@russellwadey Inflation as the Price-Level Representation of Claim Dilution
"If equity exists on the macro balance sheet, then inflation is the logical and empirical representation of claim dilution — i.e., the price-level adjustment that reconciles expanding nominal claims with real output."
"If equity exists on the macro balance sheet, then inflation is the logical and empirical representation of claim dilution — i.e., the price-level adjustment that reconciles expanding nominal claims with real output."
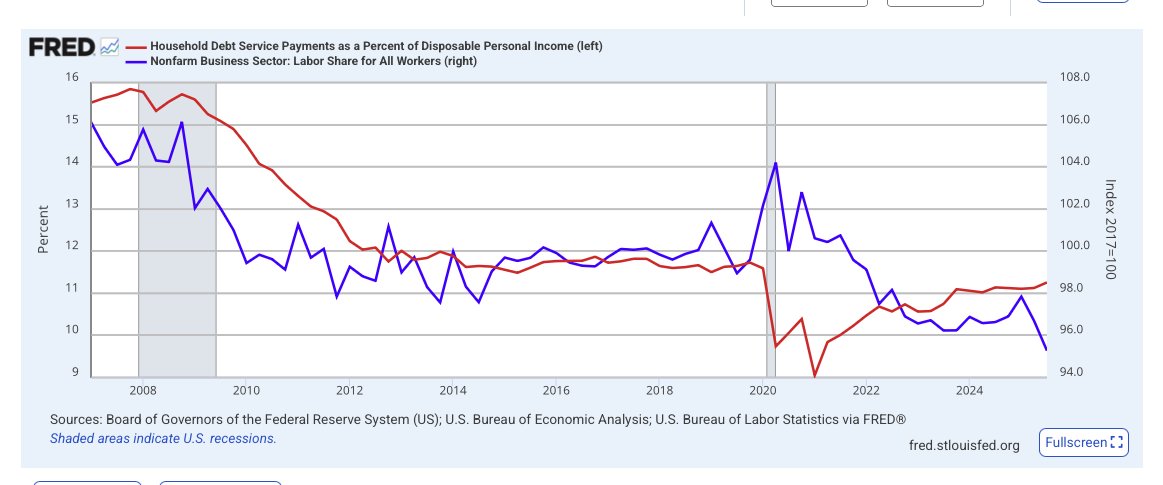
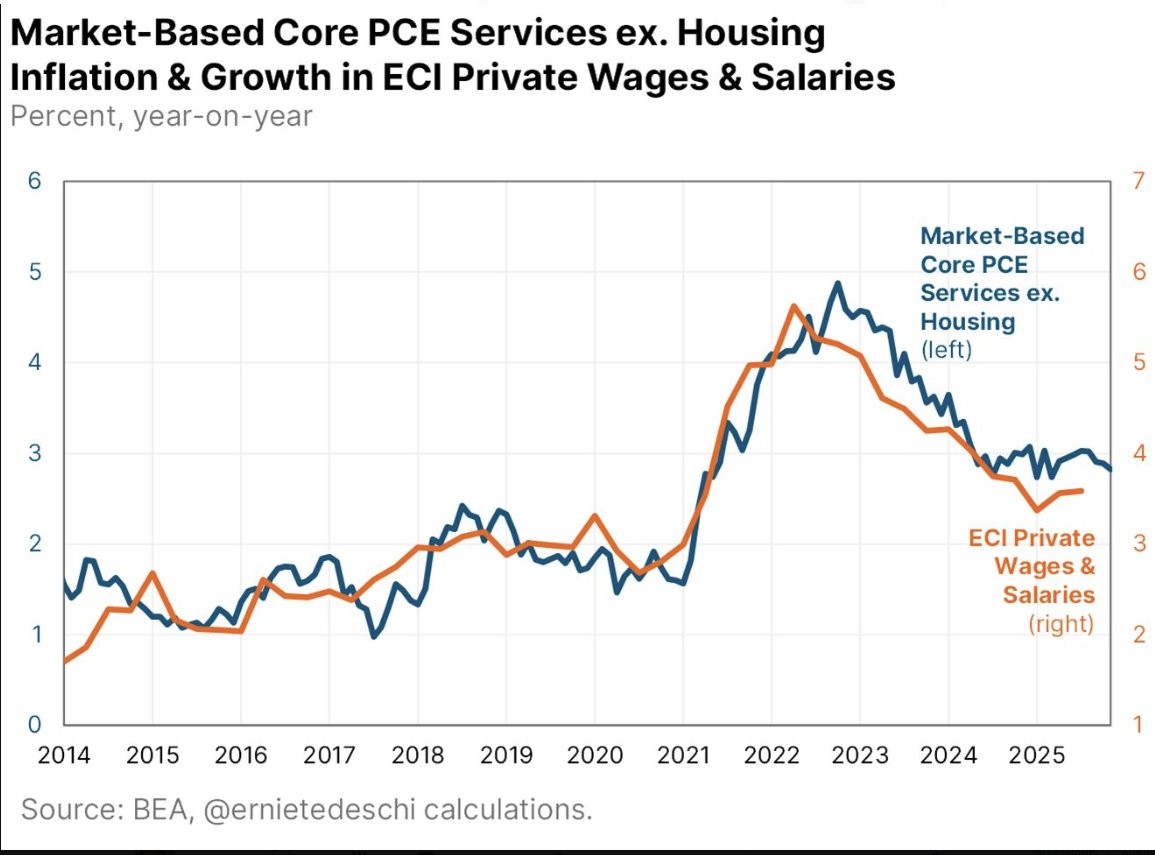
@russellwadey When the total stock of nominal claims expands more rapidly than real output, the purchasing power of each existing claim declines. 
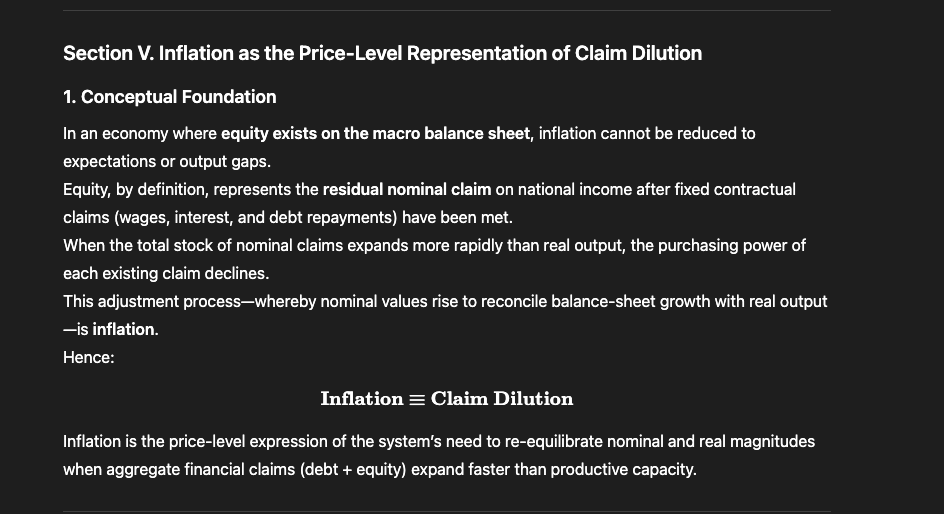
@russellwadey Thus, if equity exists on the balance sheet, inflation is the arithmetic reconciliation of nominal claim expansion with real output. 

@russellwadey Inflation therefore emerges not from excess demand but from excess nominal claims relative to real output. 

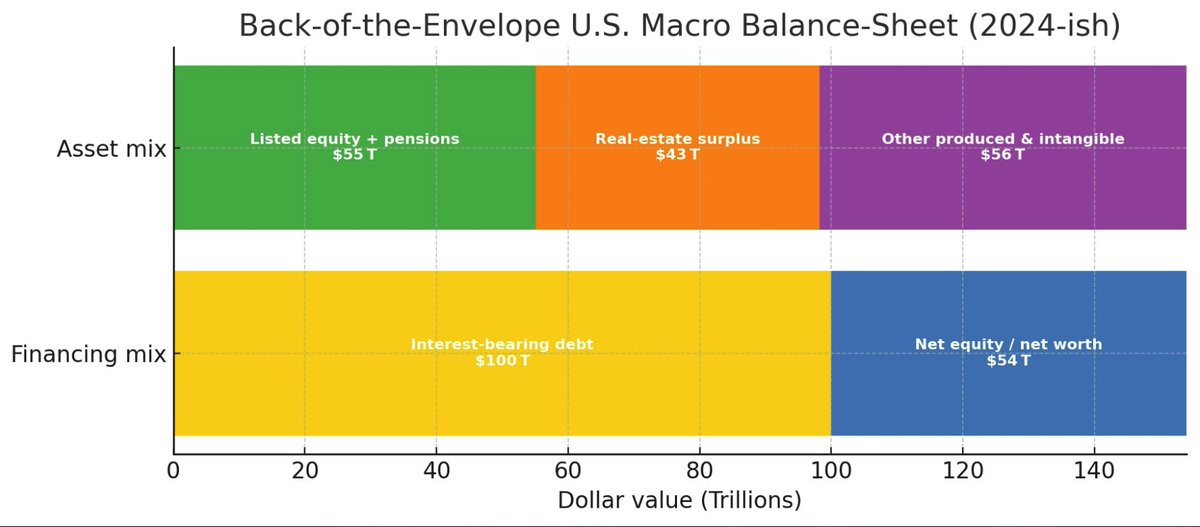
Given supply = demand (aggregate identity), the only independent macro variable is the composition of financial claims.
If equity exists, the system must periodically dilute claims via price-level adjustment.
Inflation is therefore not contingent but structurally necessary in a balance-sheet economy.
If equity exists, the system must periodically dilute claims via price-level adjustment.
Inflation is therefore not contingent but structurally necessary in a balance-sheet economy.

@russellwadey Where equity exists as a residual claim, the dilution of those claims is mathematically equivalent to inflation. 

@russellwadey
https://x.com/JamesYo43532848/status/1965309238655549809
@russellwadey @threadreaderapp
unroll
unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh