👉Independent journalism. 👉Top Daily articles on #health 👉 subscribed by 1 million plus readers 👉Side effects of following us may include: critical thinking
7 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App
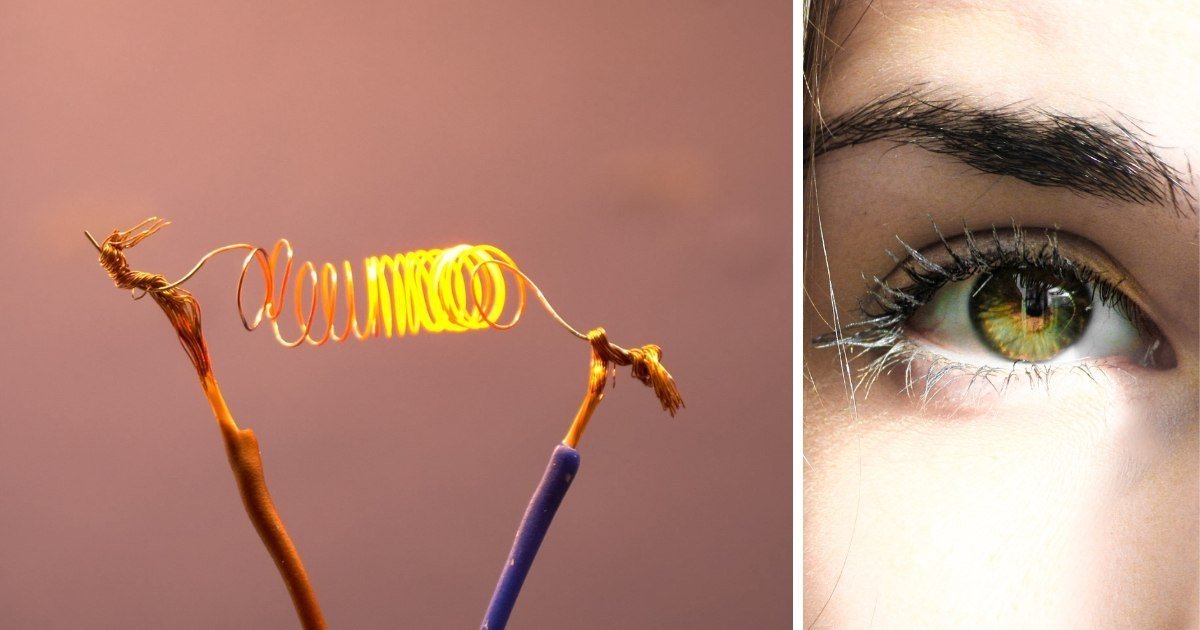



 A chemistry professor trying to heat cartilage with electricity made a mistake that could change eye surgery.
A chemistry professor trying to heat cartilage with electricity made a mistake that could change eye surgery.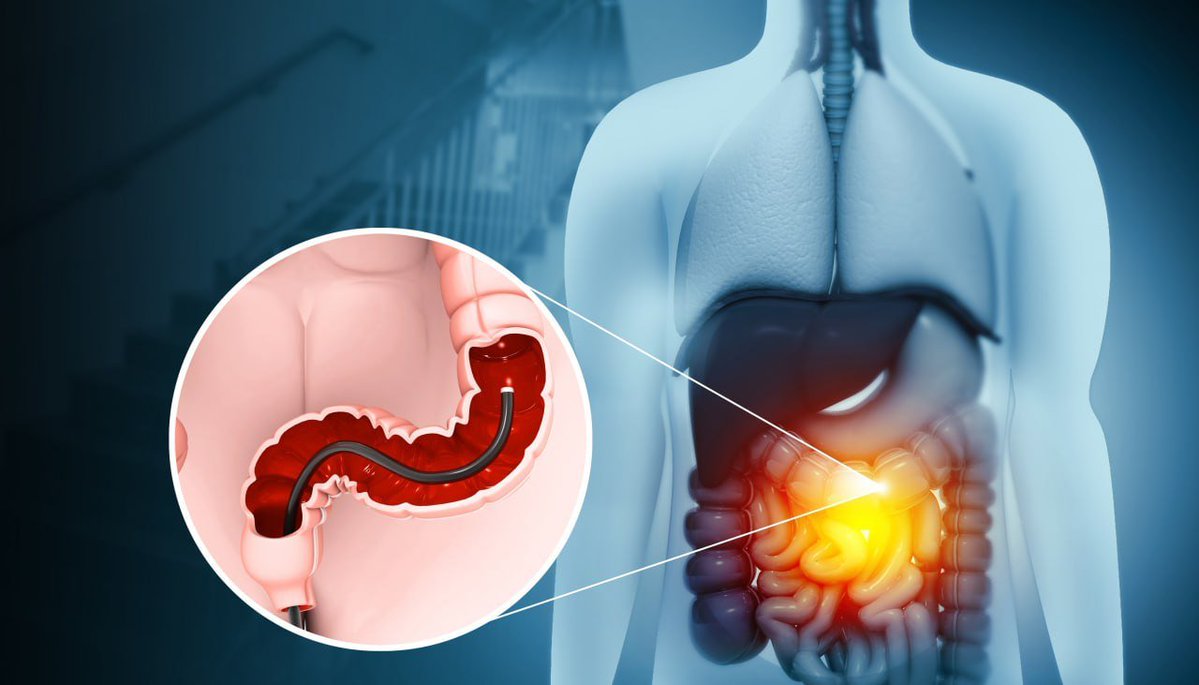
 Although many view a colonoscopy as an uncomfortable or even scary procedure, around 15 million of them are carried out annually in the United States, and 60.6 percent of people aged 50 to 75 without a personal history of colorectal cancer have had one in the past 10 years.
Although many view a colonoscopy as an uncomfortable or even scary procedure, around 15 million of them are carried out annually in the United States, and 60.6 percent of people aged 50 to 75 without a personal history of colorectal cancer have had one in the past 10 years.
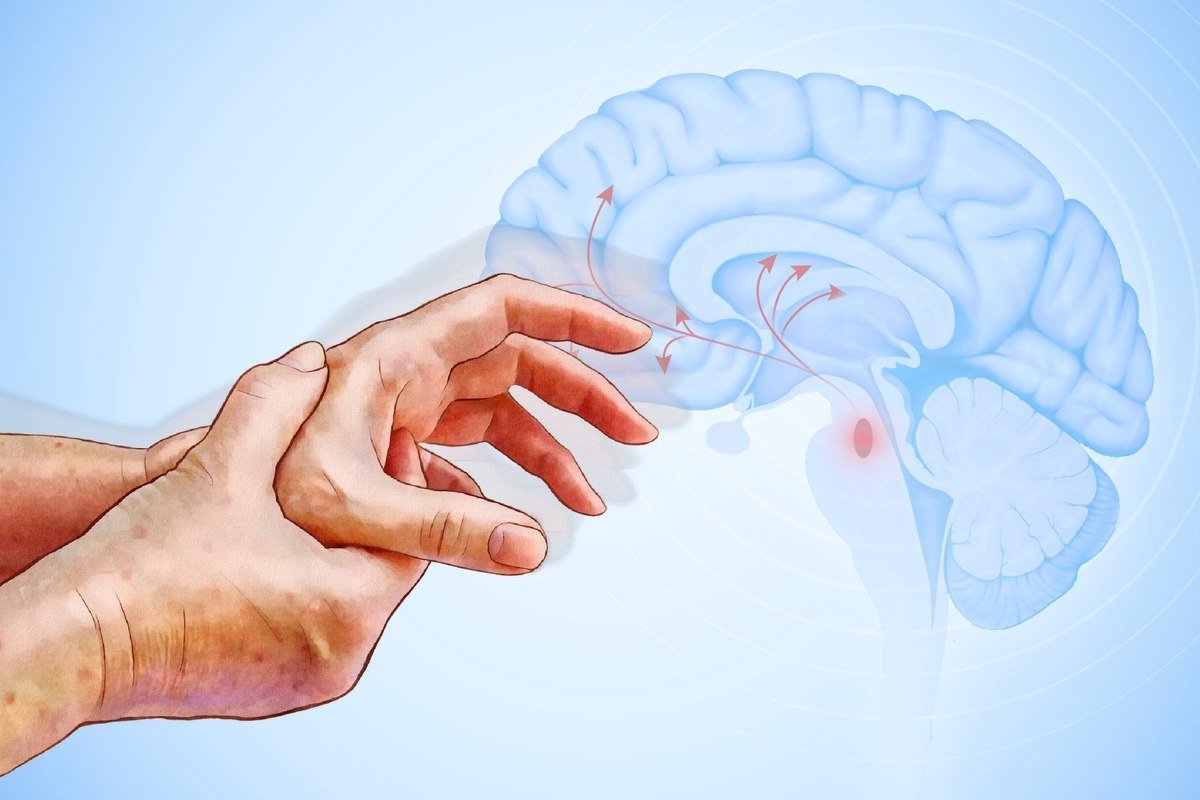
 Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer’s disease.
Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer’s disease. 
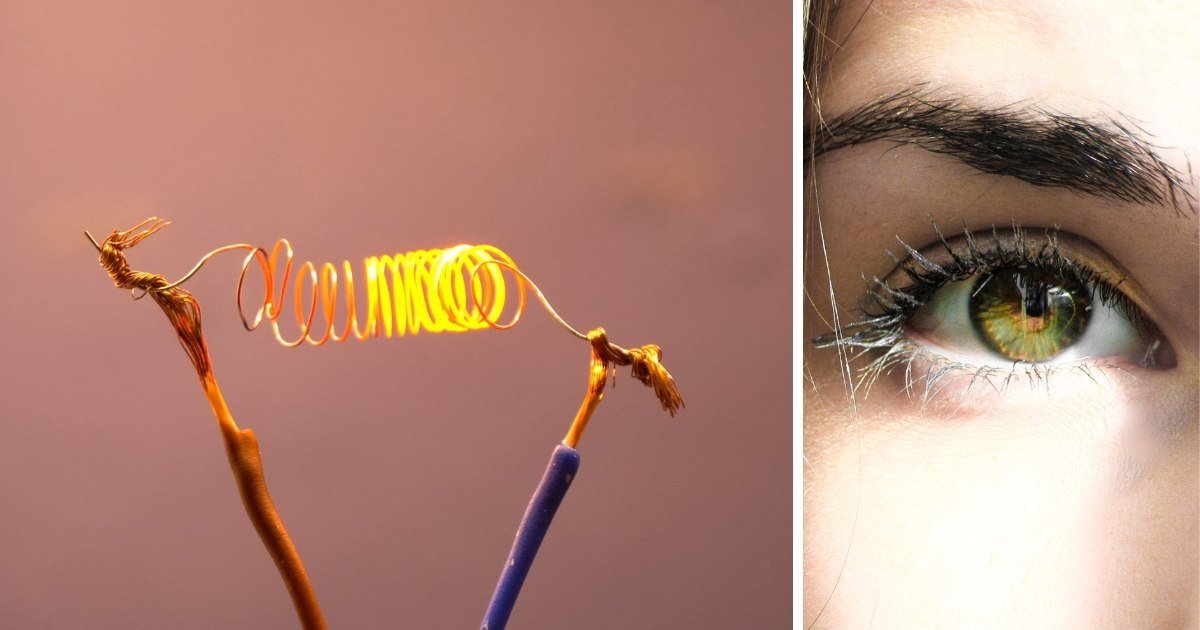

 A chemistry professor trying to heat cartilage with electricity made a mistake that could change eye surgery.
A chemistry professor trying to heat cartilage with electricity made a mistake that could change eye surgery.
 The eastern concept of the kidney extends beyond the anatomical organ. It refers to a broader energy system, where the kidney’s vital energy (qi) and the life’s essence are stored.
The eastern concept of the kidney extends beyond the anatomical organ. It refers to a broader energy system, where the kidney’s vital energy (qi) and the life’s essence are stored.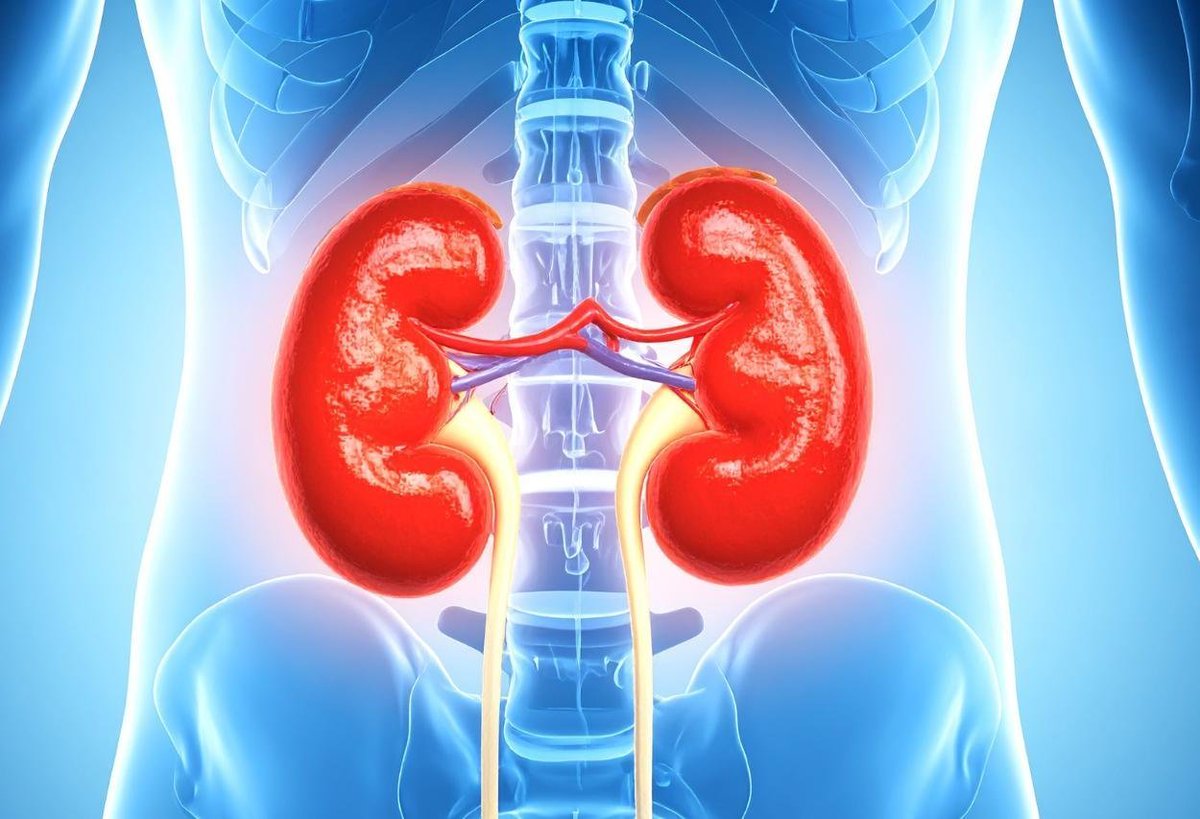
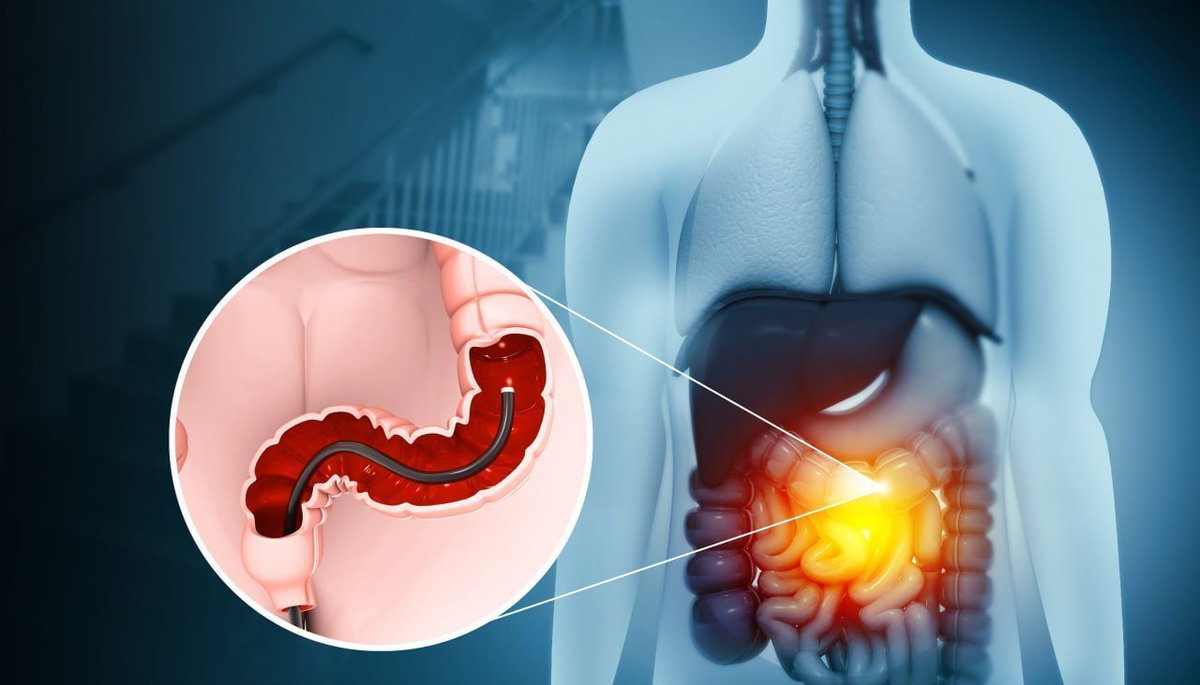
 Although many view a colonoscopy as an uncomfortable or even scary procedure, around 15 million of them are carried out annually in the United States, and 60.6 percent of people aged 50 to 75 without a personal history of colorectal cancer have had one in the past 10 years.
Although many view a colonoscopy as an uncomfortable or even scary procedure, around 15 million of them are carried out annually in the United States, and 60.6 percent of people aged 50 to 75 without a personal history of colorectal cancer have had one in the past 10 years.

 If you’ve never heard of Boswellia, don’t worry, you’ve definitely sniffed it. Or wafted it. Or had a minor spiritual epiphany while someone burned it at a yoga class that you regretted taking halfway through.
If you’ve never heard of Boswellia, don’t worry, you’ve definitely sniffed it. Or wafted it. Or had a minor spiritual epiphany while someone burned it at a yoga class that you regretted taking halfway through.
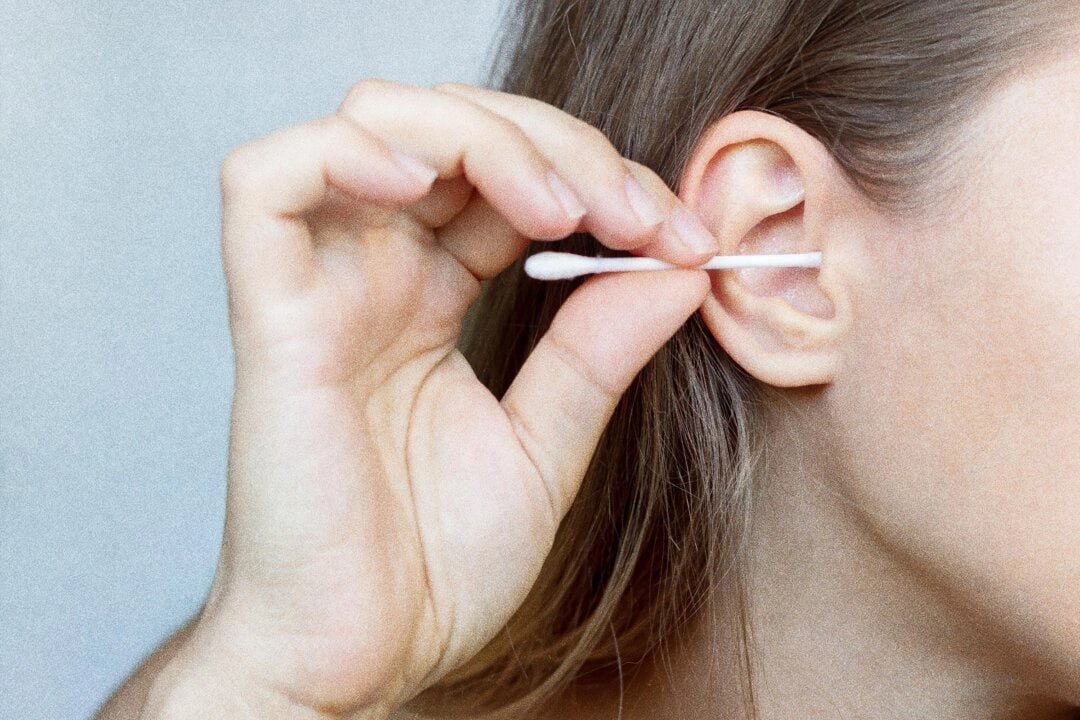

 We all likely take earwax for granted—and prefer not to think about it.
We all likely take earwax for granted—and prefer not to think about it.
 Popping an ibuprofen for that pounding headache or twisted ankle can provide quick relief from pain.
Popping an ibuprofen for that pounding headache or twisted ankle can provide quick relief from pain.

 Michael Jimenez is the founder and CEO of JMZ Farms in Texas, where he raises approximately 500 chickens and produces organic, pasture-raised eggs.
Michael Jimenez is the founder and CEO of JMZ Farms in Texas, where he raises approximately 500 chickens and produces organic, pasture-raised eggs.

 A chemistry professor trying to heat cartilage with electricity made a mistake that could change eye surgery.
A chemistry professor trying to heat cartilage with electricity made a mistake that could change eye surgery.
 Nearly every American adult has a health condition that could lead to heart failure, yet nine out of 10 have never even heard of it.
Nearly every American adult has a health condition that could lead to heart failure, yet nine out of 10 have never even heard of it.
 Kefir is one of the world’s oldest functional beverages. Originating in the mountains of the Northern Caucasus, Russia, it was a dietary staple for centuries.
Kefir is one of the world’s oldest functional beverages. Originating in the mountains of the Northern Caucasus, Russia, it was a dietary staple for centuries.
 A woman in her mid-30s went to see Dr. Priyal Modi, an integrative medicine practitioner.
A woman in her mid-30s went to see Dr. Priyal Modi, an integrative medicine practitioner.

 A food preservative used in sodas and thousands of other products may help improve memory and thinking skills in people with Alzheimer’s disease, raising the possibility that an inexpensive household chemical could help combat the nation’s sixth-leading cause of death.
A food preservative used in sodas and thousands of other products may help improve memory and thinking skills in people with Alzheimer’s disease, raising the possibility that an inexpensive household chemical could help combat the nation’s sixth-leading cause of death.
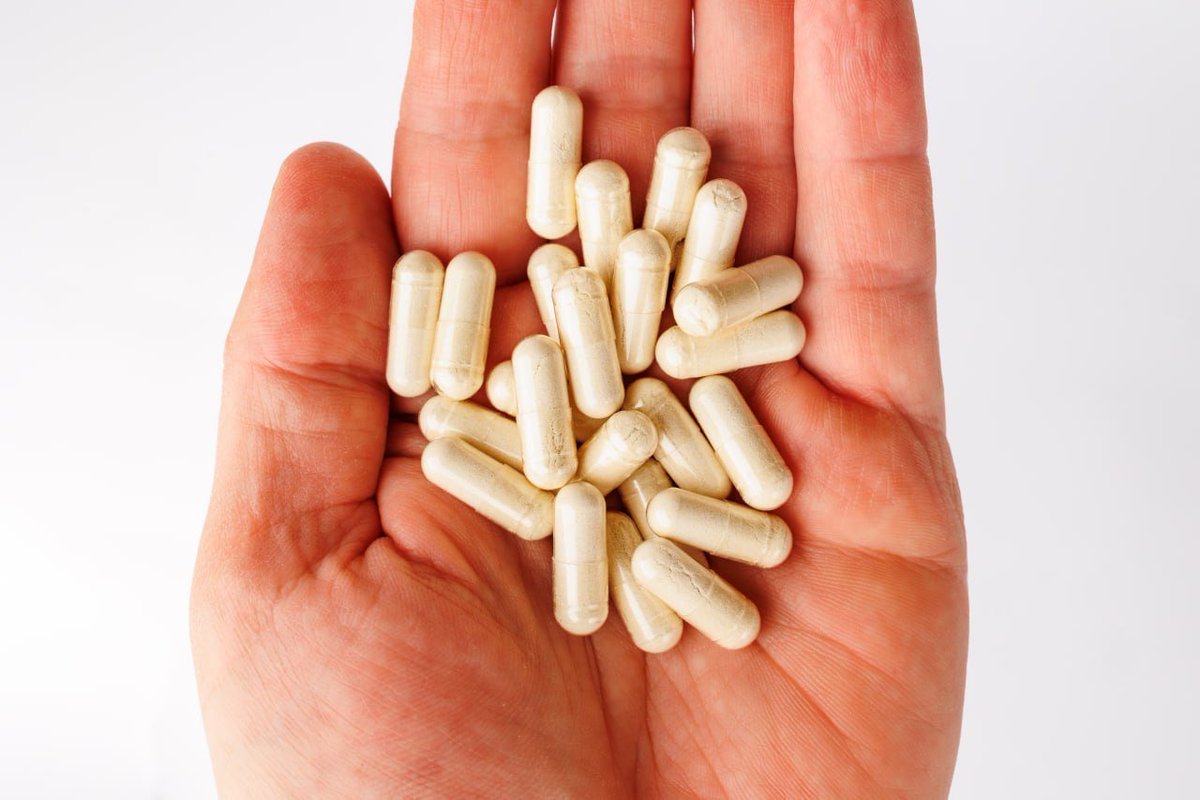

 The improper use of health supplements is a growing concern, especially for people with chronic conditions such as diabetes and kidney disease.
The improper use of health supplements is a growing concern, especially for people with chronic conditions such as diabetes and kidney disease.

 What begins as a choice to watch pornography can evolve into a neurological and physical battle, with new research showing that frequent viewing rewires the brain in ways that mirror drug addiction.
What begins as a choice to watch pornography can evolve into a neurological and physical battle, with new research showing that frequent viewing rewires the brain in ways that mirror drug addiction.
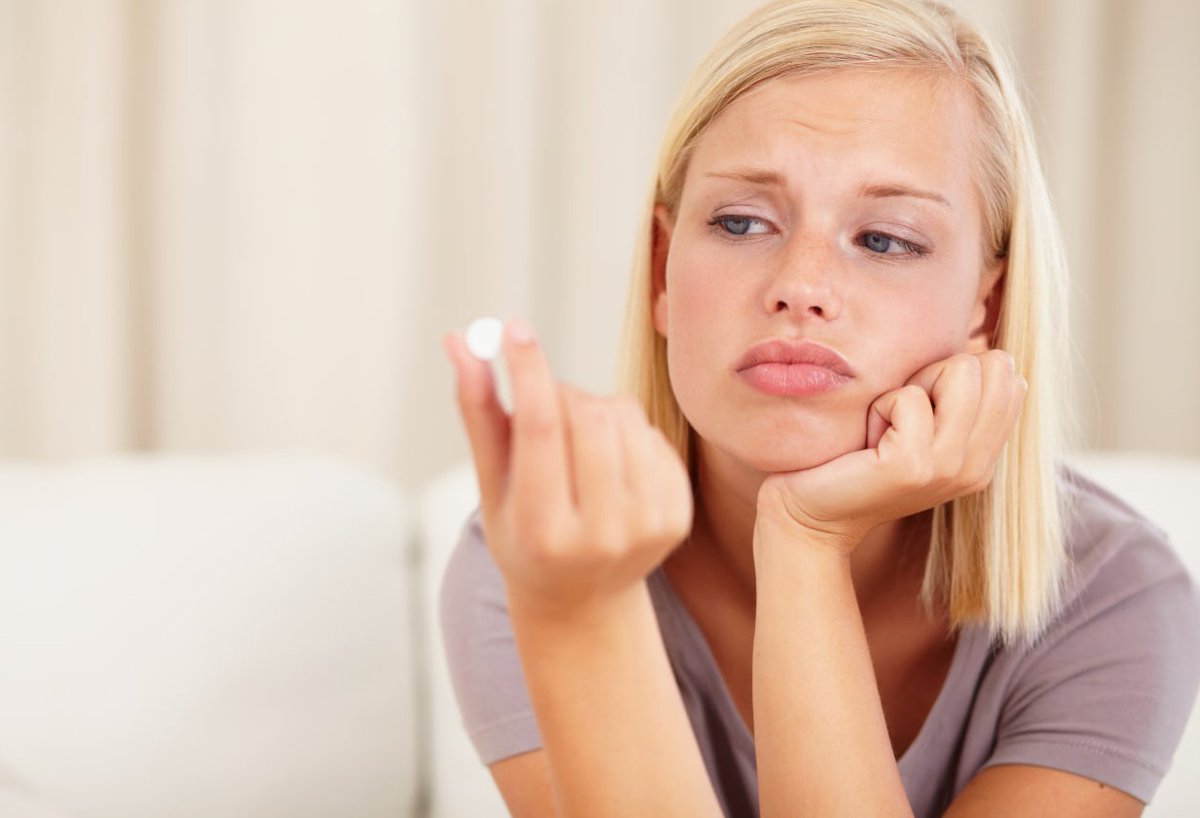

 While nearly one in three Americans takes a daily multivitamin, a large study challenges the belief that these supplements improve health or promote longevity.
While nearly one in three Americans takes a daily multivitamin, a large study challenges the belief that these supplements improve health or promote longevity.
 Once considered exotic and only eaten in tropical climates, mangoes have become one of the world’s most popular fruits.
Once considered exotic and only eaten in tropical climates, mangoes have become one of the world’s most popular fruits.

 We’ve all experienced intuition in some form or another.
We’ve all experienced intuition in some form or another. 