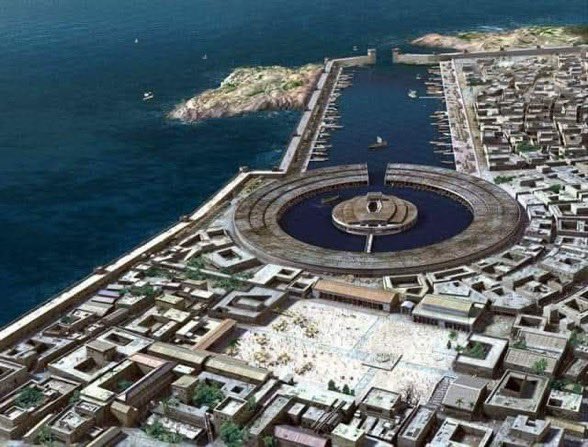
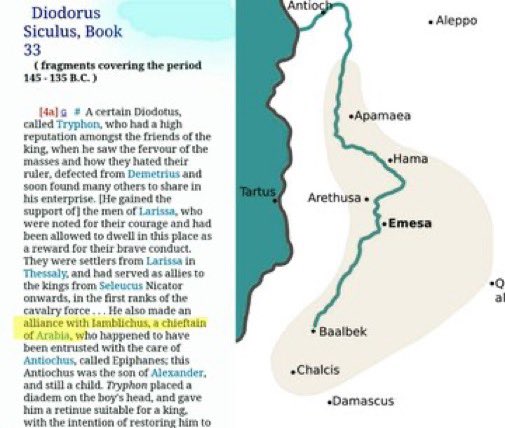
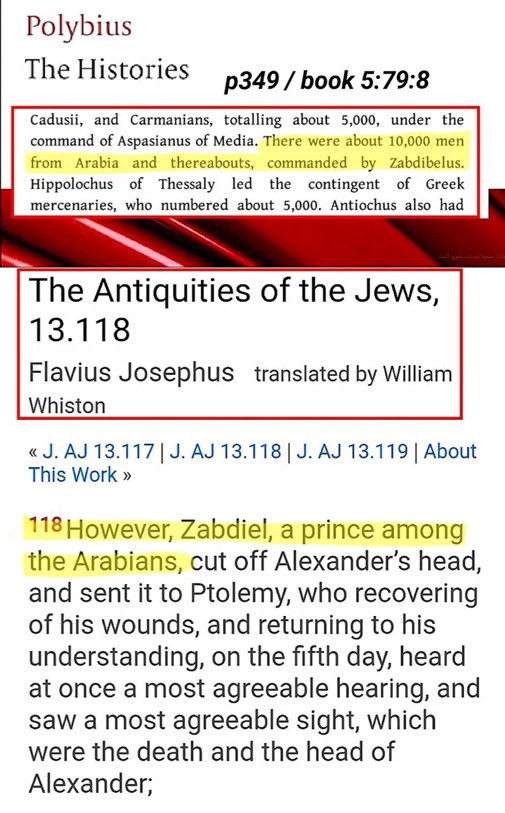
• Safi al-Din al-Irmawi (from Persian Iraq) was the first to develop musical notation for melodies using alphabetical letters.
• Umar ibn Sahlan al-Sawi (from Persian Iraq) invented the earliest known manual instrument used to measure the altitude of celestial bodies with..+



• Umar ibn Sahlan al-Sawi (from Persian Iraq) invented the earliest known manual instrument used to measure the altitude of celestial bodies with..+
https://twitter.com/baytalhikmah1/status/1966046767700377918




precision in minutes.
• The book *Firdaws al-Hikma*, written in Arabic by Ali ibn Sahl al-Tabari, was the first medical encyclopedia to compile all branches of medical sciences in a single book.
• The book *Firdaws al-Hikma*, written in Arabic by Ali ibn Sahl al-Tabari, was the first medical encyclopedia to compile all branches of medical sciences in a single book.
• The book *On Urine* by Ishaq ibn Sulayman al-Israili al-Misri, written in Arabic, contributed to establishing urology as one of the most important branches of medicine in the Latin Middle Ages.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh