The Oldest Woman (117) Had “High” Cholesterol 🩸— Here’s What That Really Means🤔(Link 🔗 in 8/8)
1/8) The world’s oldest woman just died. Before she passed, she pleaded, “Please study me.”
A new paper in Cell Reports Medicine (PMID: 39322234) just published provides a deep dive into her genes, metabolism and microbiome. What made this 117-year-old such a supercentenarian?
As a metabolism scientist, this is the kind of data I’d die for (figuratively speaking). Stick with me. I’ll break down what her biology really tells us about aging, and why we might be obsessed with the wrong biomarkers.
1/8) The world’s oldest woman just died. Before she passed, she pleaded, “Please study me.”
A new paper in Cell Reports Medicine (PMID: 39322234) just published provides a deep dive into her genes, metabolism and microbiome. What made this 117-year-old such a supercentenarian?
As a metabolism scientist, this is the kind of data I’d die for (figuratively speaking). Stick with me. I’ll break down what her biology really tells us about aging, and why we might be obsessed with the wrong biomarkers.

2/8) When I first read the paper, I noticed something odd.
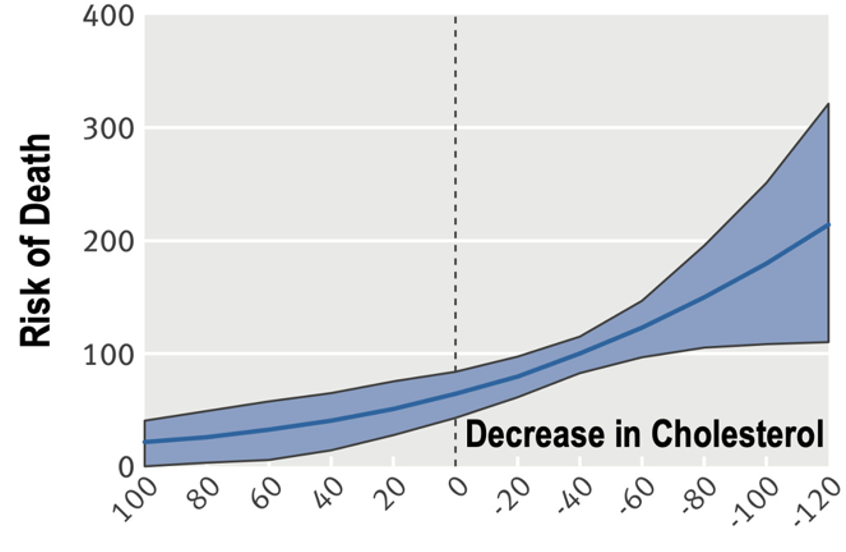
The authors detailed her lipid profile (HDL, VLDL-TG, etc.) but her LDL-C and ApoB—the numbers most doctors obsess over—was nowhere in the main text.
I had to go hunting in the supplementary data. There it was, buried in a single line of Supplemental Figure 8B: elevated, and in the “red.” -- Granted, it wasn’t super high… but it wasn’t low either.
So what gives? Why was it not mentioned in the main text. I provide thoughts (not conspiracy theories) in the letter. But now I know I have your attention…
cc @realDaveFeldman @AdrianSotoMota
The authors detailed her lipid profile (HDL, VLDL-TG, etc.) but her LDL-C and ApoB—the numbers most doctors obsess over—was nowhere in the main text.
I had to go hunting in the supplementary data. There it was, buried in a single line of Supplemental Figure 8B: elevated, and in the “red.” -- Granted, it wasn’t super high… but it wasn’t low either.
So what gives? Why was it not mentioned in the main text. I provide thoughts (not conspiracy theories) in the letter. But now I know I have your attention…
cc @realDaveFeldman @AdrianSotoMota

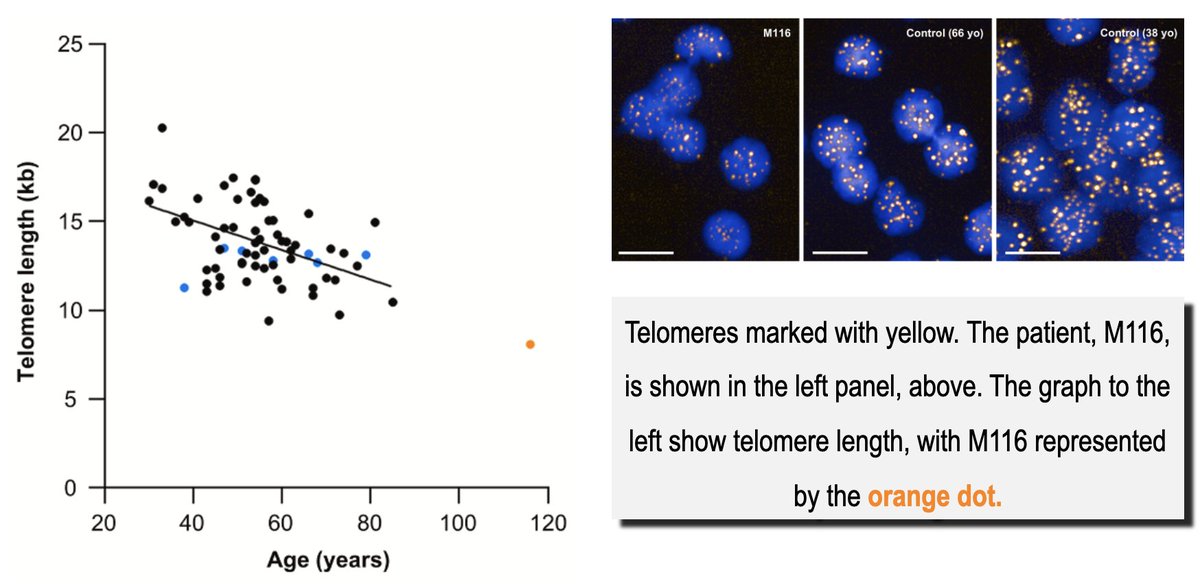
3/8) Now for the next “paradox” - her telomeres 🧬😲
Telomeres are the protective caps on our chromosomes. Think of them like the plastic tips on a shoelace. The prevailing wisdom is that as they shorten with age, our health declines.
You’d expect a 117-year-old to have either freakishly long telomeres or be riddled with disease. Maria Morera had neither.
Her telomeres were tiny!!! I was expecting Godzilla telomeres and was met with chihuahuas exactly as short as you'd predict for her chronological age.
Yet, she was remarkably healthy. This is a crucial finding: telomere length may simply be a clock, not a direct measure of your healthspan.
cc @bryan_johnson, of interest?
Telomeres are the protective caps on our chromosomes. Think of them like the plastic tips on a shoelace. The prevailing wisdom is that as they shorten with age, our health declines.
You’d expect a 117-year-old to have either freakishly long telomeres or be riddled with disease. Maria Morera had neither.
Her telomeres were tiny!!! I was expecting Godzilla telomeres and was met with chihuahuas exactly as short as you'd predict for her chronological age.
Yet, she was remarkably healthy. This is a crucial finding: telomere length may simply be a clock, not a direct measure of your healthspan.
cc @bryan_johnson, of interest?
4/8) So if it wasn't long telomeres, what set her apart?
Her mitochondria. As every high schooler knows, these are the “powerhouses in our cells,” and their decline is a key hallmark of aging.
Maria’s, however, were functioning like those of someone decades younger. The paper notes her mitochondria showed "not only preserved but also robust mitochondrial function."
cc @ChrisPalmerMD @MitoPsychoBio
Her mitochondria. As every high schooler knows, these are the “powerhouses in our cells,” and their decline is a key hallmark of aging.
Maria’s, however, were functioning like those of someone decades younger. The paper notes her mitochondria showed "not only preserved but also robust mitochondrial function."
cc @ChrisPalmerMD @MitoPsychoBio

5/8) The evidence for her low "inflammaging" status is compelling. Beyond her genetics, her bloodwork showed remarkably low levels of GlycA and GlycB—advanced biomarkers of systemic inflammation. 🔥
Summary so far: Genetics gave her an edge → leading to highly efficient mitochondria and a low inflammatory burden → which created a biological environment where factors like high LDL or short telomeres didn't lead to disease.
Summary so far: Genetics gave her an edge → leading to highly efficient mitochondria and a low inflammatory burden → which created a biological environment where factors like high LDL or short telomeres didn't lead to disease.

6/8) So, what about her lifestyle? For the last 20 years of her life, she ate a consistent diet that included a conspicuous amount of yogurt—three servings per day.
And the paper even specified the bacterial strains: Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. She was also a heavy user of egg protein and olive oil.
I feel almost as if I designed her diet!
P.S. Smoked Maldon Salt Greek Yogurt is a 12/10
And the paper even specified the bacterial strains: Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. She was also a heavy user of egg protein and olive oil.
I feel almost as if I designed her diet!
P.S. Smoked Maldon Salt Greek Yogurt is a 12/10
7/8) The clinical implications here are profound. Her case suggests that a state of low inflammation, a “highly engaged lipid metabolism,” and good mitochondrial health can grant resilience against factors we typically view as "bad." Yes, she was genetically gifted. But we can still turn her insights into action… What do we do with this knowledge?
8/8) In the rest of the letter (linked below), we turn these insights into action.
While you can't change your genes, you can support your mitochondria.
I break down her full meal plan, the specific U.S. yogurt brands I found that contain those exact bacterial strains, and actionable strategies — from fasting protocols to light exposure — that support the same mitochondrial resilience seen in this remarkable supercentenarian.
Premium subscribers get full access for less than 67 cents per letter. Read the full breakdown here → staycuriousmetabolism.substack.com/p/the-oldest-w…
While you can't change your genes, you can support your mitochondria.
I break down her full meal plan, the specific U.S. yogurt brands I found that contain those exact bacterial strains, and actionable strategies — from fasting protocols to light exposure — that support the same mitochondrial resilience seen in this remarkable supercentenarian.
Premium subscribers get full access for less than 67 cents per letter. Read the full breakdown here → staycuriousmetabolism.substack.com/p/the-oldest-w…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh