For the first time, Google has measured how much energy AI really uses in production.
Spoiler: the gap vs. all previous estimates is huge... 🧵
Spoiler: the gap vs. all previous estimates is huge... 🧵

Despite AI transforming healthcare, education, and research, we've been flying blind on its environmental footprint.
Every estimate was based on lab benchmarks, not real-world production systems serving billions of users.
Google decided to measure what actually happens.
Every estimate was based on lab benchmarks, not real-world production systems serving billions of users.
Google decided to measure what actually happens.

The results from measuring Gemini in production:
• 0.24 watt-hours per text prompt
• Equivalent to watching TV for 9 seconds
• 5 drops of water consumed
• 0.03 grams of CO2 emissions
Substantially lower than public estimates.
• 0.24 watt-hours per text prompt
• Equivalent to watching TV for 9 seconds
• 5 drops of water consumed
• 0.03 grams of CO2 emissions
Substantially lower than public estimates.

Even if you add the water used in nearby power plants to generate electricity, the total rises only to 2.7 mL per prompt.
That’s 0.0001% of the average American’s daily water use.
Substantially lower than public estimates.
That’s 0.0001% of the average American’s daily water use.
Substantially lower than public estimates.
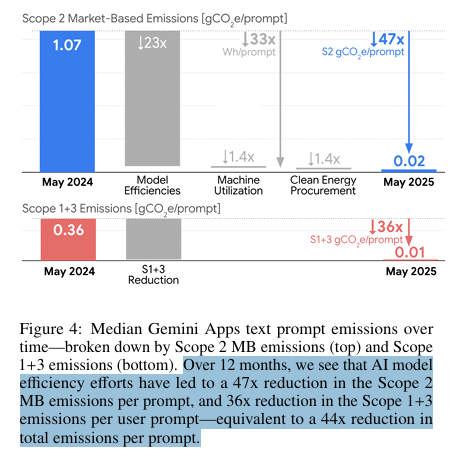
Over just 12 months, while AI quality improved dramatically, Gemini's environmental impact plummeted:
• Energy per prompt: down 33x
• Carbon footprint: down 44x
This is efficiency innovation at scale.
• Energy per prompt: down 33x
• Carbon footprint: down 44x
This is efficiency innovation at scale.
Why were all previous estimates wrong?
They measured isolated chips running perfect benchmarks.
Google measured the full reality: idle machines for reliability, cooling systems, power distribution, CPU overhead... everything needed for global AI service.
They measured isolated chips running perfect benchmarks.
Google measured the full reality: idle machines for reliability, cooling systems, power distribution, CPU overhead... everything needed for global AI service.

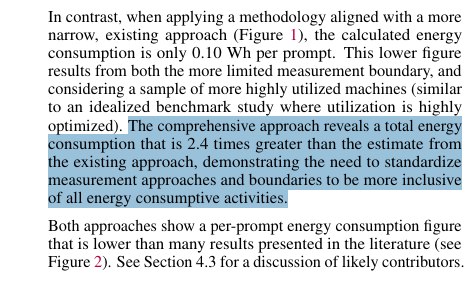
The measurement gap is enormous:
• Lab benchmark approach: 0.10 Wh per prompt
• Full production reality: 0.24 Wh per prompt
That 2.4x difference reveals the infrastructure complexity everyone else ignored.
• Lab benchmark approach: 0.10 Wh per prompt
• Full production reality: 0.24 Wh per prompt
That 2.4x difference reveals the infrastructure complexity everyone else ignored.
→ The efficiency breakthroughs come from Google's full-stack AI approach.
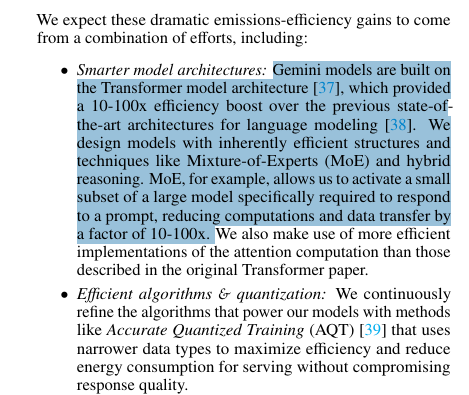
Transformer architecture (invented at Google) delivers 10-100x efficiency over previous language models.
Mixture-of-Experts activates only needed model parts, cutting computation by 10-100x.
Transformer architecture (invented at Google) delivers 10-100x efficiency over previous language models.
Mixture-of-Experts activates only needed model parts, cutting computation by 10-100x.
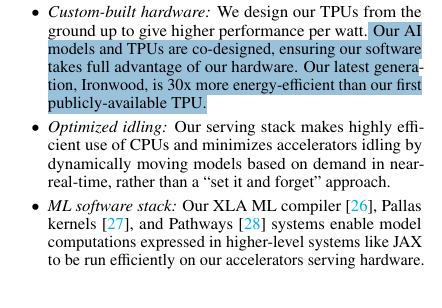
→ Google builds custom chips specifically for AI instead of using regular computer chips.
Their latest AI chips are 30x more energy-efficient than their first generation.
Like designing a race car for Formula 1 instead of using a family sedan.
Their latest AI chips are 30x more energy-efficient than their first generation.
Like designing a race car for Formula 1 instead of using a family sedan.
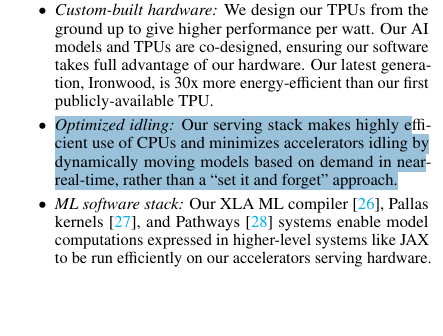
→ Smart software tricks that save massive energy
Small AI models write rough drafts, big models just check the work.
Models automatically move between chips based on demand, so nothing sits idle.
Small AI models write rough drafts, big models just check the work.
Models automatically move between chips based on demand, so nothing sits idle.
→ Infrastructure efficiency that matters at billions of prompts
Google's data centers operate at 1.09 PUE, only 9% energy overhead beyond actual computing.
Advanced cooling balances energy, water, and emissions with science-backed watershed assessments.
Google's data centers operate at 1.09 PUE, only 9% energy overhead beyond actual computing.
Advanced cooling balances energy, water, and emissions with science-backed watershed assessments.

This measurement revolution matters because AI adoption is exploding.
Without understanding real environmental impact, we can't make responsible decisions about technology that could reshape the entire global economy.
Without understanding real environmental impact, we can't make responsible decisions about technology that could reshape the entire global economy.
Google is open-sourcing this measurement methodology to create industry standards.
As AI unlocks trillions in economic value, we need to ensure we're tracking, and minimizing, its true environmental cost.
You can read the full paper here: cloud.google.com/blog/products/…
As AI unlocks trillions in economic value, we need to ensure we're tracking, and minimizing, its true environmental cost.
You can read the full paper here: cloud.google.com/blog/products/…
If you found this thread valuable:
1. Follow me @RubenHssd for more threads around what's happening around AI and it's implications.
2. RT the first tweet
1. Follow me @RubenHssd for more threads around what's happening around AI and it's implications.
2. RT the first tweet
https://twitter.com/1269541526/status/1959996012984152398
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh