🧵 Thread: Ultrasound in Arthritis — A Rheumatologist’s Tool:
Tweet 1
🖤🤍In Rheumatology, USG is becoming an extension of clinical exam.
Let’s decode why and how we use it in arthritis 👇
@IhabFathiSulima @DrAkhilX @CelestinoGutirr @Janetbirdope @Lupusreference #MedTwitter #Rheumatology
Tweet 1
🖤🤍In Rheumatology, USG is becoming an extension of clinical exam.
Let’s decode why and how we use it in arthritis 👇
@IhabFathiSulima @DrAkhilX @CelestinoGutirr @Janetbirdope @Lupusreference #MedTwitter #Rheumatology

Tweet 2
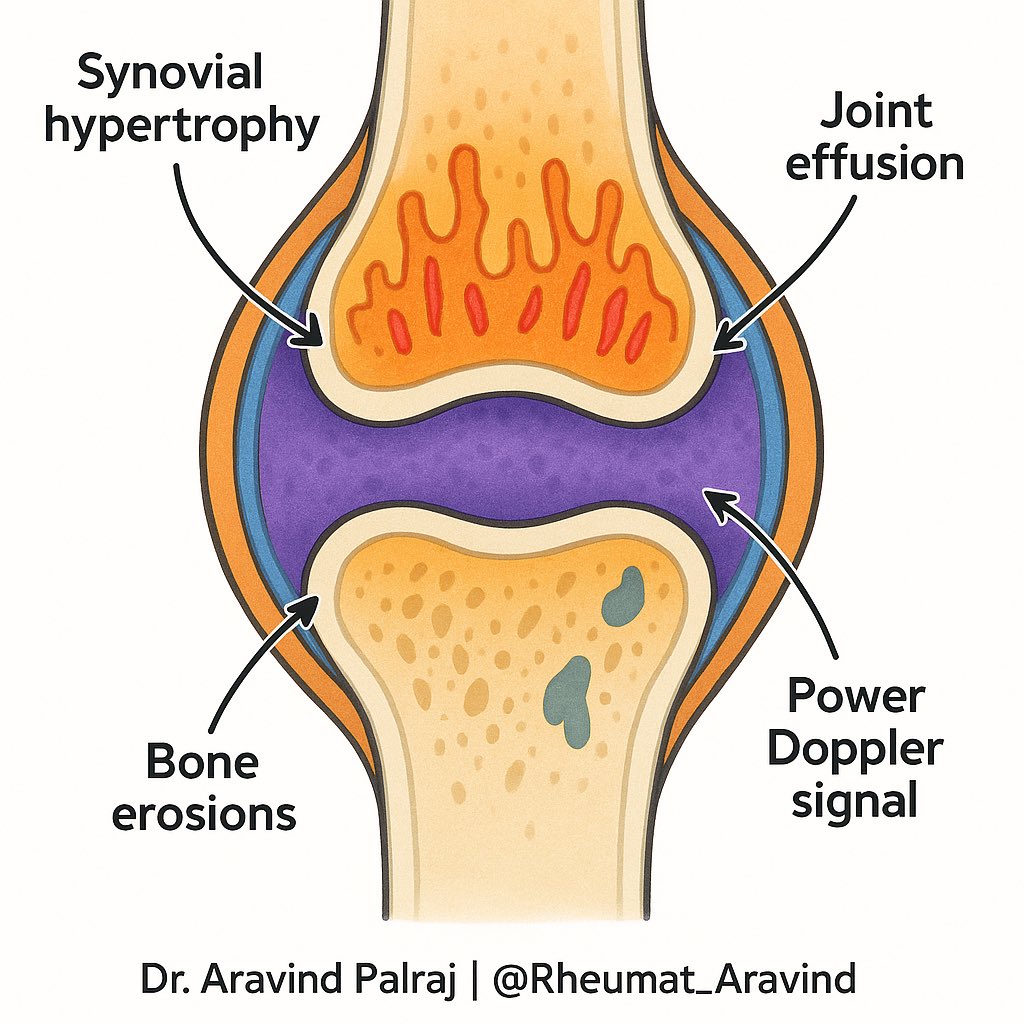
🔍 What USG shows in arthritis:
• Synovial hypertrophy
•Joint effusion
•Power Doppler (blood flow = inflammation)
•Bone erosions
👉 Real-time look at inflammation.
🔍 What USG shows in arthritis:
• Synovial hypertrophy
•Joint effusion
•Power Doppler (blood flow = inflammation)
•Bone erosions
👉 Real-time look at inflammation.
Tweet 3
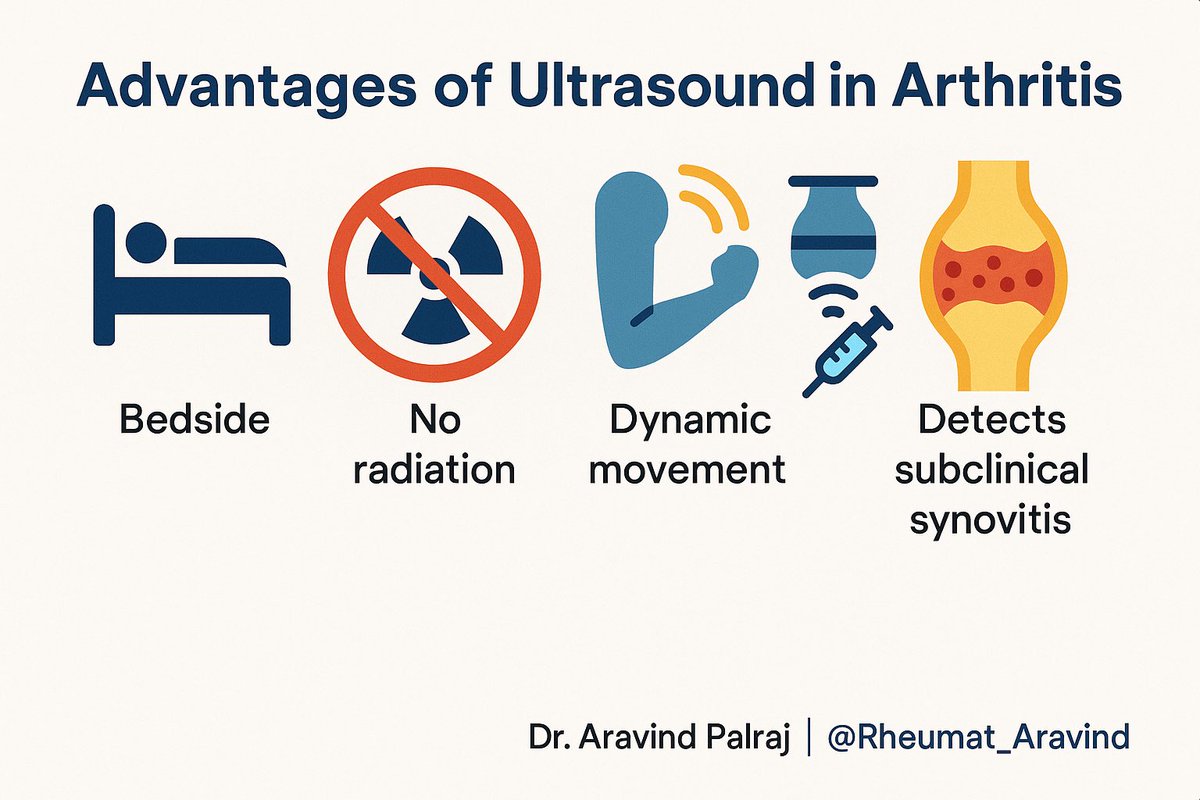
✨ Advantages of USG in Rheumatology:
1. Bedside, no radiation
2. Dynamic — see movement
3. Guides aspiration & injections
4. Detects subclinical synovitis (before X-ray/clinical exam)
✨ Advantages of USG in Rheumatology:
1. Bedside, no radiation
2. Dynamic — see movement
3. Guides aspiration & injections
4. Detects subclinical synovitis (before X-ray/clinical exam)
Tweet 4
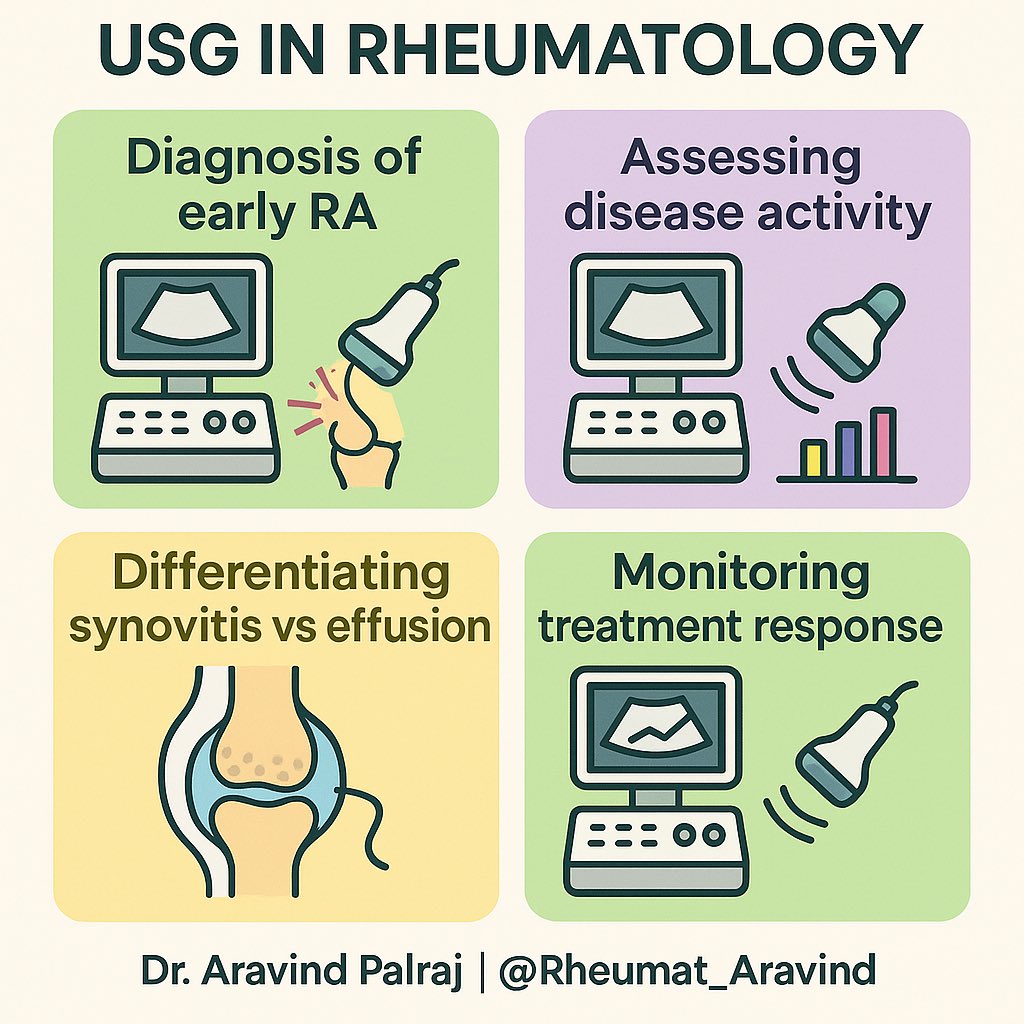
📌 Key uses in Arthritis:
•Diagnosis of early RA
•Assessing disease activity
•Differentiating synovitis vs effusion
•Monitoring treatment response
📌 Key uses in Arthritis:
•Diagnosis of early RA
•Assessing disease activity
•Differentiating synovitis vs effusion
•Monitoring treatment response
Tweet 5
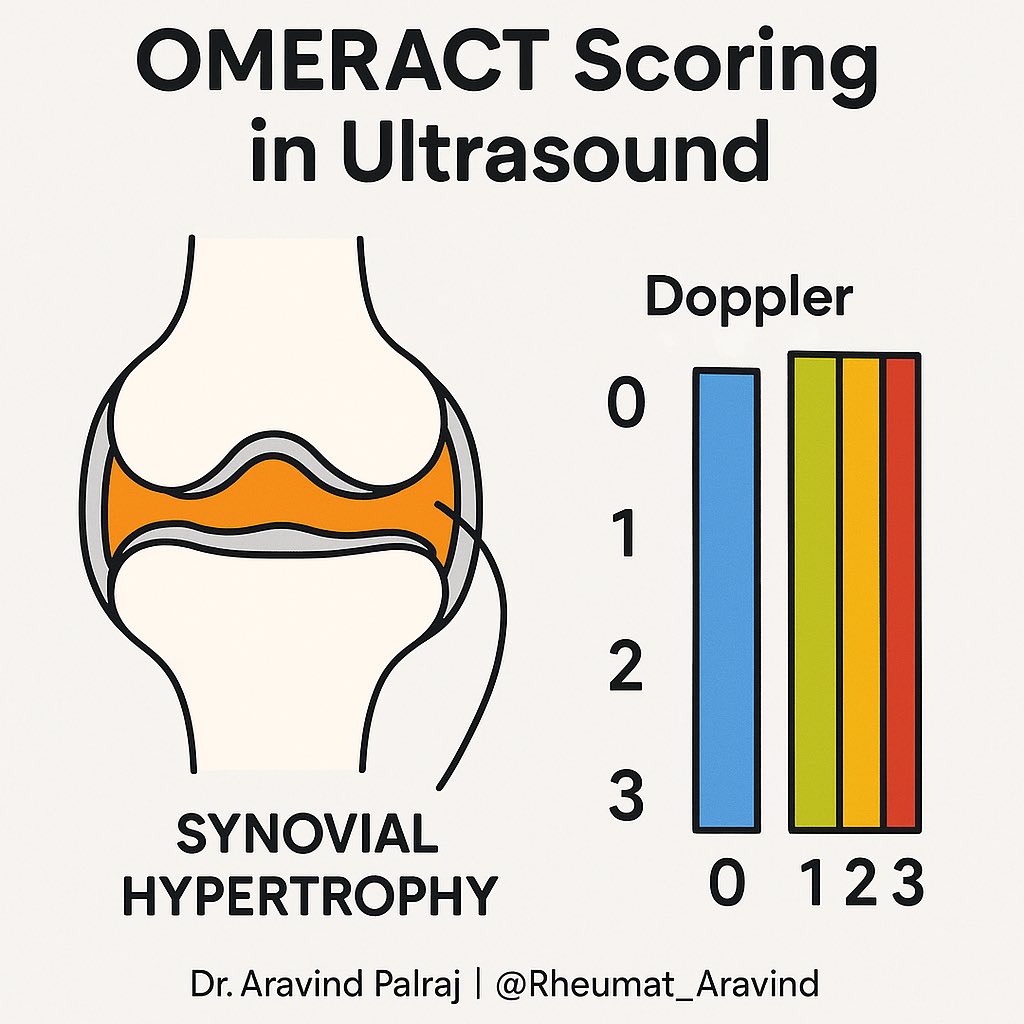
🎯 Scoring systems:
•OMERACT defines synovial hypertrophy & Doppler grades
•Helps standardize reporting
•Increasingly used in trials & treat-to-target
🎯 Scoring systems:
•OMERACT defines synovial hypertrophy & Doppler grades
•Helps standardize reporting
•Increasingly used in trials & treat-to-target
Tweet 6 (Final)
✅ Take-home:
Ultrasound = stethoscope of modern rheumatology.
It bridges the gap between exam & imaging, helping us treat arthritis earlier & better.
✅ Take-home:
Ultrasound = stethoscope of modern rheumatology.
It bridges the gap between exam & imaging, helping us treat arthritis earlier & better.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh