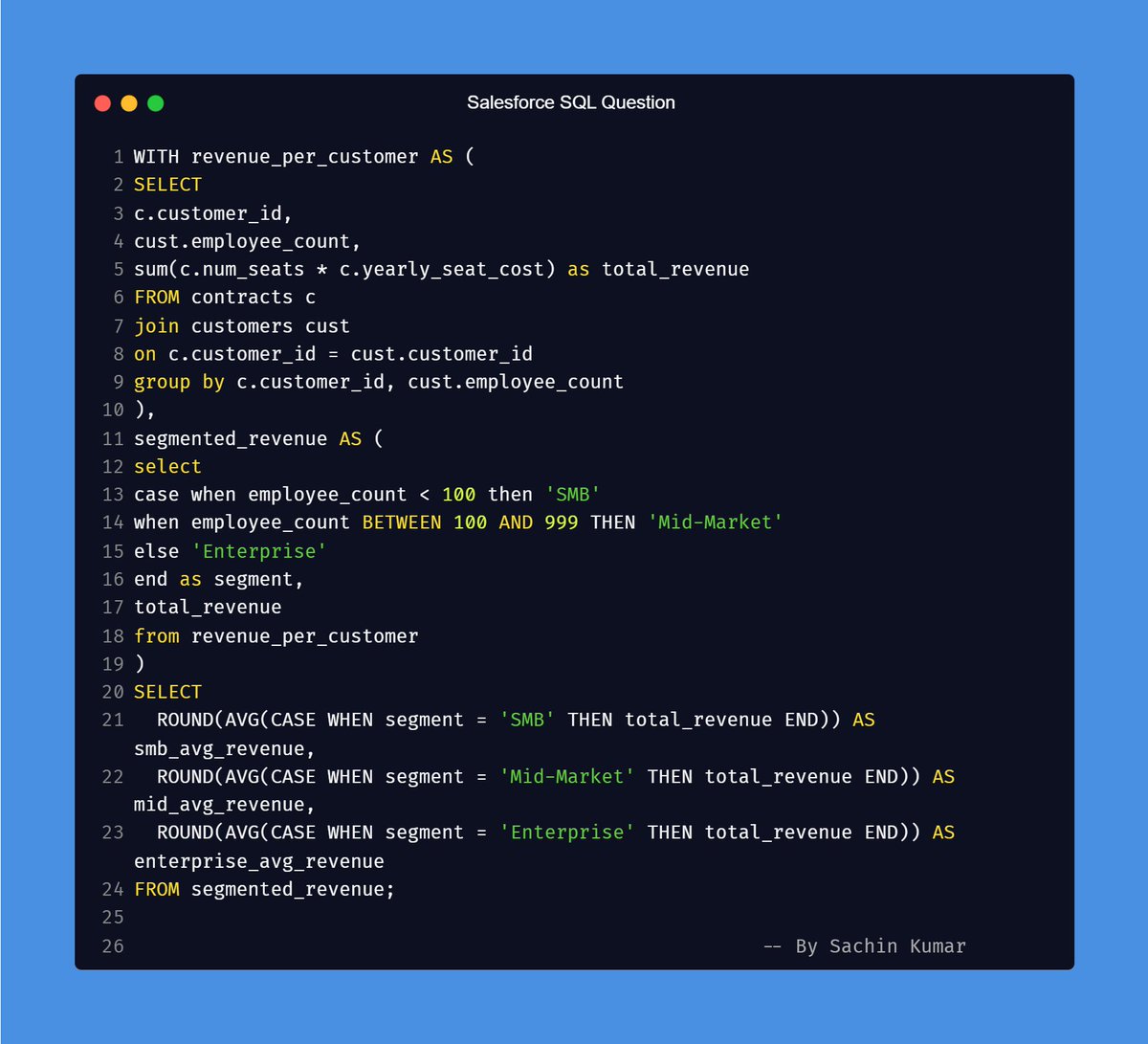
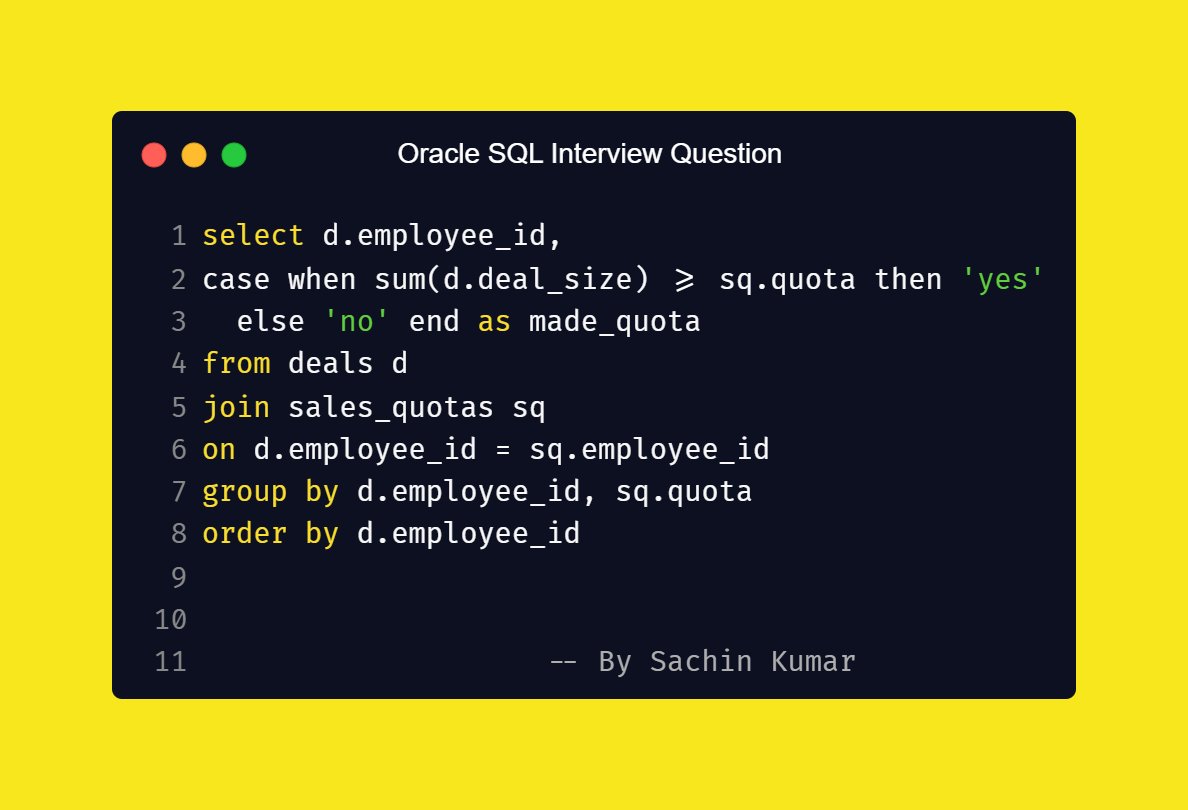
Think of data modeling as brain of Power BI — without it, everything else is just decoration
When I first started using #PowerBI, I thought visuals & DAX were “main game.”
But soon I realized: If your data model is weak, nothing else will save your dashboard.
A Complete🧵
When I first started using #PowerBI, I thought visuals & DAX were “main game.”
But soon I realized: If your data model is weak, nothing else will save your dashboard.
A Complete🧵

Think of it like this:
1) Visuals = House front
2) DAX = Electricity & plumbing
3) Data Model = Foundation
Without a strong foundation, everything else collapses.
☑️ What exactly is a Data Model?
It’s simply the way you organize & connect your data so Power BI can:
- Understand it
- Perform fast calculations
- Show correct insights
And this magic happens inside Model View of Power BI.
1) Visuals = House front
2) DAX = Electricity & plumbing
3) Data Model = Foundation
Without a strong foundation, everything else collapses.
☑️ What exactly is a Data Model?
It’s simply the way you organize & connect your data so Power BI can:
- Understand it
- Perform fast calculations
- Show correct insights
And this magic happens inside Model View of Power BI.
Here are the building blocks of a strong data model
1) Fact Table → Numbers & metrics (e.g., Sales, Revenue)
2) Dimension Table → Descriptions/details (e.g., Products, Dates, Customers)
3) Relationships → Connections between tables (usually 1 → many)
4) Primary Key → Unique ID (e.g., ProductID)
5) Foreign Key → The matching ID in another table (e.g., Sales[ProductID])
1) Fact Table → Numbers & metrics (e.g., Sales, Revenue)
2) Dimension Table → Descriptions/details (e.g., Products, Dates, Customers)
3) Relationships → Connections between tables (usually 1 → many)
4) Primary Key → Unique ID (e.g., ProductID)
5) Foreign Key → The matching ID in another table (e.g., Sales[ProductID])
🩼 Easy Way to Remember
- Fact Table = Numbers
- Dimension Table = Descriptions
- Relationships = Connections
- Star Schema = 1 Fact + Multiple Dimensions
- Fact Table = Numbers
- Dimension Table = Descriptions
- Relationships = Connections
- Star Schema = 1 Fact + Multiple Dimensions
☑️ Where do Measures belong?
Always in the Fact Table, Because measures represent aggregated business events (e.g., Total Sales).
Dimensions are only there to categorize & filter those events (e.g., Sales by Product or City).
☑️ Filter Flow Types
1) Single (→) → Filter flows one way (Dimension → Fact), Default & Recommended
2) Both (↔) → Filter flows both ways, Use only in special scenarios
Always in the Fact Table, Because measures represent aggregated business events (e.g., Total Sales).
Dimensions are only there to categorize & filter those events (e.g., Sales by Product or City).
☑️ Filter Flow Types
1) Single (→) → Filter flows one way (Dimension → Fact), Default & Recommended
2) Both (↔) → Filter flows both ways, Use only in special scenarios
Interview Question
Q1). Why is Star Schema preferred in Power BI even though Snowflake saves space?.
Snowflake normalizes data more, which saves storage but increases query complexity (more joins).
Power BI is optimized for Star Schema:
Simple 1-to-many relationships
Faster DAX queries
Easier for business users to understand
In analytics, query performance > storage optimization, so Star Schema wins.
Q2). What would happen if your data model doesn’t have a Calendar (Date Dimension) table?
Without a proper Date table:
Time intelligence functions (YTD, MTD, DATESBETWEEN) won’t work correctly.
You can’t ensure continuous dates (missing days won’t show).
Business reporting like “Sales growth YoY” would break.
So a dedicated Date Dimension is critical for serious analytics.
Q1). Why is Star Schema preferred in Power BI even though Snowflake saves space?.
Snowflake normalizes data more, which saves storage but increases query complexity (more joins).
Power BI is optimized for Star Schema:
Simple 1-to-many relationships
Faster DAX queries
Easier for business users to understand
In analytics, query performance > storage optimization, so Star Schema wins.
Q2). What would happen if your data model doesn’t have a Calendar (Date Dimension) table?
Without a proper Date table:
Time intelligence functions (YTD, MTD, DATESBETWEEN) won’t work correctly.
You can’t ensure continuous dates (missing days won’t show).
Business reporting like “Sales growth YoY” would break.
So a dedicated Date Dimension is critical for serious analytics.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh