Holy shit. MIT just built an AI that can rewrite its own code to get smarter 🤯
It’s called SEAL (Self-Adapting Language Models).
Instead of humans fine-tuning it, SEAL reads new info, rewrites it in its own words, and runs gradient updates on itself literally performing self-directed learning.
The results?
✅ +40% boost in factual recall
✅ Outperforms GPT-4.1 using data it generated *itself*
✅ Learns new tasks without any human in the loop
LLMs that finetune themselves are no longer sci-fi.
We just entered the age of self-evolving models.
Paper: jyopari. github. io/posts/seal
It’s called SEAL (Self-Adapting Language Models).
Instead of humans fine-tuning it, SEAL reads new info, rewrites it in its own words, and runs gradient updates on itself literally performing self-directed learning.
The results?
✅ +40% boost in factual recall
✅ Outperforms GPT-4.1 using data it generated *itself*
✅ Learns new tasks without any human in the loop
LLMs that finetune themselves are no longer sci-fi.
We just entered the age of self-evolving models.
Paper: jyopari. github. io/posts/seal

Today, most AI models are static once trained, they can’t update themselves.
SEAL flips that.
It runs a reinforcement loop where the model:
1. Generates a “self-edit” (instructions on how to update itself)
2. Tests the result
3. Reinforces only what improves performance
It’s basically RL for self-improvement.
SEAL flips that.
It runs a reinforcement loop where the model:
1. Generates a “self-edit” (instructions on how to update itself)
2. Tests the result
3. Reinforces only what improves performance
It’s basically RL for self-improvement.
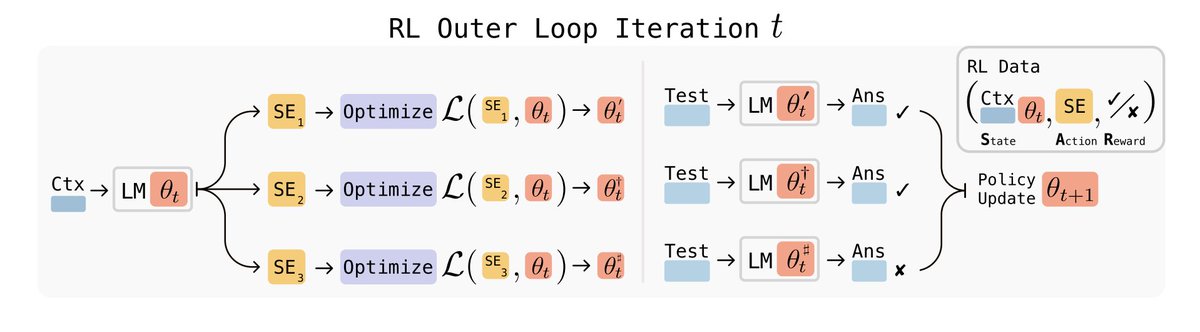
Here’s what self-editing looks like in action 👇
SEAL reads a new passage (say, about the Apollo Program) and rewrites it into logical “implications” like condensed study notes.
Then it finetunes itself on those notes.
The result?
+13.5% factual accuracy without external data.
This is how models start to teach themselves knowledge.
SEAL reads a new passage (say, about the Apollo Program) and rewrites it into logical “implications” like condensed study notes.
Then it finetunes itself on those notes.
The result?
+13.5% factual accuracy without external data.
This is how models start to teach themselves knowledge.

Few-shot learning just got a massive upgrade.
Instead of relying on fixed heuristics, SEAL decides its own training strategy.
It chooses which data augmentations to apply, how to optimize, and even sets its own learning rate.
The outcome:
→ 72.5% success rate
→ 3.6× improvement over standard test-time training
The model is literally designing its own experiments.
Instead of relying on fixed heuristics, SEAL decides its own training strategy.
It chooses which data augmentations to apply, how to optimize, and even sets its own learning rate.
The outcome:
→ 72.5% success rate
→ 3.6× improvement over standard test-time training
The model is literally designing its own experiments.

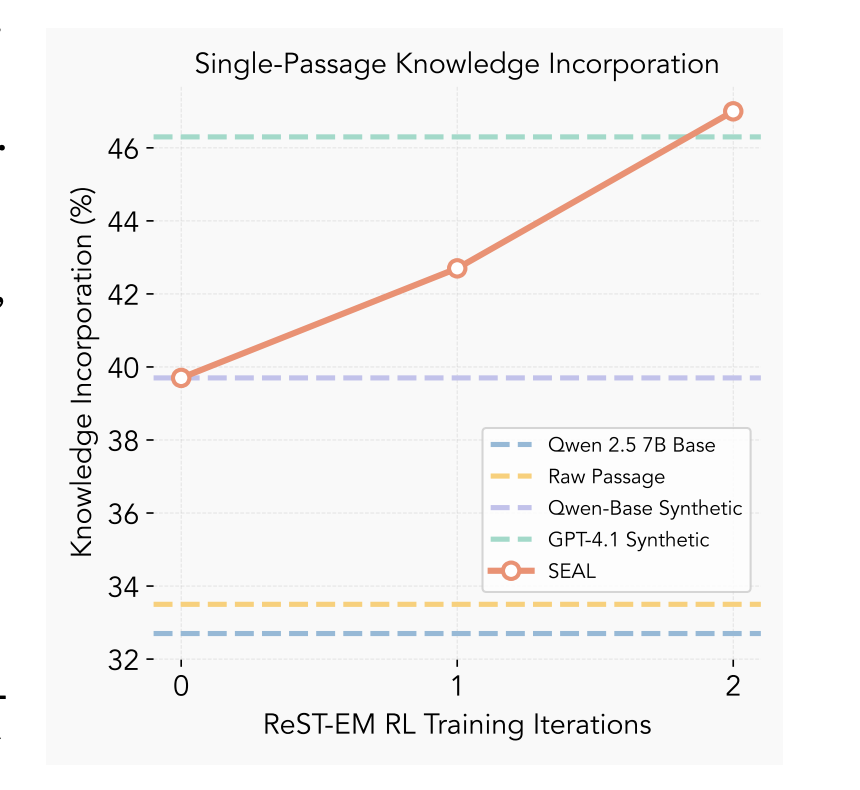
In just two rounds of self-reinforcement, SEAL surpassed GPT-4.1-generated data.
The model learned to write more “learnable” data for itself reformulating facts into simple, atomic truths that stick.
It’s not just learning what to know it’s learning how to learn better.
That’s recursive intelligence in motion.
The model learned to write more “learnable” data for itself reformulating facts into simple, atomic truths that stick.
It’s not just learning what to know it’s learning how to learn better.
That’s recursive intelligence in motion.
Even as SEAL self-updates over time, it mostly remembers what it learned before a huge step toward continual learning.
There’s still some forgetting, but the retention curve shows promise.
Imagine future LLMs that grow their knowledge continuously without starting from scratch.
We’re watching self-evolution begin.
There’s still some forgetting, but the retention curve shows promise.
Imagine future LLMs that grow their knowledge continuously without starting from scratch.
We’re watching self-evolution begin.

Stop wasting hours writing prompts
→ 10,000+ ready-to-use prompts
→ Create your own in seconds
→ Lifetime access. One-time payment.
Claim your copy 👇
godofprompt.ai/pricing
→ 10,000+ ready-to-use prompts
→ Create your own in seconds
→ Lifetime access. One-time payment.
Claim your copy 👇
godofprompt.ai/pricing
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh