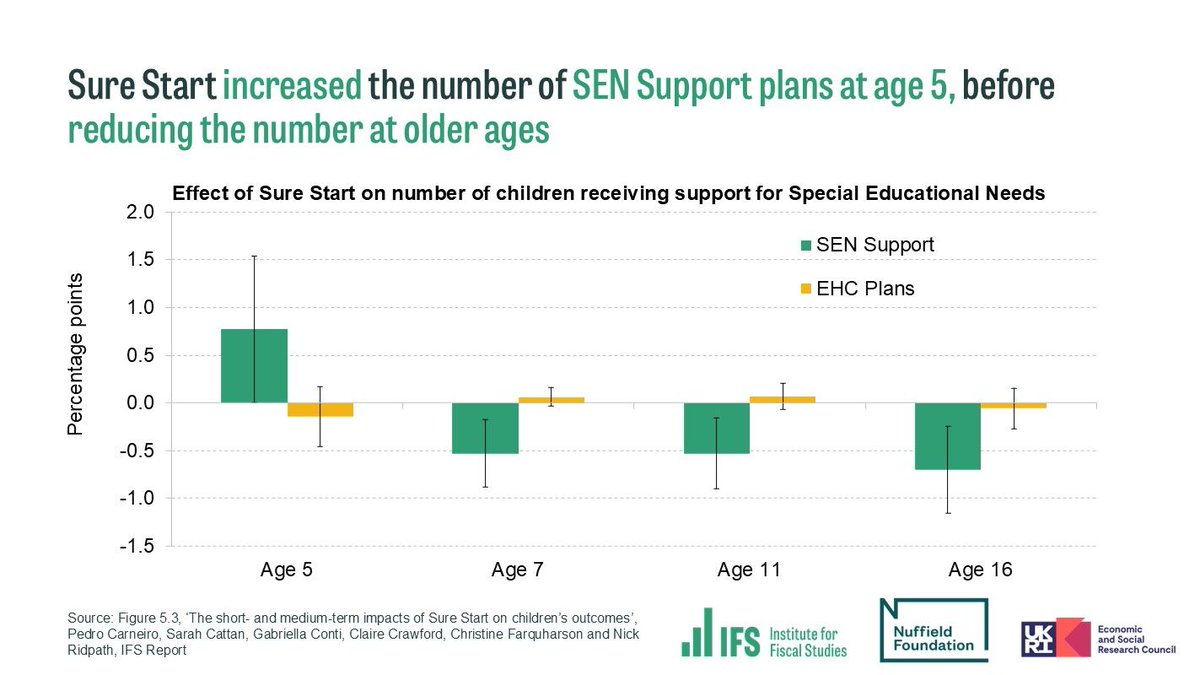
@NuffieldFound Effects on socio-emotional development and behaviour were more mixed.
Sure Start increased the number of youth cautions, especially at ages 10-12, with no significant evidence of a reduction in more serious offending. But behaviour in school and mental health improved.
[6/11]
Sure Start increased the number of youth cautions, especially at ages 10-12, with no significant evidence of a reduction in more serious offending. But behaviour in school and mental health improved.
[6/11]
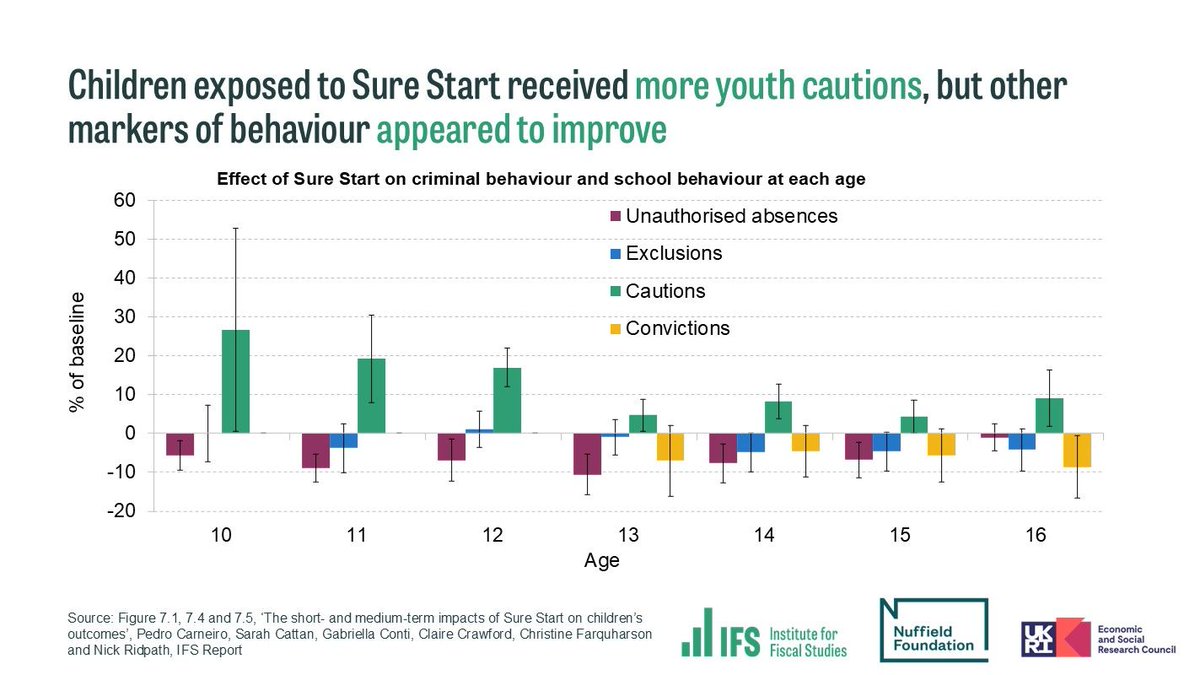
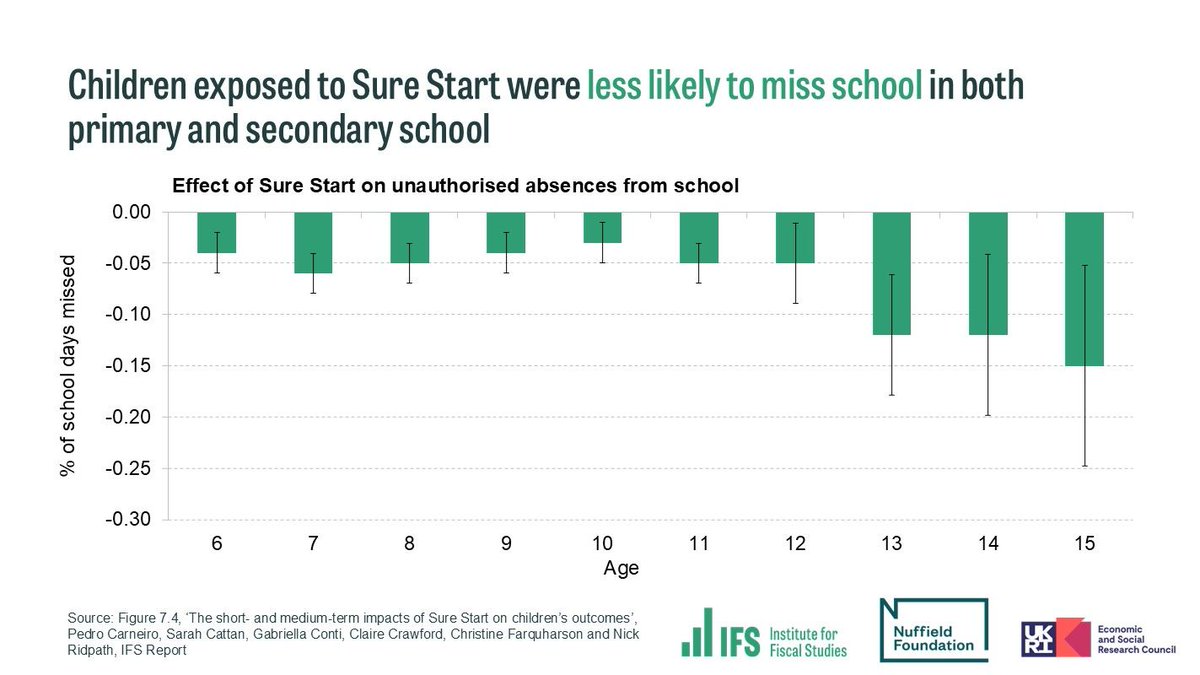
@NuffieldFound Longer-term improvements could have come from changes in parental behaviour, reflected in reductions in unauthorised absences from primary school.
Increased interaction with other services and improved language skills at age 5 may have also generated long-run benefits.
[7/11]
Increased interaction with other services and improved language skills at age 5 may have also generated long-run benefits.
[7/11]
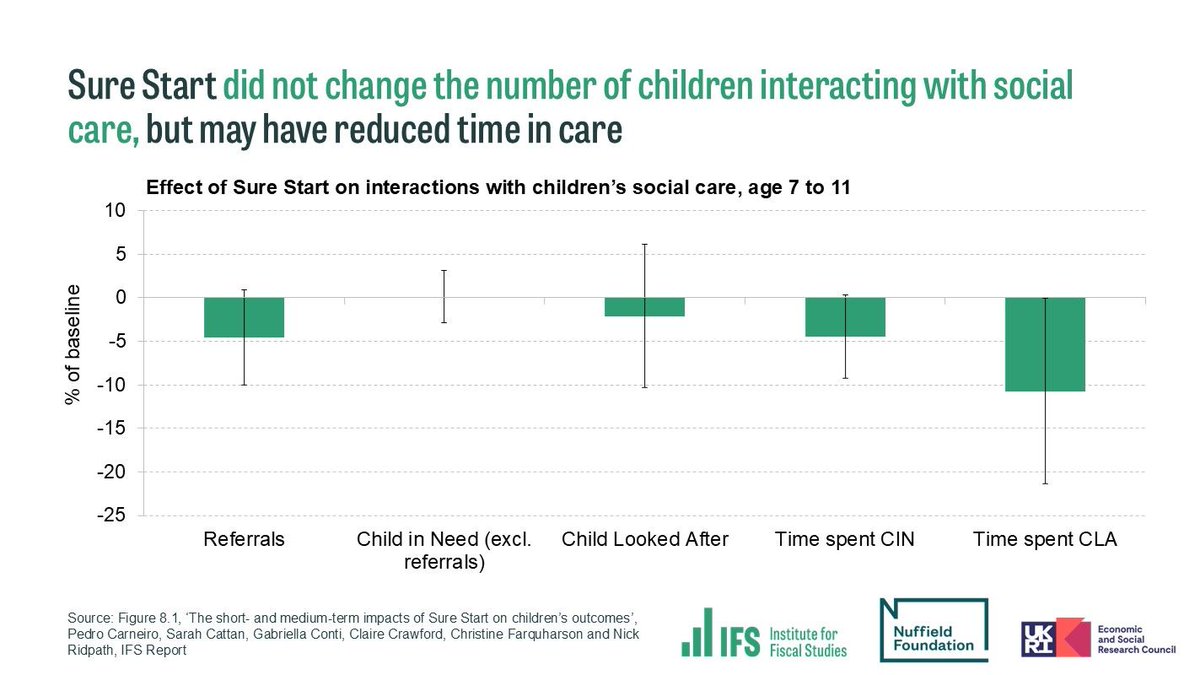
@NuffieldFound Sure Start’s effects on more severe outcomes were limited. We find little effect on contact with children’s social care; Education Health and Care Plans; and serious crime. This suggests that universal light-touch services on their own don’t meet the highest needs.
[8/11]
[8/11]
@NuffieldFound At most ages, children from disadvantaged backgrounds experienced greater benefits from Sure Start, though other children also benefitted.
In general, boys and children from ethnic minority backgrounds also tended to experience slightly larger effects.
[9/11]
In general, boys and children from ethnic minority backgrounds also tended to experience slightly larger effects.
[9/11]

@NuffieldFound At its peak, Sure Start cost around £2.7bn per year (in today's prices).
We estimate that over the long run, it might generate £2.4bn in savings for government per cohort.
Including wider benefits like higher earnings, total long-run benefits could be twice the cost.
[10/11]
We estimate that over the long run, it might generate £2.4bn in savings for government per cohort.
Including wider benefits like higher earnings, total long-run benefits could be twice the cost.
[10/11]

@NuffieldFound “If this government wants to boost children’s life chances, it should take a serious look at integrated early years services.”
Read @carneiro_econ, @Sarah_Cattan, @Gabri_EllaConti, @claire_l_crawf, @ckfarquharson, @nridpathecon's report:
[11/11] ifs.org.uk/publications/s…
Read @carneiro_econ, @Sarah_Cattan, @Gabri_EllaConti, @claire_l_crawf, @ckfarquharson, @nridpathecon's report:
[11/11] ifs.org.uk/publications/s…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh