The first study investigating this topic was in 2003.
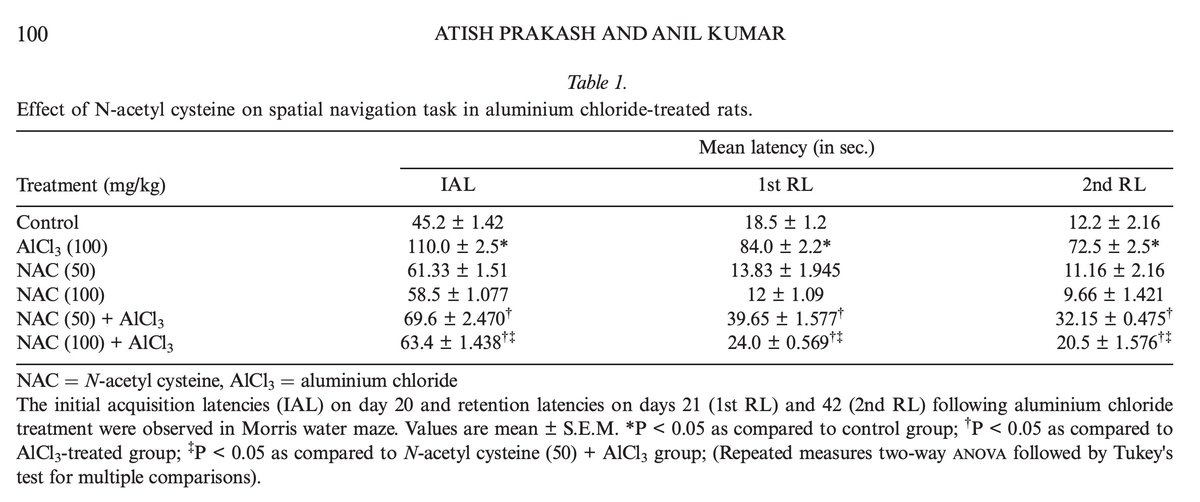
They took vegetarians in their mid 20s and gave them 5g of (or placebo) for 6 weeks, then no creatine for 6 weeks, and then switched groups for another 6 weeks.
The break was done to see if any benefit went away without creatine.
(2/7)
They took vegetarians in their mid 20s and gave them 5g of (or placebo) for 6 weeks, then no creatine for 6 weeks, and then switched groups for another 6 weeks.
The break was done to see if any benefit went away without creatine.
(2/7)

Subjects took two cognitive assessments.
Raven’s Advanced Progressive Matrices (RAPM) = nonverbal test of abstract reasoning & pattern spotting.
Wechsler Backward Digit Span (BDS) = working memory test (recall numbers in reverse).
Both tap core cognitive abilities that strongly predict IQ scores.
(3/7)
Raven’s Advanced Progressive Matrices (RAPM) = nonverbal test of abstract reasoning & pattern spotting.
Wechsler Backward Digit Span (BDS) = working memory test (recall numbers in reverse).
Both tap core cognitive abilities that strongly predict IQ scores.
(3/7)
During the creatine portions (weeks 0-6 & 12-18) - both intelligence metrics markedly improved.
Scores began to decline once creatine was stopped, but remained higher than starting levels for weeks after.
(4/7)
Scores began to decline once creatine was stopped, but remained higher than starting levels for weeks after.
(4/7)
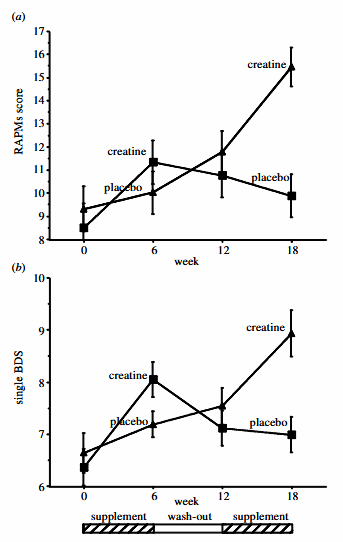
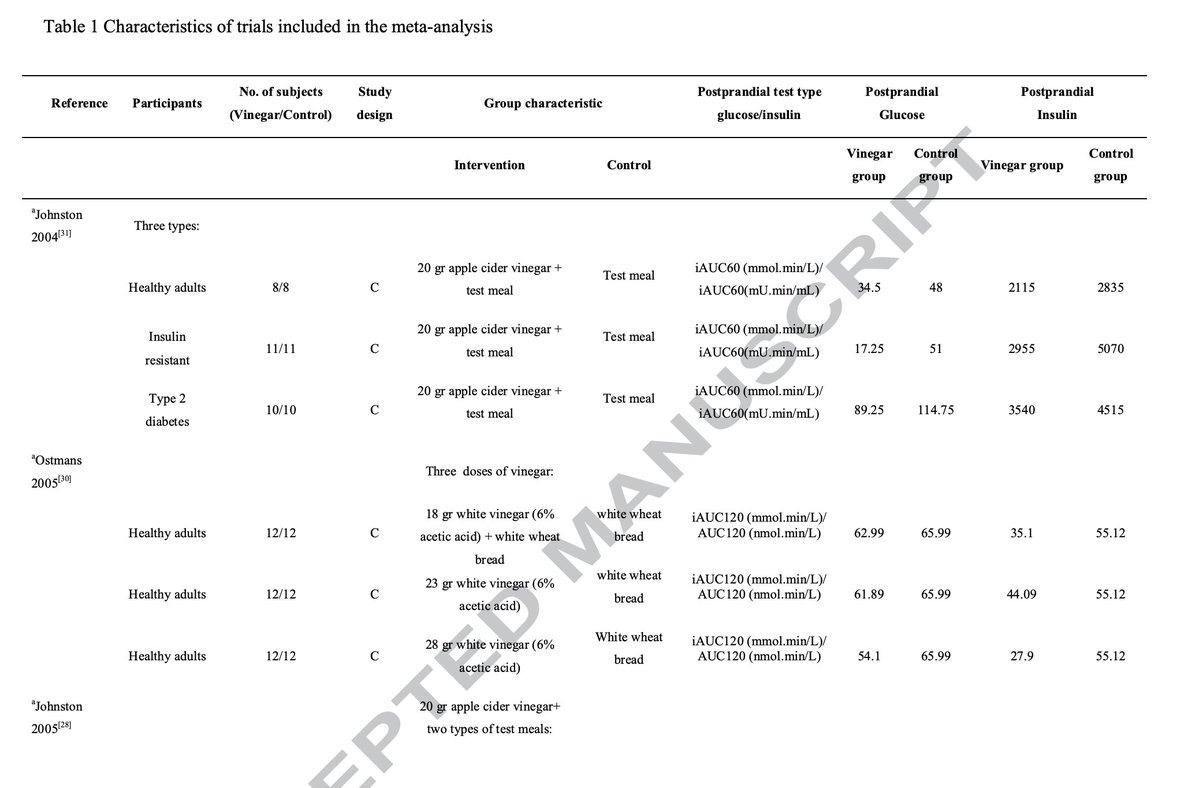
A more recent study showed similar effects.
Creatine (or placebo) was taken at 5g a day for 6 weeks.
They did the same 2 cognitive tests.
(5/7)
Creatine (or placebo) was taken at 5g a day for 6 weeks.
They did the same 2 cognitive tests.
(5/7)

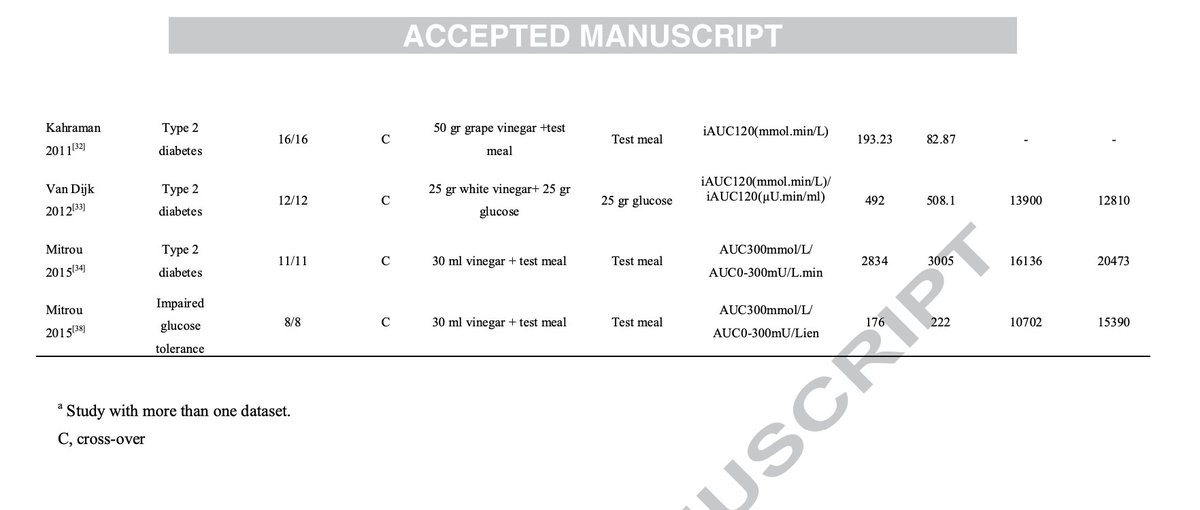
Once again, both intelligence metrics improved with creatine.
When trying to compare the results directly to IQ tests, the researchers stated:
"If these were IQ tests, the increase in raw scores would
mean 1 and 2.5 IQ points."
(6/7)
When trying to compare the results directly to IQ tests, the researchers stated:
"If these were IQ tests, the increase in raw scores would
mean 1 and 2.5 IQ points."
(6/7)

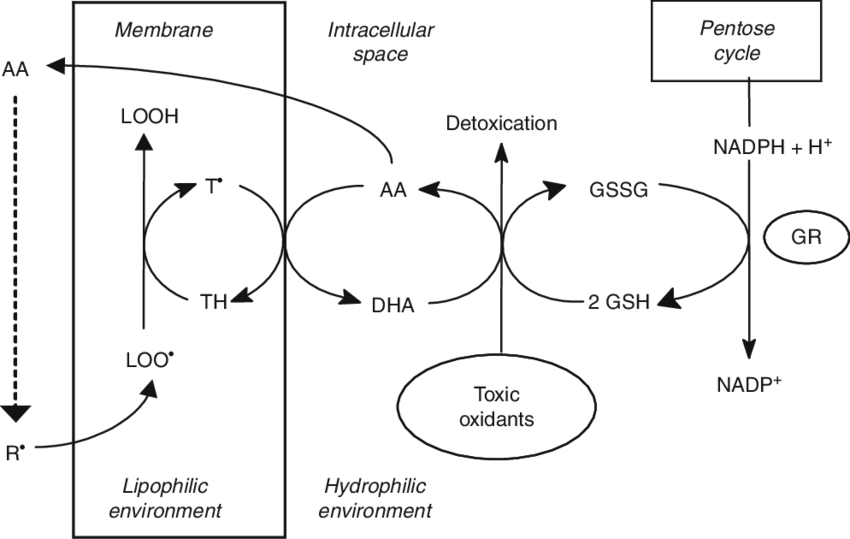
Creatine is incredibly important for the brain.
Like the muscles, creatine is stored in large amounts in the brain, and supports energy metabolism by acting as a way to replenish ATP.
This is vital for all functions of the brain, but in particular is needed for maintaining the charge of the neurons.
Without constant maintenance of this gradient, neurotransmitter signals and brain activity is not possible.
The brain is electric in nature. Creatine supports this.
(7/7)
Like the muscles, creatine is stored in large amounts in the brain, and supports energy metabolism by acting as a way to replenish ATP.
This is vital for all functions of the brain, but in particular is needed for maintaining the charge of the neurons.
Without constant maintenance of this gradient, neurotransmitter signals and brain activity is not possible.
The brain is electric in nature. Creatine supports this.
(7/7)

I've written more about the importance of creatine to the brain here, along with additional context:
https://x.com/Outdoctrination/status/1925552276841886151
If you want to improve long term brain / cognitive and general health, we'd be happy to help.
Book a free call with us here, and we can get you on the right path: go.prism.miami/consultation
Book a free call with us here, and we can get you on the right path: go.prism.miami/consultation
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh