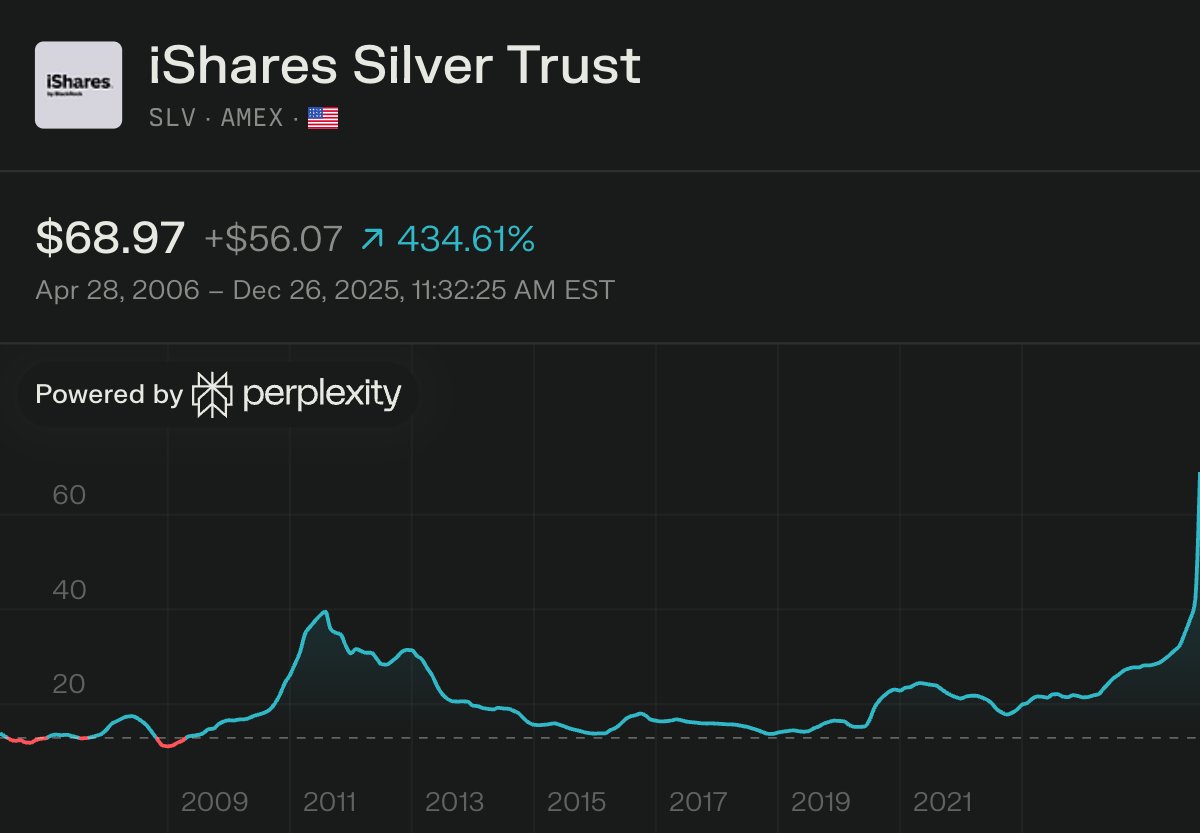
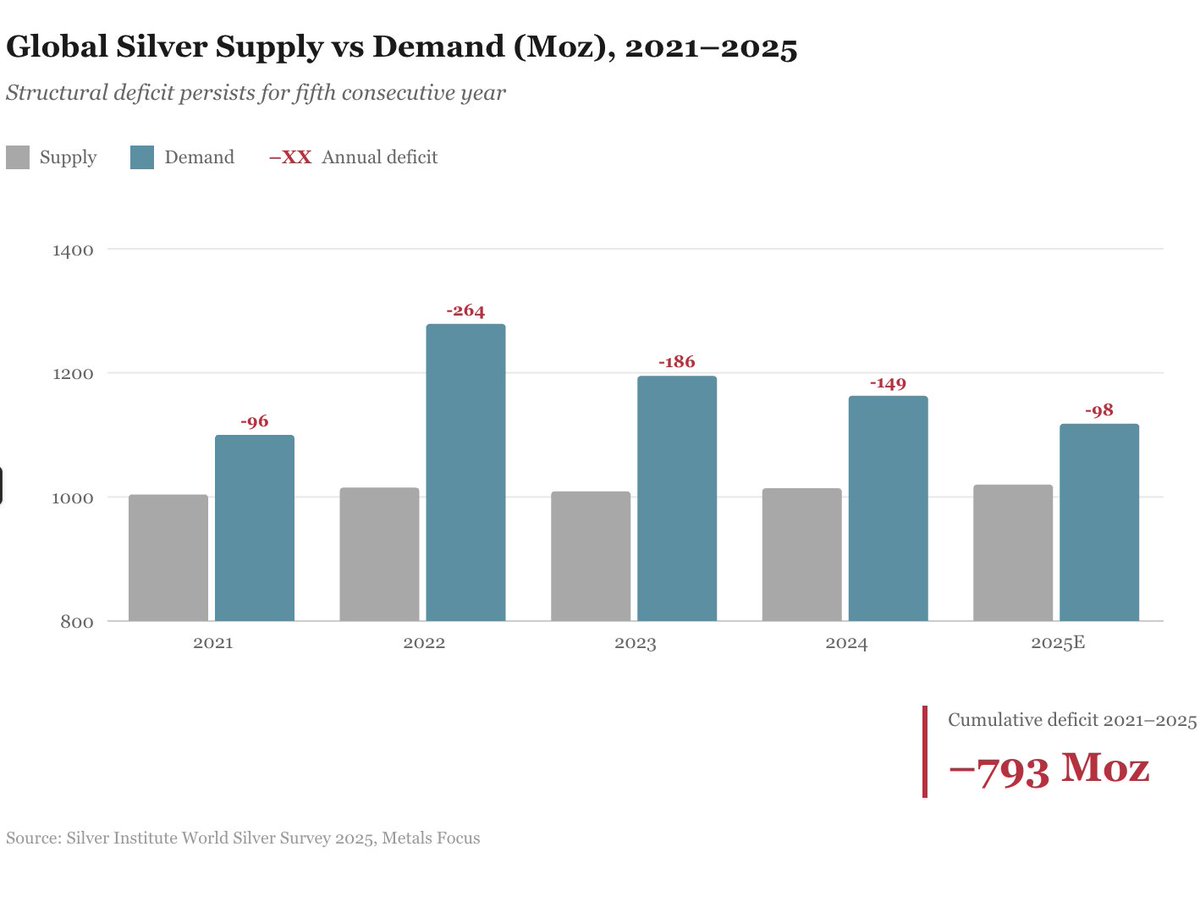
The most powerful rocket ever built launches today.
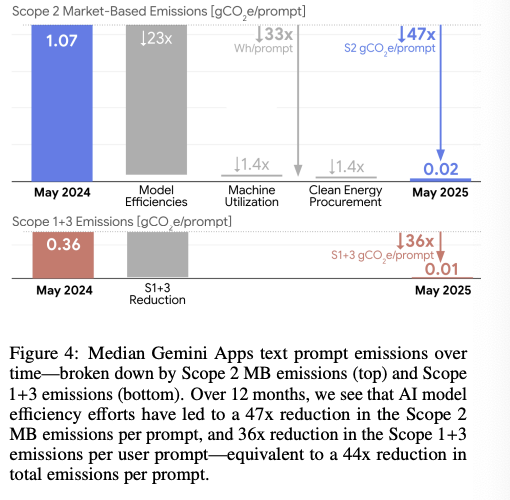
SpaceX Starship Flight 11 lifts off from Starbase, Texas at 6:15 PM CT. 121m tall, 39 engines, 7,500 tons of thrust—3X Saturn V. This is IFT-11, the final Block 2 test before the even larger V3.
Mission objectives: 13→5 engine landing burn, heat shield stress testing (intentional tile gaps), 8 Starlink deployment sims, in-space Raptor relights.
If successful: launch costs drop from $67M to <$10M per flight. That's 85% cheaper access to space.
Here's the engineering that makes it possible:
SpaceX Starship Flight 11 lifts off from Starbase, Texas at 6:15 PM CT. 121m tall, 39 engines, 7,500 tons of thrust—3X Saturn V. This is IFT-11, the final Block 2 test before the even larger V3.
Mission objectives: 13→5 engine landing burn, heat shield stress testing (intentional tile gaps), 8 Starlink deployment sims, in-space Raptor relights.
If successful: launch costs drop from $67M to <$10M per flight. That's 85% cheaper access to space.
Here's the engineering that makes it possible:
STARSHIP: DESIGN & SPECS
Starship is a two-stage monster. Fully stacked: 121 meters tall, 5,000 tons at liftoff.
The skin? 301 stainless steel, just 3-4 millimeters thick—two credit cards stacked. Why steel? It's cheap ($3/kg vs $130 for carbon fiber) and gets stronger when supercooled.
It burns methalox—4,600 tons total. Thrust at liftoff: 7,500 tons—THREE times the Saturn V.
The numbers: 33 Raptor engines on the booster, 6 on the upper stage. 39 engines firing at once. Payload: 150 tons to orbit. Falcon 9 does 22 tons for comparison.
Starship is a two-stage monster. Fully stacked: 121 meters tall, 5,000 tons at liftoff.
The skin? 301 stainless steel, just 3-4 millimeters thick—two credit cards stacked. Why steel? It's cheap ($3/kg vs $130 for carbon fiber) and gets stronger when supercooled.
It burns methalox—4,600 tons total. Thrust at liftoff: 7,500 tons—THREE times the Saturn V.
The numbers: 33 Raptor engines on the booster, 6 on the upper stage. 39 engines firing at once. Payload: 150 tons to orbit. Falcon 9 does 22 tons for comparison.

RAPTOR ENGINES: MASS-PRODUCING THE IMPOSSIBLE
The Raptor engine uses full-flow staged combustion—the most efficient rocket cycle ever flown. Raptor 3: 30 megapascals chamber pressure, 280 tons of thrust each.
Here's what's insane: SpaceX has built over 1,000 of these by 2025. They're mass-producing rocket engines like cars.
Why methane? You can make it on Mars. CO2 from the atmosphere + hydrogen = methane and oxygen. 95% efficient with solar power. Mars becomes its own gas station.

The Raptor engine uses full-flow staged combustion—the most efficient rocket cycle ever flown. Raptor 3: 30 megapascals chamber pressure, 280 tons of thrust each.
Here's what's insane: SpaceX has built over 1,000 of these by 2025. They're mass-producing rocket engines like cars.
Why methane? You can make it on Mars. CO2 from the atmosphere + hydrogen = methane and oxygen. 95% efficient with solar power. Mars becomes its own gas station.


THE HARDEST PROBLEMS
Now the hard parts.
First: the heat shield. 18,000 hexagonal silica tiles protecting the ship during reentry at 1,400 to 1,600 degrees Celsius.
Early flights lost tiles—plasma melted the steel underneath. The fixes? Backup ablative layers, redesigned flaps, and metallic tiles with active cooling. Goal: 100 reuses.
Second: catching a rocket with chopsticks. IFT-5 proved it works. Super Heavy does a boostback burn, reverses course, and those giant mechanical arms just grab it out of the air.
Now the hard parts.
First: the heat shield. 18,000 hexagonal silica tiles protecting the ship during reentry at 1,400 to 1,600 degrees Celsius.
Early flights lost tiles—plasma melted the steel underneath. The fixes? Backup ablative layers, redesigned flaps, and metallic tiles with active cooling. Goal: 100 reuses.
Second: catching a rocket with chopsticks. IFT-5 proved it works. Super Heavy does a boostback burn, reverses course, and those giant mechanical arms just grab it out of the air.

THE JOURNEY: FROM EXPLOSIONS TO SUCCESS
The road here has been brutal. IFT-1 in April 2023: giant explosion at staging. IFT-4: first full-duration burns, both stages survived. IFT-5: the booster catch that broke the internet.
Between each flight, they tweak over 1,000 variables. Tile gap sizes. Flap hinge angles. Engine ignition sequences. This is what 'move fast and break things' looks like when you're building rockets.
The road here has been brutal. IFT-1 in April 2023: giant explosion at staging. IFT-4: first full-duration burns, both stages survived. IFT-5: the booster catch that broke the internet.
Between each flight, they tweak over 1,000 variables. Tile gap sizes. Flap hinge angles. Engine ignition sequences. This is what 'move fast and break things' looks like when you're building rockets.

THE ROADMAP: MOON, MARS & BEYOND
The roadmap is aggressive:
2025: Full orbital refueling demonstration
2026: Uncrewed Mars cargo mission and Artemis lunar landing
2028: First crewed Mars landing—aspirational, but that's the goal
And here's why this matters: if Starship works, the cost per kilogram to orbit drops below $100. Right now, Falcon 9—already the cheapest rocket flying—costs $2,700 per kilogram. That's a 27-times improvement.

The roadmap is aggressive:
2025: Full orbital refueling demonstration
2026: Uncrewed Mars cargo mission and Artemis lunar landing
2028: First crewed Mars landing—aspirational, but that's the goal
And here's why this matters: if Starship works, the cost per kilogram to orbit drops below $100. Right now, Falcon 9—already the cheapest rocket flying—costs $2,700 per kilogram. That's a 27-times improvement.
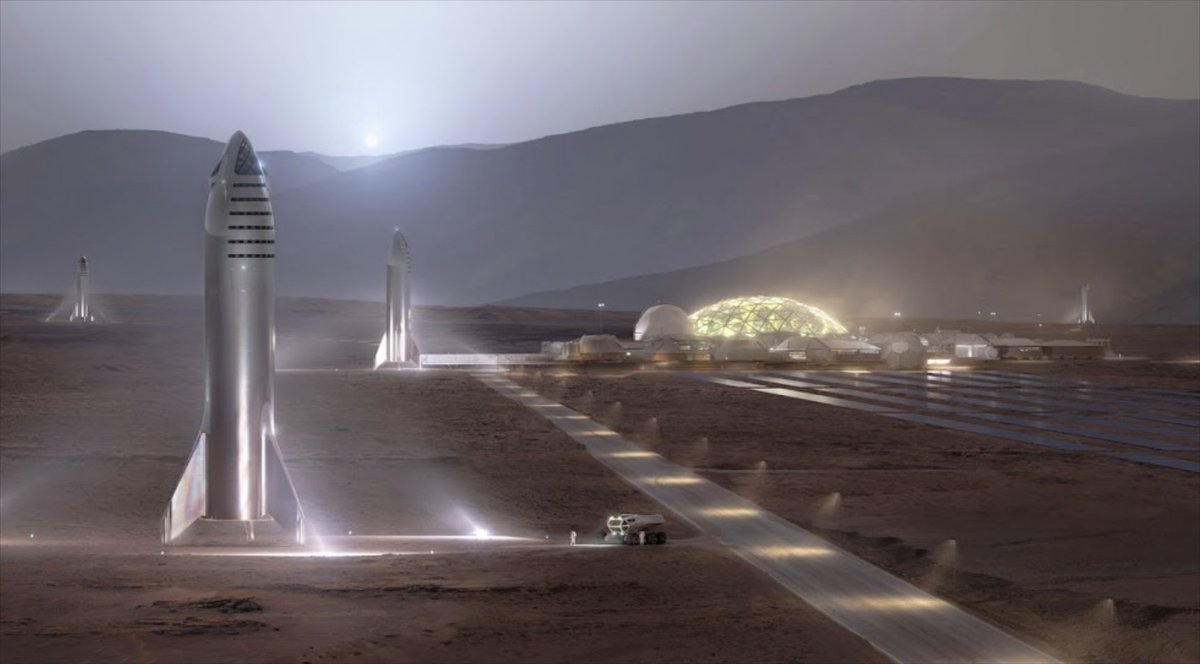


FLIGHT 11: WHAT'S BEING TESTED TODAY
So here we are. Flight 11 is testing a new landing burn configuration, stress-testing the heat shield with intentionally missing tiles, simulating Starlink deployments, and attempting in-space Raptor relights for future Mars transfers.
Starship isn't just a rocket—it's the key that unlocks moon bases, Mars colonies, and our multiplanetary future.
And it's happening... right... NOW.
So here we are. Flight 11 is testing a new landing burn configuration, stress-testing the heat shield with intentionally missing tiles, simulating Starlink deployments, and attempting in-space Raptor relights for future Mars transfers.
Starship isn't just a rocket—it's the key that unlocks moon bases, Mars colonies, and our multiplanetary future.
And it's happening... right... NOW.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh