🧵 Procalcitonin (PCT) –
Tweet 1:
Procalcitonin- once just a peptide in calcitonin synthesis, now a powerful biomarker in infection & sepsis care. But when should we trust it, and when not? 🧵@IhabFathiSulima @DrAkhilX @CelestinoGutirr #MedTwitter #Rheumatology #ID
Tweet 1:
Procalcitonin- once just a peptide in calcitonin synthesis, now a powerful biomarker in infection & sepsis care. But when should we trust it, and when not? 🧵@IhabFathiSulima @DrAkhilX @CelestinoGutirr #MedTwitter #Rheumatology #ID
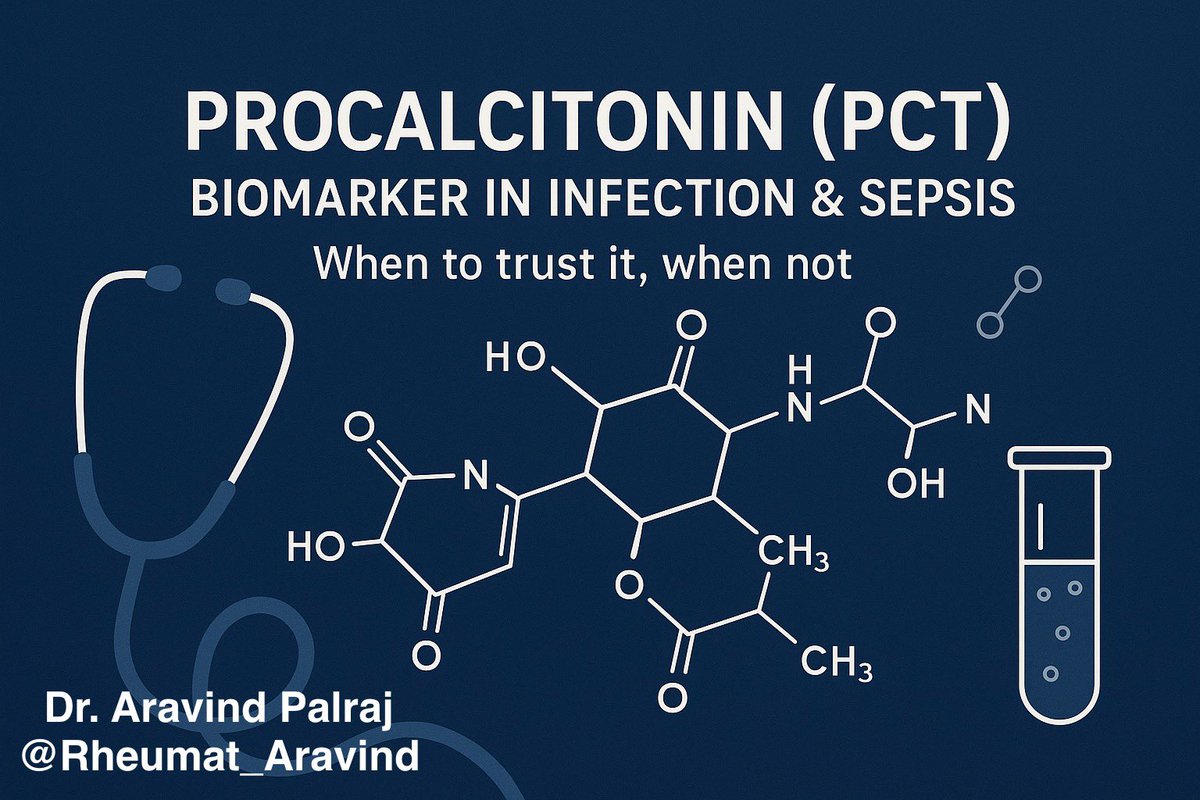
Tweet 2 (Basics):
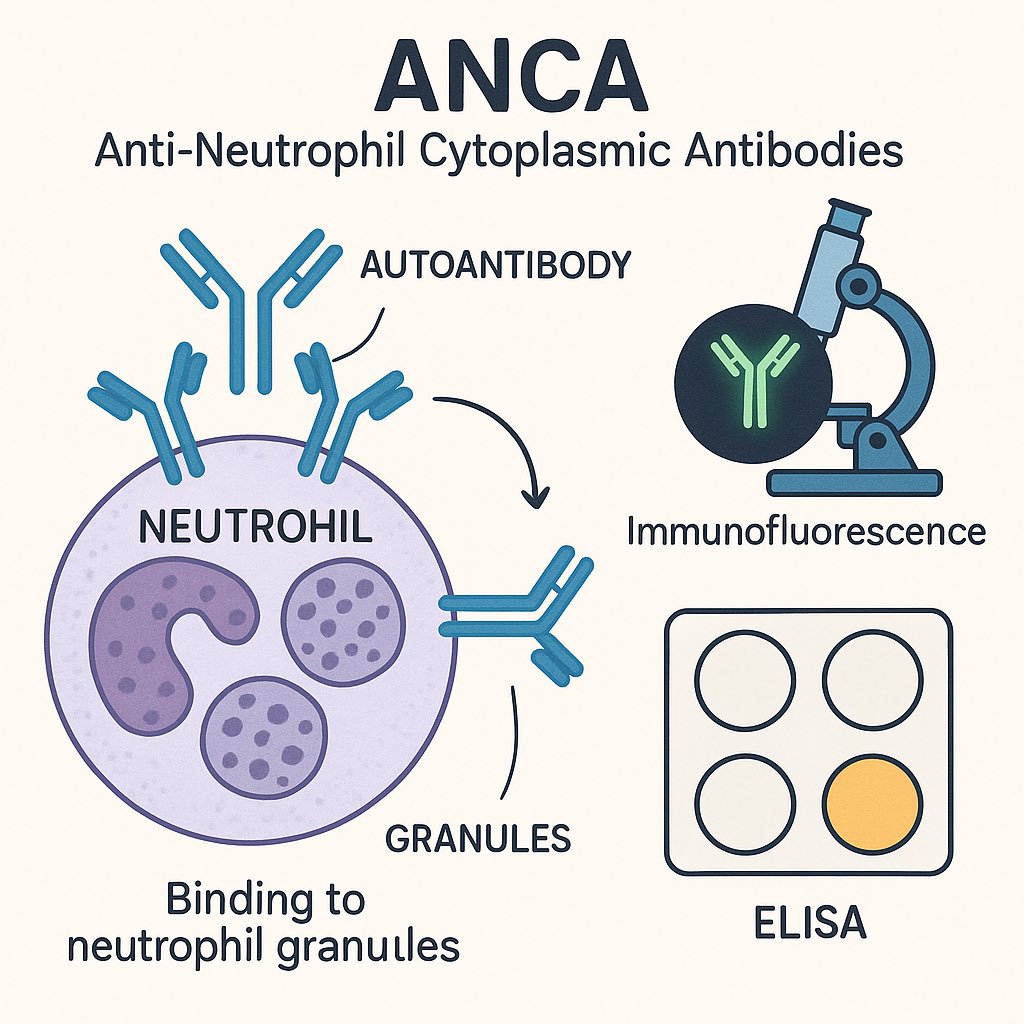
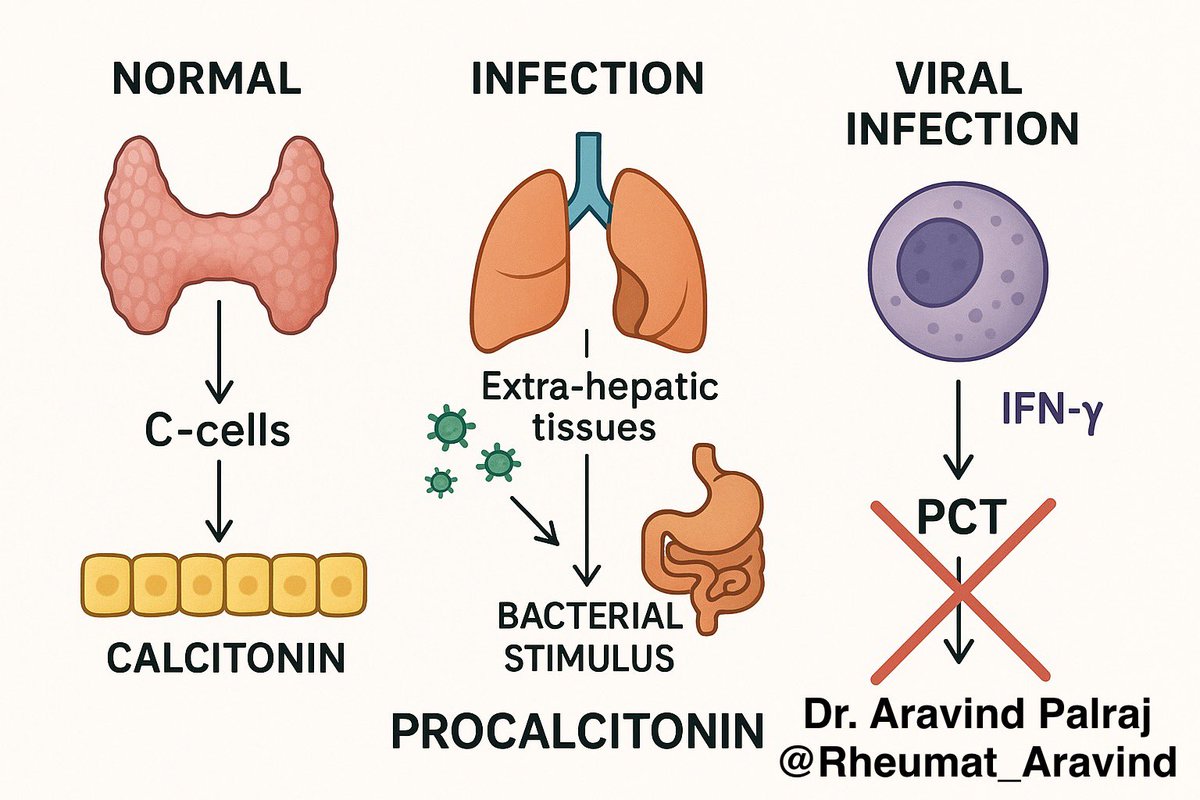
🔹 What is Procalcitonin?
•Precursor of calcitonin, normally produced in thyroid C-cells.
•During bacterial infection, PCT is released from multiple tissues in response to endotoxins & cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α).
•Viral infections usually suppress PCT.
🔹 What is Procalcitonin?
•Precursor of calcitonin, normally produced in thyroid C-cells.
•During bacterial infection, PCT is released from multiple tissues in response to endotoxins & cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α).
•Viral infections usually suppress PCT.
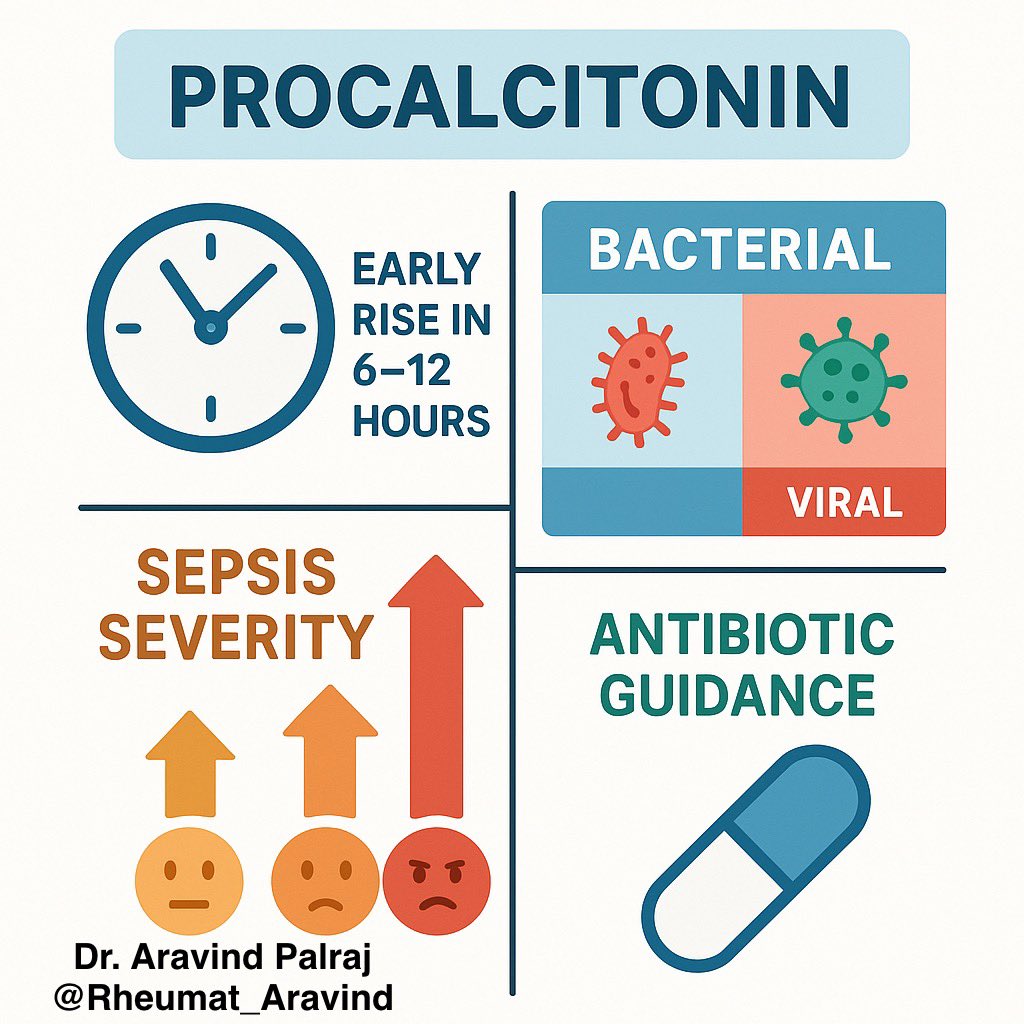
Tweet 3 (Why important?):
✨ PCT rises early (within 6–12 hrs) in systemic bacterial infection → helps clinicians:
•Differentiate bacterial vs viral infections
•Assess sepsis severity
•Guide antibiotic decisions
✨ PCT rises early (within 6–12 hrs) in systemic bacterial infection → helps clinicians:
•Differentiate bacterial vs viral infections
•Assess sepsis severity
•Guide antibiotic decisions
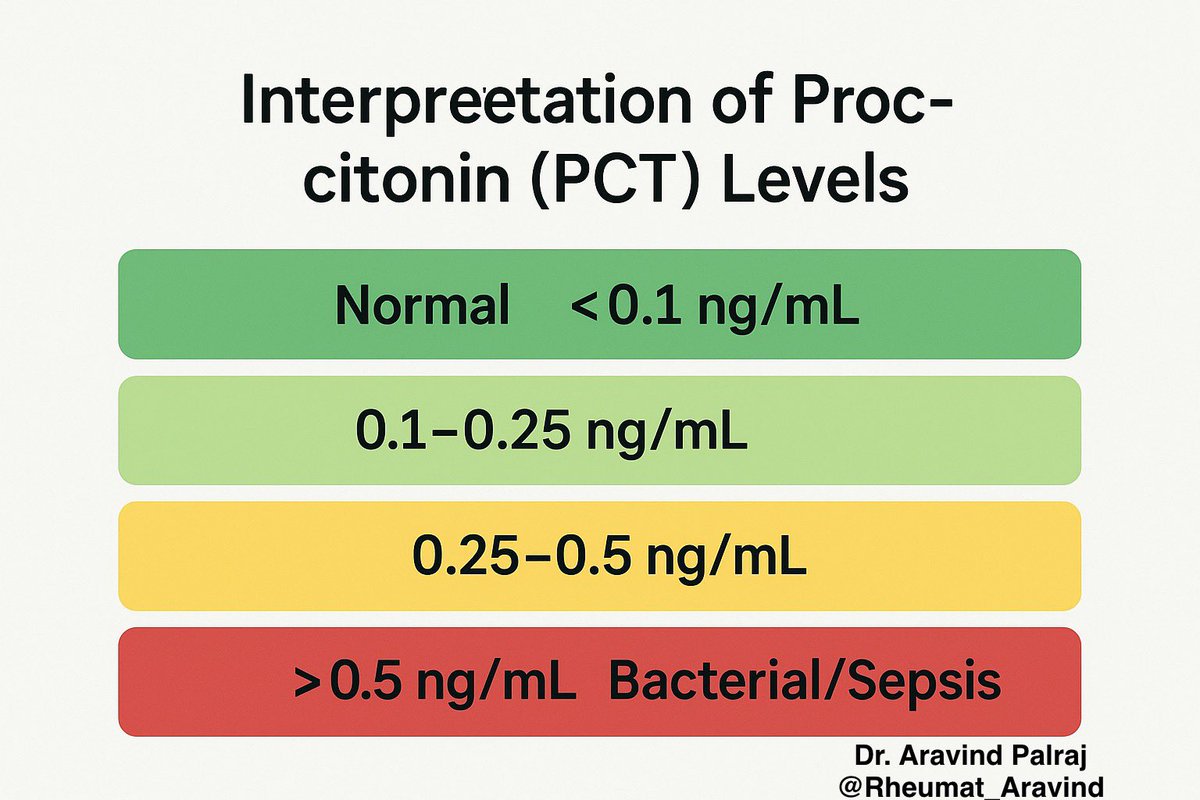
Tweet 4 (Interpretation):
📊 Levels & meaning (general guide):
•<0.1 ng/mL → Normal
•0.1–0.25 → Low likelihood of bacterial infection
•0.25–0.5 → Possible bacterial infection
•0.5 → Suggestive of bacterial infection/sepsis
(Higher = more severe infection)
📊 Levels & meaning (general guide):
•<0.1 ng/mL → Normal
•0.1–0.25 → Low likelihood of bacterial infection
•0.25–0.5 → Possible bacterial infection
•0.5 → Suggestive of bacterial infection/sepsis
(Higher = more severe infection)
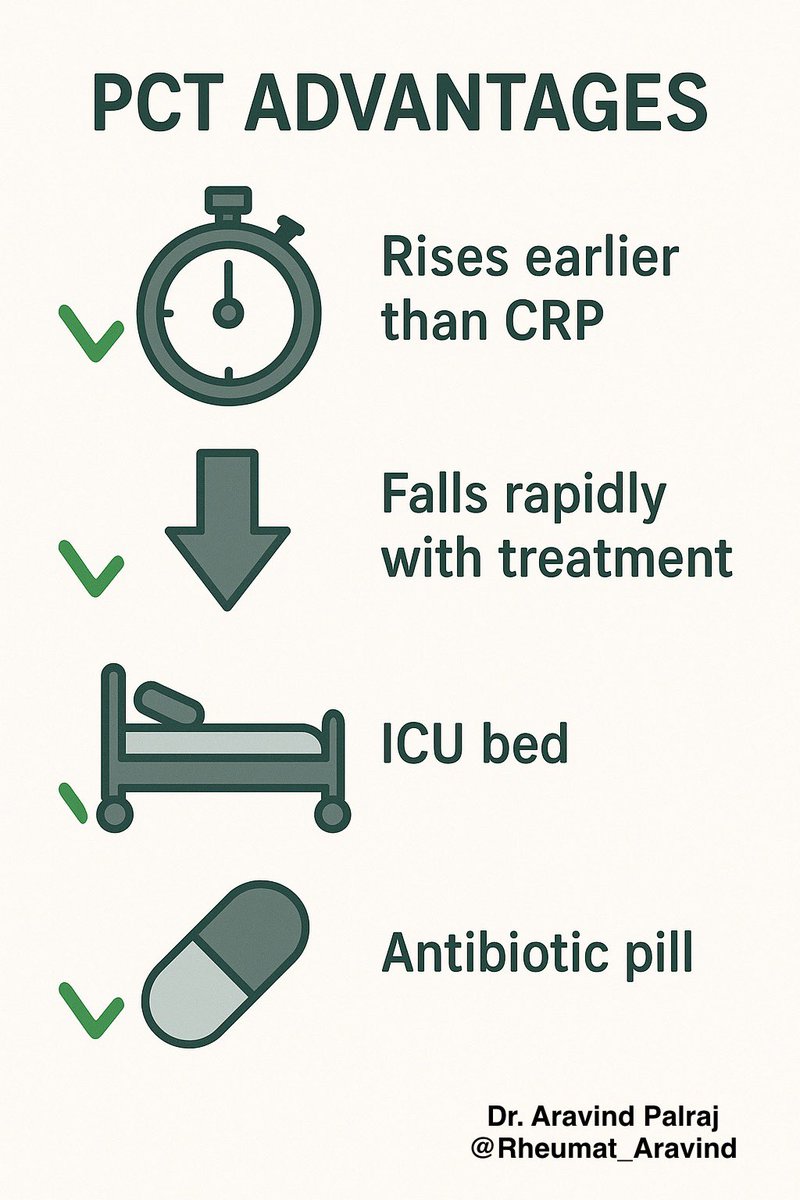
Tweet 5 (Pros):
✅ Advantages of PCT:
•Rises earlier than CRP in sepsis
•Falls rapidly with infection control → good for monitoring
•Useful in ICU, pneumonia, sepsis management
•Helps reduce unnecessary antibiotics
✅ Advantages of PCT:
•Rises earlier than CRP in sepsis
•Falls rapidly with infection control → good for monitoring
•Useful in ICU, pneumonia, sepsis management
•Helps reduce unnecessary antibiotics
Tweet 6 (Cons & pitfalls):
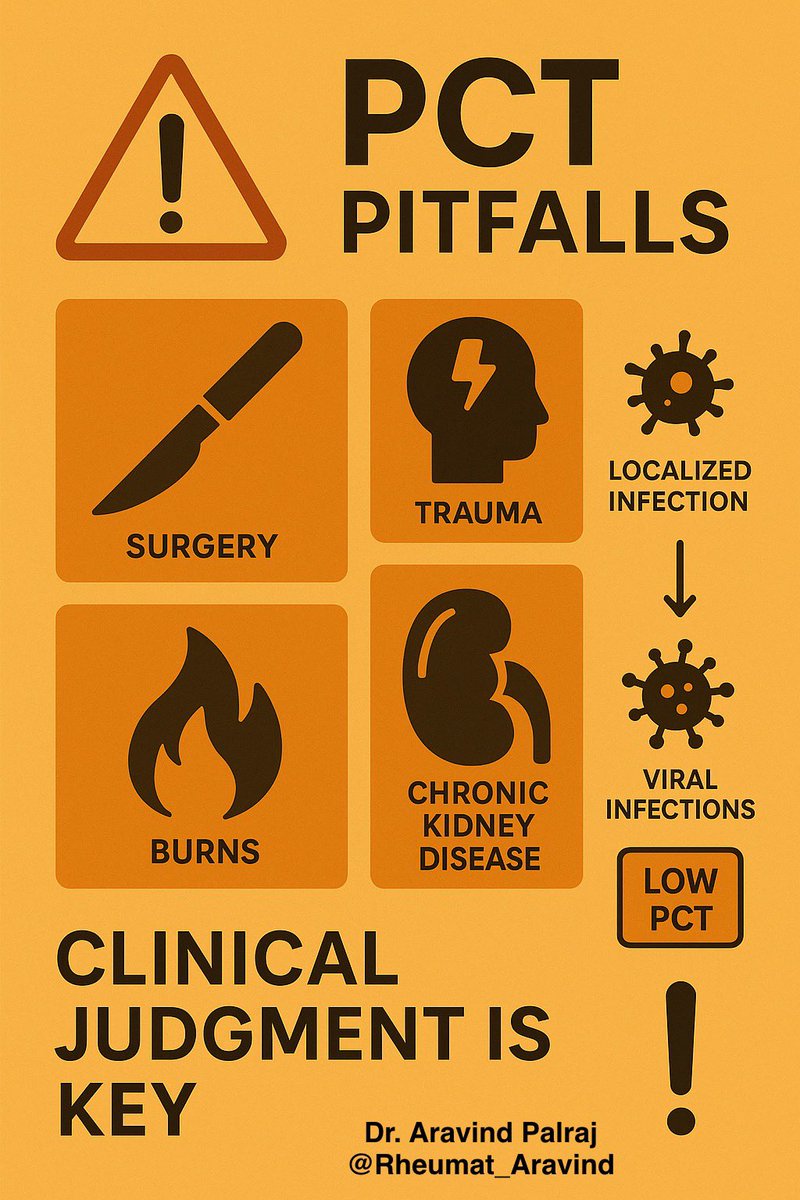
⚠️ Limitations:
•Can rise in non-infectious inflammation (major surgery, trauma, burns, CKD)
•May not rise in localized infections (e.g., abscess)
•Viral infections may keep it low despite illness
•Should never replace clinical judgment
⚠️ Limitations:
•Can rise in non-infectious inflammation (major surgery, trauma, burns, CKD)
•May not rise in localized infections (e.g., abscess)
•Viral infections may keep it low despite illness
•Should never replace clinical judgment
Tweet 7 (Special note for Rheumatology):
💡 In autoimmune & rheumatic diseases, PCT helps:
•Distinguish flare vs infection in patients on immunosuppressants
•Guide safe antibiotic use
But beware → high-dose steroids & biologics may blunt inflammatory markers.
💡 In autoimmune & rheumatic diseases, PCT helps:
•Distinguish flare vs infection in patients on immunosuppressants
•Guide safe antibiotic use
But beware → high-dose steroids & biologics may blunt inflammatory markers.

Tweet 8 (Take-home):
Procalcitonin = 🧪 helpful tool, not a magic bullet.
Best used with clinical exam + other labs (CRP, cultures, imaging).
👉 It guides antibiotics, but doesn’t write the prescription for you.
#MedEd #Procalcitonin #Sepsis
Procalcitonin = 🧪 helpful tool, not a magic bullet.
Best used with clinical exam + other labs (CRP, cultures, imaging).
👉 It guides antibiotics, but doesn’t write the prescription for you.
#MedEd #Procalcitonin #Sepsis

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh