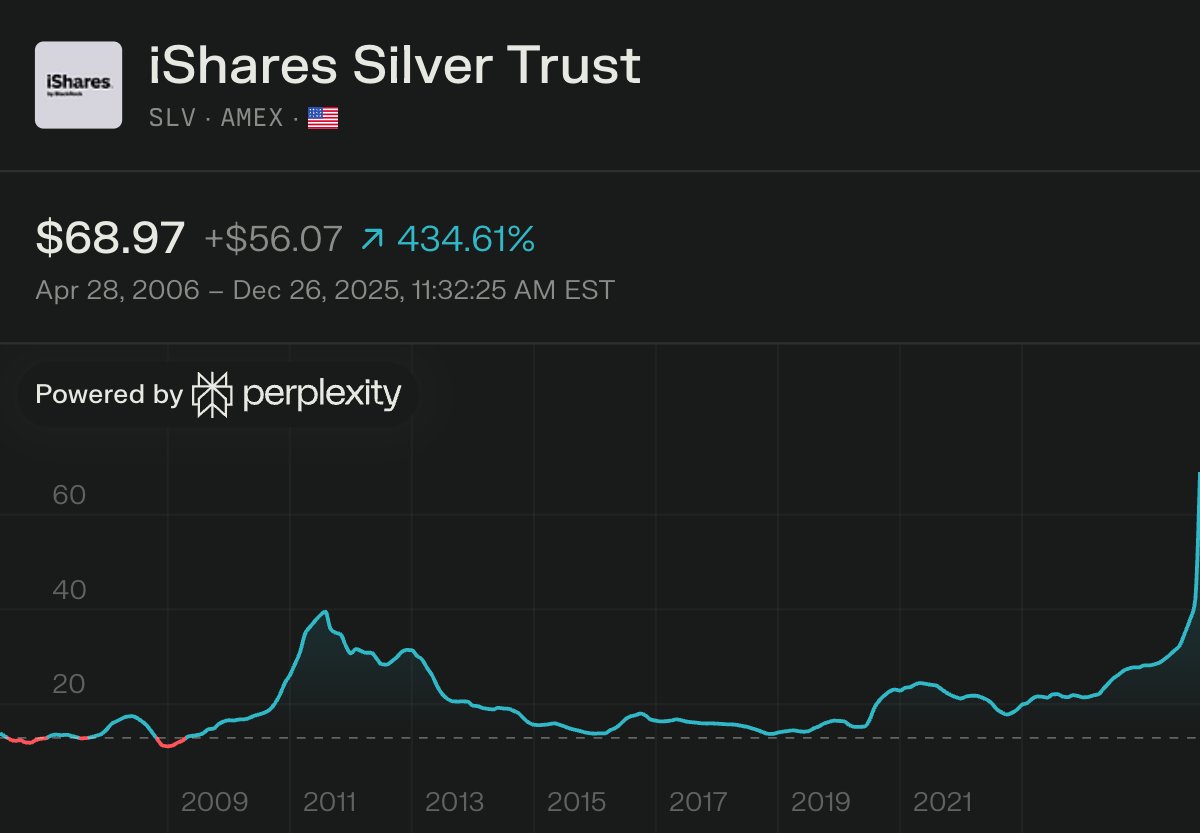
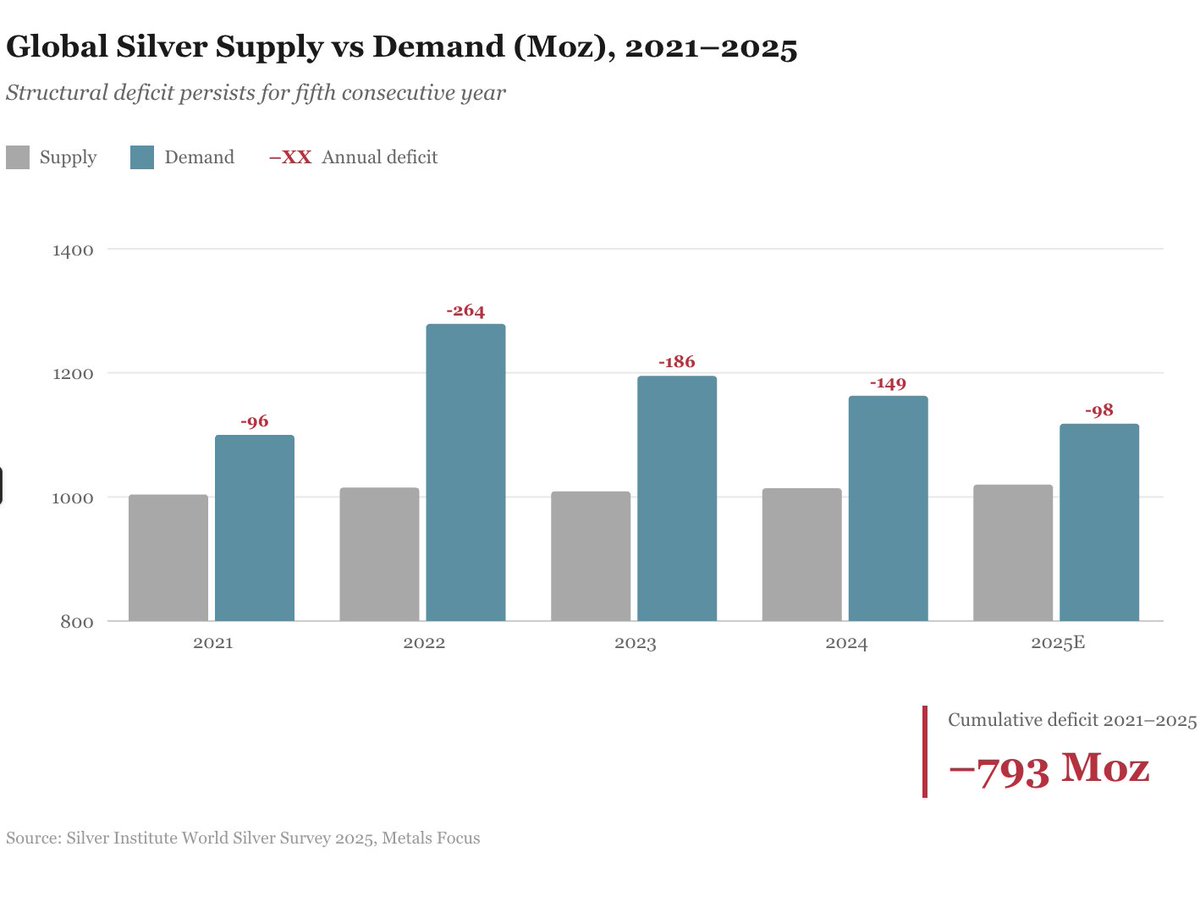
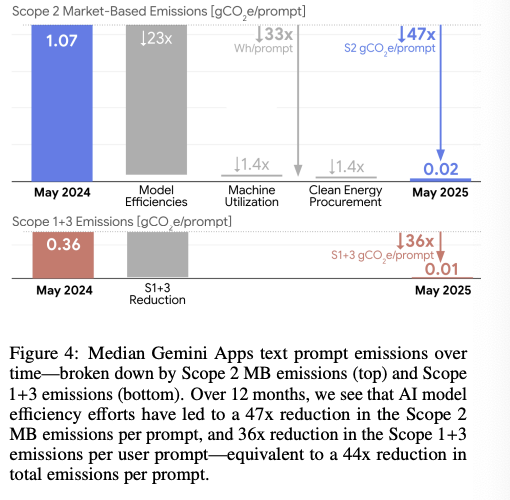
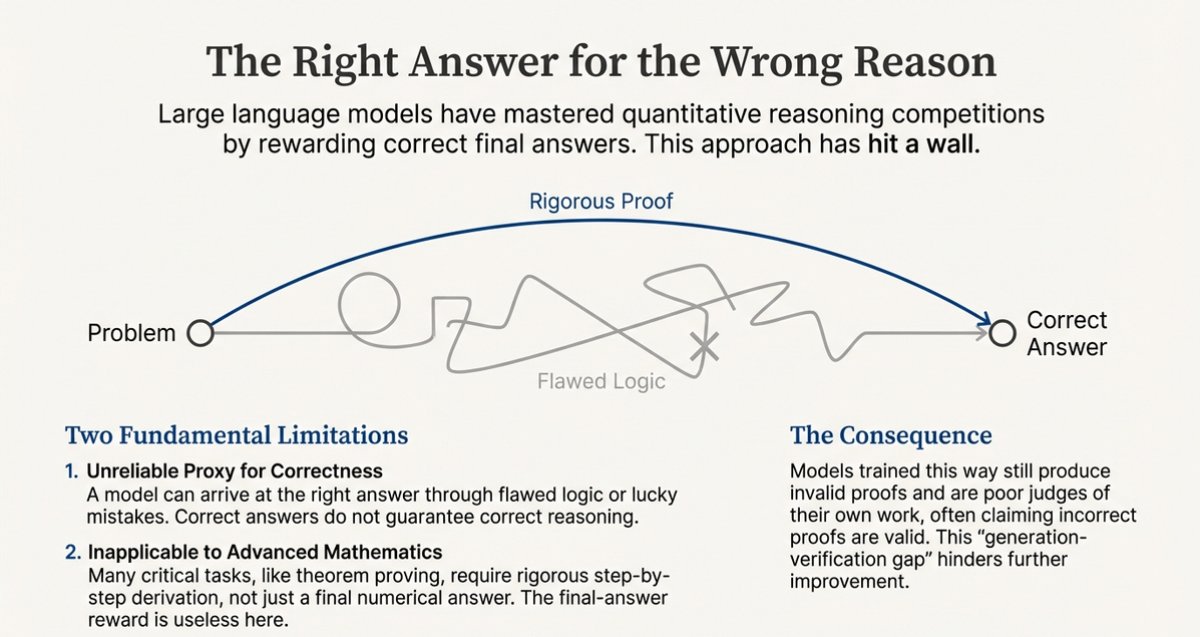
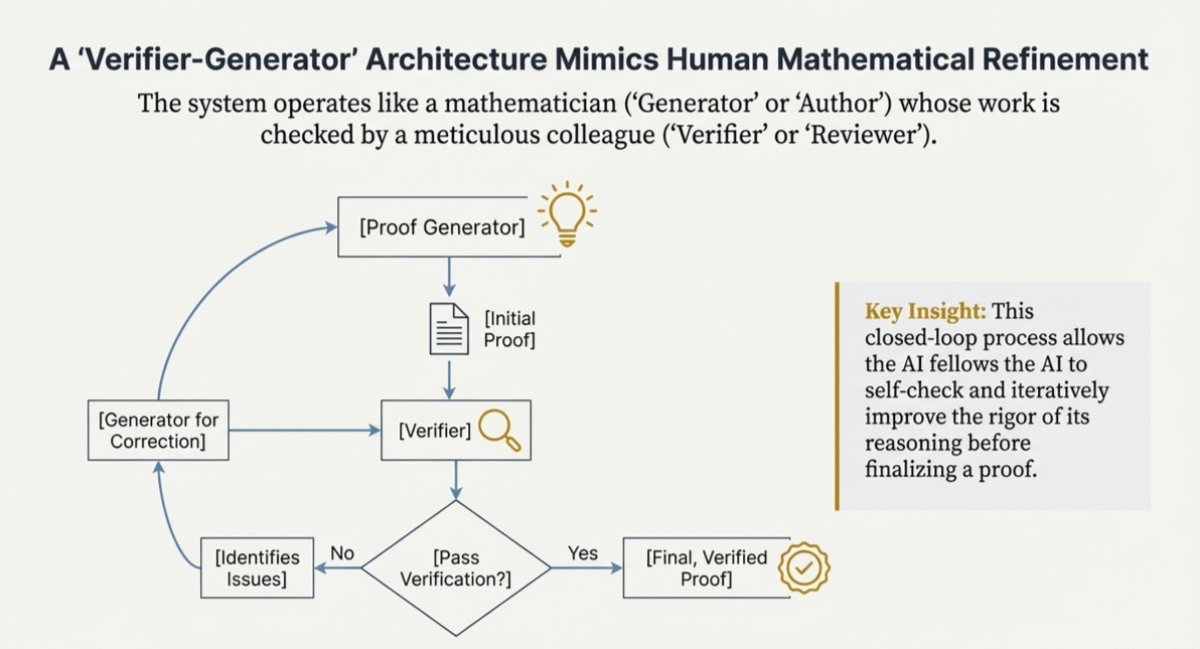
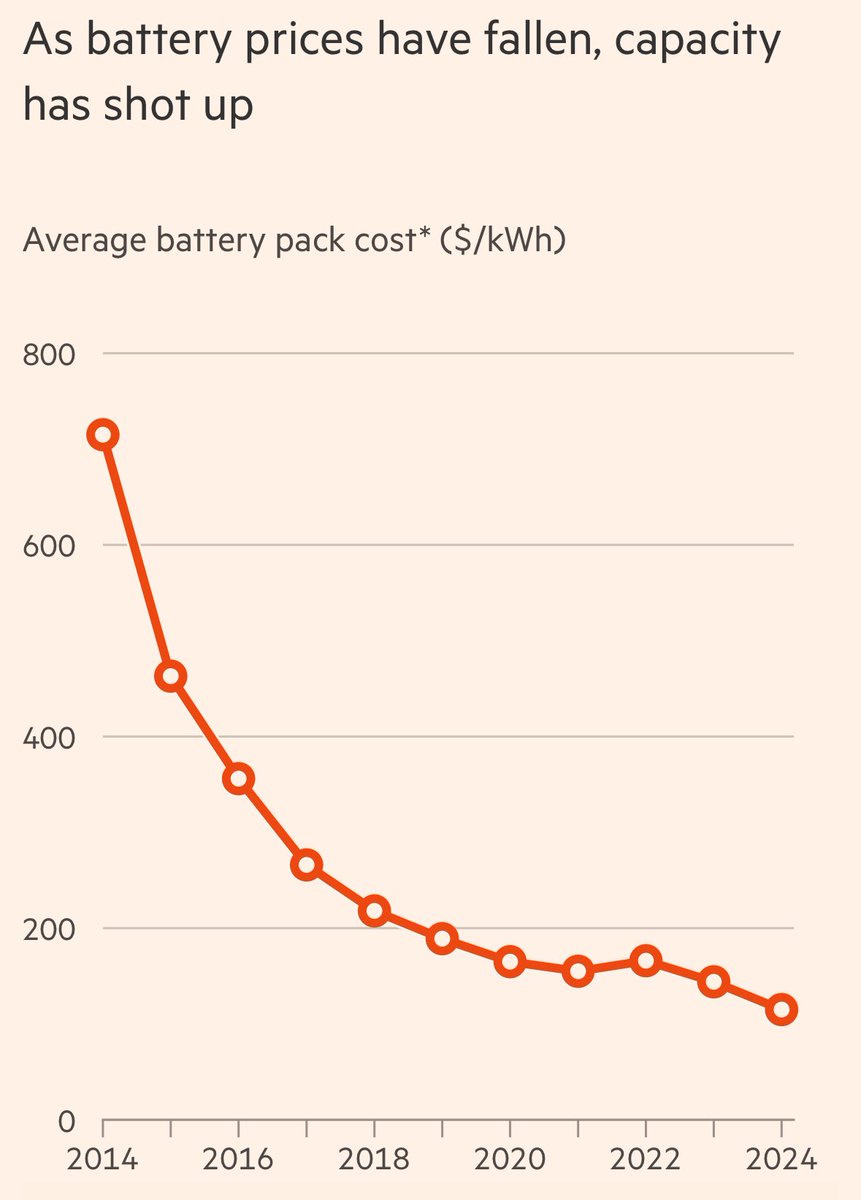
Oct 9, 2025: China's Ministry of Commerce issued Announcements No. 61 & 62, expanding rare earth export controls to 12 of 17 elements and imposing extraterritorial licensing requirements.
This is direct retaliation for U.S. semiconductor export bans announced days earlier.
China controls 70% of global mining, 90% of processing, and 93% of permanent magnet production. Each F-35 requires 417kg of rare earths. China refines 100% of global samarium.
What does this mean for U.S. defense? How will this affect AI data centers? What happens to semiconductor and EV supply chains? Let's dive in:
This is direct retaliation for U.S. semiconductor export bans announced days earlier.
China controls 70% of global mining, 90% of processing, and 93% of permanent magnet production. Each F-35 requires 417kg of rare earths. China refines 100% of global samarium.
What does this mean for U.S. defense? How will this affect AI data centers? What happens to semiconductor and EV supply chains? Let's dive in:

1/12: TIMING IS EVERYTHING
The announcement came days after U.S. expanded chip export bans (Oct 7, targeting ASML/TSMC) and weeks before two critical deadlines:
• 90-day U.S.-China trade truce expires
• Trump-Xi meeting in South Korea
Strategic retaliation designed to maximize Beijing's leverage in upcoming negotiations.
The announcement came days after U.S. expanded chip export bans (Oct 7, targeting ASML/TSMC) and weeks before two critical deadlines:
• 90-day U.S.-China trade truce expires
• Trump-Xi meeting in South Korea
Strategic retaliation designed to maximize Beijing's leverage in upcoming negotiations.
2/12: RARE EARTHS 101
17 elements (lanthanides + yttrium/scandium) critical for high-tech applications—magnets, lasers, semiconductors.
They're not "rare" geologically, but incredibly hard to process:
• Only 0.1-1% concentration in ore
• Creates radioactive byproducts (thorium), driving up environmental and political costs
China dominates via low-cost mining and vertical integration. The Bayan Obo mine alone produces 70% of global light rare earths.
17 elements (lanthanides + yttrium/scandium) critical for high-tech applications—magnets, lasers, semiconductors.
They're not "rare" geologically, but incredibly hard to process:
• Only 0.1-1% concentration in ore
• Creates radioactive byproducts (thorium), driving up environmental and political costs
China dominates via low-cost mining and vertical integration. The Bayan Obo mine alone produces 70% of global light rare earths.

3/12: WHAT'S ACTUALLY RESTRICTED - ELEMENTS & MATERIALS
China added 5 rare earths to the restricted list: holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), europium (Eu), and ytterbium (Yb)—critical for lasers, fiber optics, and defense systems.
That means 12 out of 17 rare earths are now restricted, including neodymium (Nd), praseodymium (Pr), and dysprosium (Dy) from April.
Plus dozens of refining and mining equipment items.
Effective: Nov 8 for elements/equipment, Dec 1 full implementation.
China added 5 rare earths to the restricted list: holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), europium (Eu), and ytterbium (Yb)—critical for lasers, fiber optics, and defense systems.
That means 12 out of 17 rare earths are now restricted, including neodymium (Nd), praseodymium (Pr), and dysprosium (Dy) from April.
Plus dozens of refining and mining equipment items.
Effective: Nov 8 for elements/equipment, Dec 1 full implementation.
4/12: FOREIGN PRODUCTS
Any product with >0.1% Chinese-sourced rare earths needs Beijing's export license for re-export.
Even if it's made in Taiwan. Or Vietnam. Or Texas.
This is China's version of the U.S. Foreign Direct Product Rule. Extraterritorial control over global supply chains.
Any product with >0.1% Chinese-sourced rare earths needs Beijing's export license for re-export.
Even if it's made in Taiwan. Or Vietnam. Or Texas.
This is China's version of the U.S. Foreign Direct Product Rule. Extraterritorial control over global supply chains.
5/12: MORE CONTROLS
END-USE BANS:
• No licenses for foreign militaries, or weapons
• Case-by-case review for ≤14nm chips, ≥256-layer memory, AI/military R&D
TECHNOLOGY & LABOR:
• Ban on exporting REE mining/processing/recycling tech
• Chinese citizens need government approval to join overseas REE projects
Full compliance deadline: Dec 1, 2025.
END-USE BANS:
• No licenses for foreign militaries, or weapons
• Case-by-case review for ≤14nm chips, ≥256-layer memory, AI/military R&D
TECHNOLOGY & LABOR:
• Ban on exporting REE mining/processing/recycling tech
• Chinese citizens need government approval to join overseas REE projects
Full compliance deadline: Dec 1, 2025.
6/12: CHINA'S DOMINANCE - THE NUMBERS
Mining: 70% global share (240k tons vs U.S. 43k tons)
But here's where it gets scary:
• 90% of global separation/refining
• 93% of permanent magnet production
• 44M tons reserves (37% global)
Global demand: 200k tons/year, growing 7-10% annually from EVs/AI/renewables.
Alternatives exist (Australia's Lynas 8%, U.S. MP Materials 15%), but they all still send ore to China for processing.
Mining: 70% global share (240k tons vs U.S. 43k tons)
But here's where it gets scary:
• 90% of global separation/refining
• 93% of permanent magnet production
• 44M tons reserves (37% global)
Global demand: 200k tons/year, growing 7-10% annually from EVs/AI/renewables.
Alternatives exist (Australia's Lynas 8%, U.S. MP Materials 15%), but they all still send ore to China for processing.

7/12: DEFENSE IMPACT
This is where it gets serious.
Rare earths are irreplaceable in military hardware due to magnetic/thermal properties:
• F-35 fighter: 417kg of REEs
• Virginia-class submarine: 4.2 tons
• Tomahawk missiles: REEs in guidance
• Predator drones/JDAMs: precision optics/motors
China refines 100% of global samarium—the element critical for high-temp military magnets.
This is where it gets serious.
Rare earths are irreplaceable in military hardware due to magnetic/thermal properties:
• F-35 fighter: 417kg of REEs
• Virginia-class submarine: 4.2 tons
• Tomahawk missiles: REEs in guidance
• Predator drones/JDAMs: precision optics/motors
China refines 100% of global samarium—the element critical for high-temp military magnets.

8/12: THE DEFENSE CAPABILITY GAP
The implications are stark:
• China builds military hardware 5-6x faster than the U.S.
• U.S. has zero domestic samarium refining capacity
• Short-term: Stockpiles last months
• Long-term: 5-10 years to build independent supply chains
With Indo-Pacific tensions rising, Beijing now has leverage over the foundation of U.S. defense production.
The implications are stark:
• China builds military hardware 5-6x faster than the U.S.
• U.S. has zero domestic samarium refining capacity
• Short-term: Stockpiles last months
• Long-term: 5-10 years to build independent supply chains
With Indo-Pacific tensions rising, Beijing now has leverage over the foundation of U.S. defense production.

9/12: SEMICONDUCTOR CHOKEPOINT
REEs are critical for chip manufacturing:
• Magnets in lithography equipment (ASML's EUV tools)
• Wafer processing equipment
Ban targets ≤14nm chips (Nvidia A100/H100 territory).
TSMC, Samsung, SK Hynix ALL need licenses if using Chinese REEs.
That 0.1% threshold = de-facto veto power over the semiconductor supply chain.
REEs are critical for chip manufacturing:
• Magnets in lithography equipment (ASML's EUV tools)
• Wafer processing equipment
Ban targets ≤14nm chips (Nvidia A100/H100 territory).
TSMC, Samsung, SK Hynix ALL need licenses if using Chinese REEs.
That 0.1% threshold = de-facto veto power over the semiconductor supply chain.

10/12: BROADER ECONOMIC RIPPLES
Markets reacted immediately: Chinese REE stocks surged 9-10%. U.S. miners like MP Materials rose on investment flows.
Short-term: 20-50% price spikes
Key impacts:
• EVs: 30% REE-dependent
• Wind turbines: up to 200kg/MW
• AI data centers: REE magnets for cooling
REE magnet market: $20B (2023) → $30B (2030)
Escalation risk: China controls 80% gallium (LEDs/chips) + 70% lithium refining.
Historical precedent: China's 2010 embargo on Japan sent REE prices up 10x.

Markets reacted immediately: Chinese REE stocks surged 9-10%. U.S. miners like MP Materials rose on investment flows.
Short-term: 20-50% price spikes
Key impacts:
• EVs: 30% REE-dependent
• Wind turbines: up to 200kg/MW
• AI data centers: REE magnets for cooling
REE magnet market: $20B (2023) → $30B (2030)
Escalation risk: China controls 80% gallium (LEDs/chips) + 70% lithium refining.
Historical precedent: China's 2010 embargo on Japan sent REE prices up 10x.


11/12: U.S. COUNTERMOVES
DoD response:
• $400M equity in MP Materials (largest shareholder)
• $150M loan for heavy REE separation
• 10-year offtake for new magnet facility
• Lynas-Noveon partnership for U.S. production
India/Australia ramping exploration.
Recycling emerging: 10-20% recovery potential from e-waste.
Reality check: 5-10 years minimum to scale. U.S. = <5% global processing today.
DoD response:
• $400M equity in MP Materials (largest shareholder)
• $150M loan for heavy REE separation
• 10-year offtake for new magnet facility
• Lynas-Noveon partnership for U.S. production
India/Australia ramping exploration.
Recycling emerging: 10-20% recovery potential from e-waste.
Reality check: 5-10 years minimum to scale. U.S. = <5% global processing today.

13/13: THE BOTTOM LINE
China weaponizing 90% processing monopoly to retaliate for U.S. chip bans. Targeting defense (417kg per F-35) and semiconductors ≤14nm.
Short-term: 20-50% price spikes could throttle AI boom (data centers need REE magnets).
Long-term: Forces Western reindustrialization. Diversification takes years.
THE QUESTION: Can alternatives scale faster than China leverages its monopoly?
Negotiations are possible—Trump-Xi could trade chip access ⟷ REE flow.
The decoupling isn't coming. It's here.
China weaponizing 90% processing monopoly to retaliate for U.S. chip bans. Targeting defense (417kg per F-35) and semiconductors ≤14nm.
Short-term: 20-50% price spikes could throttle AI boom (data centers need REE magnets).
Long-term: Forces Western reindustrialization. Diversification takes years.
THE QUESTION: Can alternatives scale faster than China leverages its monopoly?
Negotiations are possible—Trump-Xi could trade chip access ⟷ REE flow.
The decoupling isn't coming. It's here.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh