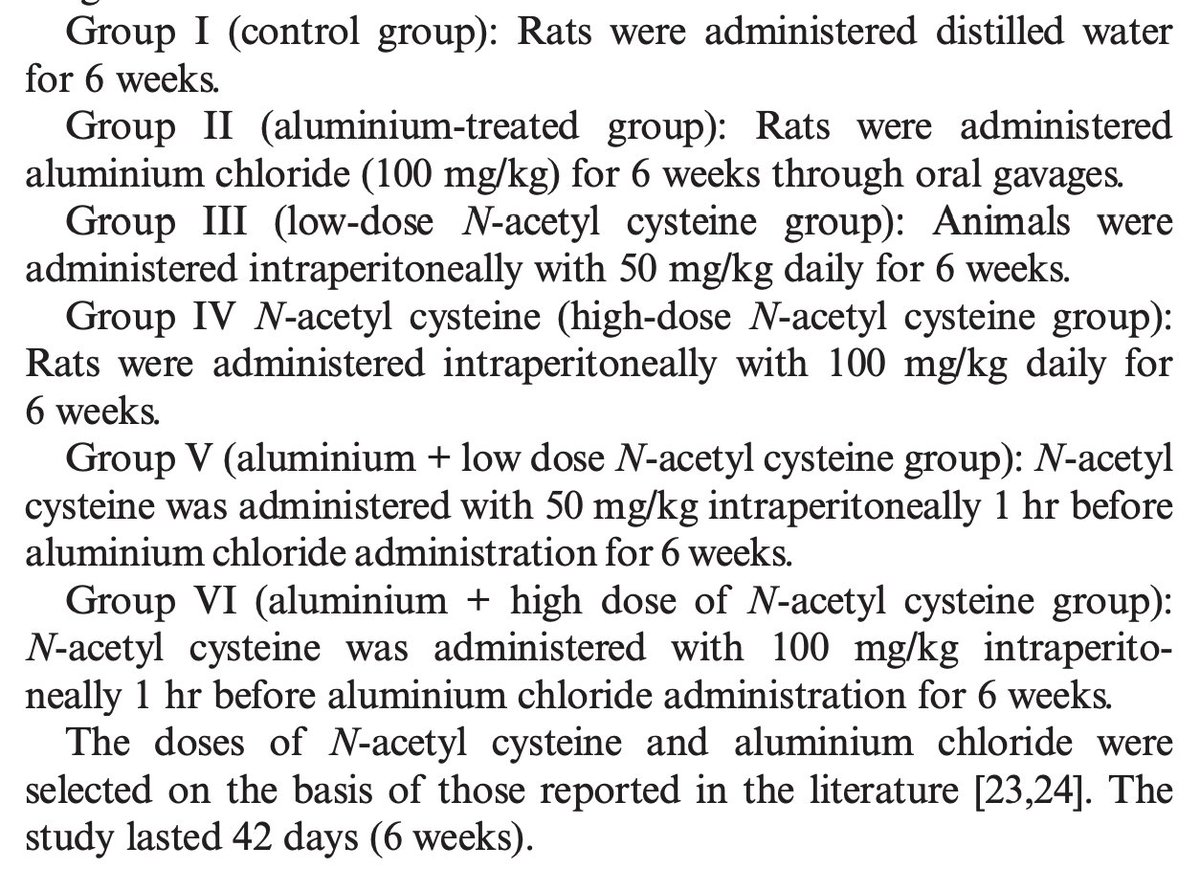
A surprising new study showed that a LOW protein diet boosts metabolism and improves insulin sensitivity.
(🧵1/9)
(🧵1/9)

This study was published in Nature back in March.
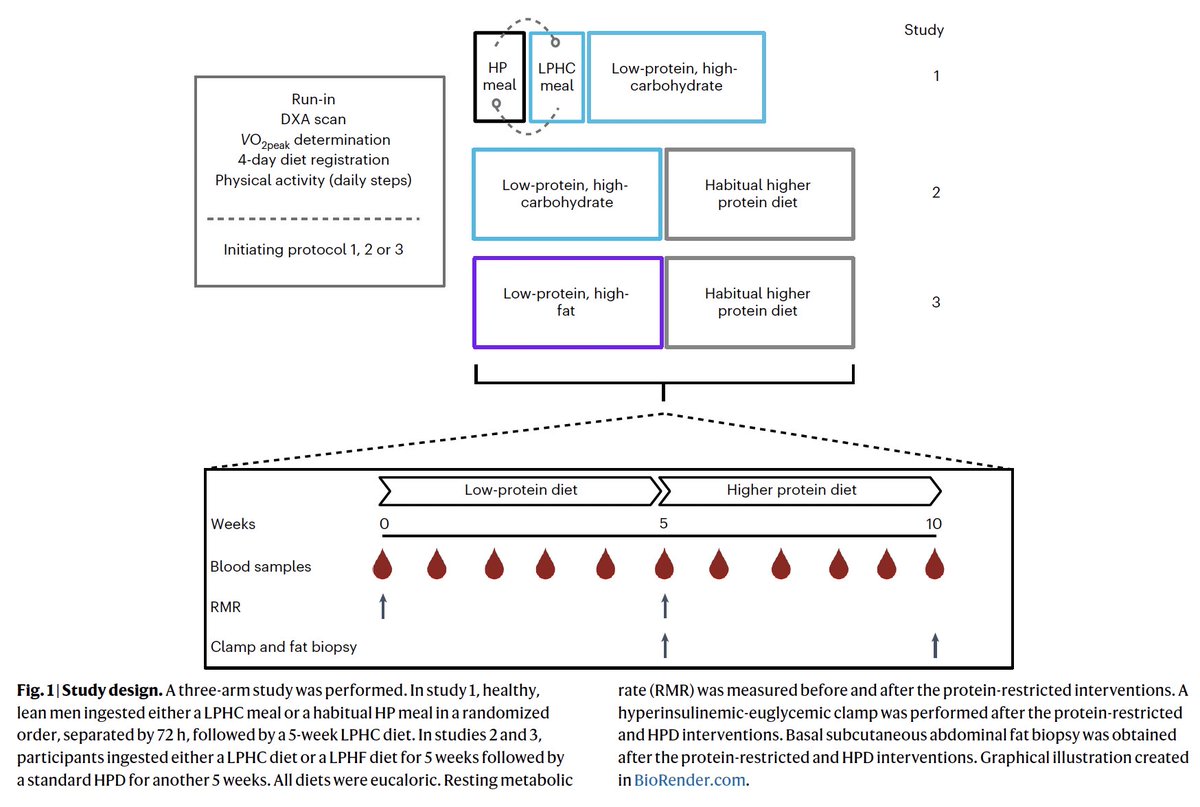
There were a few phases.
1. Studying the immediate effects of an extremely low protein meal (high in carbs or high in fat)
2. Looking at the longer term (5 week) effects of a diet low in protein (high in either carbs or fat)
The low protein meals/diets had 8-9% calories from protein, high protein meals/diets had double that.
The high carb low protein diets had ~70% calories from carbs, ~20% fat.
The high fat low protein diets ~50% calories from fat, 40% carbs.
(2/9)
There were a few phases.
1. Studying the immediate effects of an extremely low protein meal (high in carbs or high in fat)
2. Looking at the longer term (5 week) effects of a diet low in protein (high in either carbs or fat)
The low protein meals/diets had 8-9% calories from protein, high protein meals/diets had double that.
The high carb low protein diets had ~70% calories from carbs, ~20% fat.
The high fat low protein diets ~50% calories from fat, 40% carbs.
(2/9)
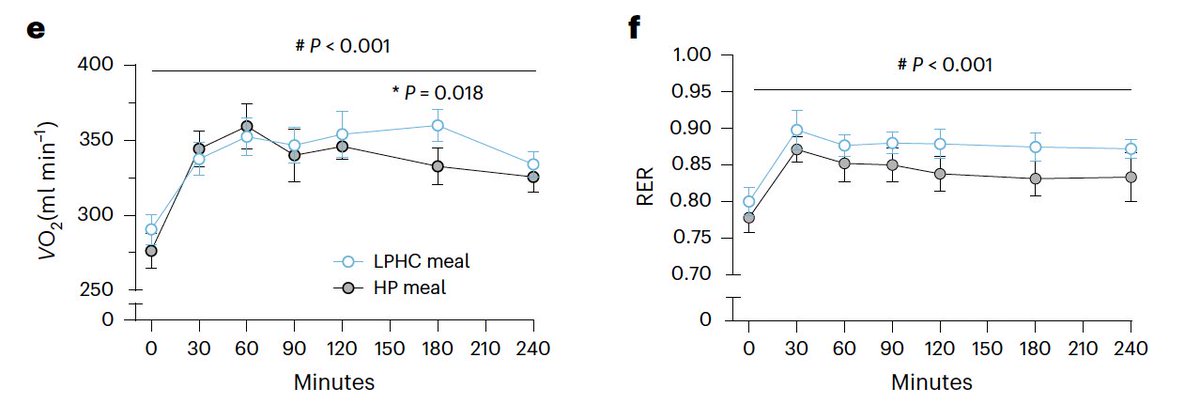
A low protein high carb meal increases oxygen uptake and respiratory exchange ratio.
More oxygen in, more CO2 out, meaning more energy production.
Higher metabolism.
(3/9)
More oxygen in, more CO2 out, meaning more energy production.
Higher metabolism.
(3/9)
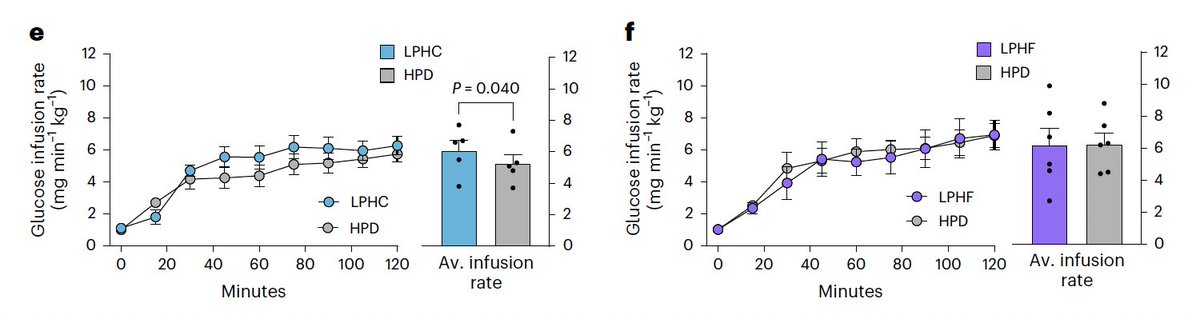
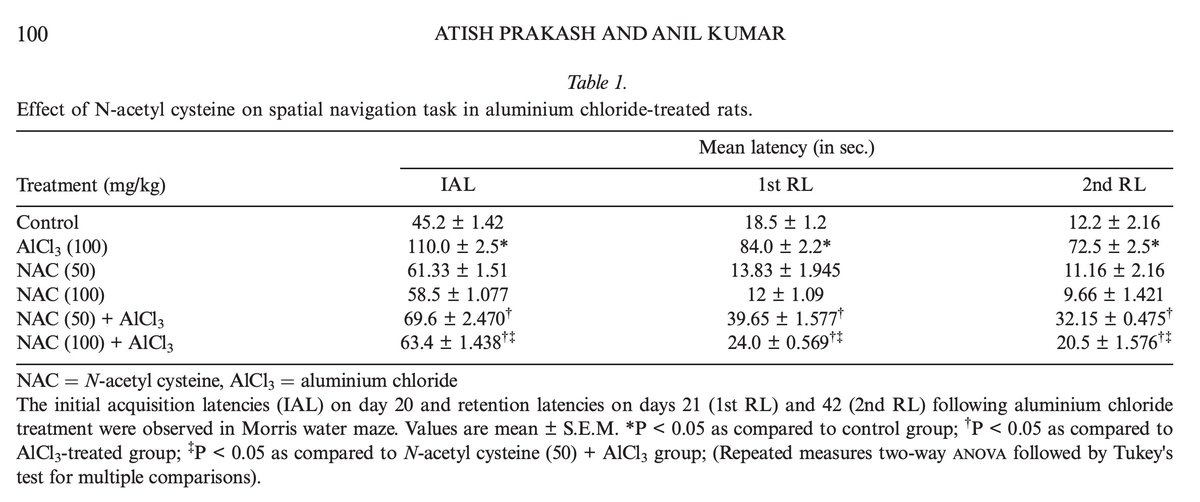
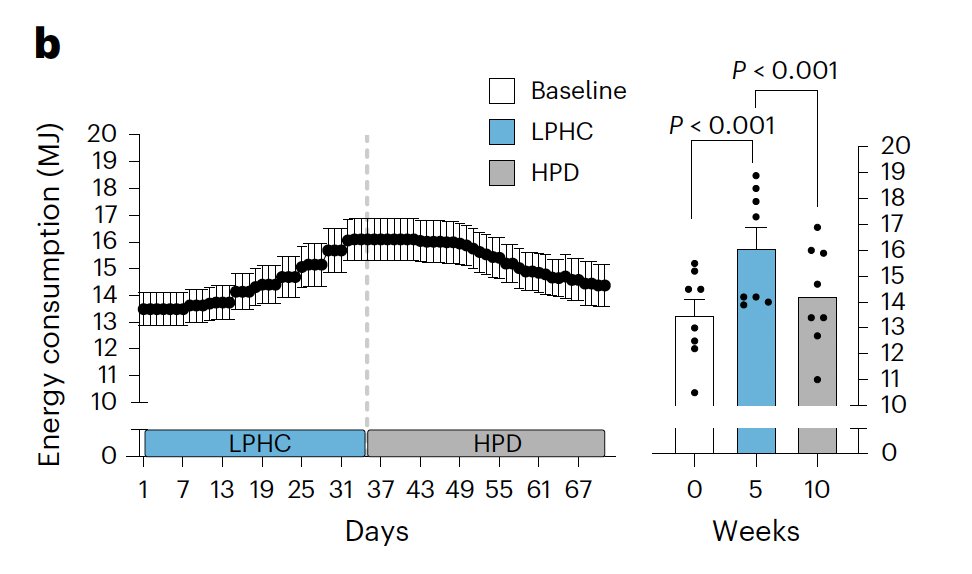
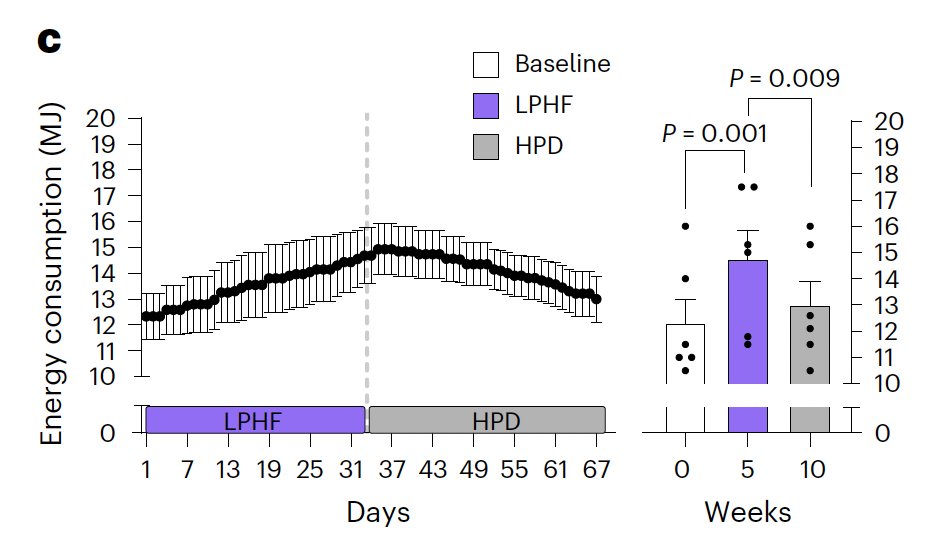
The low protein diets increased metabolism by ~20%.
People were instructed to eat as much needed to maintain their weight, and they ended up eating 20% more calories to do so.
This was true regardless of if the diet was higher carb or lower carb.
Both groups had the same amount of physical activity.
(4/9)

People were instructed to eat as much needed to maintain their weight, and they ended up eating 20% more calories to do so.
This was true regardless of if the diet was higher carb or lower carb.
Both groups had the same amount of physical activity.
(4/9)
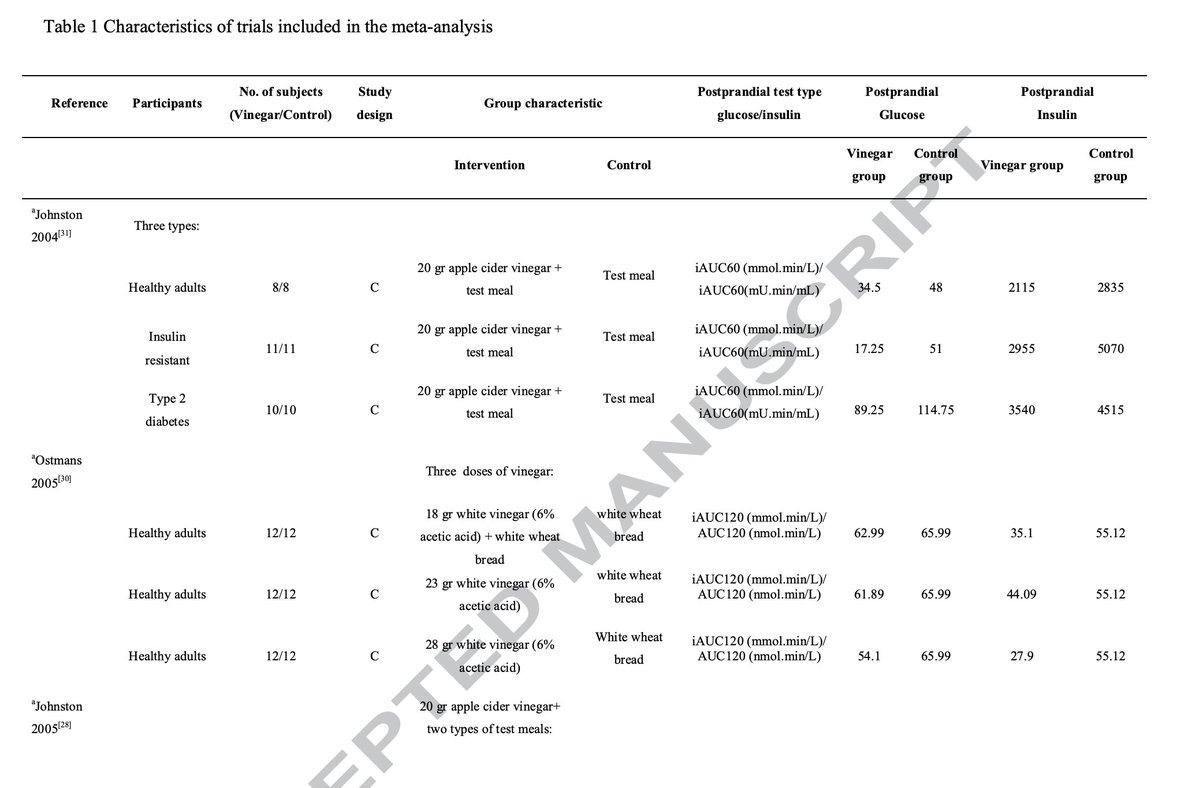
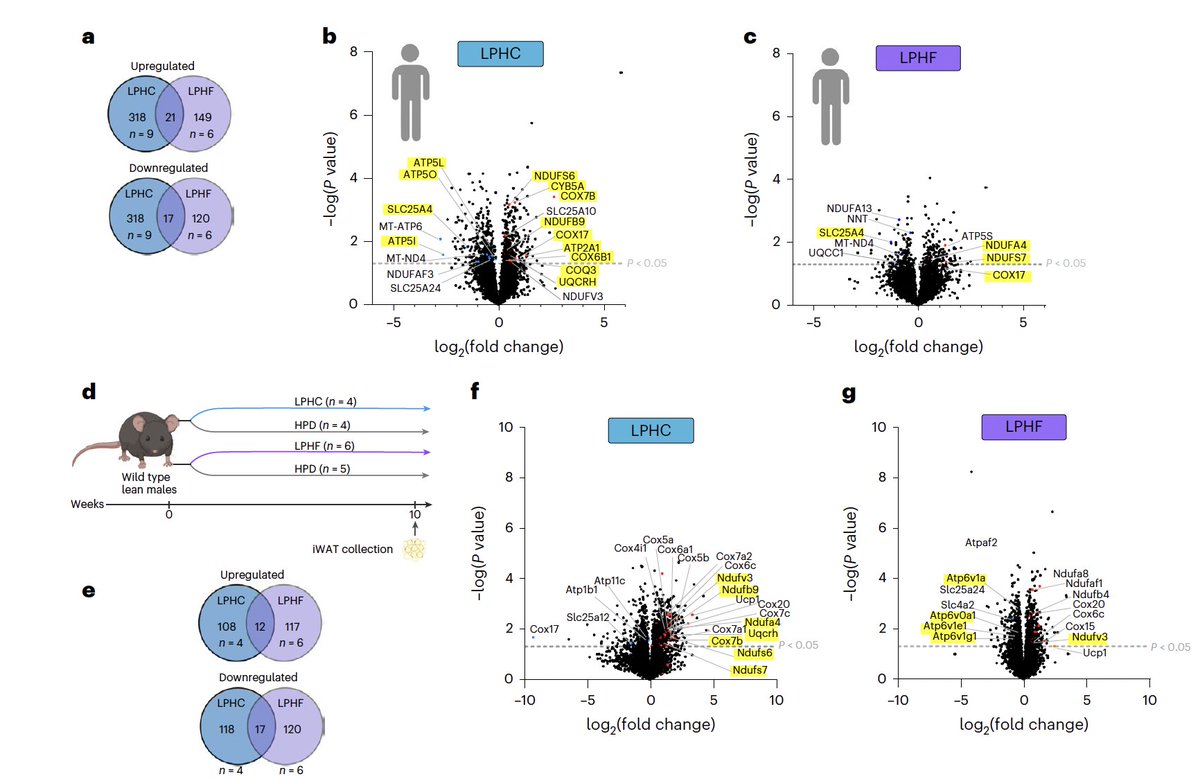
The low protein diets also changed the amounts of different proteins in both groups.
The highlighted ones here are the ones from the mitochondrial electron transport chain, where the vast majority of cellular energy is produced.
The higher carb diet resulted in more of these energy producing proteins being increased, though the lower carb diet also resulted in some increases.
(6/9)
The highlighted ones here are the ones from the mitochondrial electron transport chain, where the vast majority of cellular energy is produced.
The higher carb diet resulted in more of these energy producing proteins being increased, though the lower carb diet also resulted in some increases.
(6/9)
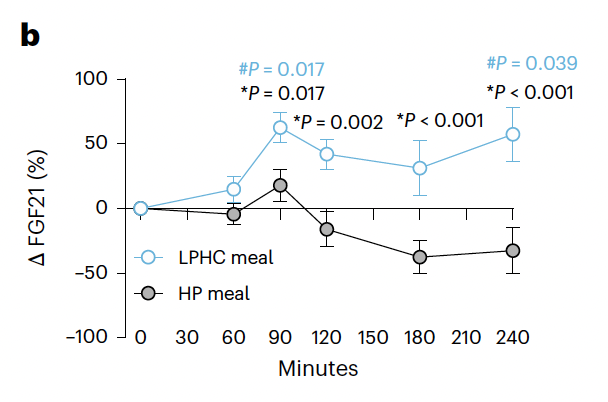
What's going on here?
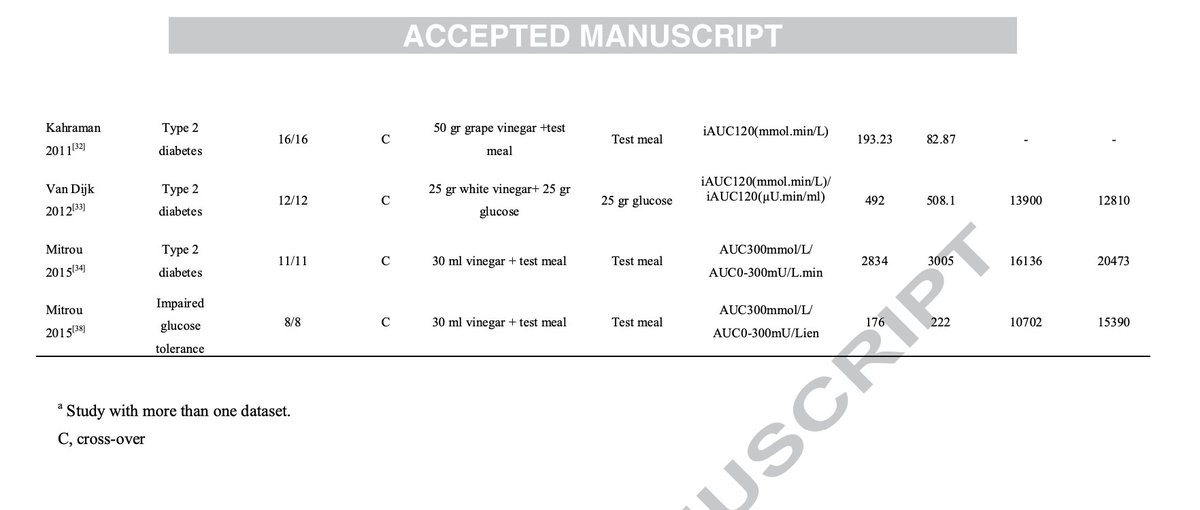
The key seems to lie in a protein called FGF21.
Protein restricted meals or diets both increased the amounts of FGF21.
(7/9)

The key seems to lie in a protein called FGF21.
Protein restricted meals or diets both increased the amounts of FGF21.
(7/9)
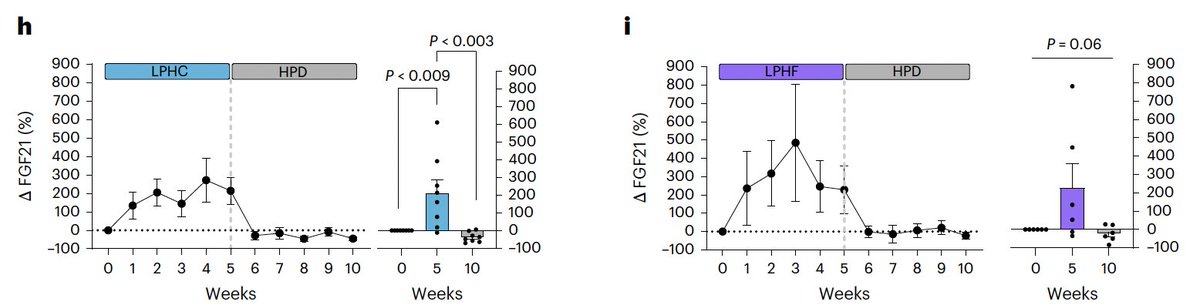
FGF21 is a master regulator of metabolism.
Several studies have shown that FGF21 not only increases metabolism, but also promotes longevity and metabolic health.
One of the main reasons it does this is because it increases UCP1 - a protein that increases heat production in the mitochondria, allowing for more food to be consumed without weight gain.
(8/9)

Several studies have shown that FGF21 not only increases metabolism, but also promotes longevity and metabolic health.
One of the main reasons it does this is because it increases UCP1 - a protein that increases heat production in the mitochondria, allowing for more food to be consumed without weight gain.
(8/9)


Table sugar also boosts FGF21.
FGF21 acts as part of a negative feedback loop to suppress sugar cravings.
That's part of why a high sugar diet can increase metabolism.
If you're confused on the sugar topic, check the thread below.
(9/9)

FGF21 acts as part of a negative feedback loop to suppress sugar cravings.
That's part of why a high sugar diet can increase metabolism.
If you're confused on the sugar topic, check the thread below.
(9/9)
https://x.com/Outdoctrination/status/1910336909341327403

Does this mean you should start skimping on protein? Not necessarily.
There are loads of potential issues that could arise with this approach.
But, it can be a viable option, and at the very least should make you think about the current narratives in nutrition.
There are loads of potential issues that could arise with this approach.
But, it can be a viable option, and at the very least should make you think about the current narratives in nutrition.
If YOU want PERSONALIZED, IN DEPTH help from us with any of your health goals, schedule a free call here: go.prism.miami/consultation
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh