THREAD 🧵 Who are the writers of the Gospels? Were they eyewitnesses? And how important is the answer? 

It was stated in the book Encyclopedia of Church Fathers:
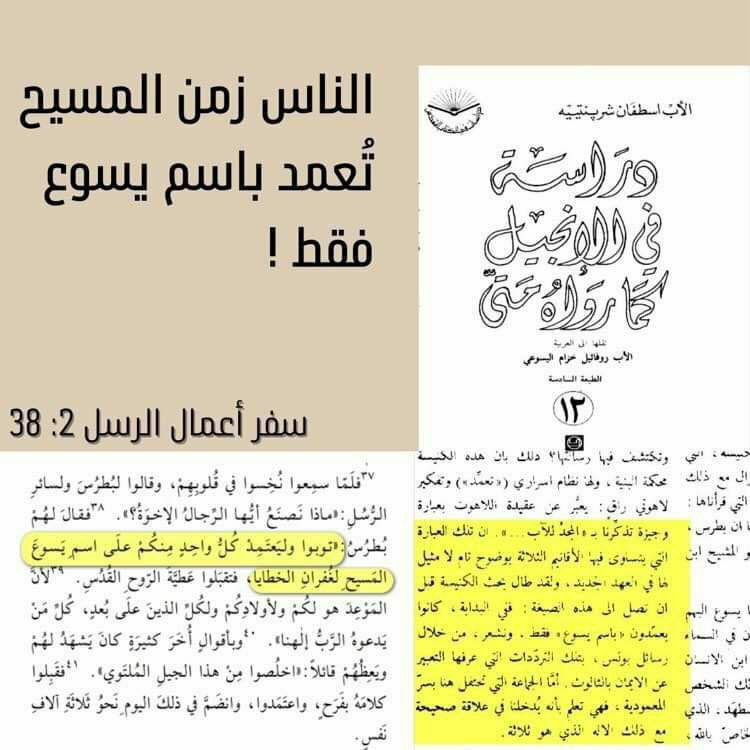
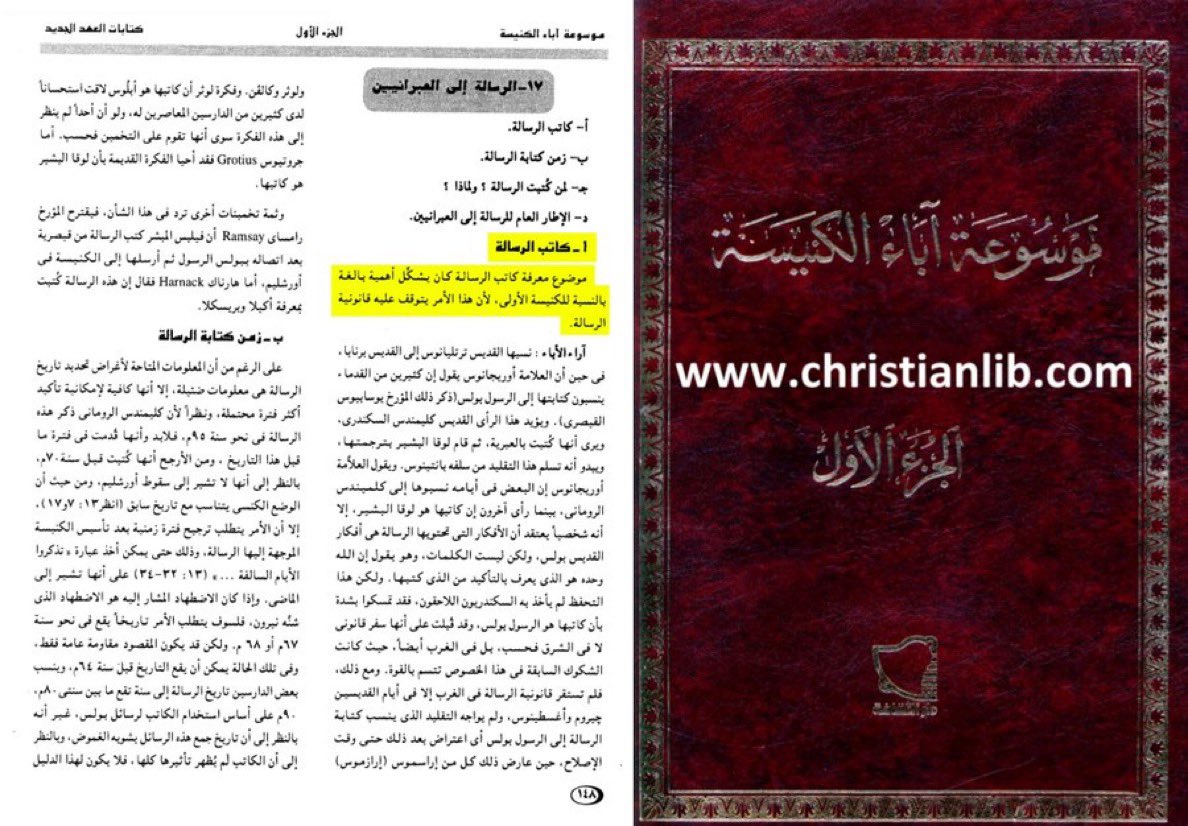
“The issue of identifying the author of the epistle was crucial to the Church, as its canonicity depended on it.
Thus, authorship was vital, since recognizing the book as canonical relied on it.”
“The issue of identifying the author of the epistle was crucial to the Church, as its canonicity depended on it.
Thus, authorship was vital, since recognizing the book as canonical relied on it.”
Father Abd al-Masih Basit writes:
“To be canonical, a book must be written by an apostle or eyewitness under the Holy Spirit’s inspiration.
If it doesn’t meet these conditions, it isn’t accepted.”
“To be canonical, a book must be written by an apostle or eyewitness under the Holy Spirit’s inspiration.
If it doesn’t meet these conditions, it isn’t accepted.”

Do these conditions apply to the Gospel writers? Were they eyewitnesses or known?
The Jesuit translation replies:
“Many Bible books were written by authors seen as God’s voice but many remained unknown.”
The Jesuit translation replies:
“Many Bible books were written by authors seen as God’s voice but many remained unknown.”

The Orthodox priest Theodore Stylianopoulos, in The New Testament: An Orthodox Perspective, states:
“Most Bible books were likely written by unknown authors addressing issues of their time and community.”
“Most Bible books were likely written by unknown authors addressing issues of their time and community.”

The Catholic priest (Raymond Brown) agrees with this, emphasizing that the gospel writers were not eyewitnesses and that most scholars doubt that any of the canonical gospels were written by an eyewitness.! 



And supporting them in this are the editors of the book (Study of the Synoptic Gospels) where it states:
"Based on this our judgment is that the Gospels were indeed author unknown and that the names of the books were not known outside the circle of their immediate acquaintances.
"Based on this our judgment is that the Gospels were indeed author unknown and that the names of the books were not known outside the circle of their immediate acquaintances.

Who wrote the Gospel of John?
Rev. Dr. Fahim Aziz writes in Introduction to the New Testament:
“This question is difficult and often ends with: only God knows who wrote it.”
Rev. Dr. Fahim Aziz writes in Introduction to the New Testament:
“This question is difficult and often ends with: only God knows who wrote it.”

The Jesuit translation states:
“No clear evidence exists for the author or date of this Gospel perhaps intentionally.”
Similarly, History of the Bible by Miller & Huber says:
“Once again, it is not known who wrote this Gospel.”

“No clear evidence exists for the author or date of this Gospel perhaps intentionally.”
Similarly, History of the Bible by Miller & Huber says:
“Once again, it is not known who wrote this Gospel.”


Who wrote the Gospel of Matthew?
Pastor Fahim Aziz says: “We can’t name the author it could be Matthew the Apostle or someone else.”
R. France (Modern Interpretation):
“Like the other Gospels, its author is unknown.”

Pastor Fahim Aziz says: “We can’t name the author it could be Matthew the Apostle or someone else.”
R. France (Modern Interpretation):
“Like the other Gospels, its author is unknown.”


Father Estefan Sherbitiyeh says:
"But the author of the current Gospel is unknown.
And Stephen Miller says:
"It does not seem that the author was an eyewitness, as he relied on Mark and other sources to obtain his material.

"But the author of the current Gospel is unknown.
And Stephen Miller says:
"It does not seem that the author was an eyewitness, as he relied on Mark and other sources to obtain his material.


Habib Saeed says in (Introduction to the Holy Bible)
"We would have liked to know who this writer was who called himself (Matthew) and indicated that he was not one of the twelve disciples."
"We would have liked to know who this writer was who called himself (Matthew) and indicated that he was not one of the twelve disciples."

Who wrote the Gospel of Mark?
Though Matthew relied on it, its author is unknown.
The Biblical Encyclopedia says:
“No clear proof that Mark was a disciple or eyewitness.”
Stephen Miller:
“No one knows for sure who wrote this Gospel.”

Though Matthew relied on it, its author is unknown.
The Biblical Encyclopedia says:
“No clear proof that Mark was a disciple or eyewitness.”
Stephen Miller:
“No one knows for sure who wrote this Gospel.”


And Father Pauls Al-Faghaly says: Nothing in the biblical text helps us identify the author of the Gospel of Mark.
Nor was the writer of the Gospel of Luke an eyewitness, like the rest of the gospel writers.

Nor was the writer of the Gospel of Luke an eyewitness, like the rest of the gospel writers.


Likewise, the Epistle to the Hebrews is such that the author of this epistle is not known with certainty. 



The Second Epistle of Peter fares no better. William Barclay says:
“Ancient and modern scholars nearly all agree Peter didn’t write it.”
Pope Tawadros II affirms:
“There’s no doubt it wasn’t written by the Apostle Peter.”
The author of Jude is also unknown, like the rest.


“Ancient and modern scholars nearly all agree Peter didn’t write it.”
Pope Tawadros II affirms:
“There’s no doubt it wasn’t written by the Apostle Peter.”
The author of Jude is also unknown, like the rest.



Were the Gospel writers inspired by the Holy Spirit?
Habib Saeed writes:
“New Testament authors likely never thought they were writing sacred scripture. That idea never occurred to them.”
Habib Saeed writes:
“New Testament authors likely never thought they were writing sacred scripture. That idea never occurred to them.”

“None of the sacred scripture writers knew their words would become part of the Bible not even Paul.”
So, the conditions set by Church tradition for accepting epistles as canonical don’t apply to the current Gospels.
So, the conditions set by Church tradition for accepting epistles as canonical don’t apply to the current Gospels.

James D. Tabor says all four Gospels are anonymous, written after the apostles, and not eyewitness accounts. The names were added later by tradition, not by the authors themselves. 



Barrie Wilson in Searching for the Messiah says the Gospel of Mark was written around 70 CE in Greek by an anonymous author. The name “Mark” was added later to give it authority, but scholars agree there’s no solid reason to accept it. The Gospels are effectively anonymous. 



Yale scholar Dale B. Martin says we don’t accept the old traditions that Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John wrote the Gospels. They were originally published anonymously. 



The New Oxford Annotated Bible says the Gospels were written decades after Jesus to support faith, not as eyewitness accounts. Matthew, Mark, and Luke share many stories, so they’re called the Synoptic Gospels. 



Scholars like Bart Ehrman, Graham Stanton, and others all agree the Gospels were written anonymously and not by Jesus’ disciples. The names were added later by unknown church figures. 



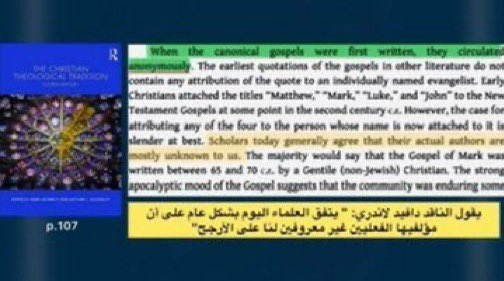
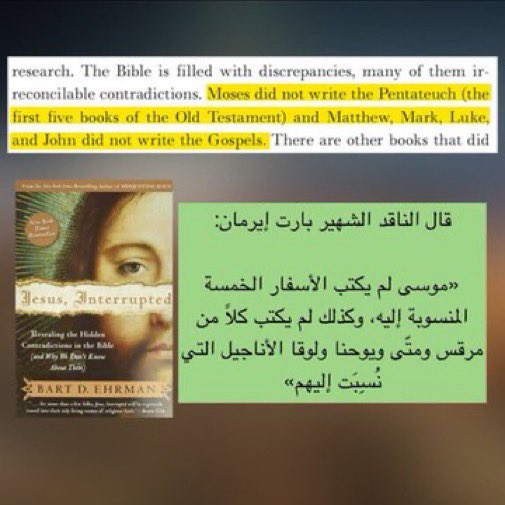
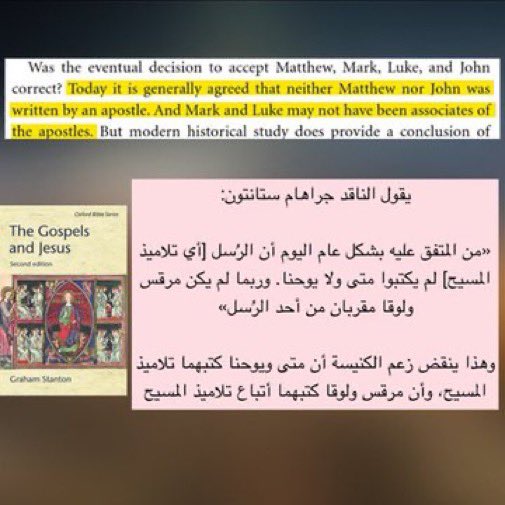

Ph.D. scholar Dan McClellan affirms the data shows all four Gospels were written anonymously, with traditional names only added in the 2nd century. He states this is the scholarly consensus no direct or indirect eyewitness accounts of Jesus’ life exist.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh