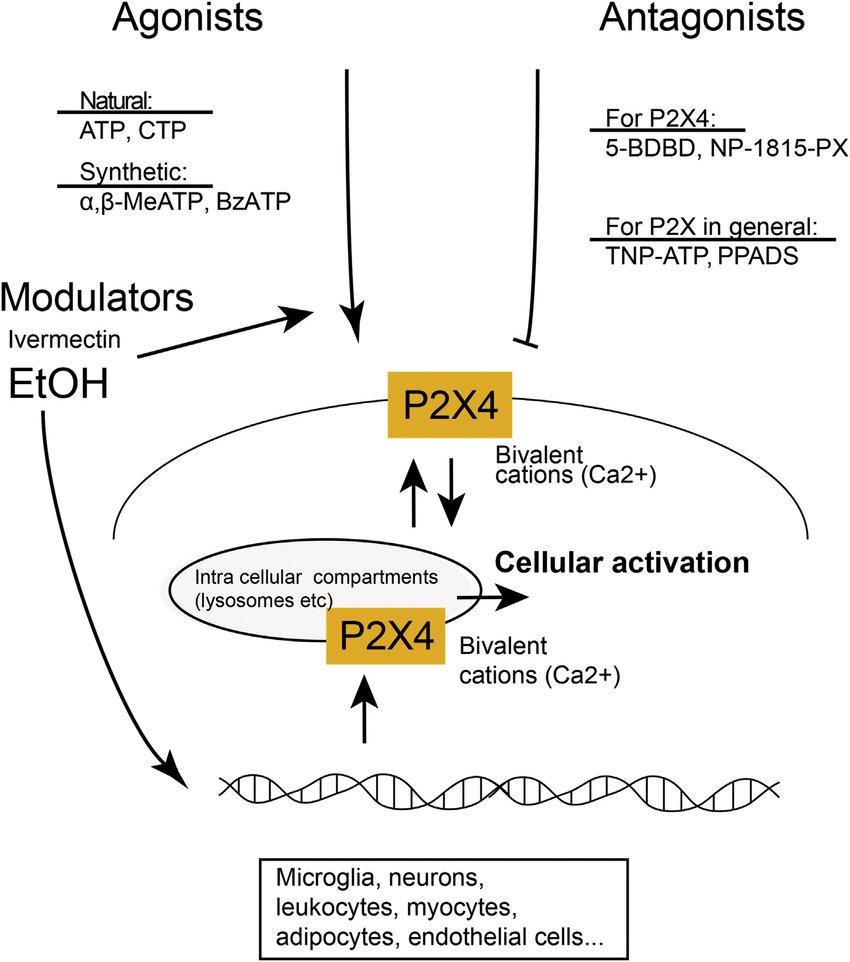
Wi-Fi radiation can have devastating consequences on testosterone and sperm health, as multiple studies have demonstrated.
(🧵1/7)
(🧵1/7)
For example, here's one study examining the impact of just 2 hours of Wi-Fi radiation exposure.
The parameters were matched to meet most modern WiFi standards.
◇ 2.45-GHz (frequency)
◇ 64.776 mW (power output)
◇ 0.029812 mW/cm² (power density)
◇ 0.018 W/Kg (specific absorption rate, or how much radiation tissues actually absorb)
Keep in mind that both your Wi-Fi router AND your phone put out this type of radiation within these parameters.
(2/7)
The parameters were matched to meet most modern WiFi standards.
◇ 2.45-GHz (frequency)
◇ 64.776 mW (power output)
◇ 0.029812 mW/cm² (power density)
◇ 0.018 W/Kg (specific absorption rate, or how much radiation tissues actually absorb)
Keep in mind that both your Wi-Fi router AND your phone put out this type of radiation within these parameters.
(2/7)

Wi-Fi at just 2 hours a day ripped apart the structure of the seminiferous tubules, the main functional unit of the testicles.
The diameter of these tubules was smaller and the Leydig cells, which produce testosterone, were also degenerated.
(3/7)

The diameter of these tubules was smaller and the Leydig cells, which produce testosterone, were also degenerated.
(3/7)
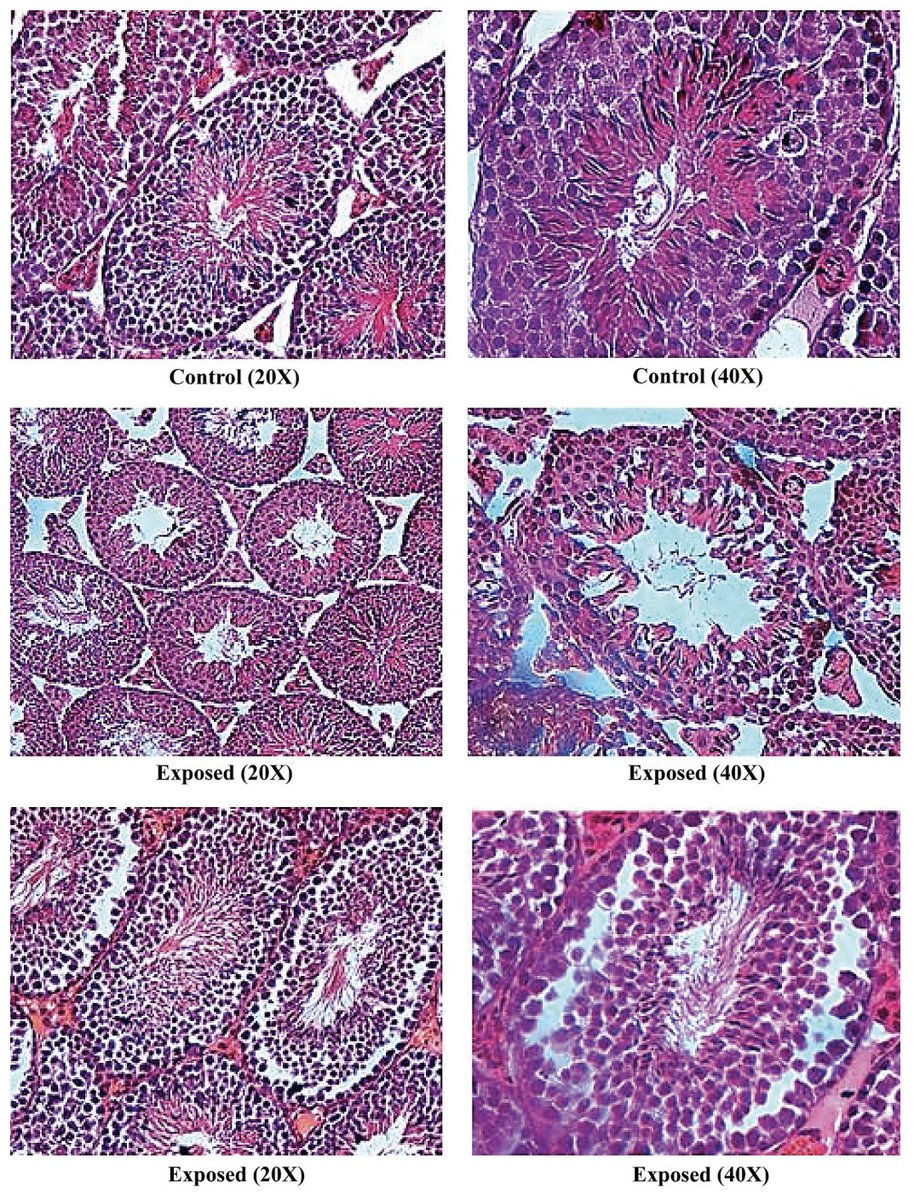
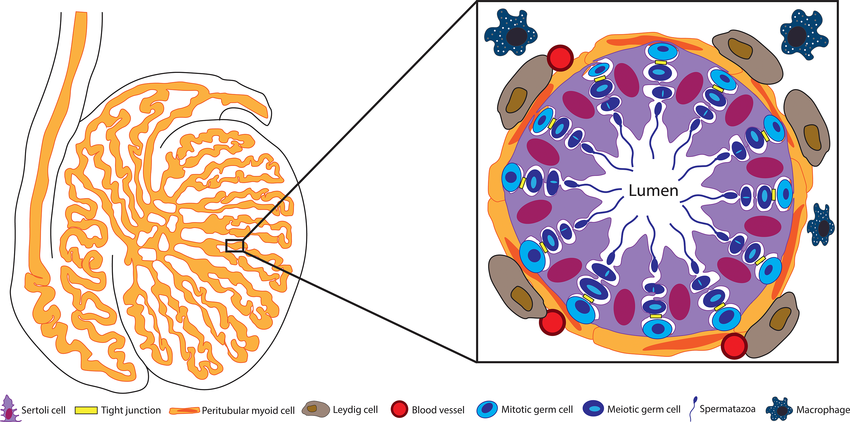
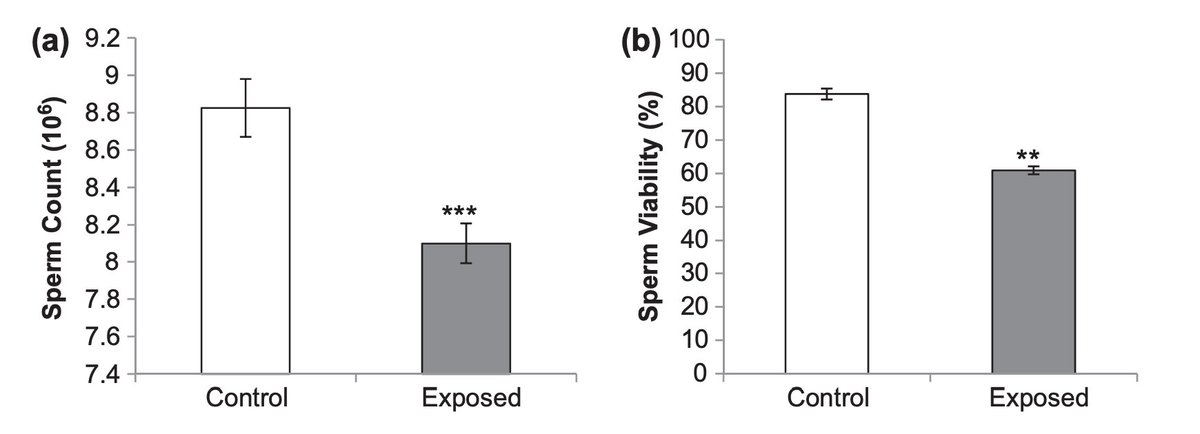
Wi-Fi also worsened sperm health.
Both sperm count and viability were reduced with exposure.
Previous studies showed that they could cause DNA damage in these cells, and even hypothesized that putting a laptop on your lap could directly cause this.
(4/7)
Both sperm count and viability were reduced with exposure.
Previous studies showed that they could cause DNA damage in these cells, and even hypothesized that putting a laptop on your lap could directly cause this.
(4/7)
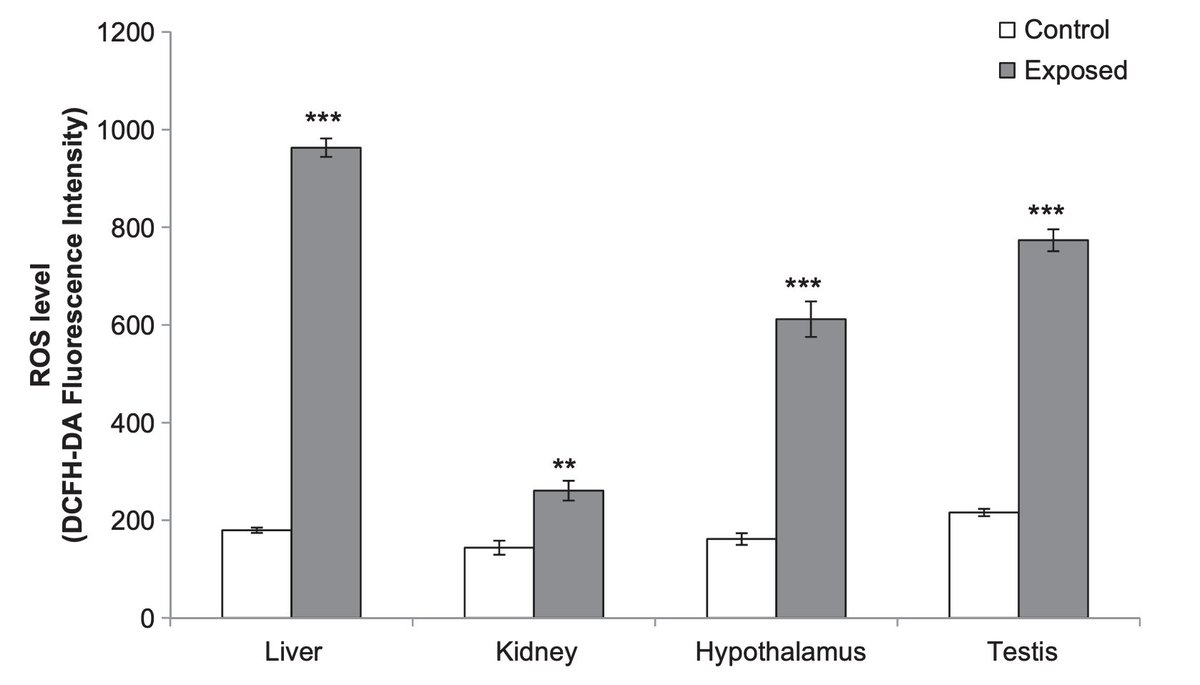
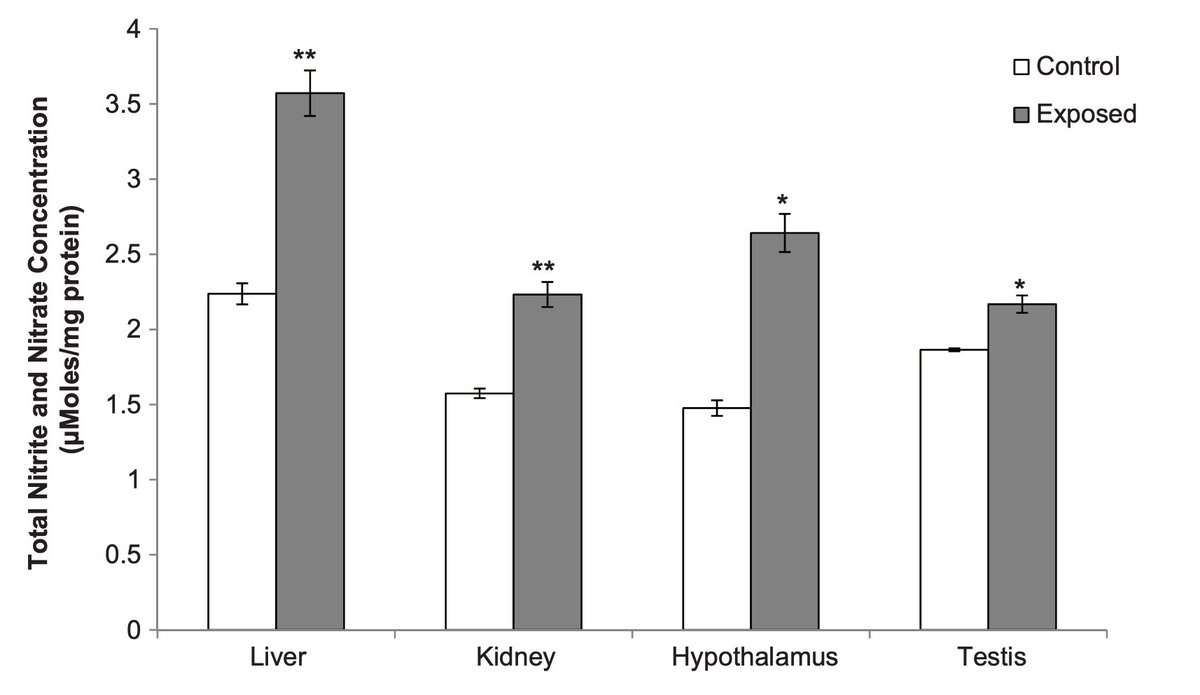
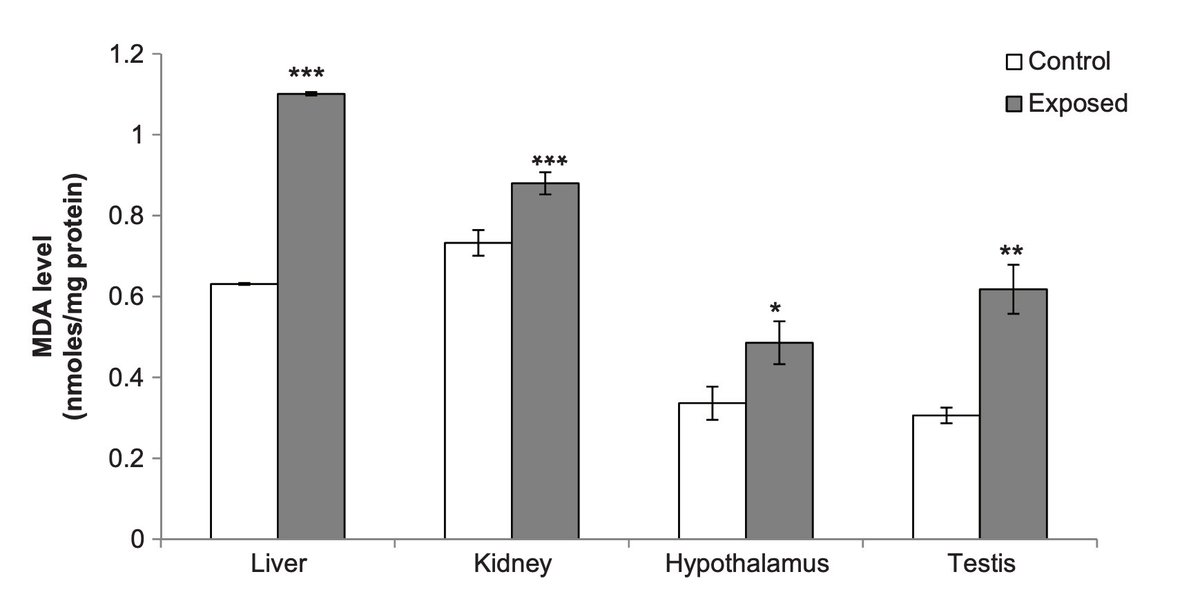
Wi-Fi was able to do this by inducing oxidative and nitrosative stress.
Essentially, it causes the production of small but highly reactive molecules made of oxygen and nitrogen.
These can cause damage to tissues and alter hormonal / signaling functions.
(5/7)


Essentially, it causes the production of small but highly reactive molecules made of oxygen and nitrogen.
These can cause damage to tissues and alter hormonal / signaling functions.
(5/7)
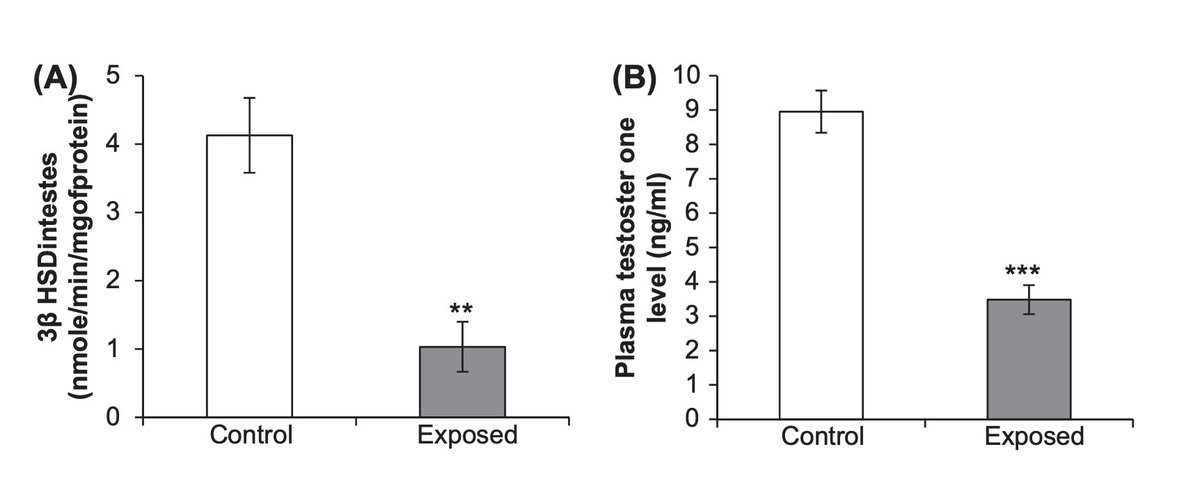
Strikingly, testosterone was a THIRD of control values when exposed to Wi-Fi.
2 hours a day, all parameters similar to what you and I get exposed to just by using our phones.
(6/7)
2 hours a day, all parameters similar to what you and I get exposed to just by using our phones.
(6/7)
A recent systematic review of the literature included 19 studies corroborated these findings, concluding that "limiting the use of wireless devices is recommended."
It is true that most of these are animal studies, but as we've discussed, the exposure parameters match (or even underestimate) exposures in humans.
There won't be any human trials on this, ever, I can almost guarantee you that.
The human studies on exposure we do have are very limited, mainly because we're all getting blasted with Wi-Fi all the time.
(7/7)
It is true that most of these are animal studies, but as we've discussed, the exposure parameters match (or even underestimate) exposures in humans.
There won't be any human trials on this, ever, I can almost guarantee you that.
The human studies on exposure we do have are very limited, mainly because we're all getting blasted with Wi-Fi all the time.
(7/7)

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh