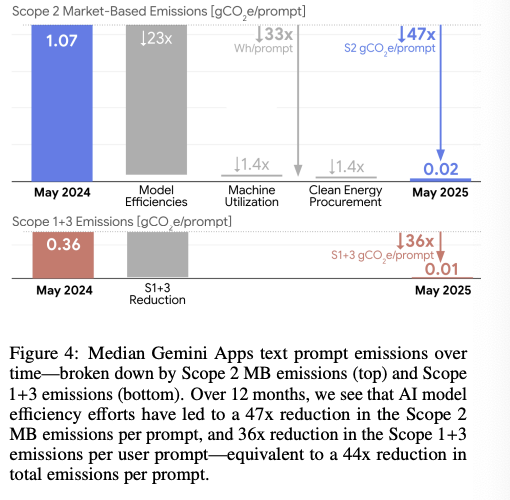
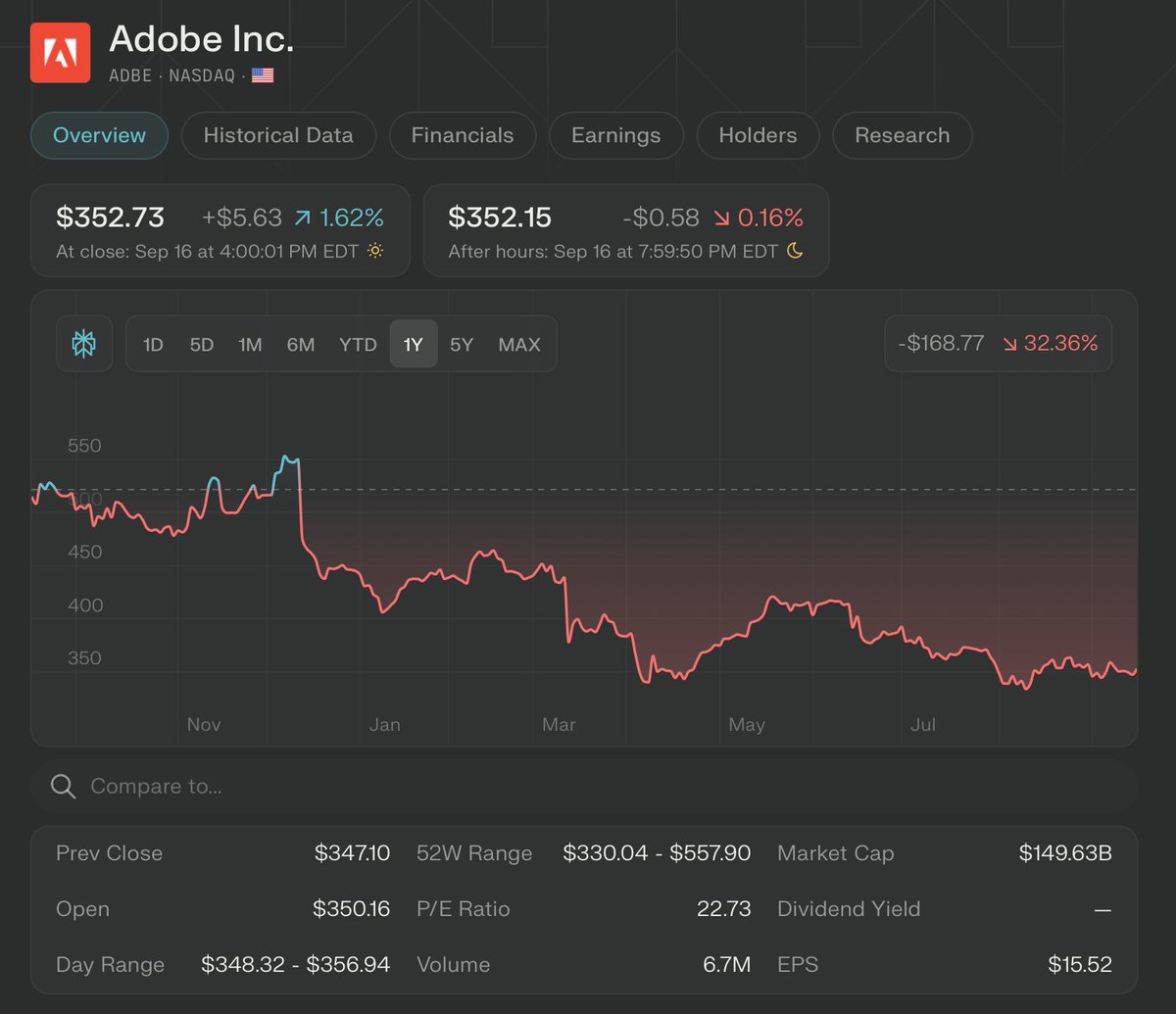
🚨 Adobe vs. The AI Revolution: Adobe's share price is down 26% since ChatGPT launched (Nov 2022: ~$400 → Sep 2025: $349).
Instead of strengthening their 34% Photoshop market dominance, they've lost $75B in market value.
How did this happen for a company that had 3 years to prepare for the AI wave? Where is the $3.5B in R&D spend each year going? Here's the full breakdown:
Instead of strengthening their 34% Photoshop market dominance, they've lost $75B in market value.
How did this happen for a company that had 3 years to prepare for the AI wave? Where is the $3.5B in R&D spend each year going? Here's the full breakdown:

1/ THE MARKET DOMINANCE
In November 2022, Adobe seemed invincible. For 40 years, they had built the ultimate creative monopoly where Design agencies built entire business models around Adobe expertise:
• 34% of the global creative software market
• 90% of professionals dependent on Photoshop
• 26 million subscribers paying $660 annually
• Revenue: $22.6 billion with 89% gross margins
Their stock traded at $400, market cap near $200 billion and CEO Shantanu Narayen called Adobe "the infrastructure for creativity itself."
In November 2022, Adobe seemed invincible. For 40 years, they had built the ultimate creative monopoly where Design agencies built entire business models around Adobe expertise:
• 34% of the global creative software market
• 90% of professionals dependent on Photoshop
• 26 million subscribers paying $660 annually
• Revenue: $22.6 billion with 89% gross margins
Their stock traded at $400, market cap near $200 billion and CEO Shantanu Narayen called Adobe "the infrastructure for creativity itself."

2/ THE YEAR EVERYTHING CHANGED: 2025
Generative AI rewired demand and collapsed barriers to creating images/video.
Competitors from Midjourney, OpenAI to Google’s Gemini nano-banana pushed quality and speed, shifting value from tool mastery to prompt‑driven outcomes.
Adobe's leadership knew this was coming. But they completely misread what was actually happening...
Generative AI rewired demand and collapsed barriers to creating images/video.
Competitors from Midjourney, OpenAI to Google’s Gemini nano-banana pushed quality and speed, shifting value from tool mastery to prompt‑driven outcomes.
Adobe's leadership knew this was coming. But they completely misread what was actually happening...

3/ ADOBE'S RESPONSE
Adobe's response revealed everything wrong with their strategy. They rebranded “All Apps” to Creative Cloud Pro and raised prices:
• Creative Cloud prices jumped 17% to $70/month (+17%).
• Student plans are $29.99/mo first year, then $39.99/mo.
• New users on standard plan were limited to only 25 monthly credits (down from 500) with fewer AI features.
Meanwhile, competitors offered superior capabilities for nearly free. Google offered Nano Banana free (100 daily edits), OpenAI charged just $0.04 per image.
Adobe's response revealed everything wrong with their strategy. They rebranded “All Apps” to Creative Cloud Pro and raised prices:
• Creative Cloud prices jumped 17% to $70/month (+17%).
• Student plans are $29.99/mo first year, then $39.99/mo.
• New users on standard plan were limited to only 25 monthly credits (down from 500) with fewer AI features.
Meanwhile, competitors offered superior capabilities for nearly free. Google offered Nano Banana free (100 daily edits), OpenAI charged just $0.04 per image.
4/ THE $3.5 BILLION R&D SPEND
Here's where Adobe's story becomes perplexing. They spent $3.5 billion annually on R&D and in 2025 launched Firefly Video Model, Image Model 4 Ultra, enhanced mobile apps.
But inside Firefly, Adobe was using Google’s Gemini 2.5 Flash Image and OpenAI models.
The most damning evidence was yet to come...
Here's where Adobe's story becomes perplexing. They spent $3.5 billion annually on R&D and in 2025 launched Firefly Video Model, Image Model 4 Ultra, enhanced mobile apps.
But inside Firefly, Adobe was using Google’s Gemini 2.5 Flash Image and OpenAI models.
The most damning evidence was yet to come...
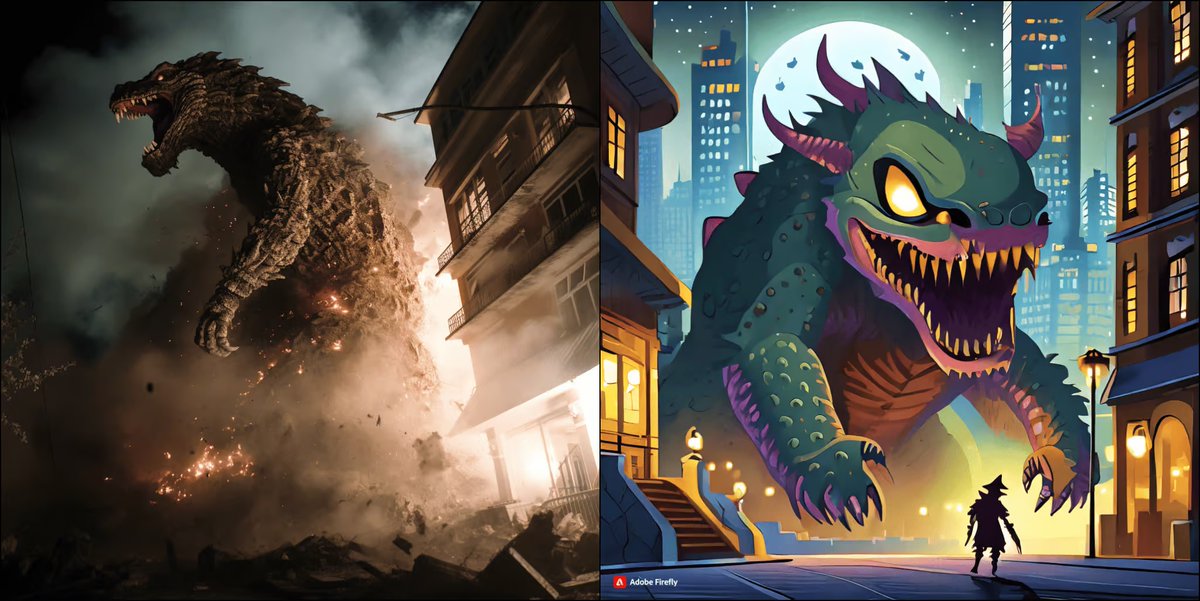
5/ THE QUALITY GAP EXPOSED
Side-by-side tests reveal uncomfortable truth: AI tools often produce superior results.
Midjourney demonstrates artistic understanding with sophisticated lighting, compelling composition, realism and emotional resonance that Adobe's algorithm-trained models couldn't match.
Side-by-side tests reveal uncomfortable truth: AI tools often produce superior results.
Midjourney demonstrates artistic understanding with sophisticated lighting, compelling composition, realism and emotional resonance that Adobe's algorithm-trained models couldn't match.

6/ WALL STREET'S RESPONSE
Despite beating earnings every quarter, Adobe's stock dropped in value: $400 to $349 = 26% decline, wiping out $75 billion in shareholder wealth.
Meanwhile, Big Tech added $8 trillion since ChatGPT launched. Even with record Q3 earnings of $5.99 billion, Adobe stock traded 35% below analyst targets.
Wall Street's message was clear: we see your current profits, but we don't believe in your future.
Despite beating earnings every quarter, Adobe's stock dropped in value: $400 to $349 = 26% decline, wiping out $75 billion in shareholder wealth.
Meanwhile, Big Tech added $8 trillion since ChatGPT launched. Even with record Q3 earnings of $5.99 billion, Adobe stock traded 35% below analyst targets.
Wall Street's message was clear: we see your current profits, but we don't believe in your future.
7/ THE ENTERPRISE SPLIT
Here's the twist: Large enterprises actually increased Adobe spending 40%+ in 2025. They payed premiums for "commercially safe" AI and legal indemnification.
But mid-market companies (Adobe's growth engine) now questions ROI.
Why pay $70/month per employee when marketing teams can create campaigns using cheaper and better AI tools?
Here's the twist: Large enterprises actually increased Adobe spending 40%+ in 2025. They payed premiums for "commercially safe" AI and legal indemnification.
But mid-market companies (Adobe's growth engine) now questions ROI.
Why pay $70/month per employee when marketing teams can create campaigns using cheaper and better AI tools?
9/ BOTTOM LINE
Adobe built a $150B empire on the assumption that professional creativity required professional tools.
AI shattered that assumption overnight.
The company isn't dying, it's evolving into a high-margin enterprise niche player. But the days of creative software monopoly are over.
This isn't just Adobe's problem, it's a preview of how technological platform shifts can invalidate decades of competitive advantage.
The creative software revolution isn't coming. It's here.
Adobe built a $150B empire on the assumption that professional creativity required professional tools.
AI shattered that assumption overnight.
The company isn't dying, it's evolving into a high-margin enterprise niche player. But the days of creative software monopoly are over.
This isn't just Adobe's problem, it's a preview of how technological platform shifts can invalidate decades of competitive advantage.
The creative software revolution isn't coming. It's here.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh