ADHD has an ~80% chance of a comorbidity.
It is often missed or misdiagnosed, leading to delayed care or inappropriate treatment.
ADHD is not a checklist, it is a longitudinal diagnosis requiring developmental history, functional impact, and contextual formulation.
Here are 10 essential points to guide diagnosis and management. 🧠👇
1/11 🧵
It is often missed or misdiagnosed, leading to delayed care or inappropriate treatment.
ADHD is not a checklist, it is a longitudinal diagnosis requiring developmental history, functional impact, and contextual formulation.
Here are 10 essential points to guide diagnosis and management. 🧠👇
1/11 🧵
#1 ADHD is a Heterogeneous Condition
An individualised approach is critical; there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Focus on specific domains, not just the label.
2/11🧵
An individualised approach is critical; there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Focus on specific domains, not just the label.
2/11🧵
#2 Six Domains to Consider in ADHD Diagnosis & Management
● Cognition
● Reward learning
● Behavioural inhibition
● Fight-flight response
● Activity
● Behavioural activation
3/12🧵
● Cognition
● Reward learning
● Behavioural inhibition
● Fight-flight response
● Activity
● Behavioural activation
3/12🧵
#3 The Prefrontal Cortex & the Goldilocks Effect
Optimal prefrontal cortex functioning requires a balanced level of dopamine and noradrenaline.
Too much or too little can impair cognition and other domains.
4/12🧵
Optimal prefrontal cortex functioning requires a balanced level of dopamine and noradrenaline.
Too much or too little can impair cognition and other domains.
4/12🧵
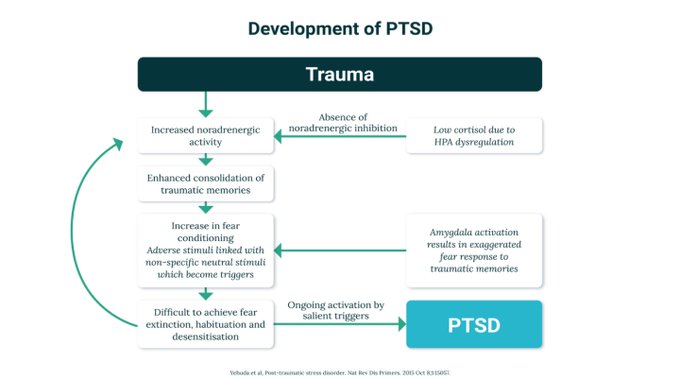
#4 High Comorbidity
ADHD often co-occurs with:
● Sleep disorders
● Trauma
● Autism spectrum disorders
● Bipolar disorder
● Depression
Comorbidity is the rule, not the exception, with up to 80% comorbidity.
5/12🧵
ADHD often co-occurs with:
● Sleep disorders
● Trauma
● Autism spectrum disorders
● Bipolar disorder
● Depression
Comorbidity is the rule, not the exception, with up to 80% comorbidity.
5/12🧵
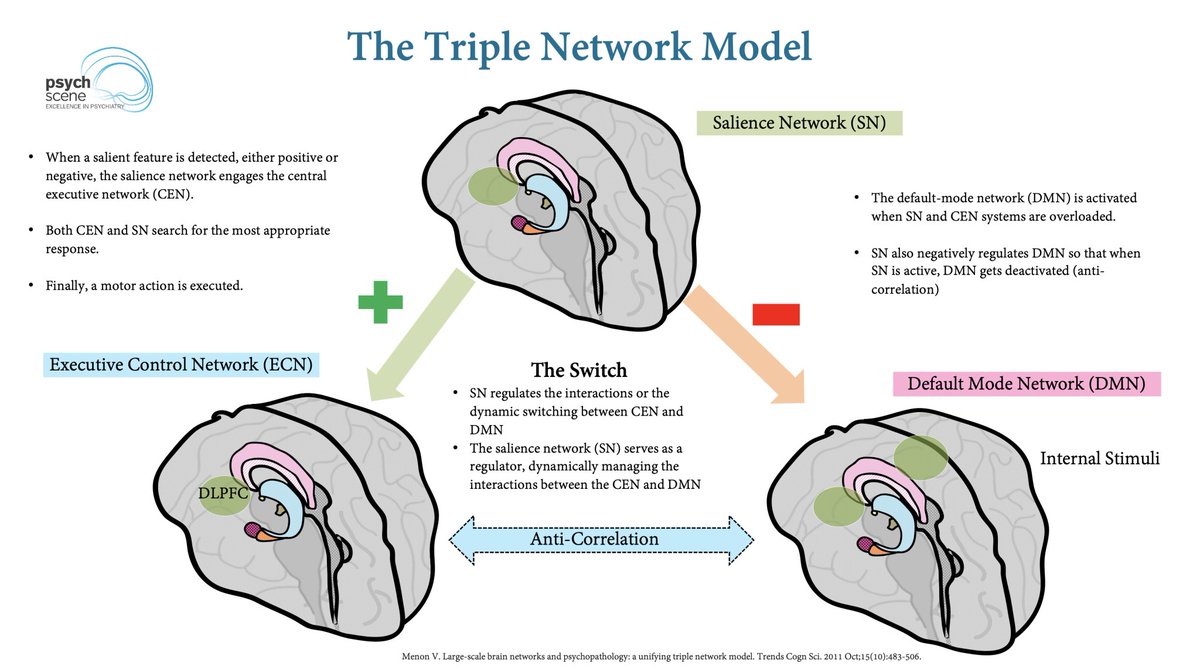
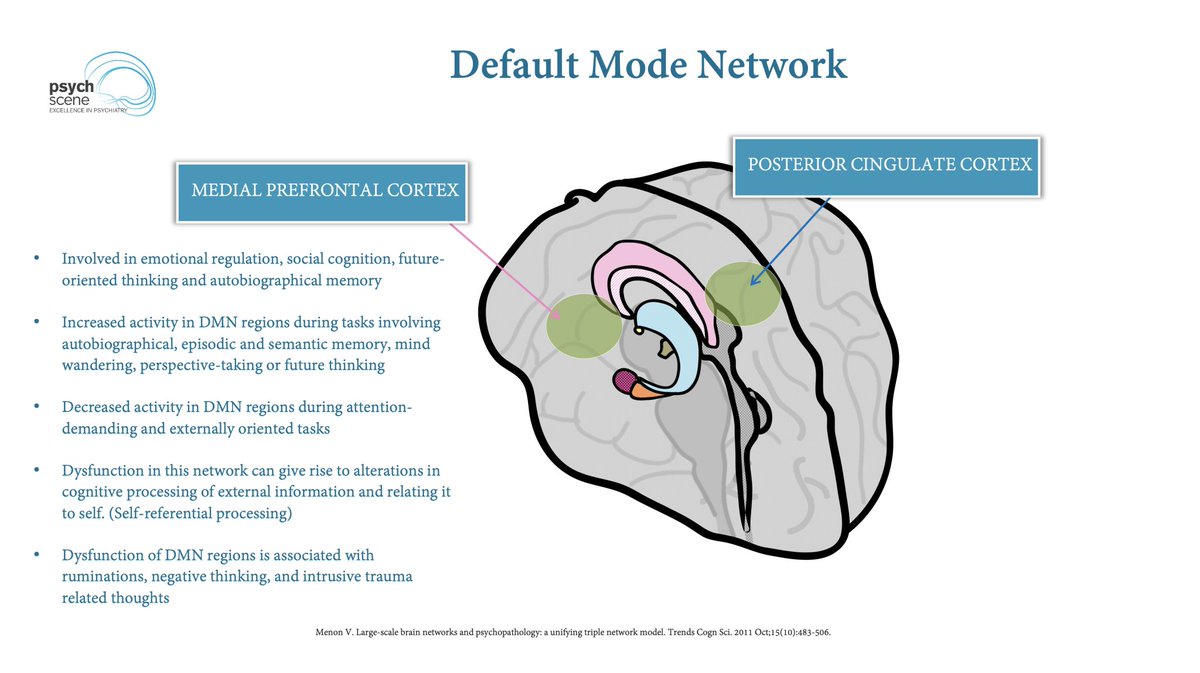
#5 Recognise the Complexity of ADHD – The Iceberg Model
ADHD is paradoxically a complex condition. Multiple factors can influence ADHD, including organic, psychological, social, dietary, and lifestyle aspects.
A comprehensive evaluation is essential for effective management.
6/12🧵
ADHD is paradoxically a complex condition. Multiple factors can influence ADHD, including organic, psychological, social, dietary, and lifestyle aspects.
A comprehensive evaluation is essential for effective management.
6/12🧵
#6 The FRAME of ADHD Treatment
ADHD treatment should prioritise long-term outcomes and functionality.
A lifespan approach is key due to prefrontal and striatal circuit changes over the lifespan.
7/12🧵
ADHD treatment should prioritise long-term outcomes and functionality.
A lifespan approach is key due to prefrontal and striatal circuit changes over the lifespan.
7/12🧵
#7 Not Just Stimulants
ADHD pharmacology requires a thorough evaluation of key functions and foreseeability.
Recognise the key role of non-stimulants in optimisation.
Consider non-pharmacological approaches alongside medication.
8/12🧵
ADHD pharmacology requires a thorough evaluation of key functions and foreseeability.
Recognise the key role of non-stimulants in optimisation.
Consider non-pharmacological approaches alongside medication.
8/12🧵
#8 Understanding the Difference between Phasic vs Tonic Dopamine
Phasic dopamine = brief, high-intensity spikes
Tonic dopamine = steady and sustained
Proper balance is crucial for optimal ADHD treatment.
9/12🧵
Phasic dopamine = brief, high-intensity spikes
Tonic dopamine = steady and sustained
Proper balance is crucial for optimal ADHD treatment.
9/12🧵
#9 Avoid Sensitisation & Desensitisation Cycles
Long-term phasic dopamine activity can lead to sensitisation and desensitisation cycles.
This may cause a diminished sense of reward over time.
These cycles are associated with side effects, tolerance, and non-adherence.
10/12🧵
Long-term phasic dopamine activity can lead to sensitisation and desensitisation cycles.
This may cause a diminished sense of reward over time.
These cycles are associated with side effects, tolerance, and non-adherence.
10/12🧵
#10 Optimal Functioning & Mesolimbic Pathways
Successful ADHD management requires balanced modulation of mesolimbic pathways (arousal and stress) and tonic dopamine receptors in the dorsal striatum (goal-directed actions and habits).
11/12🧵
Successful ADHD management requires balanced modulation of mesolimbic pathways (arousal and stress) and tonic dopamine receptors in the dorsal striatum (goal-directed actions and habits).
11/12🧵
Want to put these principles into practice?
Refine your clinical skills and gain a deeper framework for assessment and management in ADHD by visiting our course, “Adult ADHD Clinical Training Program | 6-Course Series for Psychiatrists & GPs” on The Academy:
12/12🧵psychscene.co/4fHBxLf
Refine your clinical skills and gain a deeper framework for assessment and management in ADHD by visiting our course, “Adult ADHD Clinical Training Program | 6-Course Series for Psychiatrists & GPs” on The Academy:
12/12🧵psychscene.co/4fHBxLf
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh