Common Heart Drug Linked to Heart Disease Itself: Studies
This wasn’t supposed to happen.
Roughly 40 million Americans take statins to lower cholesterol.
But an expert review suggests long-term statin use could quietly backfire and cause this deadly heart problem. 👇🧵
This wasn’t supposed to happen.
Roughly 40 million Americans take statins to lower cholesterol.
But an expert review suggests long-term statin use could quietly backfire and cause this deadly heart problem. 👇🧵
In this thread, you’ll discover:
• The deadly heart problem linked to statin use
• The nutrient statins quietly strip from the heart
• Why millions could be at risk
• The deadly heart problem linked to statin use
• The nutrient statins quietly strip from the heart
• Why millions could be at risk
For decades, statins have been heralded as reliable heroes in the battle against heart disease, the leading cause of death in the United States and globally. 

However, an expert review suggests that long-term use of statins may be aiding the enemy by accelerating coronary artery calcification instead of providing protection.
theepochtimes.com/health/long-te…
theepochtimes.com/health/long-te…
Statins Deplete Heart-Protecting Nutrients
The review, published in Clinical Pharmacology, suggests that statins may act as “mitochondrial toxins,” impairing muscle function in the heart and blood vessels by depleting coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), an antioxidant cells use for growth and maintenance.
Multiple studies show that statins inhibit CoQ10 synthesis, leading many patients to supplement.
The review, published in Clinical Pharmacology, suggests that statins may act as “mitochondrial toxins,” impairing muscle function in the heart and blood vessels by depleting coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), an antioxidant cells use for growth and maintenance.
Multiple studies show that statins inhibit CoQ10 synthesis, leading many patients to supplement.
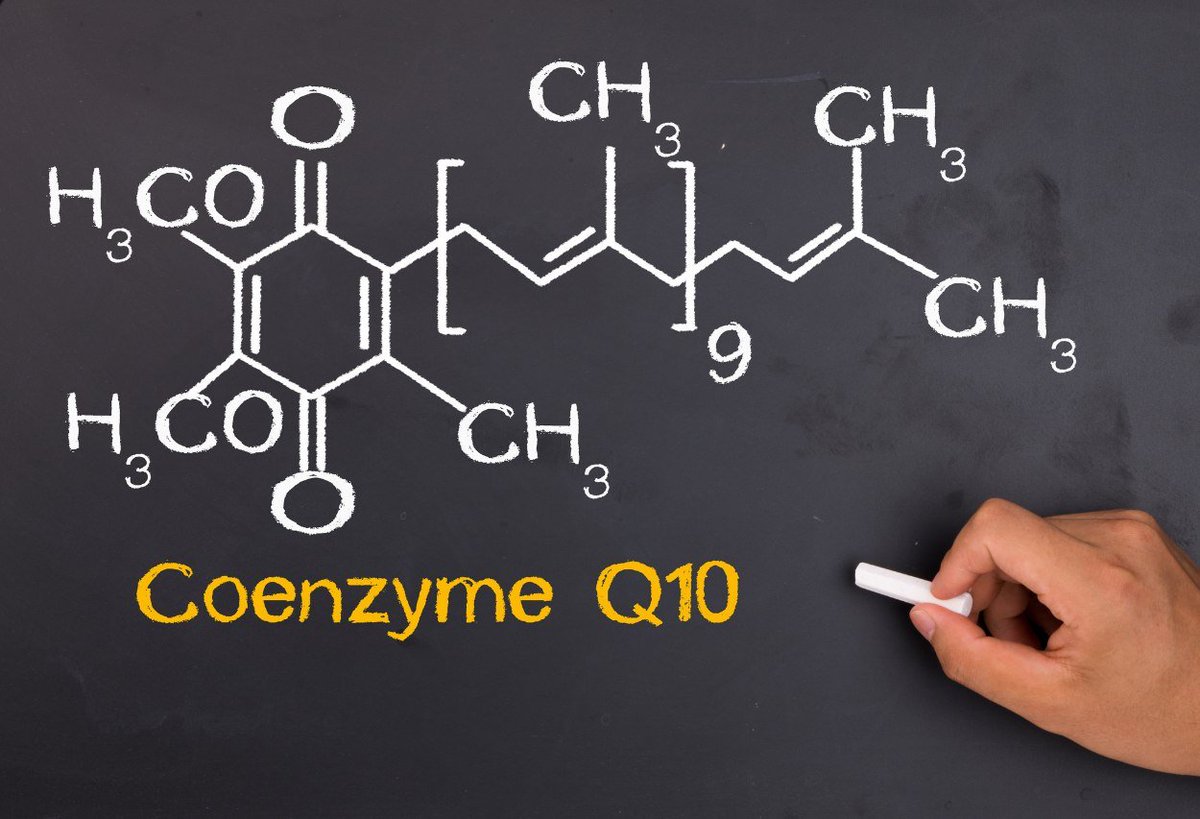
CoQ10 is vital for producing ATP, the cell’s fundamental energy carrier.
Insufficient CoQ10 inhibits ATP production, resulting in an energy deficit that the review authors say “could be a major cause for heart muscle and coronary artery damage.”
“We believe that many years of statin drug therapy result in the gradual accumulation of mitochondrial DNA damage,” the authors wrote.
Insufficient CoQ10 inhibits ATP production, resulting in an energy deficit that the review authors say “could be a major cause for heart muscle and coronary artery damage.”
“We believe that many years of statin drug therapy result in the gradual accumulation of mitochondrial DNA damage,” the authors wrote.
A 2022 study published in Biophysical Journal linked reduced ATP to heart failure.
A 2008 study published in BioFactors reaffirms the statin–CoQ10 link. Researchers evaluated 50 statin patients for side effects such as fatigue and muscle pain. All then stopped statins and supplemented CoQ10 for 22 months on average.
Heart function improved or held steady for a majority of patients.
A 2008 study published in BioFactors reaffirms the statin–CoQ10 link. Researchers evaluated 50 statin patients for side effects such as fatigue and muscle pain. All then stopped statins and supplemented CoQ10 for 22 months on average.
Heart function improved or held steady for a majority of patients.
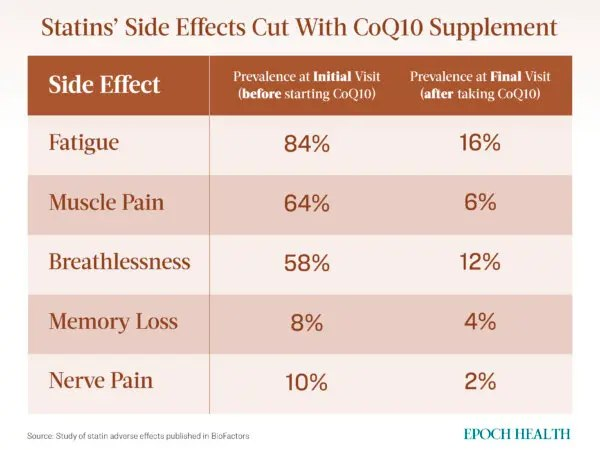
The researchers conclude that statin side effects, including statin cardiomyopathy, “are far more common than previously published and are reversible with the combination of statin discontinuation and supplemental CoQ10.” 

A little about us: We’re a team of journalists and researchers on a mission to give you REAL and honest information about your health.
Side effects of reading our posts may include: critical thinking.
Follow us for more daily threads—backed by hard data.
—> @EpochHealth
Side effects of reading our posts may include: critical thinking.
Follow us for more daily threads—backed by hard data.
—> @EpochHealth

Statins Deplete Vitamin K, Raising Heart Calcification Risk
Statins impair the production of vitamin K, an essential vitamin in managing calcification, according to the review.
Optimal vitamin K2 intake helps avoid plaque buildup of atherosclerosis—thickening or hardening of the arteries—and keeps calcification risk low.
Statins impair the production of vitamin K, an essential vitamin in managing calcification, according to the review.
Optimal vitamin K2 intake helps avoid plaque buildup of atherosclerosis—thickening or hardening of the arteries—and keeps calcification risk low.
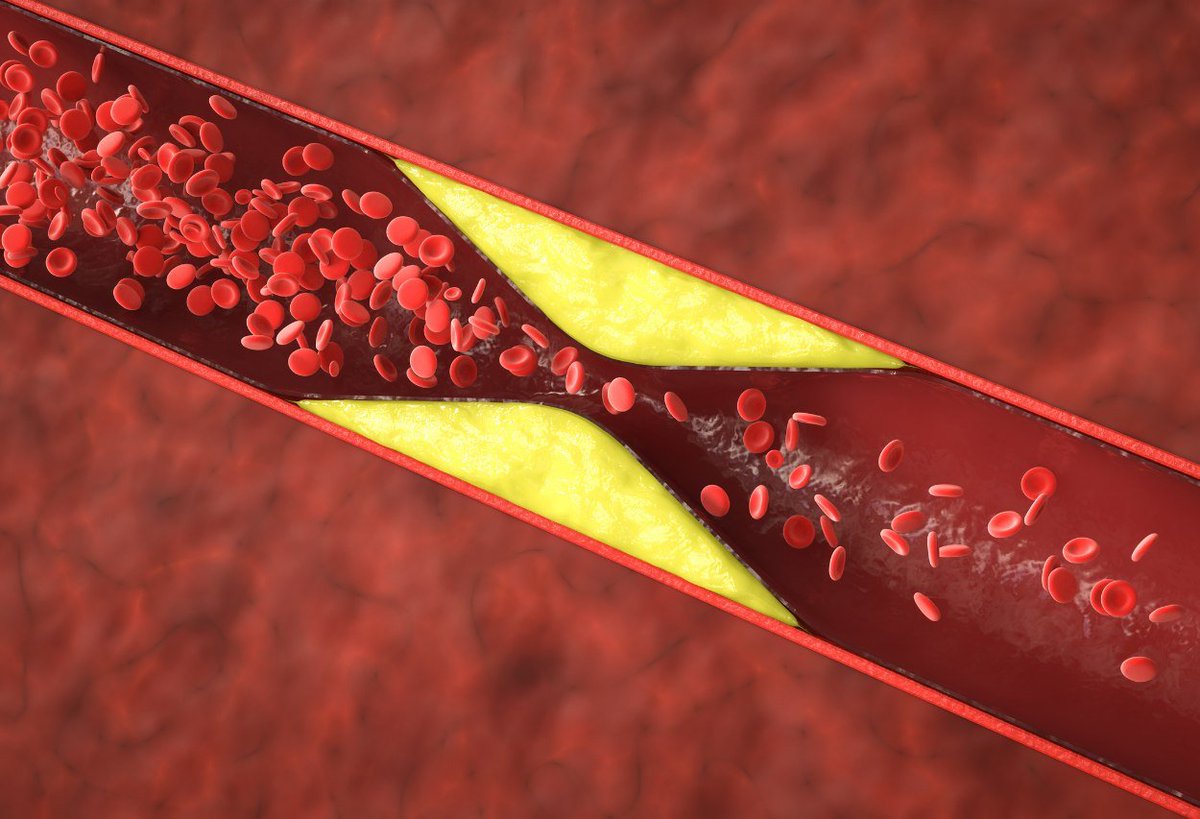
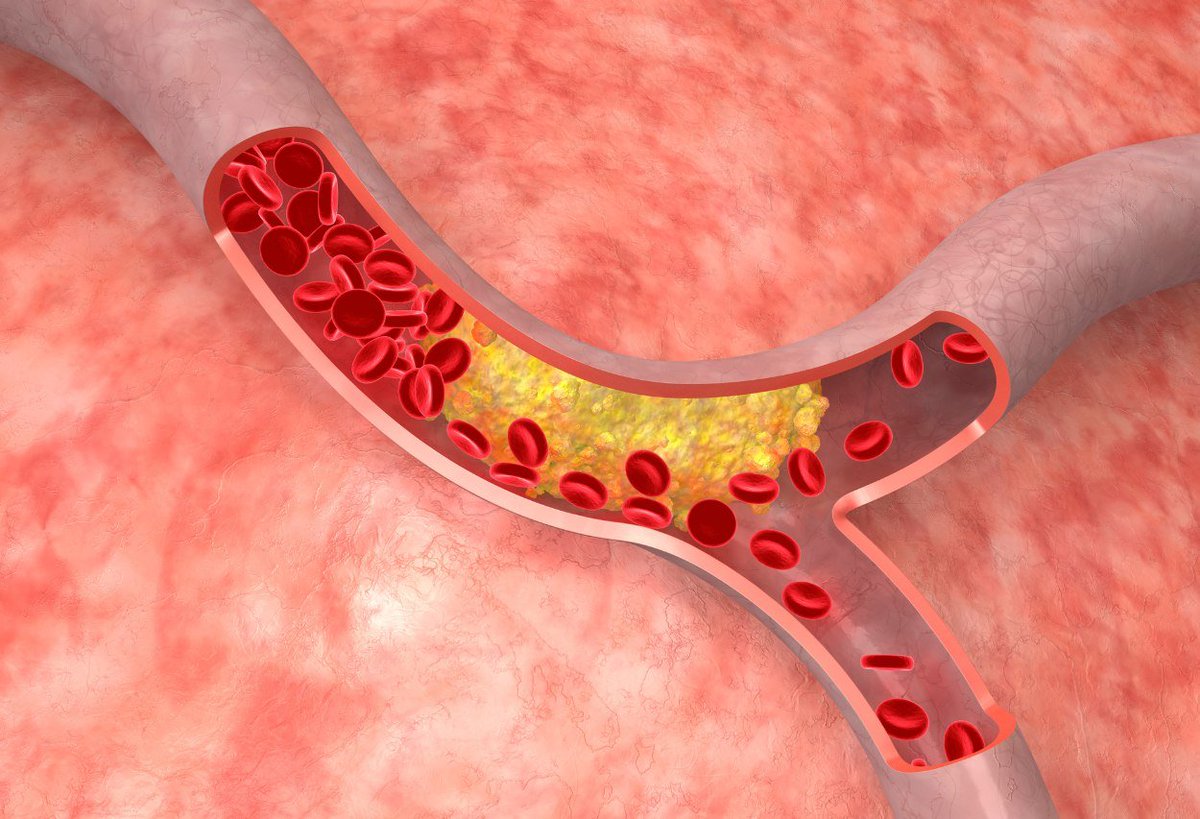
Coronary calcification happens when calcium accumulates in the walls of the coronary arteries, which provide oxygen to the heart.
This plaque buildup is a sign of early coronary artery disease, which can block blood flow and trigger a heart attack.
This plaque buildup is a sign of early coronary artery disease, which can block blood flow and trigger a heart attack.

A 2021 study published in the Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences found a connection among statin use, coronary artery calcification, and vitamin K2 deficiency.
The results shed light on how statins may spur arterial calcium accumulation by inhibiting vitamin K.
The study’s findings were “in agreement with the existing evidence about positive association between statins and vascular calcification,” the authors noted.
The results shed light on how statins may spur arterial calcium accumulation by inhibiting vitamin K.
The study’s findings were “in agreement with the existing evidence about positive association between statins and vascular calcification,” the authors noted.
Statins also damage selenoproteins, carriers of the mineral selenium, which is essential for heart health.
Statins were also linked to increased calcification in a 2022 study published in Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.
However, the authors proposed that statins may encourage calcification by heightening inflammation rather than via nutrient deficiency.
Statins were also linked to increased calcification in a 2022 study published in Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.
However, the authors proposed that statins may encourage calcification by heightening inflammation rather than via nutrient deficiency.
Physicians Overlook Statins as Driver of Heart Failure: Experts
Based on emerging evidence of statins’ potential cardiac downsides, the authors of the review warned that “physicians in general are not aware that statins can cause heart failure and are clearly not recognizing it.”
Although doctors readily diagnose heart failure in statin users, they usually attribute it to factors such as age, high blood pressure, or artery disease.
Based on emerging evidence of statins’ potential cardiac downsides, the authors of the review warned that “physicians in general are not aware that statins can cause heart failure and are clearly not recognizing it.”
Although doctors readily diagnose heart failure in statin users, they usually attribute it to factors such as age, high blood pressure, or artery disease.

Doctors prescribing cholesterol drugs “cannot ignore the moral responsibility of ‘informed consent,’” the researchers wrote, noting that patients deserve full disclosure of side effects such as cardiovascular disease and heart failure.
With more than 1 million annual heart failure hospitalizations in the United States, the condition is often referred to as an epidemic—and, according to the review, it may be that “statin drug therapy is a major contributing factor.”
With more than 1 million annual heart failure hospitalizations in the United States, the condition is often referred to as an epidemic—and, according to the review, it may be that “statin drug therapy is a major contributing factor.”

Thanks for reading! If you found this valuable, here's a special deal:
Unlock our ENTIRE library of @EpochHealth articles for just $1/week—plus unlimited access to everything else on our site.
Claim it here:
on.theepochtimes.com/vfox/health?ut…
Unlock our ENTIRE library of @EpochHealth articles for just $1/week—plus unlimited access to everything else on our site.
Claim it here:
on.theepochtimes.com/vfox/health?ut…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh