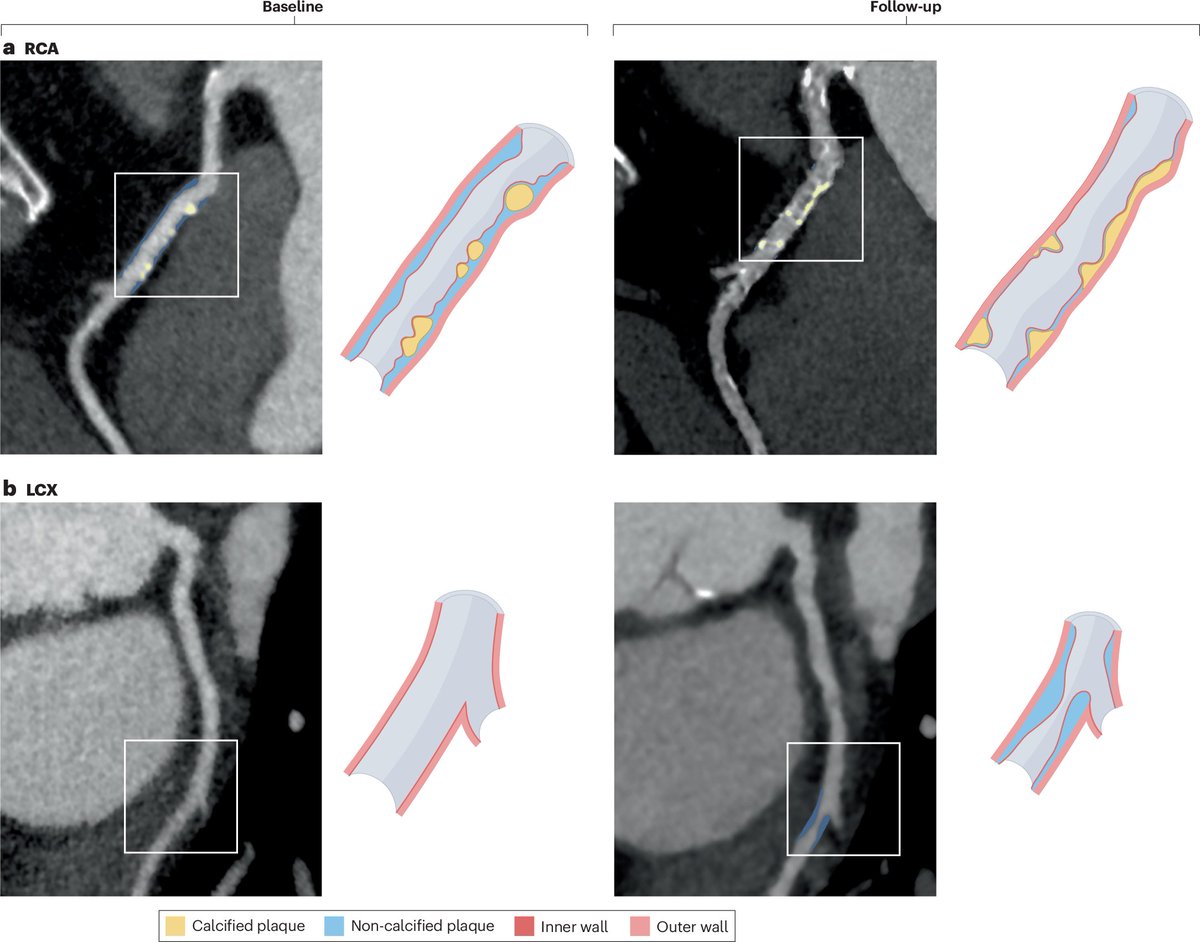
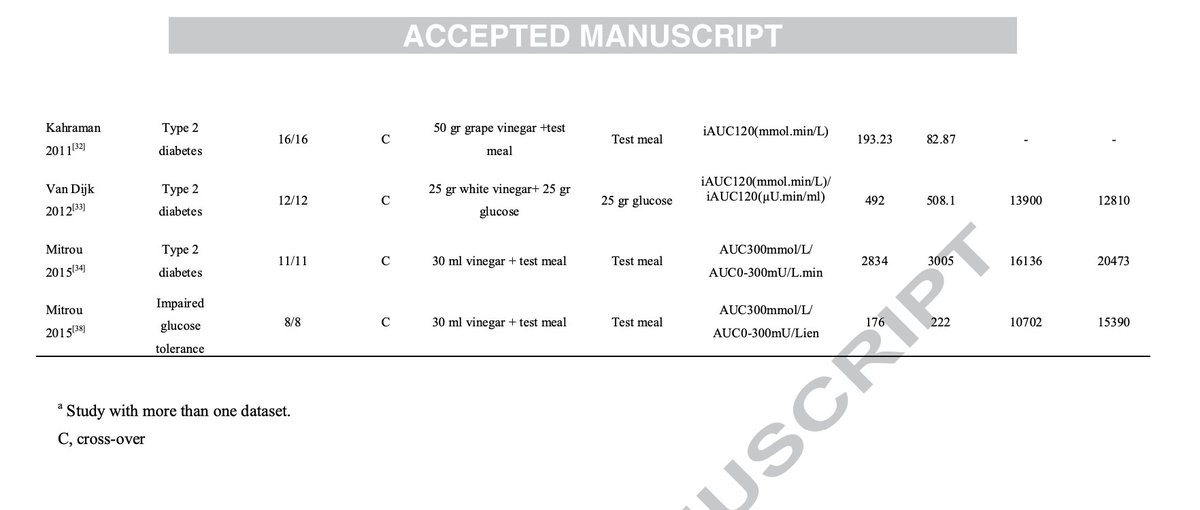
Nattokinase shrinks arterial plaques in nearly 80% of people, a landmark recent study has shown.
(🧵1/7)
(🧵1/7)

Natto is a food commonly consumed in Japan made from fermented soybeans.
The soybeans have the bacteria Bacillus subtilis var natto added,
The bacteria eats the soybeans and it produces the enzyme nattokinase.
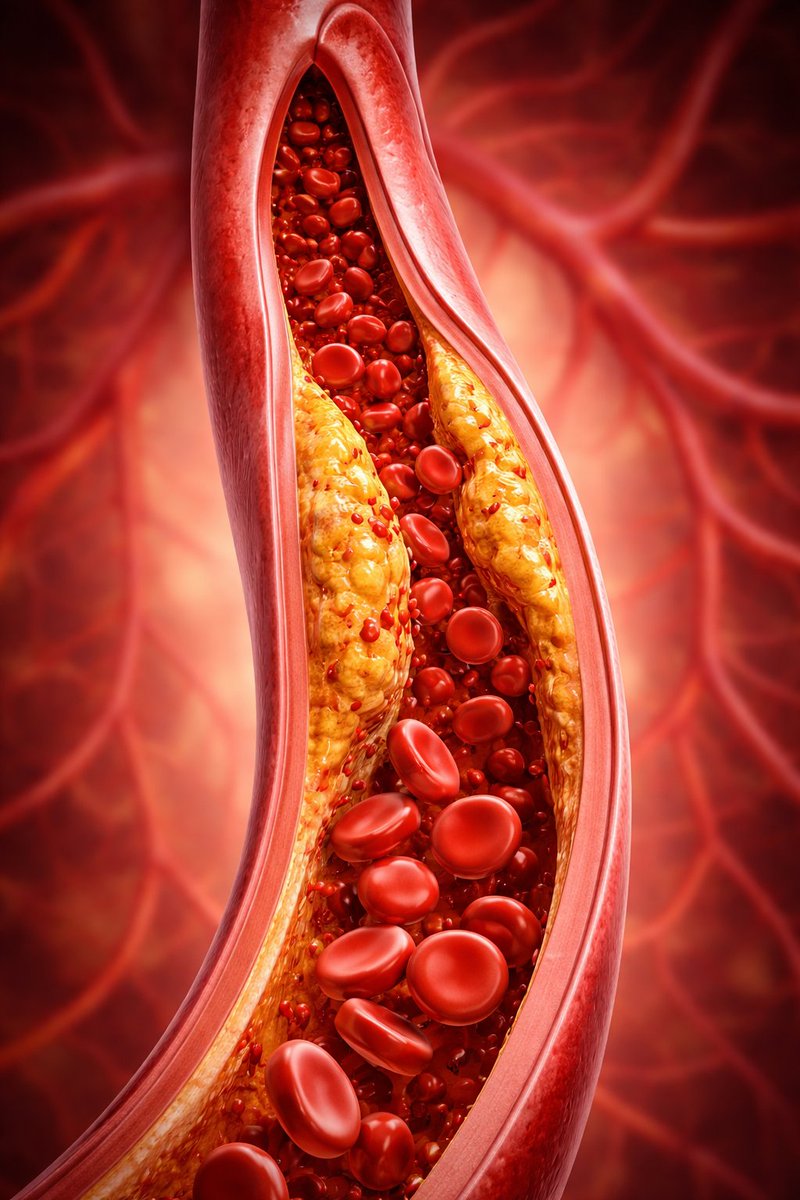
What nattokinase does is it breaks down fibrin - the primary protein that holds together blood clots.
These blood clots are what result from plaques in the arteries, leading to the blockage of blood flow and eventually heart attack.
(2/7)
The soybeans have the bacteria Bacillus subtilis var natto added,
The bacteria eats the soybeans and it produces the enzyme nattokinase.
What nattokinase does is it breaks down fibrin - the primary protein that holds together blood clots.
These blood clots are what result from plaques in the arteries, leading to the blockage of blood flow and eventually heart attack.
(2/7)

This study took over 1,000 people with evidence of mild heart disease or who were at risk.
People were given 10,800 FU of nattokinase per day.
This is equivalent to roughly 100-200 mg of nattokinase per day.
(3/7)
People were given 10,800 FU of nattokinase per day.
This is equivalent to roughly 100-200 mg of nattokinase per day.
(3/7)

People saw improvements in their lipid profiles.
➠ Triglycerides down ~16% (main fat in blood)
➠ LDL cholesterol down ~18% (main cholesterol involved in plaque buildup)
➠ HDL increased ~16% (responsible for pulling cholesterol out of arteries)
But that's just the beginning.
(4/7)
➠ Triglycerides down ~16% (main fat in blood)
➠ LDL cholesterol down ~18% (main cholesterol involved in plaque buildup)
➠ HDL increased ~16% (responsible for pulling cholesterol out of arteries)
But that's just the beginning.
(4/7)

The improvement rates were astonishing.
➠ >95% improved total cholesterol
➠ >85% LDL
➠ >84% triglycerides
➠ >89% HDL
➠ >77% CIMT (plaque thickness)
➠ >66^ CPS (plaque size)
(5/7)
➠ >95% improved total cholesterol
➠ >85% LDL
➠ >84% triglycerides
➠ >89% HDL
➠ >77% CIMT (plaque thickness)
➠ >66^ CPS (plaque size)
(5/7)

Most importantly of all, arterial thickness and plaque sizes substantially reduced.
Plaque area was reduced by nearly 40% in people taking aspirin or K2.
Thickness down >25%.
(6/7)
Plaque area was reduced by nearly 40% in people taking aspirin or K2.
Thickness down >25%.
(6/7)

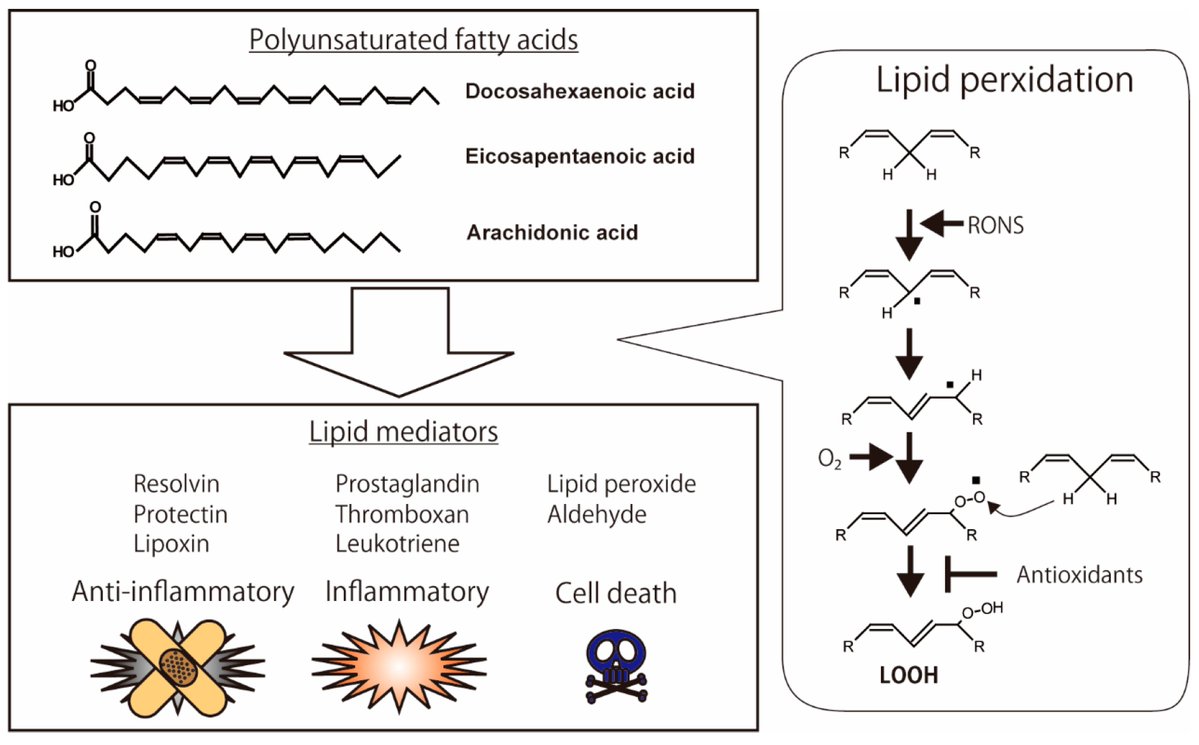
Nattokinase has multiple other effects that prevent the plaque buildup process.
➥ Reduces key inflammatory pathways (TLR4, JAK/STAT, NF-κB)
➥ Antioxidant effect
➥ Enhances lipid metabolism (increases HSL, decreases HMG-Coa Reductase - the target of statins)
More research is coming out on this, but multiple studies are now showing nattokinases' heart protective effects.
(7/7)
➥ Reduces key inflammatory pathways (TLR4, JAK/STAT, NF-κB)
➥ Antioxidant effect
➥ Enhances lipid metabolism (increases HSL, decreases HMG-Coa Reductase - the target of statins)
More research is coming out on this, but multiple studies are now showing nattokinases' heart protective effects.
(7/7)

This is the nattokinase product we suggest, 20% off using this link: tokuhealth.com/ANALYZE20
If you enjoyed this thread, we take the same creative science-based approach to help people every day with an individualized approach. Schedule a free call here and we’ll help you too: go.prism.miami/consultation
Full study here: frontiersin.org/journals/cardi…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh