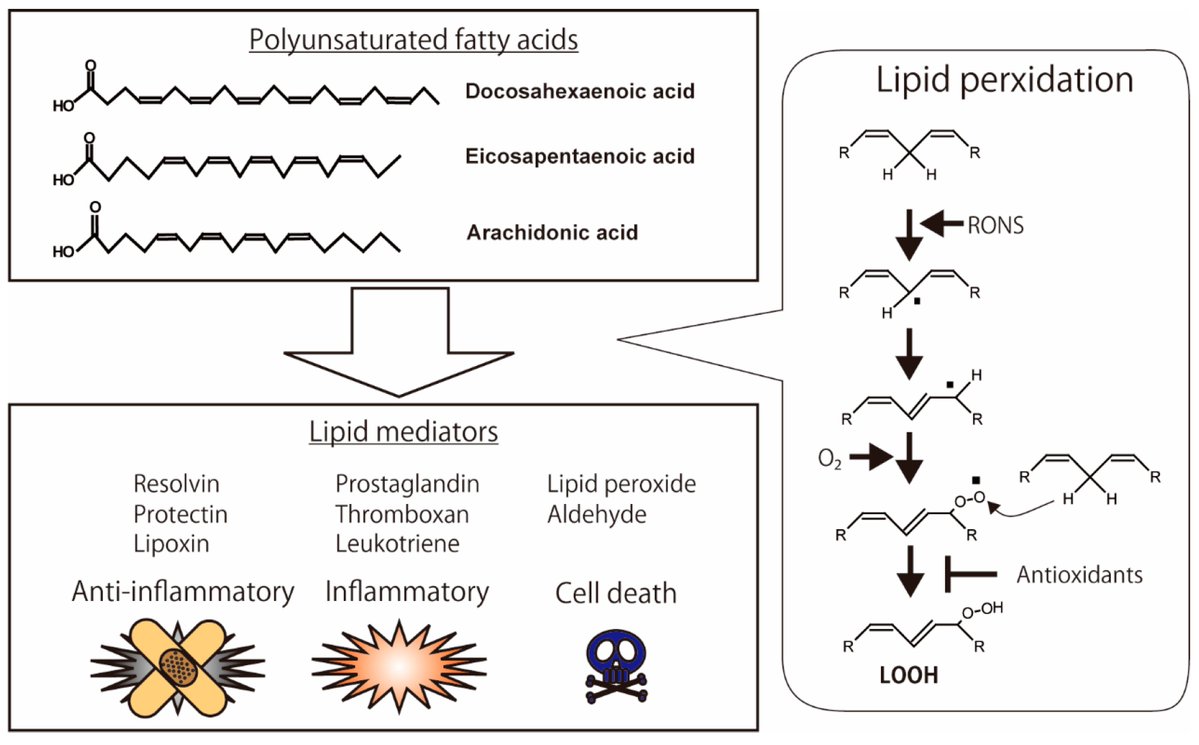
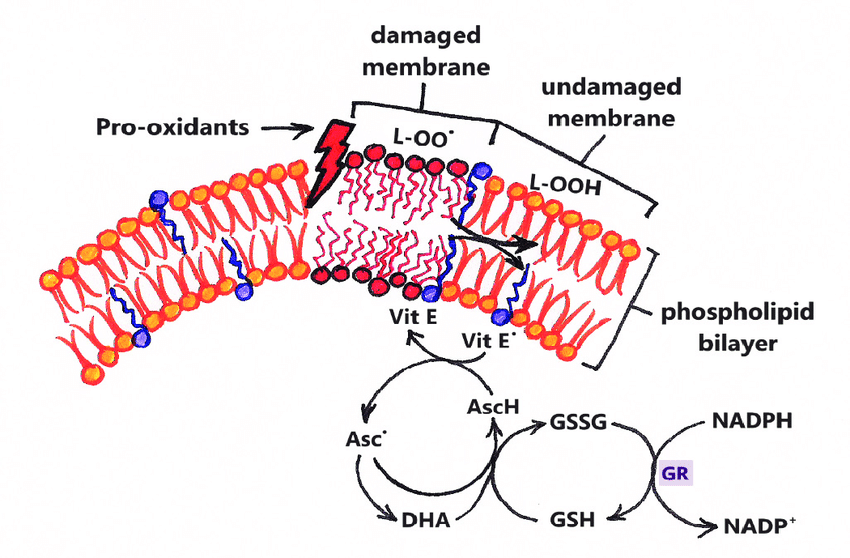
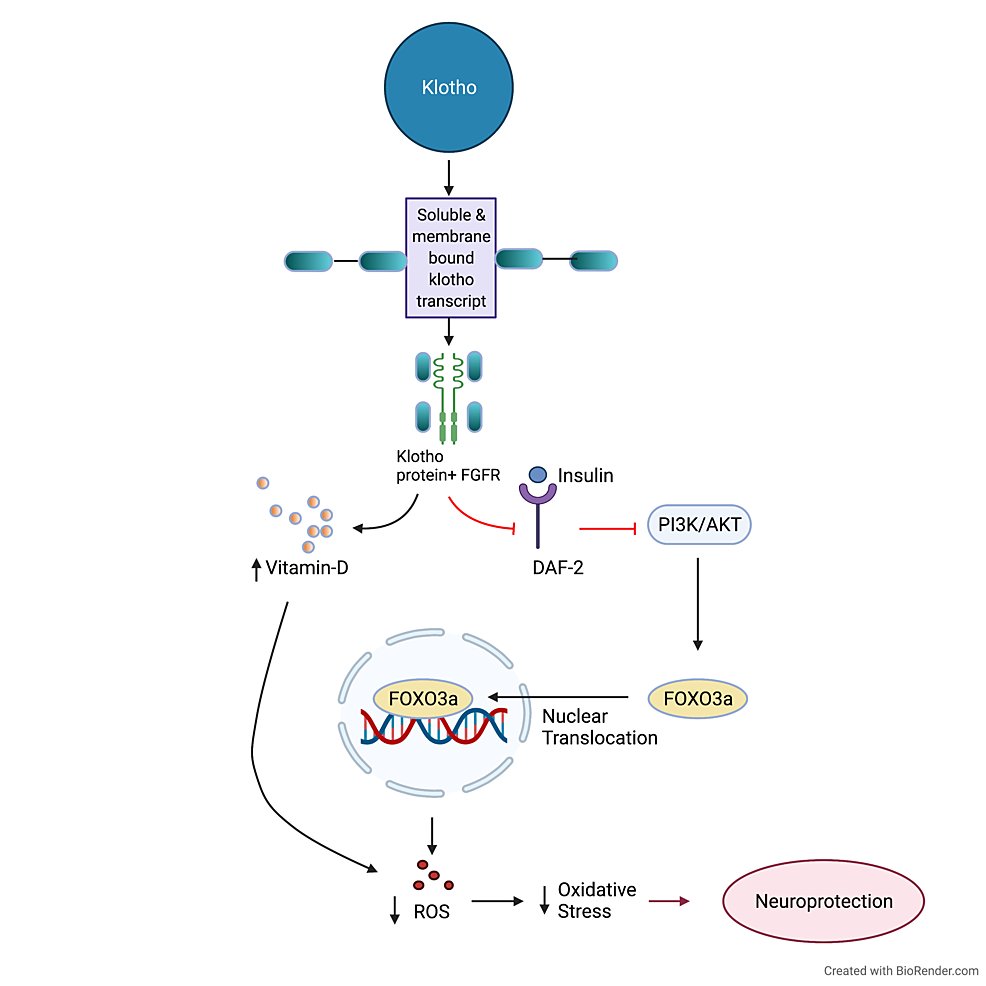
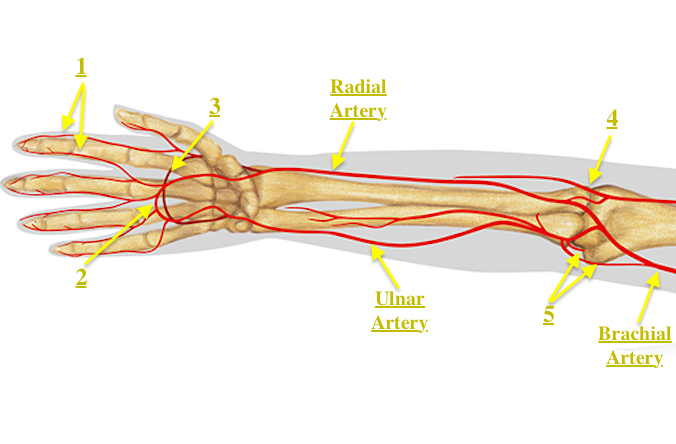
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) megadosing can massively reduce fatigue, in many cases reversing it entirely.
(🧵1/20)
(🧵1/20)

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh