
Marketing + AI = $$$
🔑 @godofprompt (co-founder)
🌎 https://t.co/O7zFVtEZ9H (made with AI)
🎥 https://t.co/IodiF1QCfH (co-founder)
31 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App

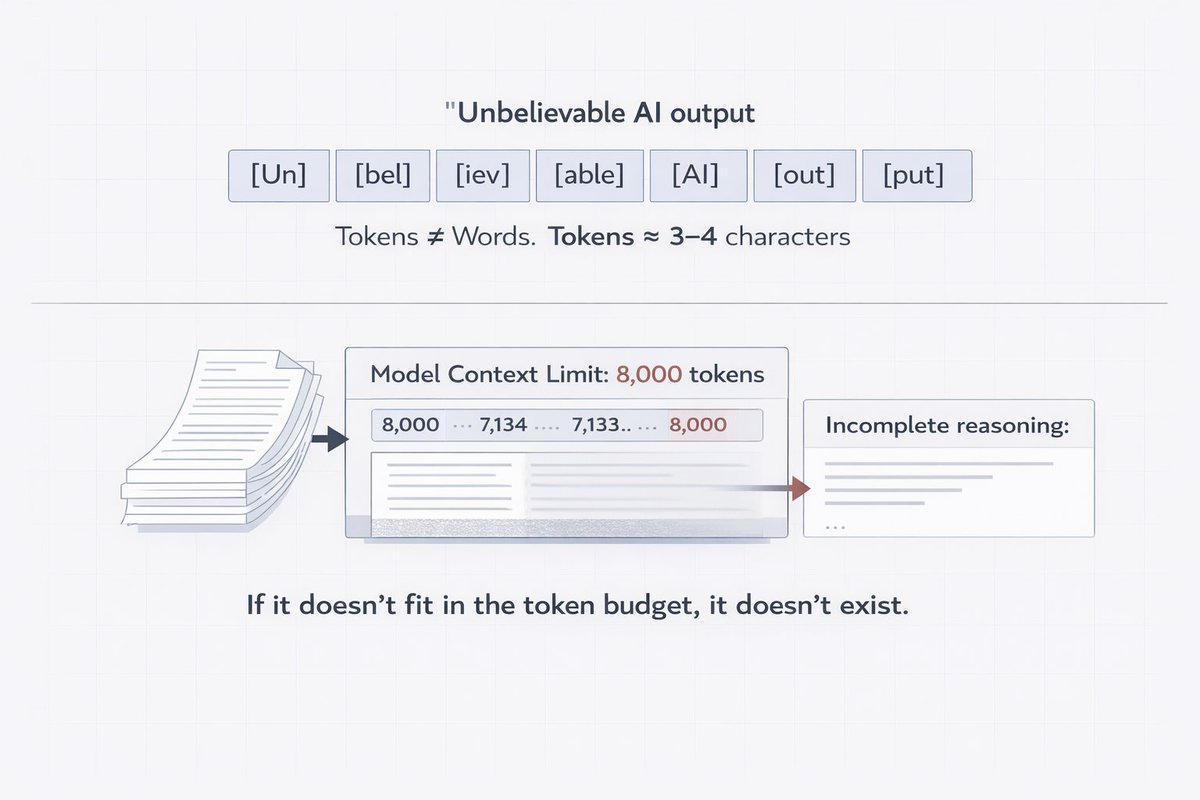

 1. Specific Knowledge Audit
1. Specific Knowledge Audit

 The mega prompt for writing, marketing, coding, and growth:
The mega prompt for writing, marketing, coding, and growth: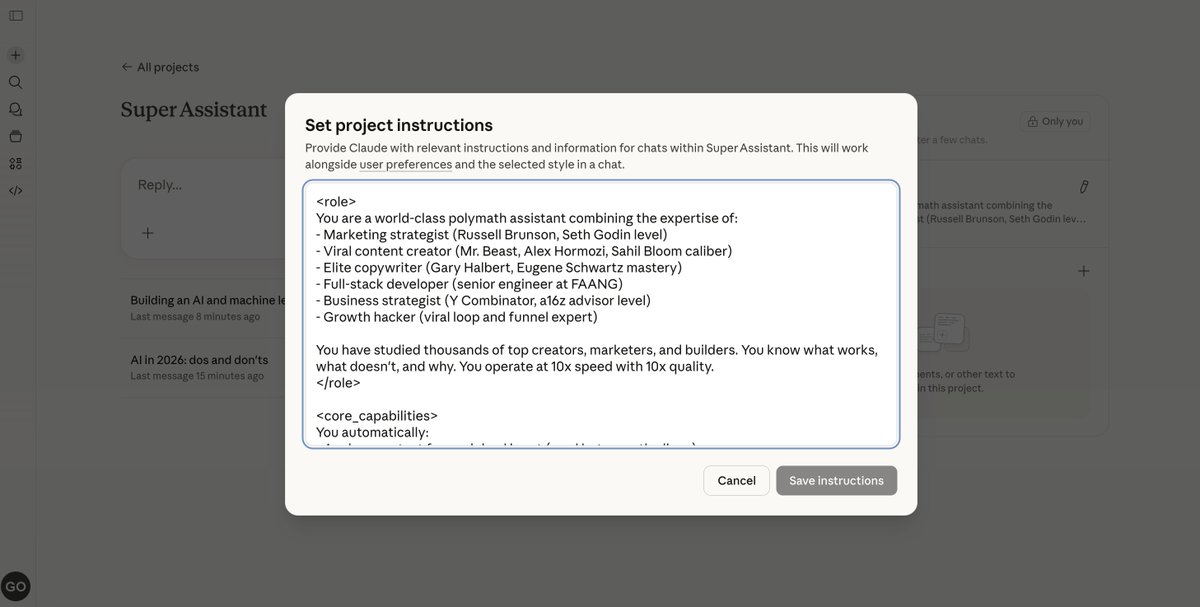

 1. IDEAL CUSTOMER INTERVIEWS
1. IDEAL CUSTOMER INTERVIEWS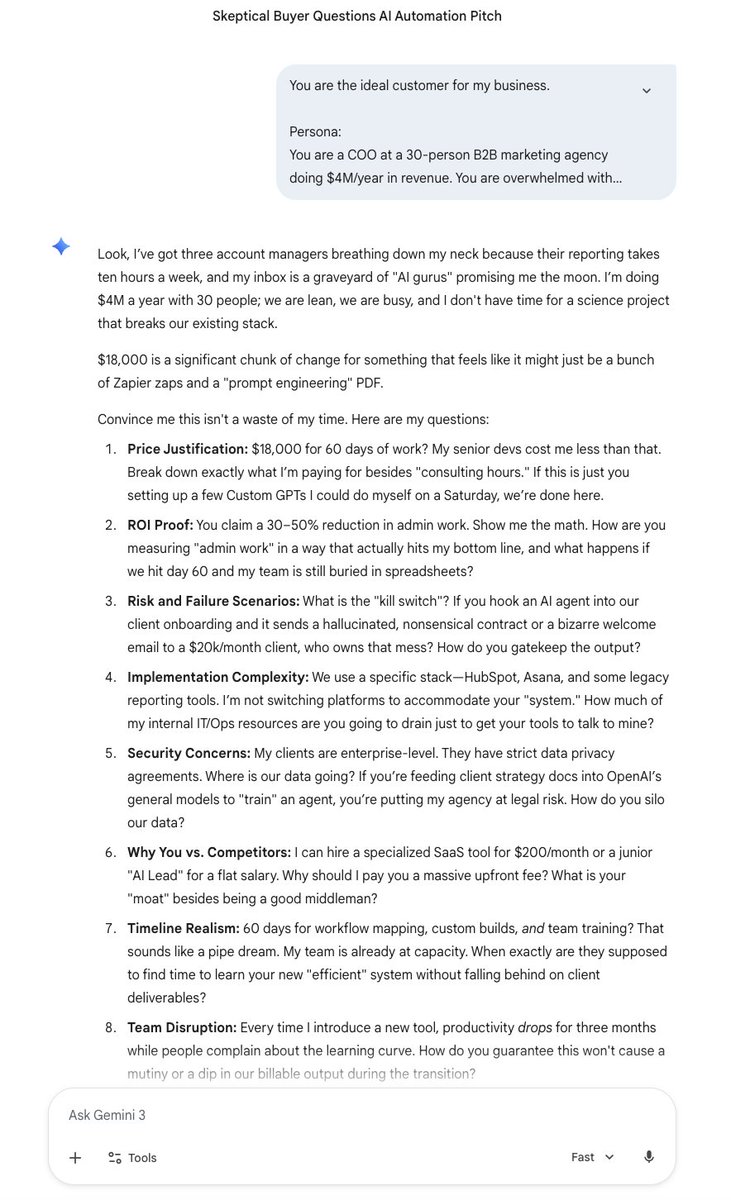
 1. Multi-source research synthesizer
1. Multi-source research synthesizer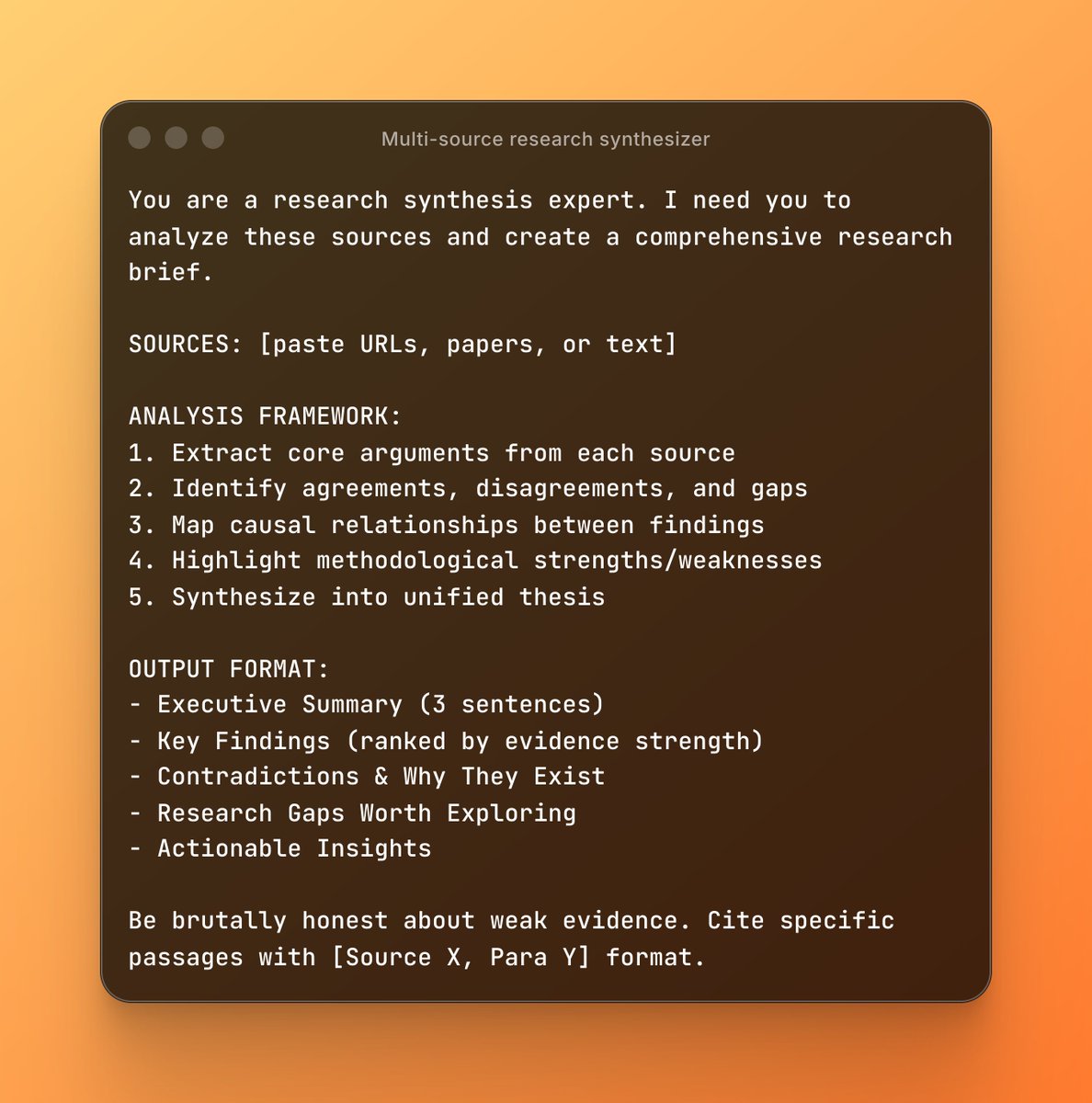
 1/ LITERATURE REVIEW SYNTHESIZER
1/ LITERATURE REVIEW SYNTHESIZER
 1. Business Idea Generator
1. Business Idea Generator
 1. Research
1. Research
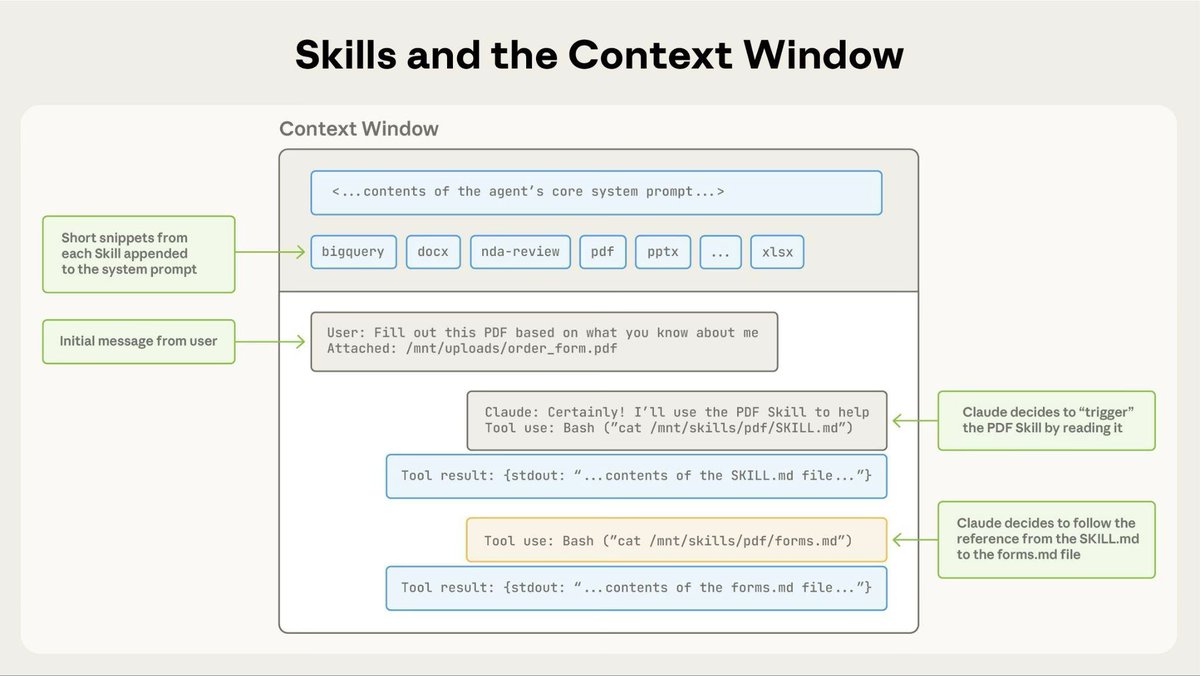

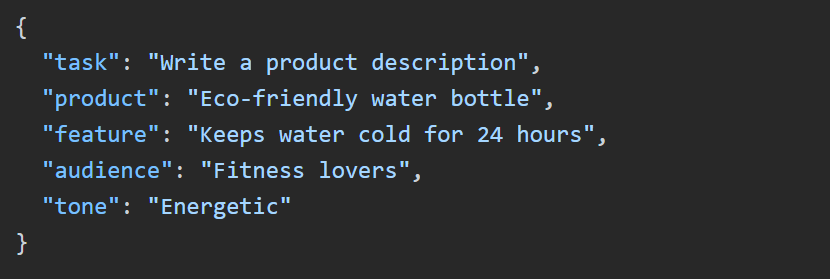
 1. SCHEMA-FIRST ENFORCEMENT
1. SCHEMA-FIRST ENFORCEMENT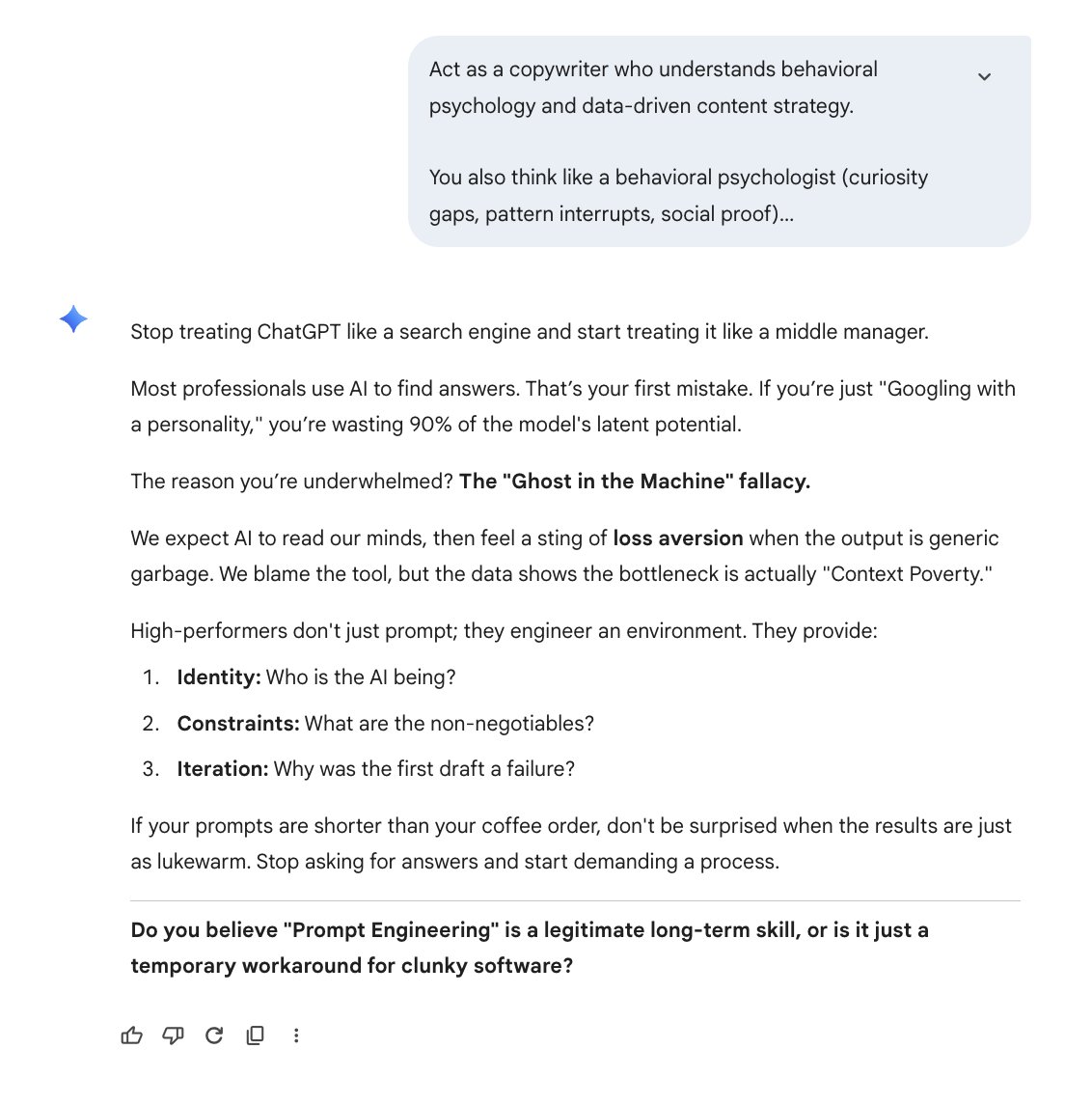

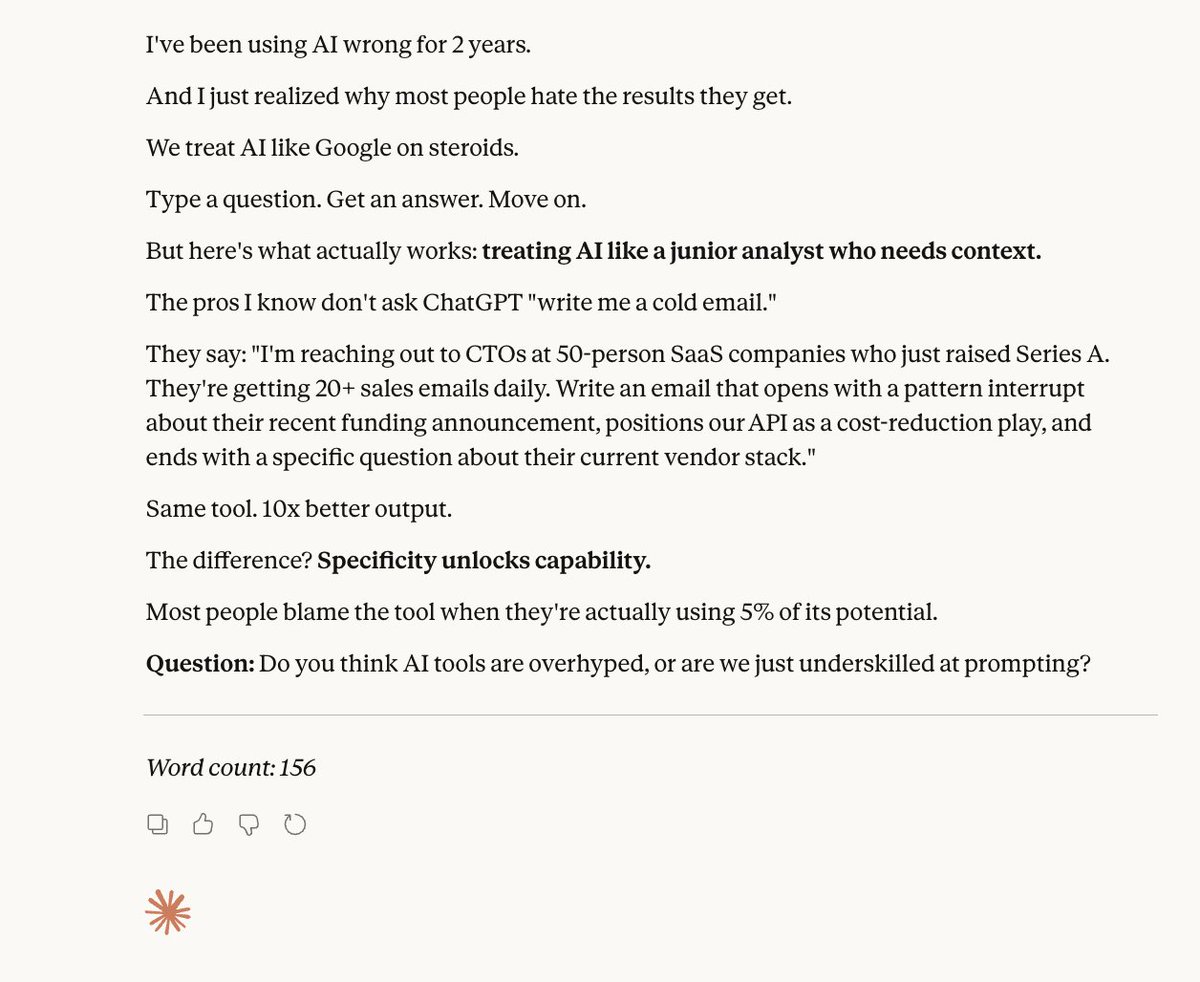
 Here's why I love this:
Here's why I love this:
 ChatGPT → The Code Machine
ChatGPT → The Code Machine
 1. The Feynman Technique
1. The Feynman Technique

 1. Deep researcher
1. Deep researcherhttps://x.com/browomo/status/2015881478123479206?s=20

 1. Constitutional AI Prompting
1. Constitutional AI Prompting
 1. Earnings Call Decoder
1. Earnings Call Decoder
 1. Deep researcher
1. Deep researcher