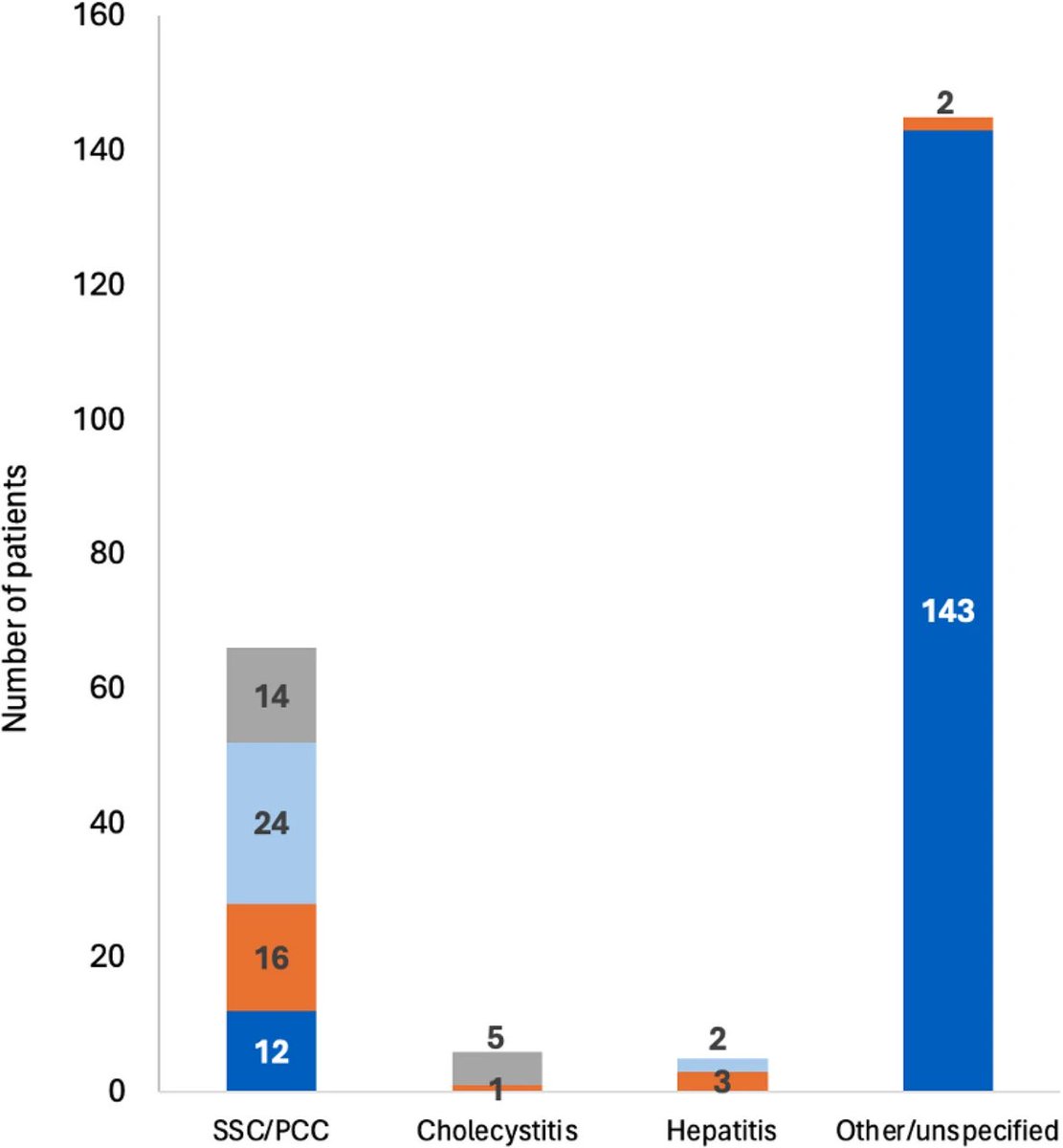
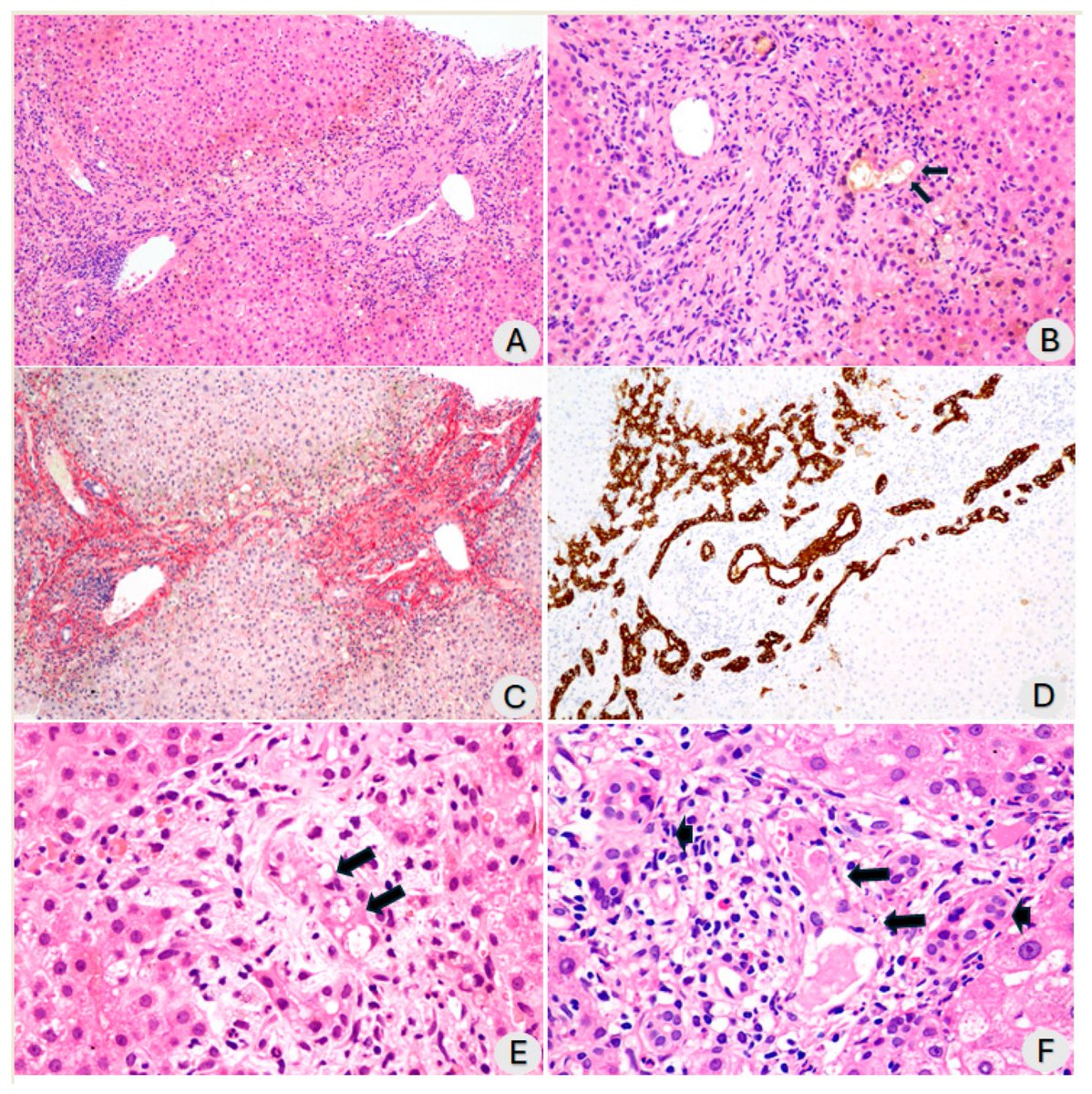
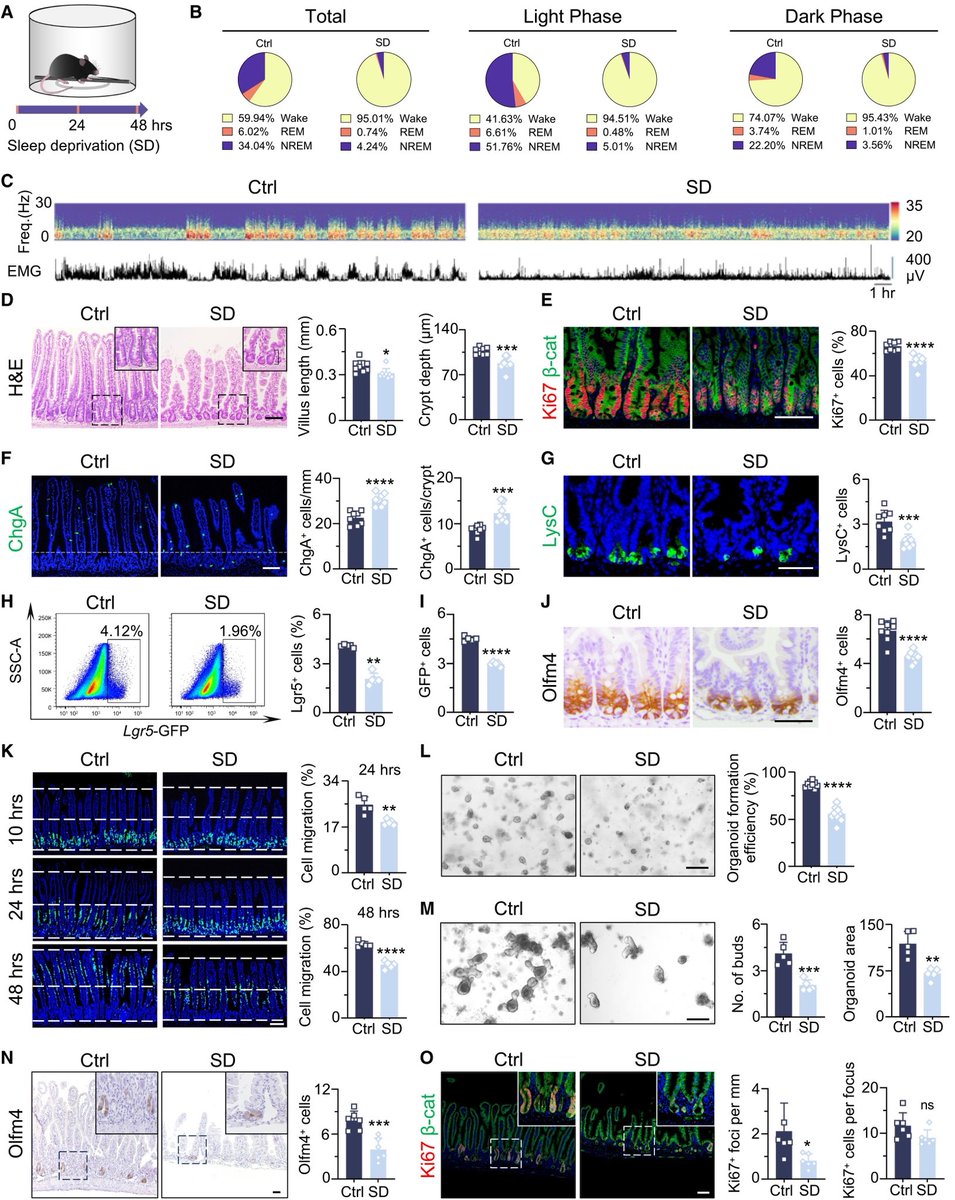
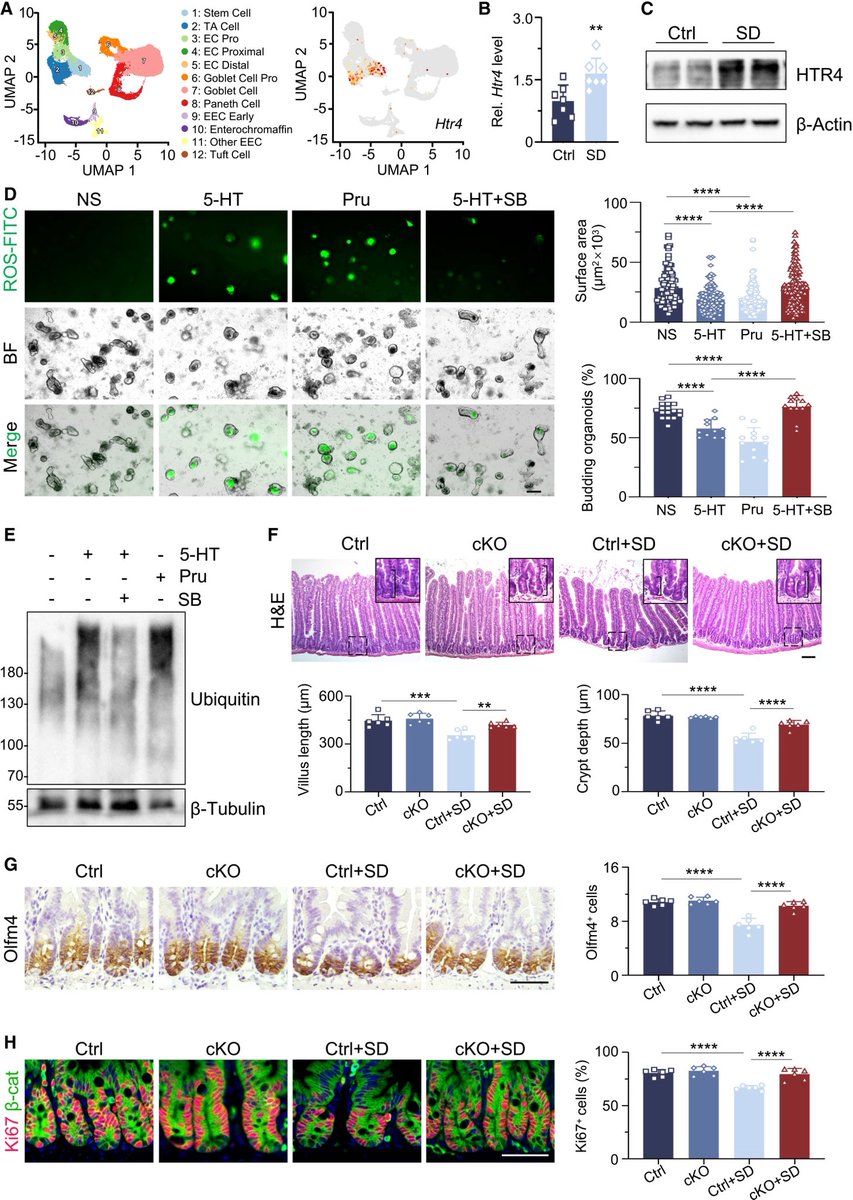
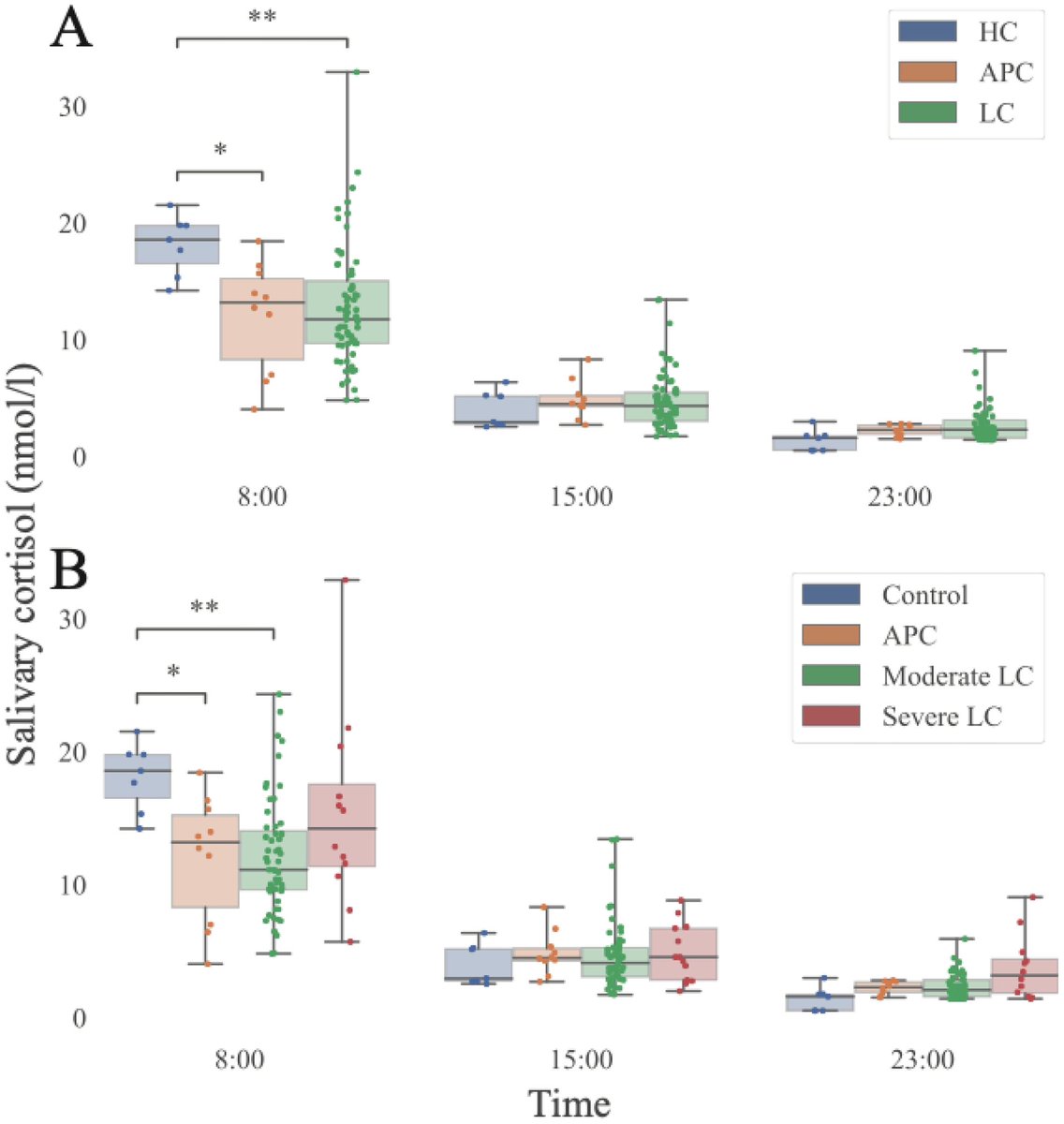
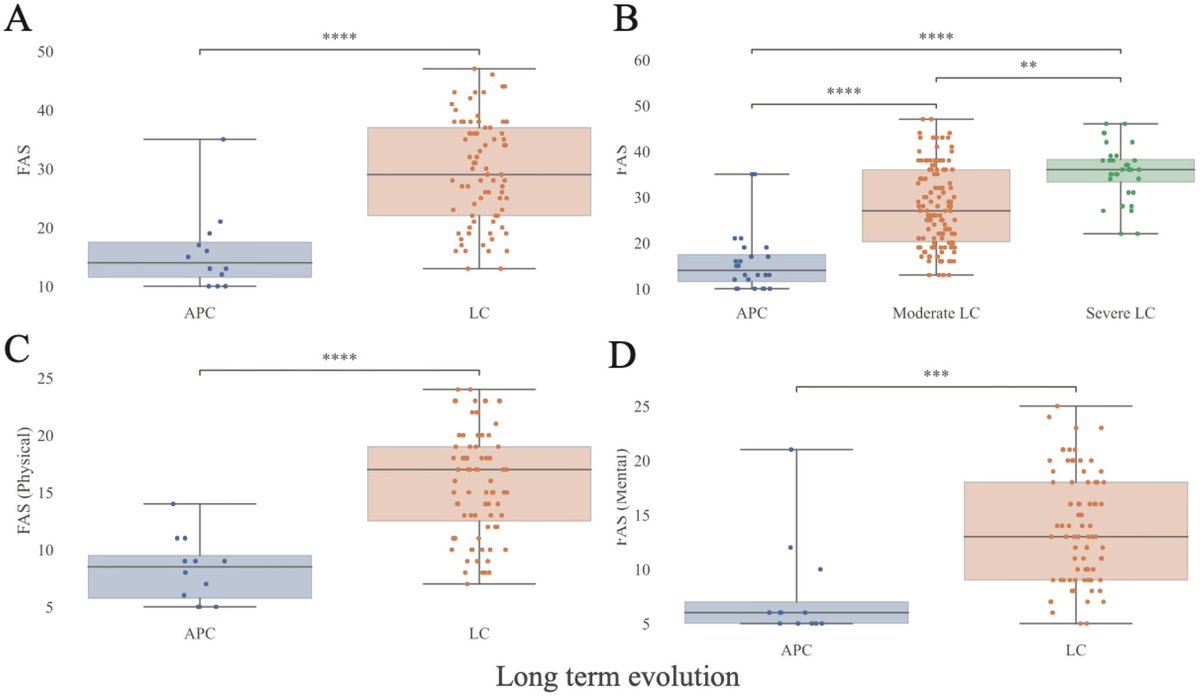
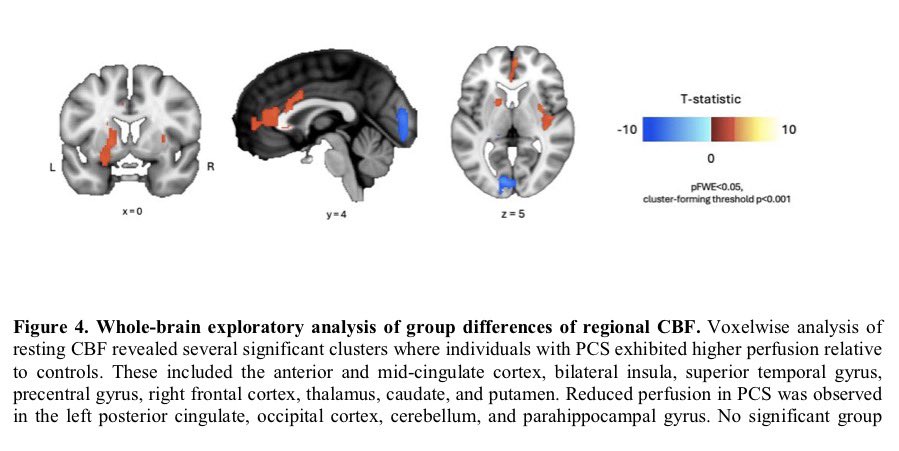
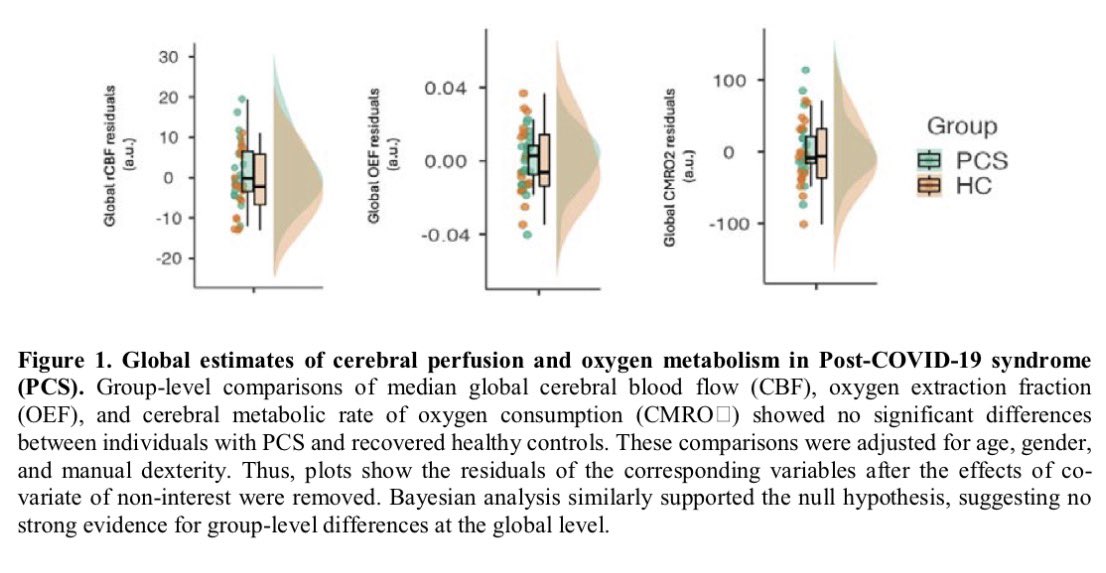
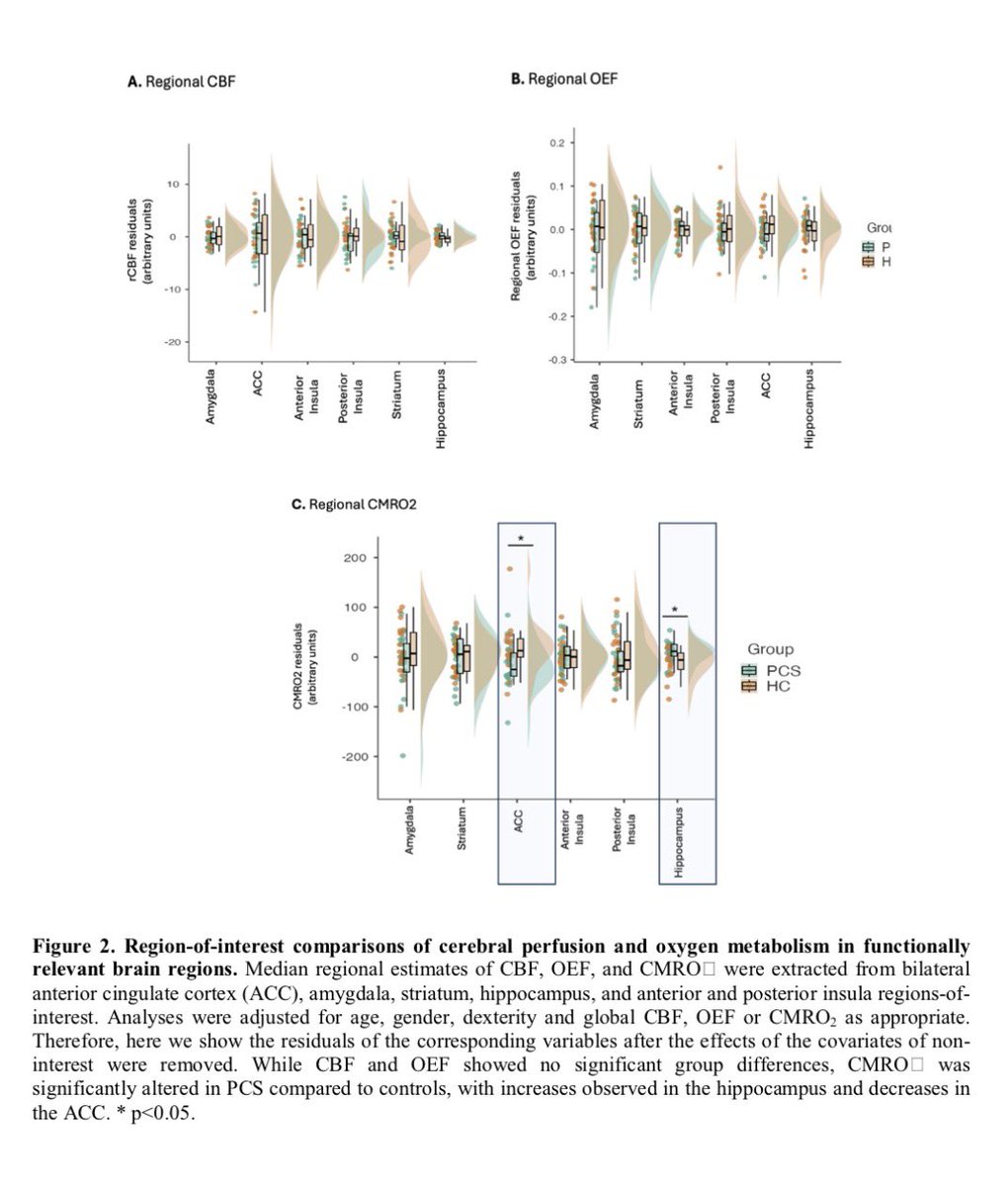
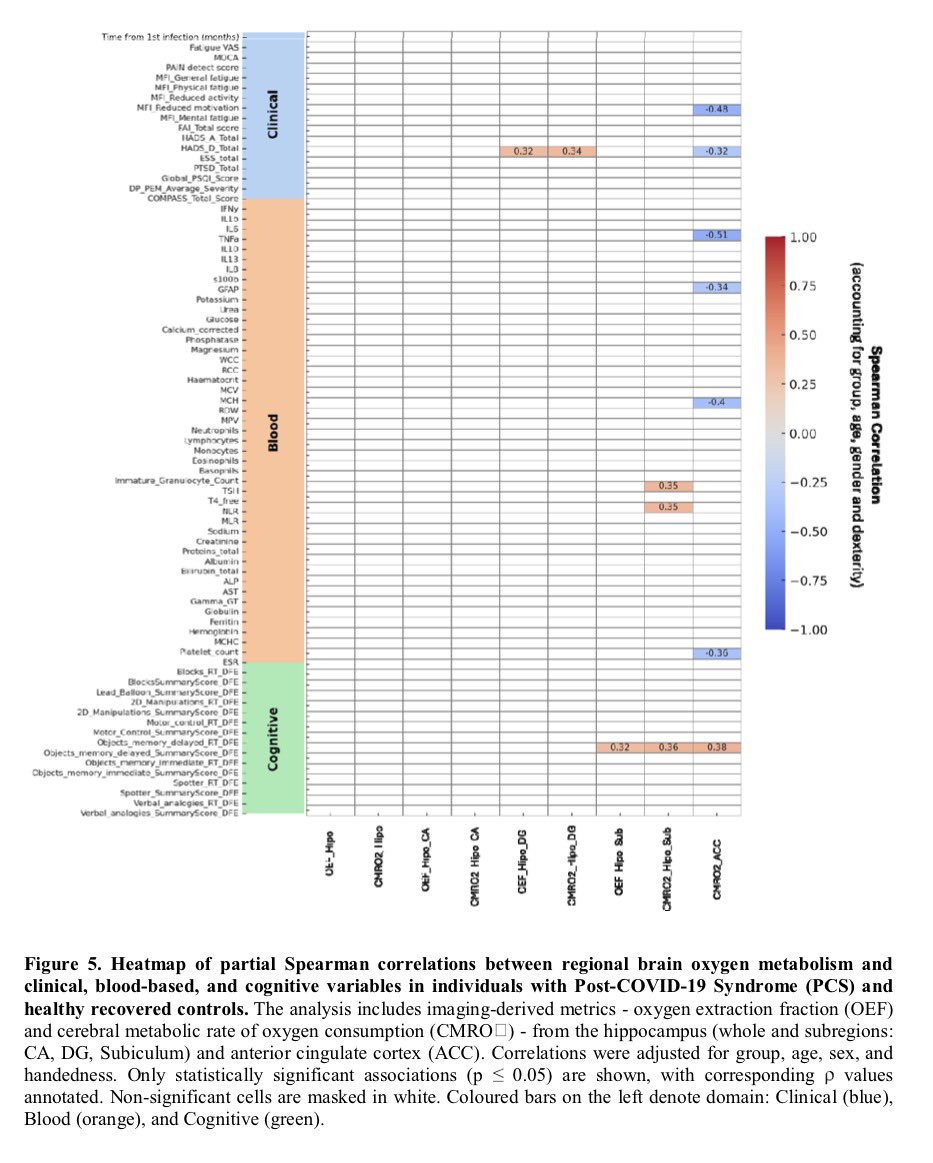
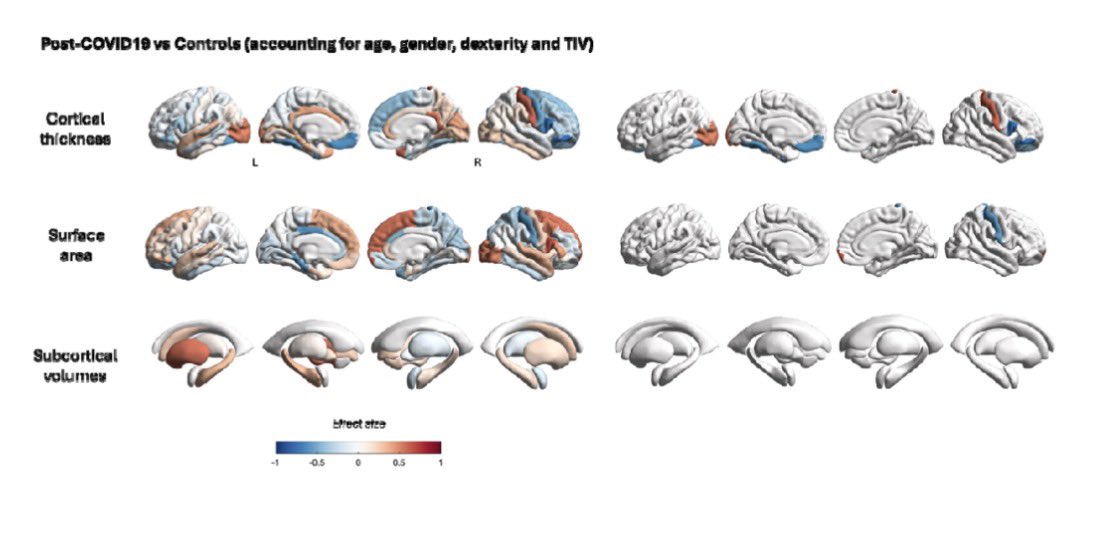
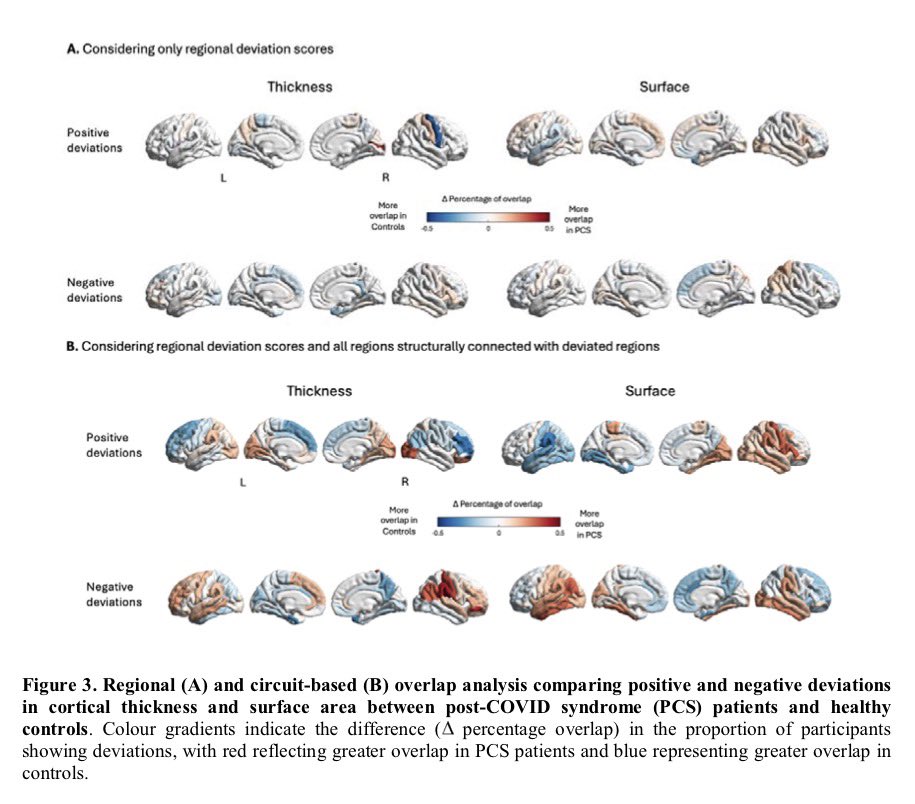
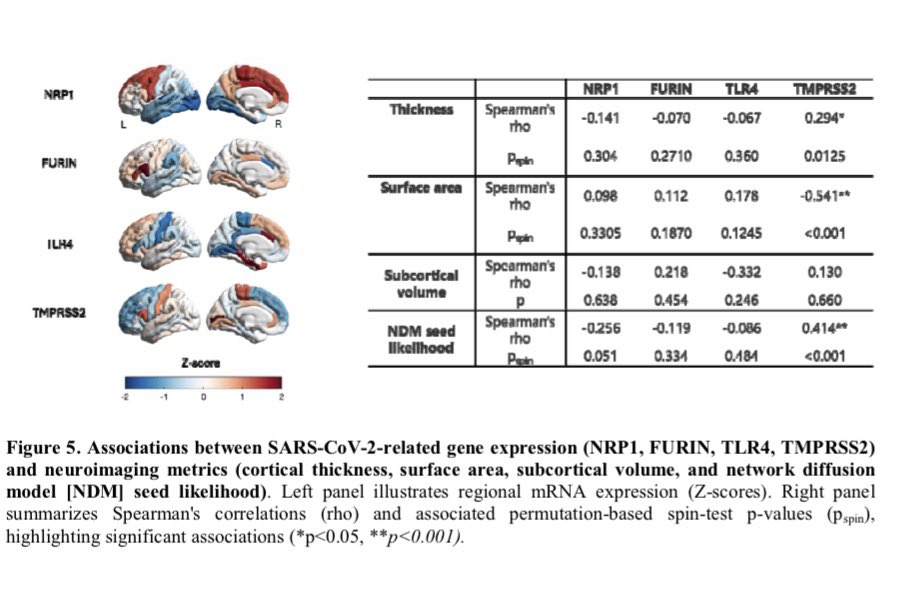
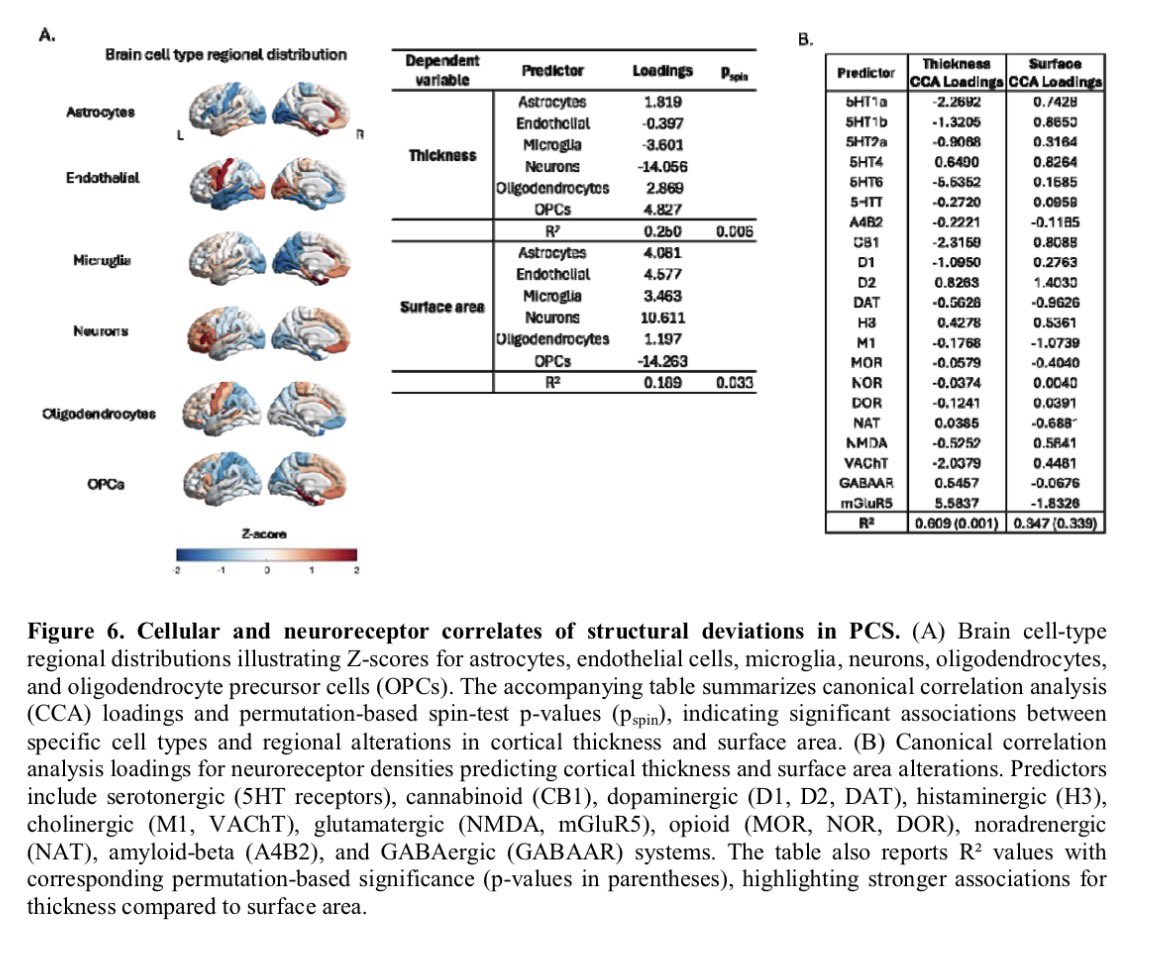
It is currently debatable whether mucosal vaccination is still warranted given that most individuals in developed countries have established a hybrid immunity from vaccination and infection.
➡️ In a new study, researchers studied how our immune system in the airways (the “mucosal” immune system) responds to COVID infection, vaccines, and special mucosal booster vaccines. 1/
➡️ In a new study, researchers studied how our immune system in the airways (the “mucosal” immune system) responds to COVID infection, vaccines, and special mucosal booster vaccines. 1/
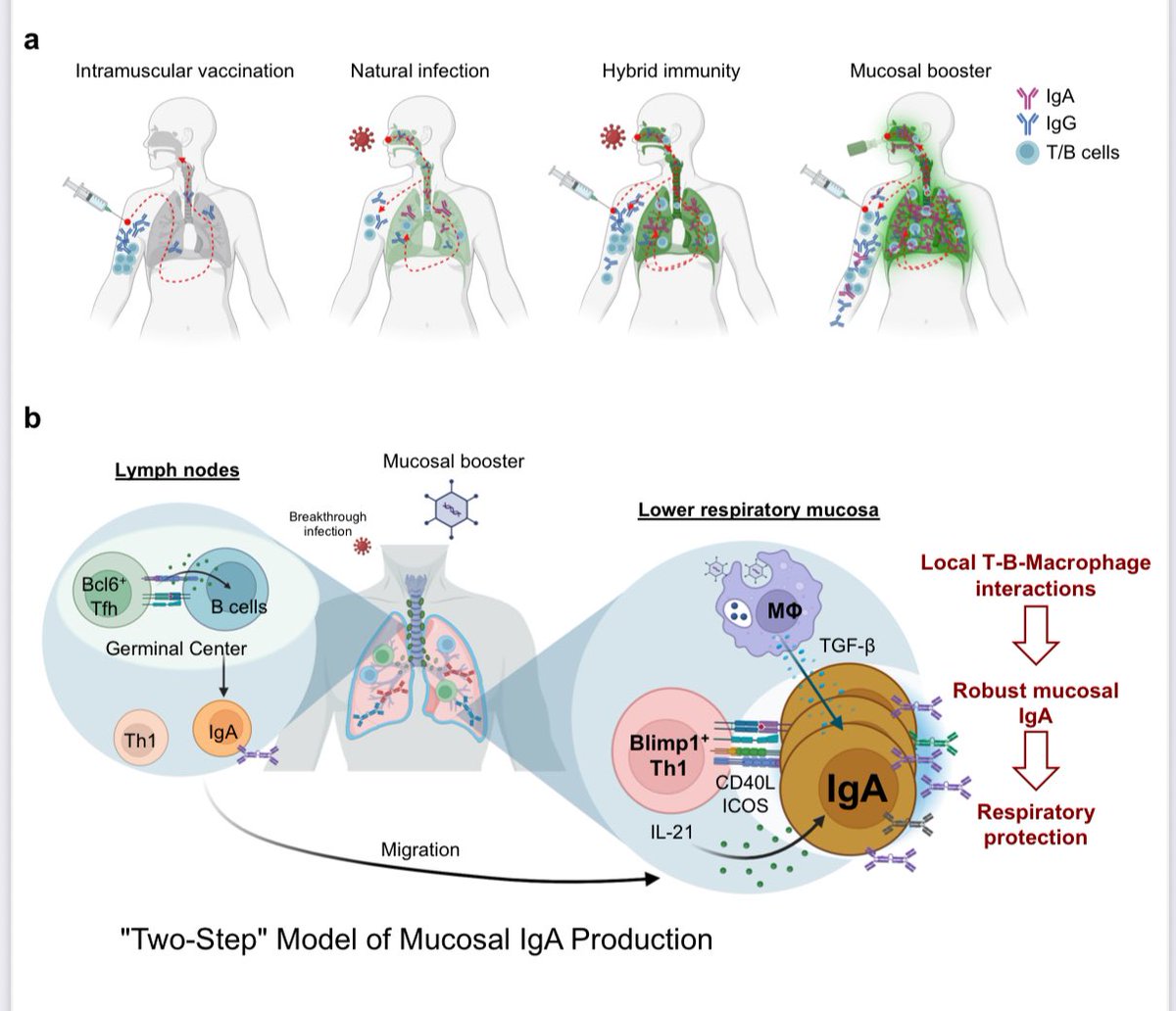
What they found in people:
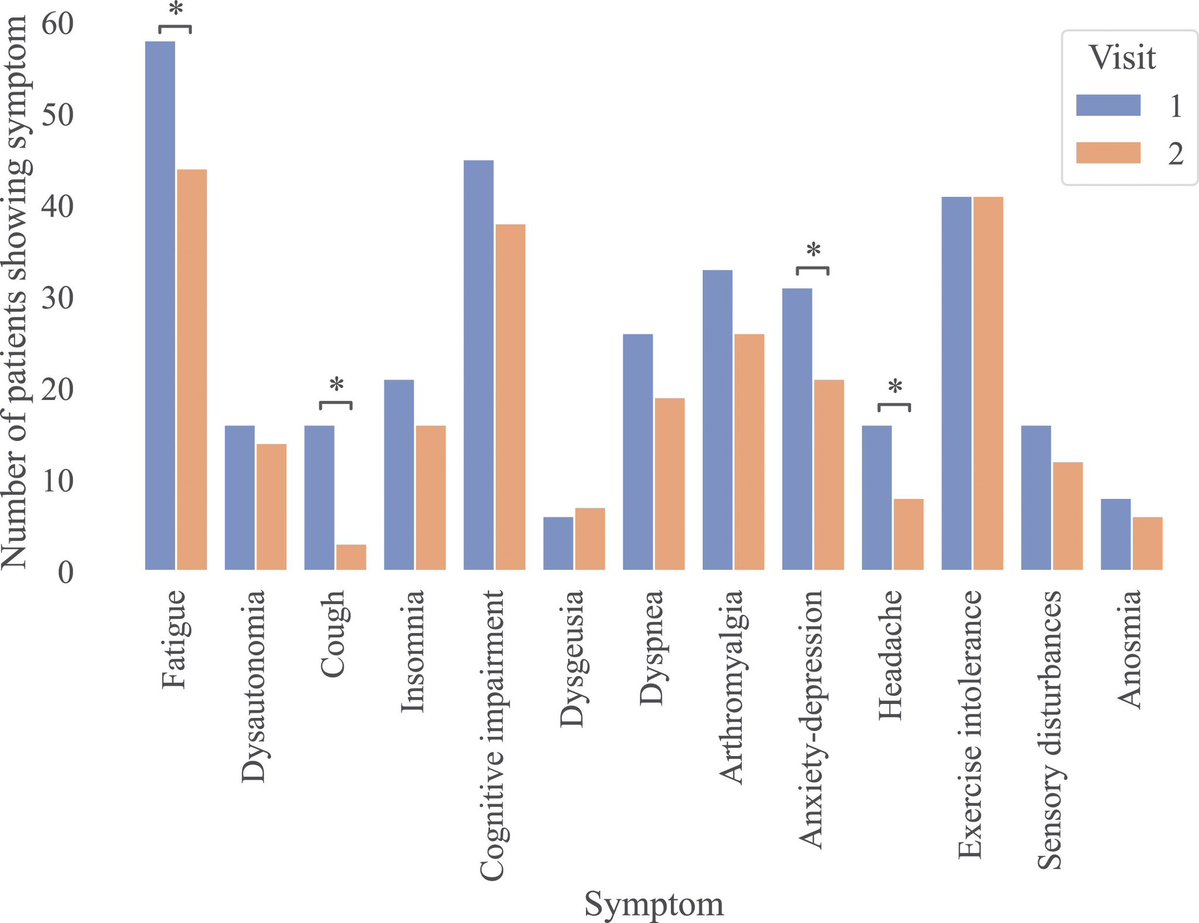
➡️ Having both vaccination + prior infection (“hybrid immunity”) gave only a modest increase in protective antibodies (IgA) in the nose and lungs compared to infection or vaccination alone. 2/
➡️ Having both vaccination + prior infection (“hybrid immunity”) gave only a modest increase in protective antibodies (IgA) in the nose and lungs compared to infection or vaccination alone. 2/

What the researchers found in animal models:
➡️ Giving a mucosal booster vaccine (delivered to the airways using an adenovirus-based vaccine) worked much better. It:
-Strongly boosted IgA antibodies in the nose and lungs
-Triggered local T-cells in the airways
-Provided stronger, longer-lasting protection against SARS-CoV-2. 3/
➡️ Giving a mucosal booster vaccine (delivered to the airways using an adenovirus-based vaccine) worked much better. It:
-Strongly boosted IgA antibodies in the nose and lungs
-Triggered local T-cells in the airways
-Provided stronger, longer-lasting protection against SARS-CoV-2. 3/

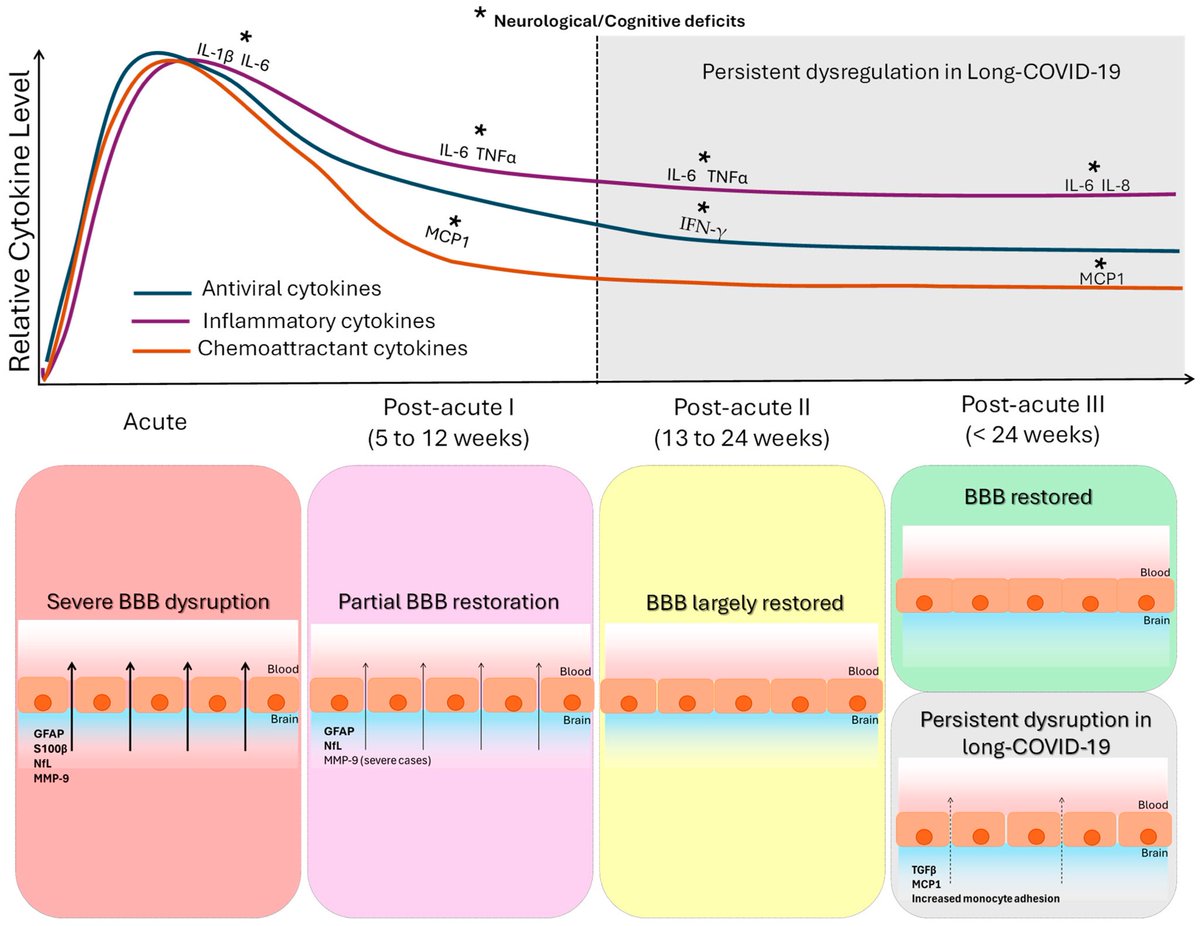
The mechanism behind above findings:
-Local CD4+ T cells in the lungs help B cells make IgA.
-Special T cells producing IL-21 (Blimp-1+ Th1 cells) are key players.
-Lung macrophages release TGF-β, which also supports IgA production.
-Importantly, delivering the vaccine directly into the lower airways was needed to get strong IgA in both upper and lower respiratory tracts. 4/
-Local CD4+ T cells in the lungs help B cells make IgA.
-Special T cells producing IL-21 (Blimp-1+ Th1 cells) are key players.
-Lung macrophages release TGF-β, which also supports IgA production.
-Importantly, delivering the vaccine directly into the lower airways was needed to get strong IgA in both upper and lower respiratory tracts. 4/

Why it matters:
➡️ Mucosal booster vaccines can build a stronger frontline defense in the airways than current vaccines or hybrid immunity, making them a promising approach for COVID and other airborne viruses. 5/
➡️ Mucosal booster vaccines can build a stronger frontline defense in the airways than current vaccines or hybrid immunity, making them a promising approach for COVID and other airborne viruses. 5/
Key Takeaway:
➡️ Hybrid immunity gives some airway protection, but mucosal booster vaccines are far more effective at triggering strong and lasting “local” immunity in the lungs and nose.
➡️ Hybrid immunity isn’t enough for the airways. Mucosal boosters could be the key to stronger, longer-lasting frontline defense against COVID & other airborne viruses. 6/6
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
➡️ Hybrid immunity gives some airway protection, but mucosal booster vaccines are far more effective at triggering strong and lasting “local” immunity in the lungs and nose.
➡️ Hybrid immunity isn’t enough for the airways. Mucosal boosters could be the key to stronger, longer-lasting frontline defense against COVID & other airborne viruses. 6/6
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh