The UK's plan to aquire 7,000 long range weapons is becoming clearer. In addition to the FC/ASW 1,000km TP15 and RJ10 subsonic stealth and supersonic cruise missiles for the RAF and RN, the Army will deploy 600km BRAKESTOP OWEs and NIGHTFALL tactical ballistic missiles. 

Both BRAKESTOP and NIGHTFALL are sovereign developed, ITAR-free and domestically produced capabilities, like FC/ASW, but unlike the Anglo-French-Italian MBDA missile programme and to be low cost and rapidly developed for fielding before 2030. 

The one programme that is less clear is ELSA, a pan-European plan to aquire a 2,000km cruise or ballistic missile. Whether this will be a new weapon programme or a development of another weapon under development or procurment of an existing weapon is unknown. 

Its also unclear if NIGHTFALL signals the deathknell for the Army's plan to aquire PrSM for M270. NIGHTFALL has a larger warhead than PrSM, but is less suitable against moving or well defended targets unless fired in large barrages, so a smaller purchase of PrSM remains possible. 

The Army has already aquired 400 Modini Dart 250 EW drones for use in SEAD/DEAD against adversary SHORAD. These UK-Ukrainian developed 250km range OWEs are currently deployed with Operation CABRIT in Estonia. Whether more will be aquired is not yet known. 

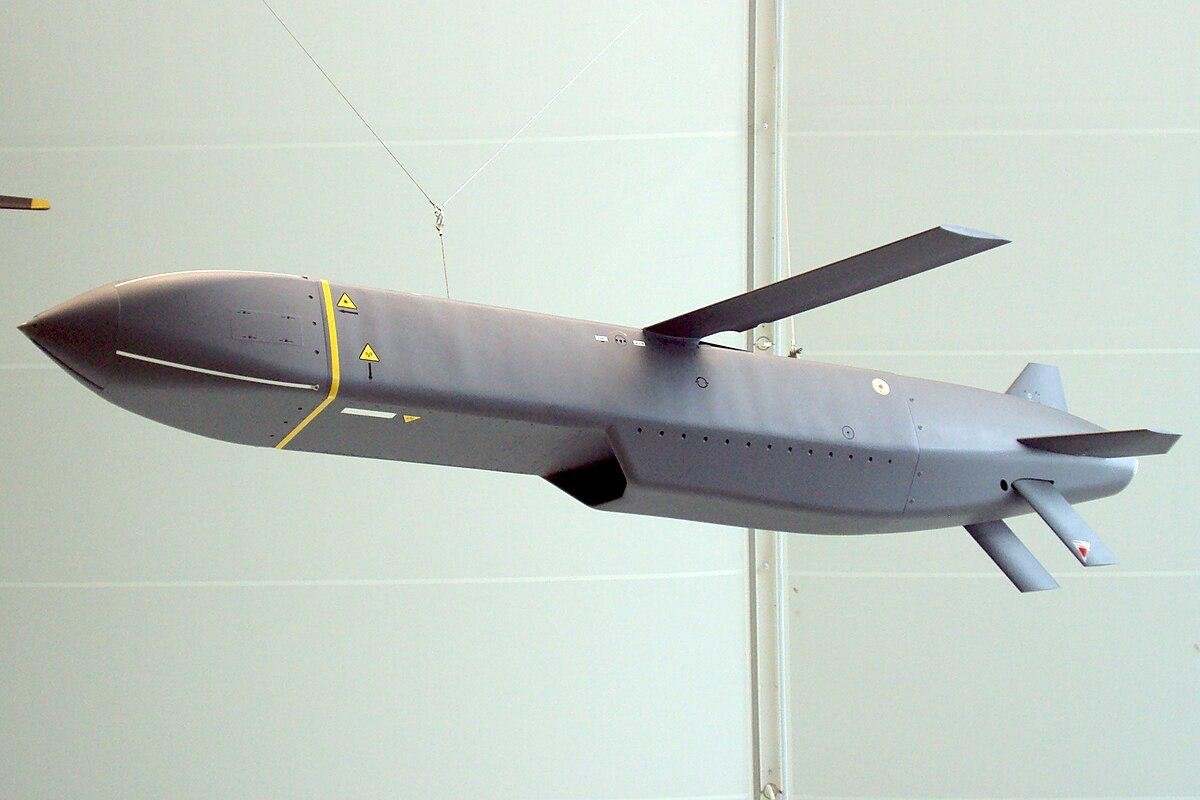
Last but not least, production of the upgraded Storm Shadow 550km range cruise missile has been restarted in both the UK and France, and more will be aquired for use by the RAF before FC/ASW enters service. Its unclear how many more, but UK's inventory of 900 is depleted. 
@threadreaderapp unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




















