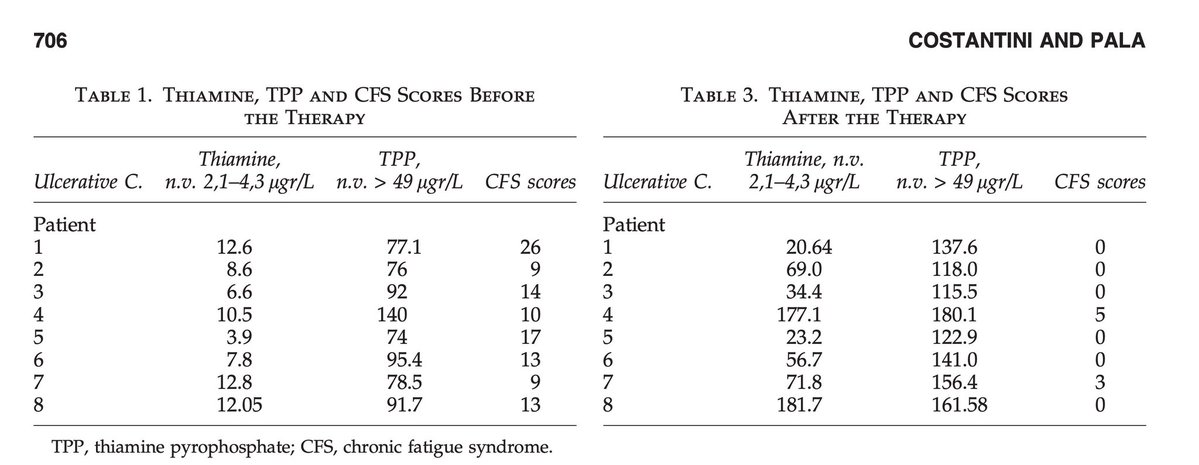
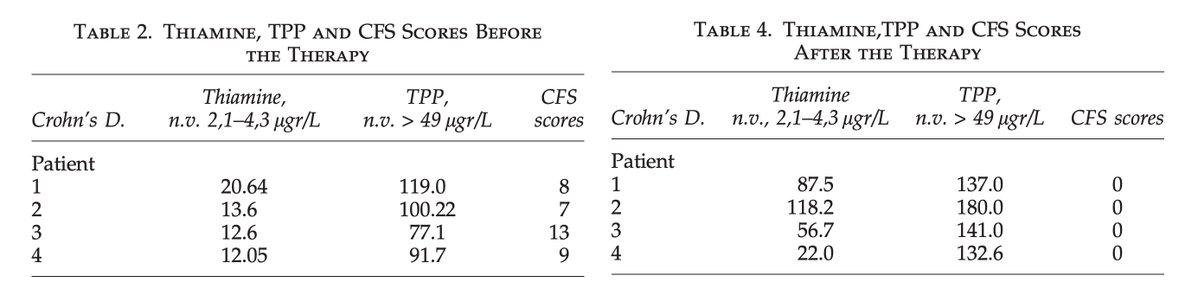
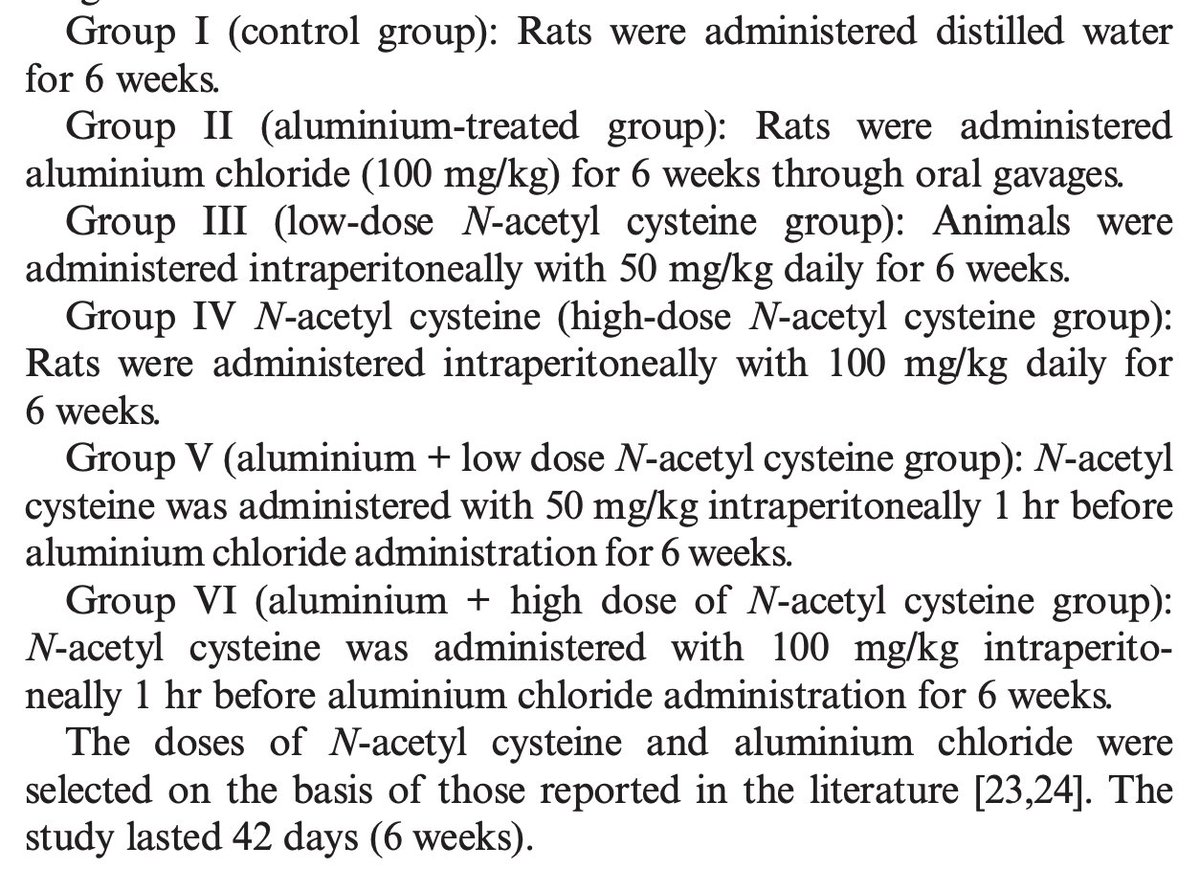
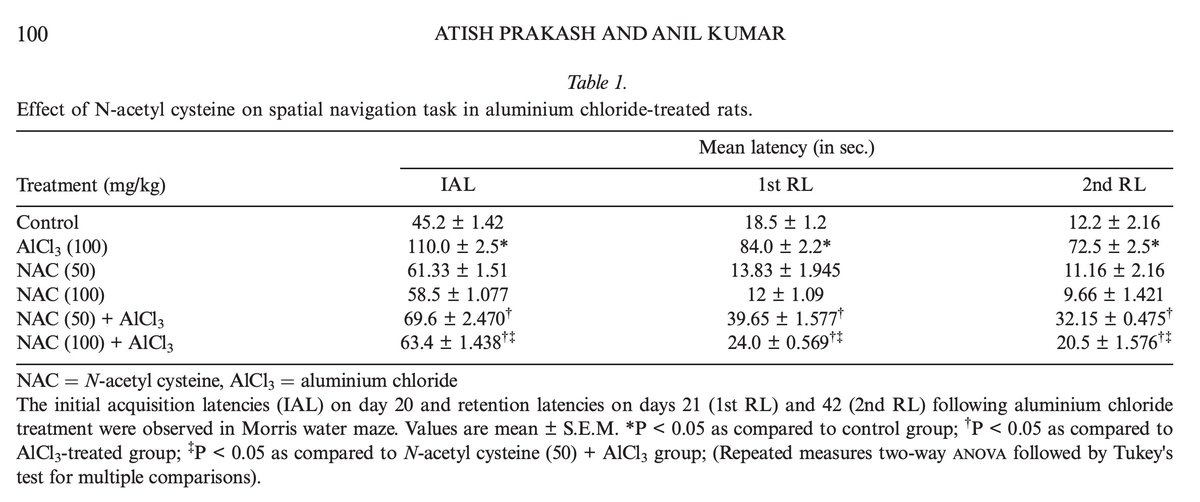
A groundbreaking new study shows that a mineral deficiency can drive Alzheimer's, and consuming it can reverse it.
(🧵1/10)
(🧵1/10)
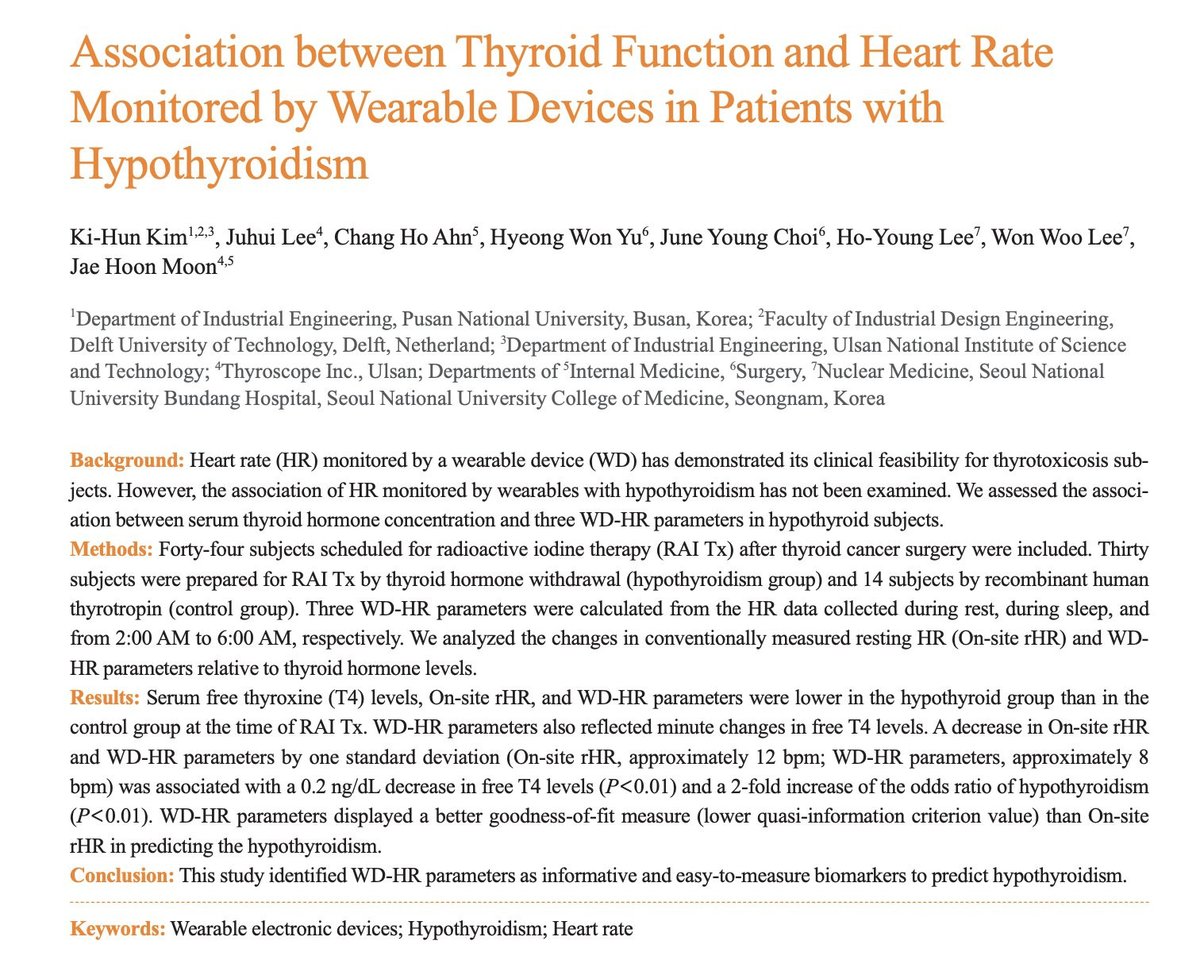
The study was published 3 days ago, in Nature.
While lithium is used as a drug in high doses for things like bipolar disorder, it is a naturally occurring mineral in some foods and water supplies.
Unexpectedly, it seems to play a major role in Alzheimer's.
(2/10)
While lithium is used as a drug in high doses for things like bipolar disorder, it is a naturally occurring mineral in some foods and water supplies.
Unexpectedly, it seems to play a major role in Alzheimer's.
(2/10)

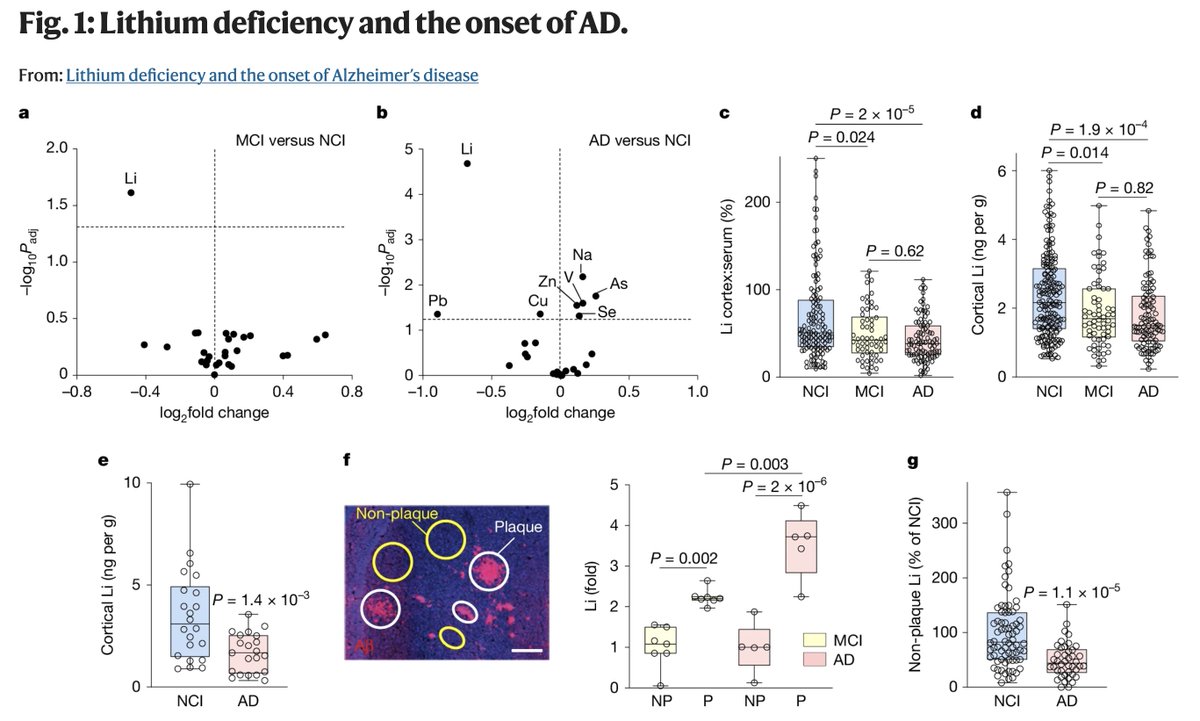
They looked at 27 different metals to see if there were any differences in the brain's of Alzheimer's disease.
Surprisingly, only lithium stood out, in two separate cohorts:
⇨ Lower levels in the prefrontal cortex
⇨ Higher levels in amyloid plaques
Thus, less lithium available for functioning brain tissue.
(3/10)
Surprisingly, only lithium stood out, in two separate cohorts:
⇨ Lower levels in the prefrontal cortex
⇨ Higher levels in amyloid plaques
Thus, less lithium available for functioning brain tissue.
(3/10)
Lithium deficiency drives Alzheimer's disease.
When animals were given low lithium diet, they had:
◇ More plaque accumulation in the hippocampus
◇ More plaque in the cortex
◇ More phosphorylated tau
◇ Impaired learning
◇ Impaired memory
◇ Worsened novel-object recognition
compared to animals given normal amounts of lithium in the diet.
(4/10)
When animals were given low lithium diet, they had:
◇ More plaque accumulation in the hippocampus
◇ More plaque in the cortex
◇ More phosphorylated tau
◇ Impaired learning
◇ Impaired memory
◇ Worsened novel-object recognition
compared to animals given normal amounts of lithium in the diet.
(4/10)
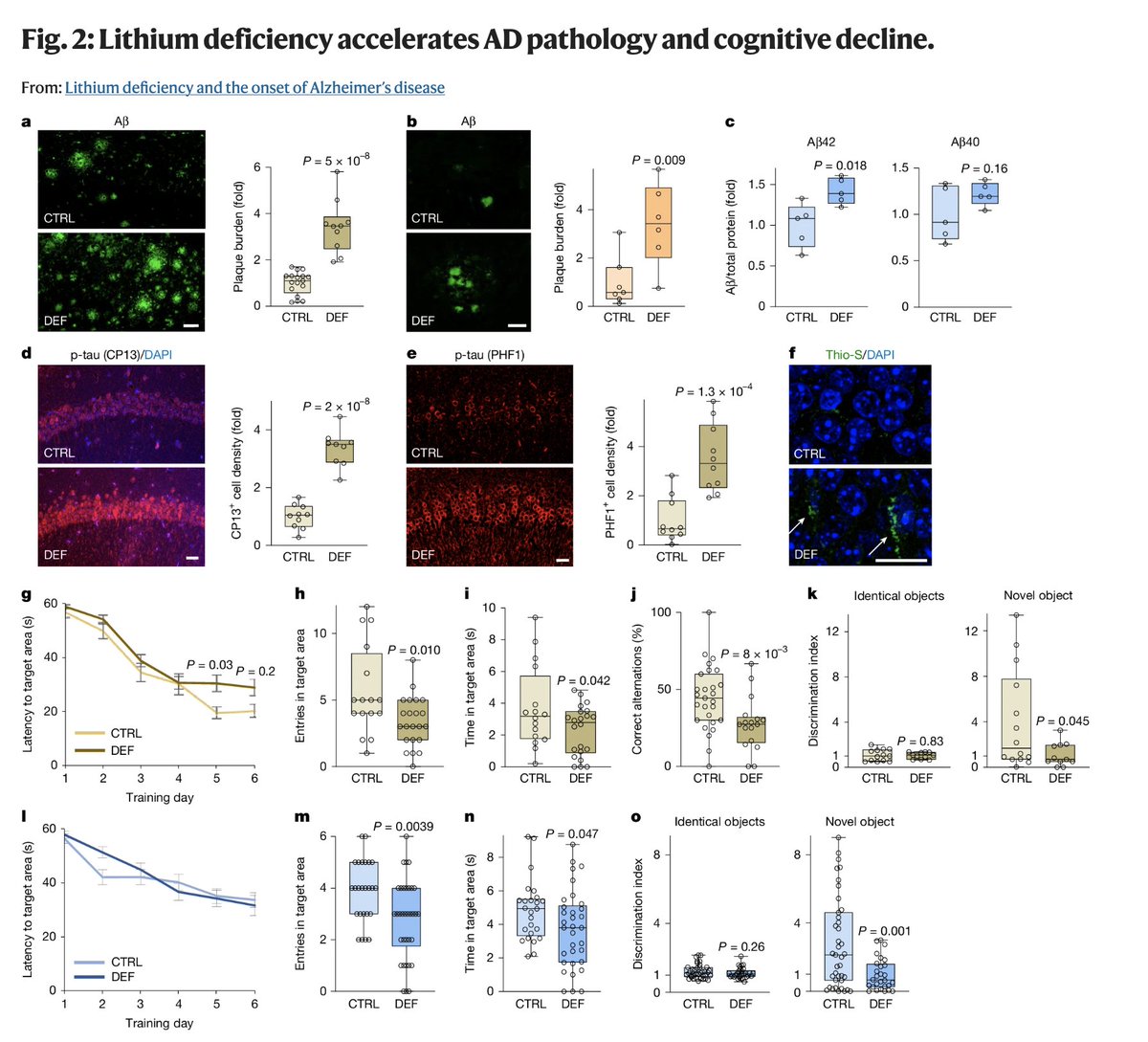
Lithium deficiency changed gene expression in several brain cell types, too.
Genes involved in:
➠ Synaptic signaling
➠ Myelination
➠ Synapse formation
were downregulated, while classical genes of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's were upregulated.
Meanwhile, the dendritic spines of neurons were also visually decreased, indicating poor neuron health.
The genetic expression profile of lithium deficient animals mimicked that of people with Alzheimer's.
(5/10)
Genes involved in:
➠ Synaptic signaling
➠ Myelination
➠ Synapse formation
were downregulated, while classical genes of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's were upregulated.
Meanwhile, the dendritic spines of neurons were also visually decreased, indicating poor neuron health.
The genetic expression profile of lithium deficient animals mimicked that of people with Alzheimer's.
(5/10)
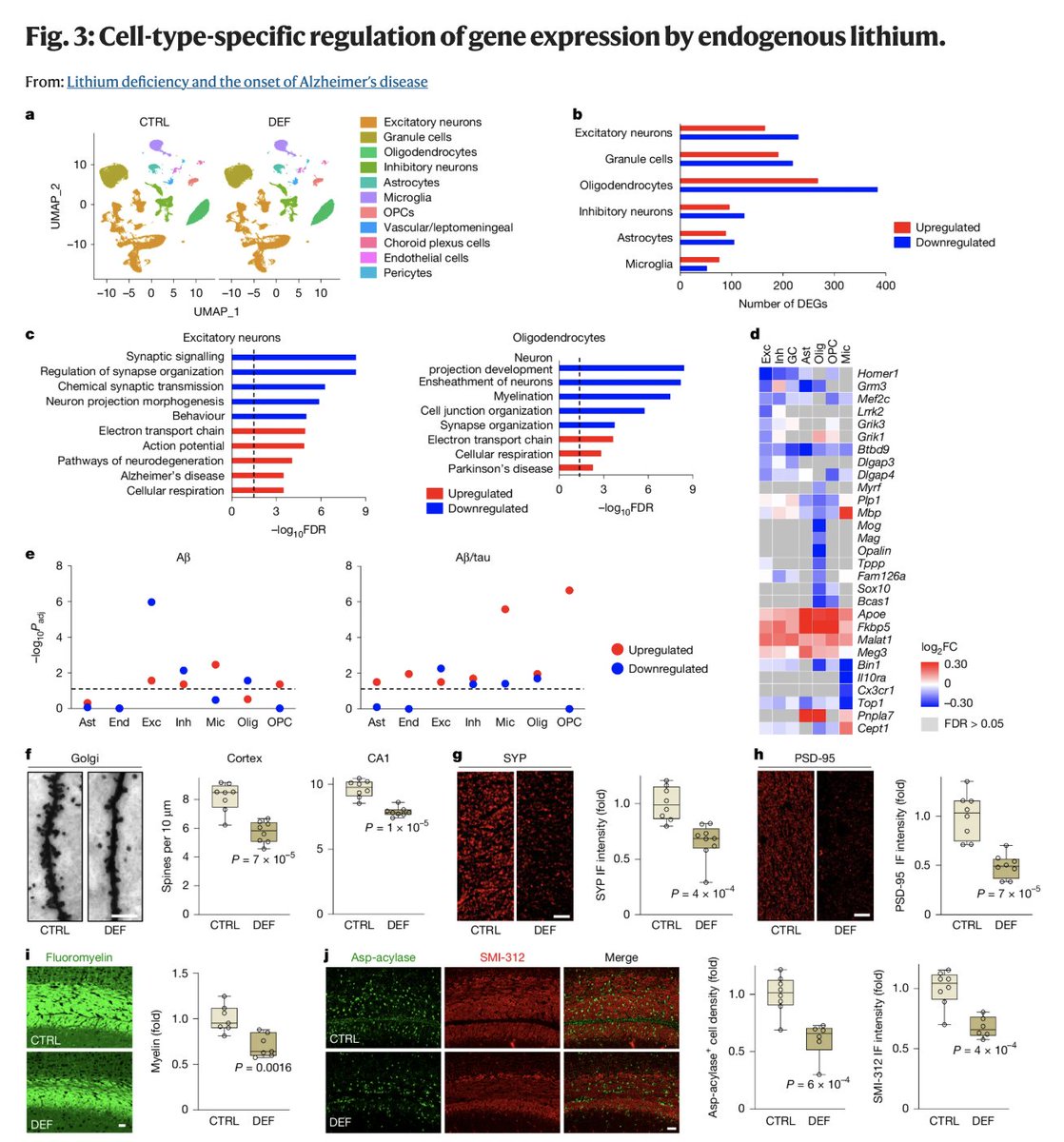
An important finding is that lithium deficiency activates microglia, the inflammatory cells in the brain.
These cells are also the key drivers of things like fatigue and brain fog, as I've discussed below.
(6/10)

These cells are also the key drivers of things like fatigue and brain fog, as I've discussed below.
(6/10)
https://x.com/Outdoctrination/status/1937894016374514146
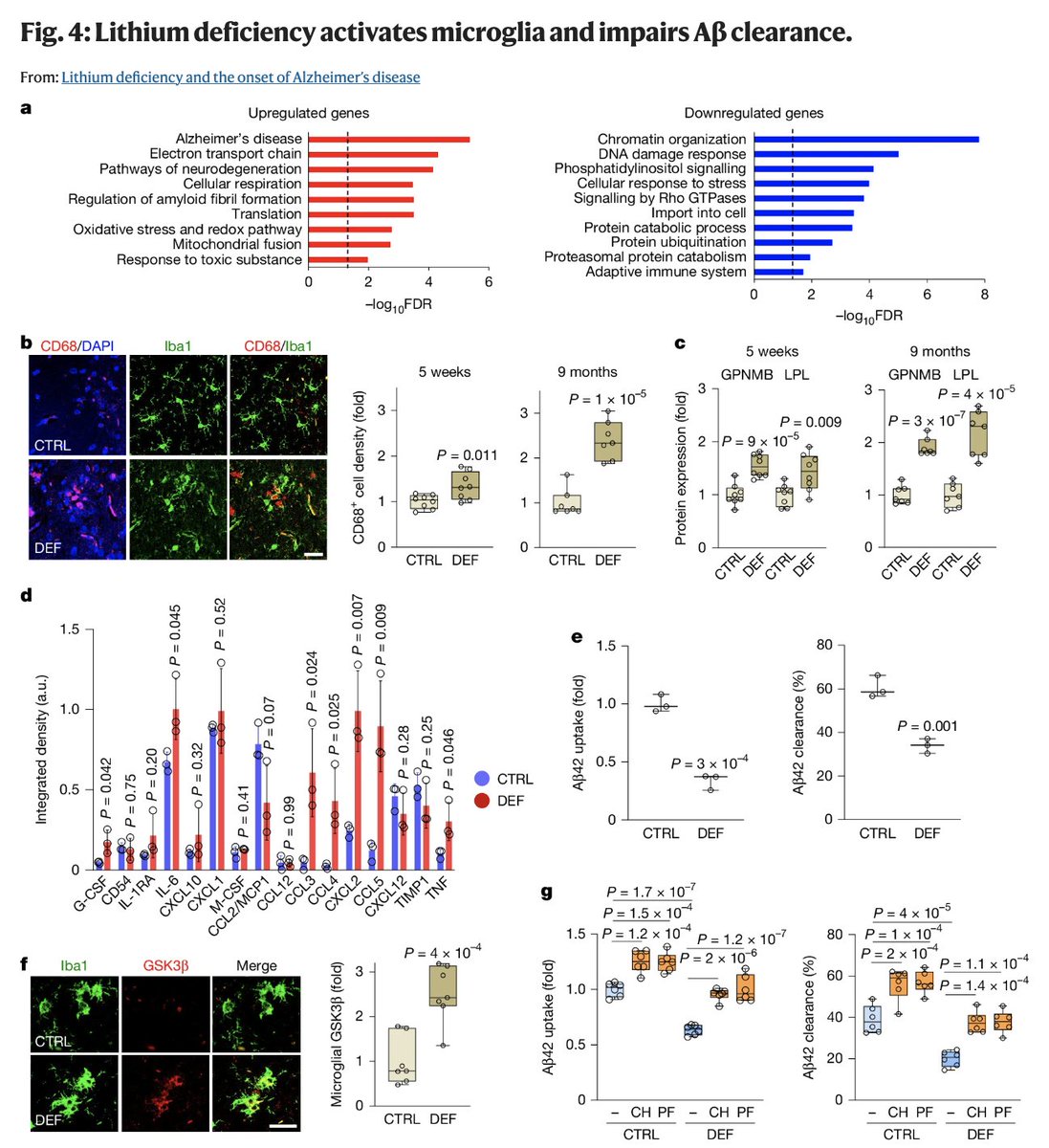
They also found that lithium orotate, which is a common cheap supplement form of lithium, was highly protective against Alzheimer's associated plaque accumulation and tau hyperphosphorylation.
(7/10)
(7/10)
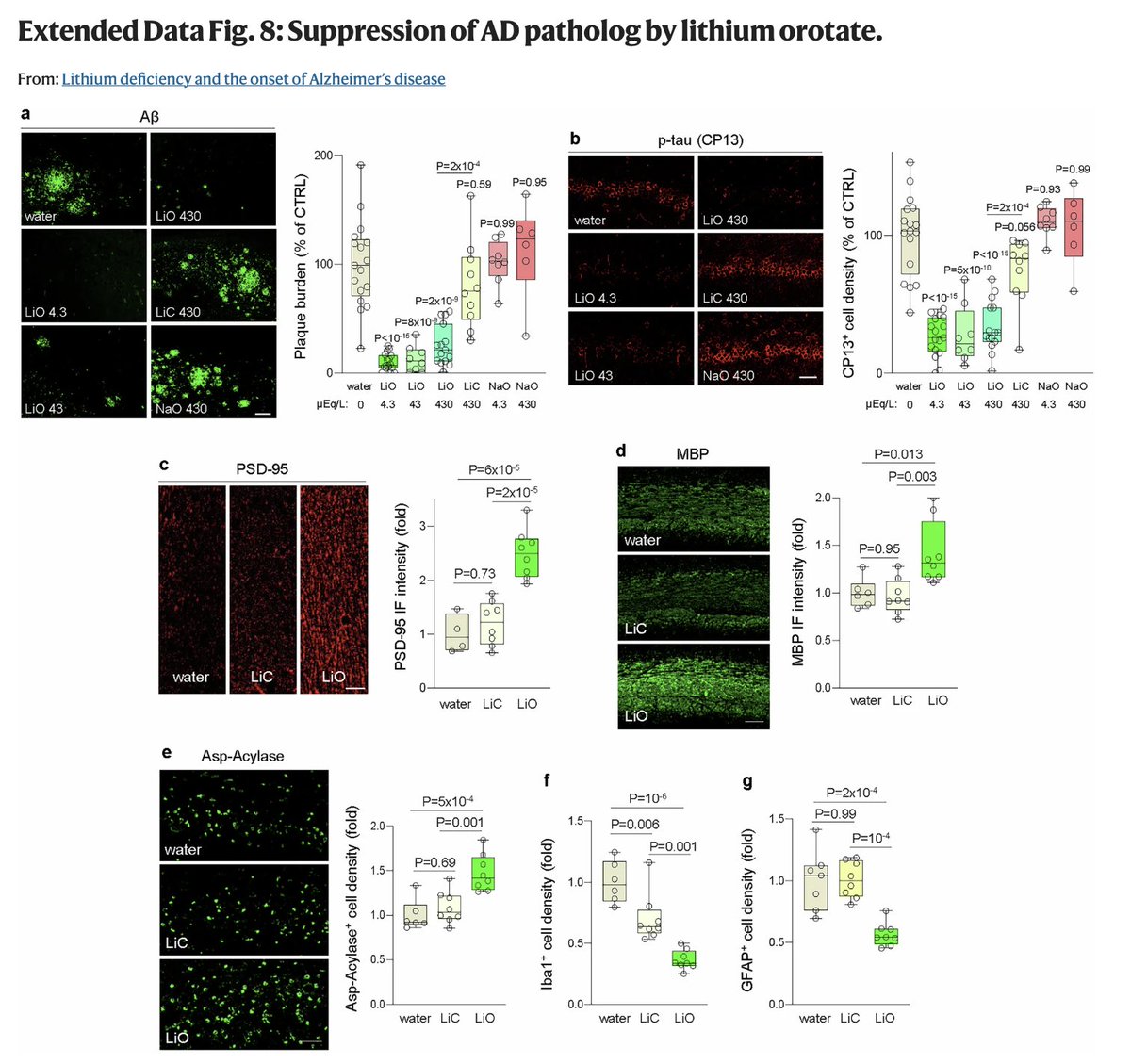
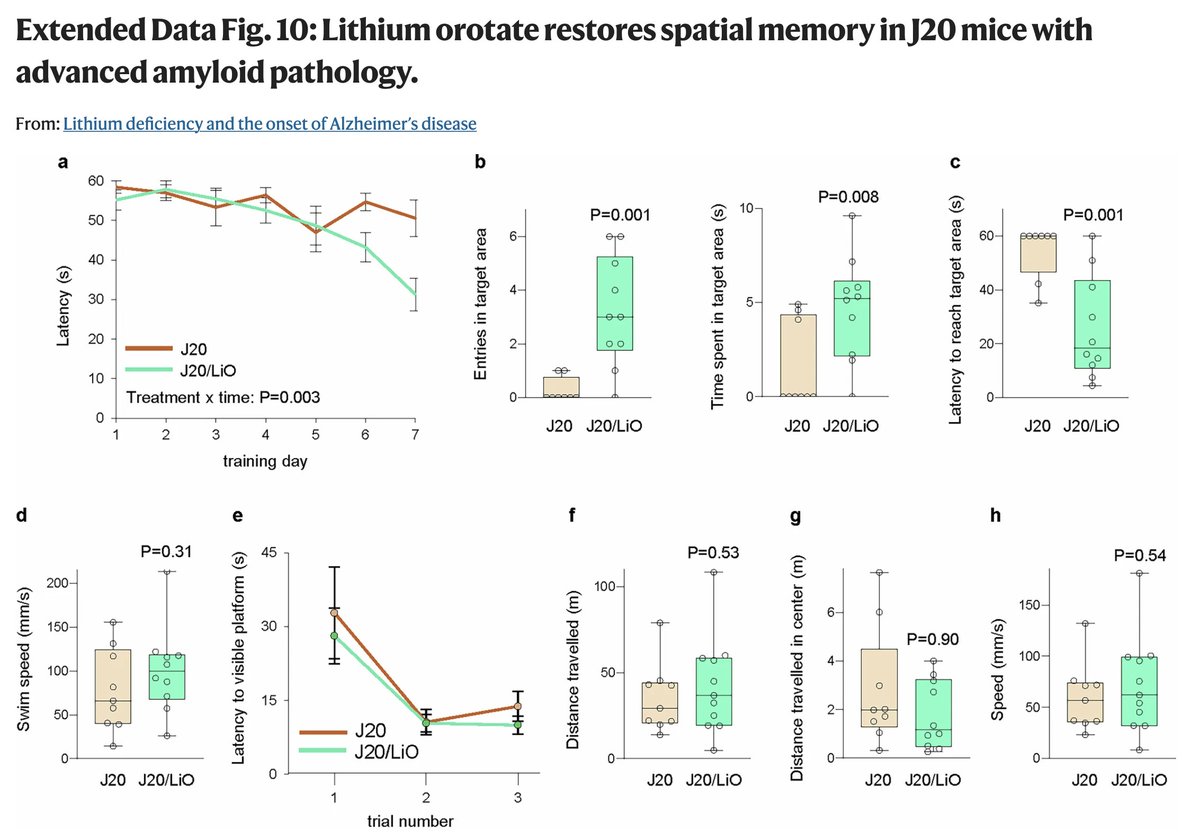
In animals with advanced Alzheimer's disease, lithium orotate was able to REVERSE some of the cognitive symptoms,
going beyond prevention.
(8/10)
going beyond prevention.
(8/10)
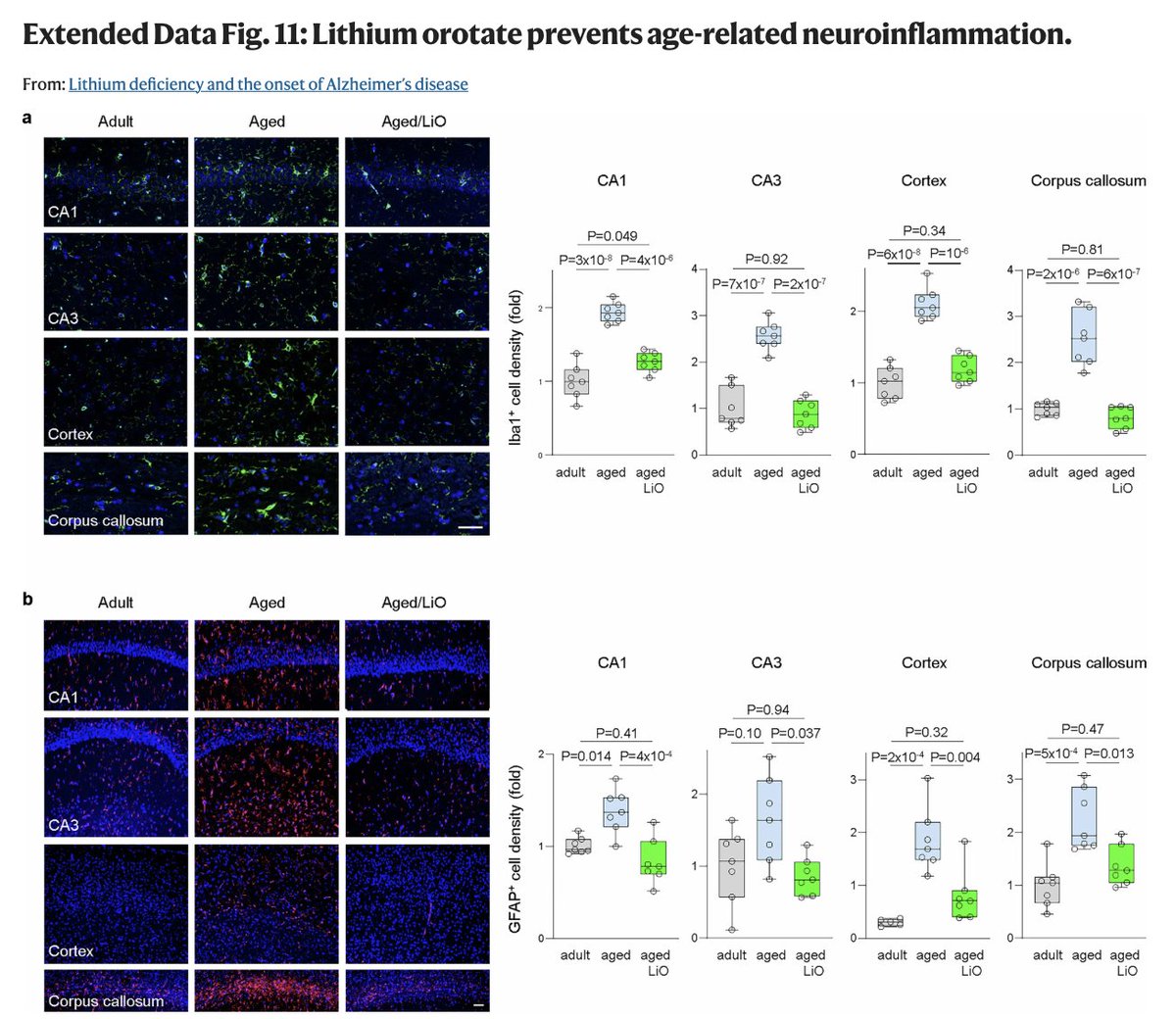
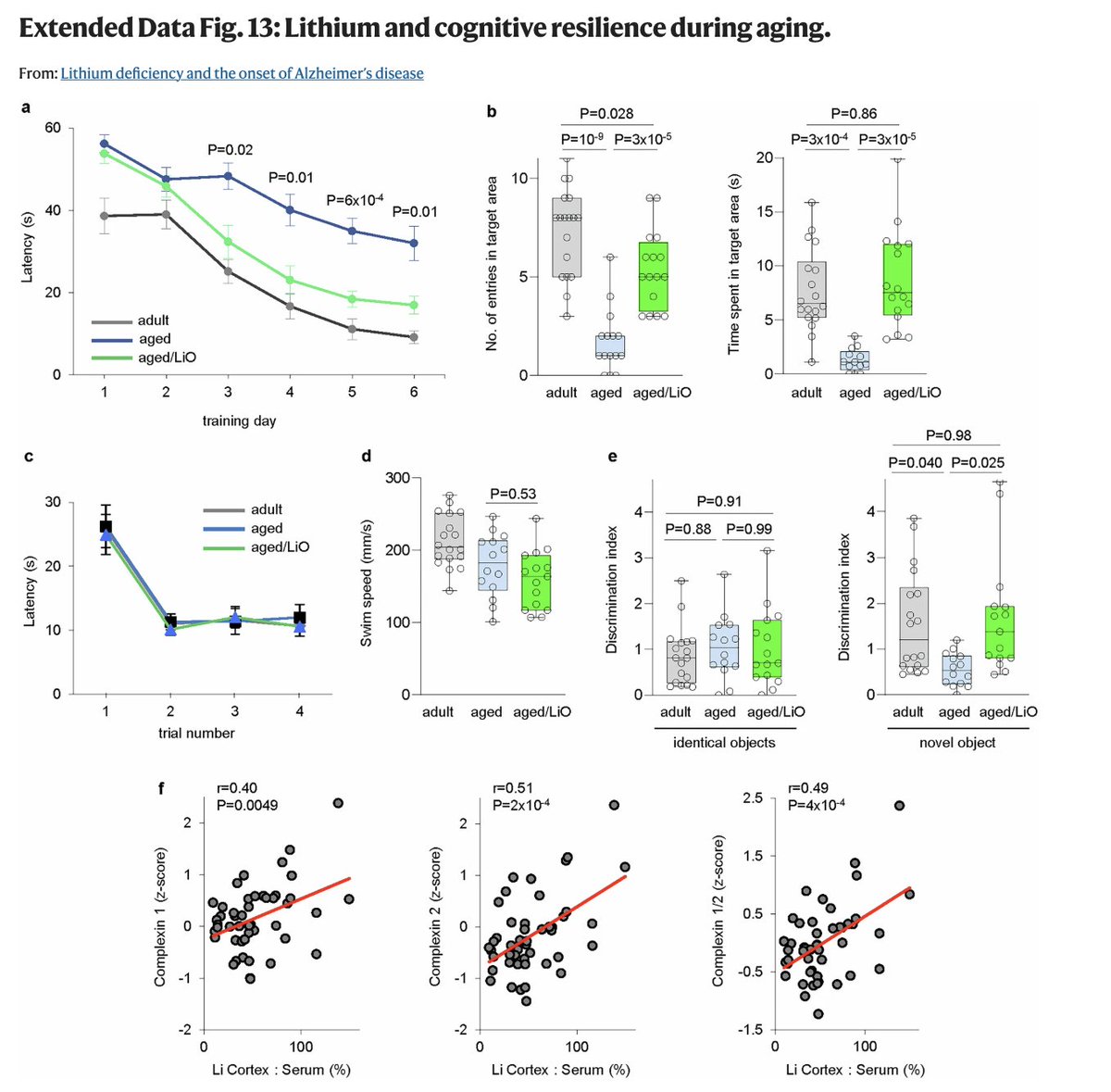
As we age, cognitive function becomes impaired alongside increased inflammation in the brain.
This tends to happen even if you don't get Alzheimer's.
Lithium prevented these signs of aging in the brain - preventing microglial activation and preserving brain power.
(9/10)

This tends to happen even if you don't get Alzheimer's.
Lithium prevented these signs of aging in the brain - preventing microglial activation and preserving brain power.
(9/10)
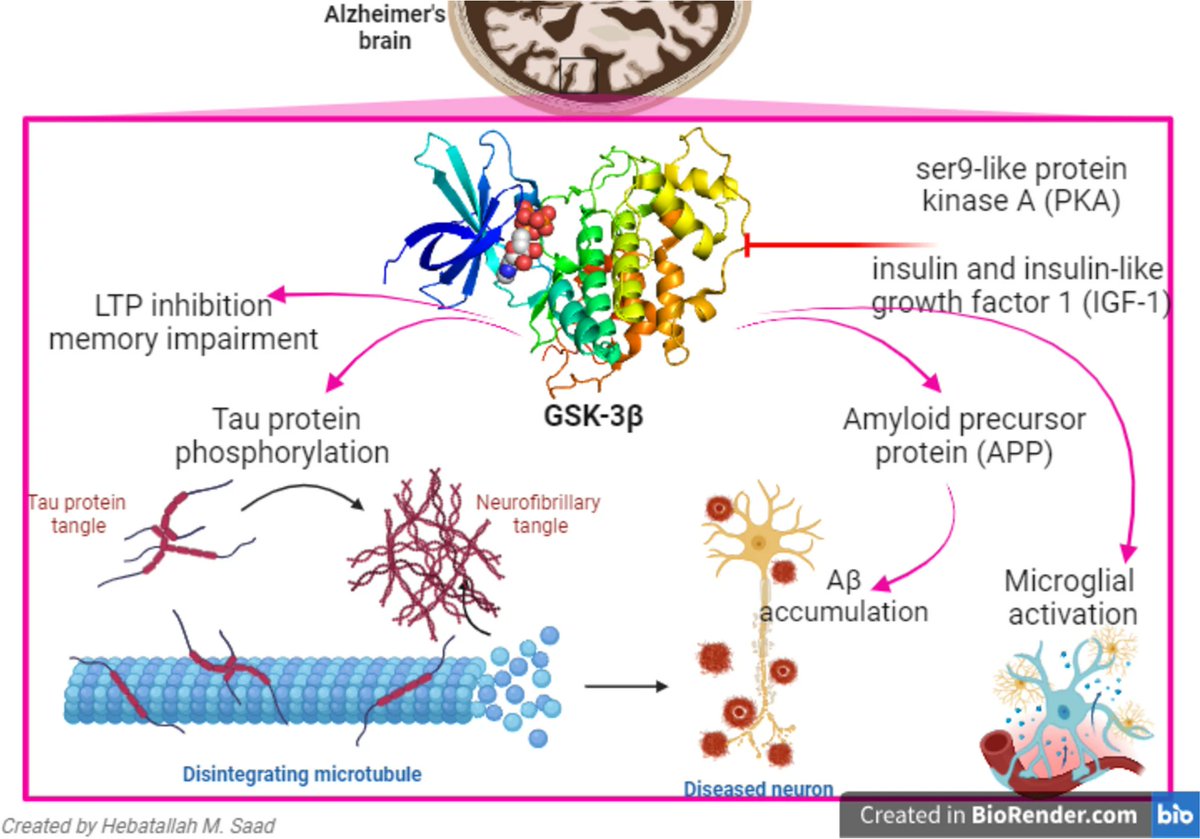
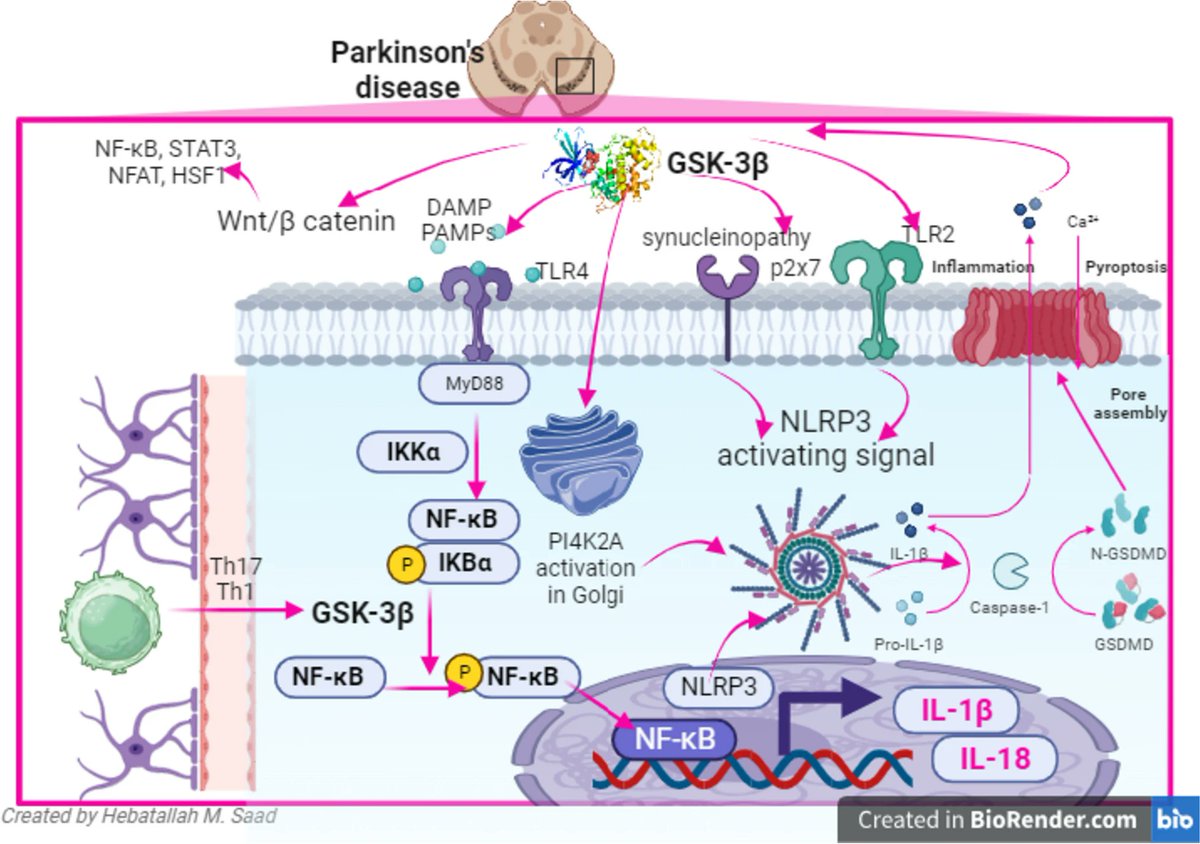
Why is lithium so helpful for the brain?
A lot of it comes down to an enzyme called glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β).
Lithium inhibits this enzyme.
This enzyme inhibits the process of glycogen synthesis. Glycogen is the storage form of SUGAR or glucose. High GSK3β means less stored sugar for metabolism.
GSK3β also has several other effects:
➜ Turns on inflammatory proteins
➜ Promotes inflammatory receptor signaling
➜ Increases phosphorylation of tau, a key player in Alzheimer's
➜ Activates microglia
Essentially, it turns on just about every known pathway that leads to neurodegenerative disease.
Lithium stops it.
The authors also note that in high dose lithium trials, benefits are not seen, while in low doses we see benefits.
(10/10)

A lot of it comes down to an enzyme called glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β).
Lithium inhibits this enzyme.
This enzyme inhibits the process of glycogen synthesis. Glycogen is the storage form of SUGAR or glucose. High GSK3β means less stored sugar for metabolism.
GSK3β also has several other effects:
➜ Turns on inflammatory proteins
➜ Promotes inflammatory receptor signaling
➜ Increases phosphorylation of tau, a key player in Alzheimer's
➜ Activates microglia
Essentially, it turns on just about every known pathway that leads to neurodegenerative disease.
Lithium stops it.
The authors also note that in high dose lithium trials, benefits are not seen, while in low doses we see benefits.
(10/10)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh