The Unexpected Alzheimer’s Breakthrough
A common preservative may succeed where billion-dollar Alzheimer’s drugs have failed.
Cheap, safe, and remarkably practical.
With Alzheimer’s now the sixth-leading cause of death, could the solution really be this simple? 🧵
A common preservative may succeed where billion-dollar Alzheimer’s drugs have failed.
Cheap, safe, and remarkably practical.
With Alzheimer’s now the sixth-leading cause of death, could the solution really be this simple? 🧵

A food preservative used in sodas and thousands of other products may help improve memory and thinking skills in people with Alzheimer’s disease, raising the possibility that an inexpensive household chemical could help combat the nation’s sixth-leading cause of death.
A recent analysis of clinical trial data from 149 people with mild Alzheimer’s disease found that taking sodium benzoate daily for 24 weeks was linked to better thinking skills and lower levels of abnormal proteins in the blood—one of the disease’s hallmarks.
A recent analysis of clinical trial data from 149 people with mild Alzheimer’s disease found that taking sodium benzoate daily for 24 weeks was linked to better thinking skills and lower levels of abnormal proteins in the blood—one of the disease’s hallmarks.

What the Study Found
Current Alzheimer’s treatments are costly and can come with serious side effects, so researchers tested whether sodium benzoate—a pantry preservative—might do more than fight spoilage.
Participants aged 50 to 90 were randomly assigned to receive either a placebo or sodium benzoate at doses of 500, 750, or 1,000 milligrams daily for 24 weeks.
The higher doses produced the most significant results: those taking 750 or 1,000 milligrams daily showed improved cognitive functions—including orientation, word finding, and word recall—along with reduced levels of amyloid beta proteins in their blood. The greatest improvements were seen in participants with higher baseline levels of the more harmful form of amyloid beta.
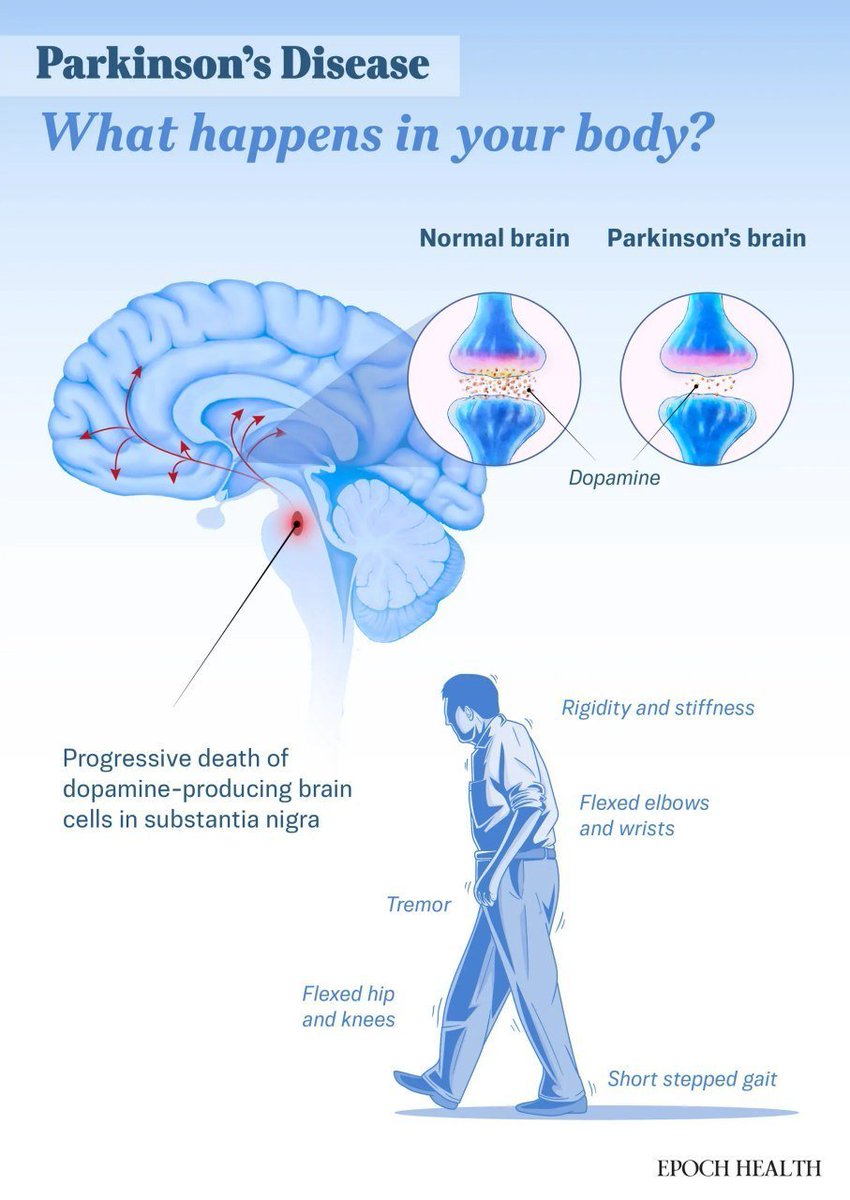
“You can think of beta amyloid as molecular ‘debris’ that piles up and jams the brain’s wiring system,” Dr. Thomas Holland, a clinician-researcher at the Rush Institute for Healthy Aging, who wasn’t involved in the study, told The Epoch Times. “Over time, this buildup contributes to memory loss and cognitive decline.”
Holland said the findings suggest sodium benzoate may have supported cognition by altering how the body manages amyloid beta—possibly by clearing more of it or producing less.
However, the researchers noted that the exact mechanism remains unknown.
Current Alzheimer’s treatments are costly and can come with serious side effects, so researchers tested whether sodium benzoate—a pantry preservative—might do more than fight spoilage.
Participants aged 50 to 90 were randomly assigned to receive either a placebo or sodium benzoate at doses of 500, 750, or 1,000 milligrams daily for 24 weeks.
The higher doses produced the most significant results: those taking 750 or 1,000 milligrams daily showed improved cognitive functions—including orientation, word finding, and word recall—along with reduced levels of amyloid beta proteins in their blood. The greatest improvements were seen in participants with higher baseline levels of the more harmful form of amyloid beta.
“You can think of beta amyloid as molecular ‘debris’ that piles up and jams the brain’s wiring system,” Dr. Thomas Holland, a clinician-researcher at the Rush Institute for Healthy Aging, who wasn’t involved in the study, told The Epoch Times. “Over time, this buildup contributes to memory loss and cognitive decline.”
Holland said the findings suggest sodium benzoate may have supported cognition by altering how the body manages amyloid beta—possibly by clearing more of it or producing less.
However, the researchers noted that the exact mechanism remains unknown.

A little about us: We’re a team of journalists and researchers on a mission to give you REAL and honest information about your health.
Side effects of reading our posts may include: critical thinking.
Follow us for more daily threads—backed by hard data.
—> @EpochHealth
Side effects of reading our posts may include: critical thinking.
Follow us for more daily threads—backed by hard data.
—> @EpochHealth

How It Might Work
Sodium benzoate is a synthetic preservative widely used in acidic foods and drinks to prevent spoilage.
It’s classified as Generally Recognized as Safe, which means it’s considered safe as long as it’s used as intended.
theepochtimes.com/health/common-…
Sodium benzoate is a synthetic preservative widely used in acidic foods and drinks to prevent spoilage.
It’s classified as Generally Recognized as Safe, which means it’s considered safe as long as it’s used as intended.
theepochtimes.com/health/common-…
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) permits sodium benzoate in foods and beverages at levels up to 0.1 percent.
Unlike the FDA’s product-based cap, the World Health Organization (WHO) sets the acceptable daily intake level for sodium benzoate at zero to 20 milligrams per kilogram of body weight, providing guidance on how much a person can safely take each day over a lifetime.
For context, an adult weighing about 150 pounds could safely ingest up to roughly 1,300 milligrams per day under the WHO standard.
The preservative does have some controversies. When combined with vitamin C, it can form benzene—a known carcinogen—under certain conditions. Some studies have linked it to hyperactivity in children and possible cellular dysfunction.
In the clinical trial, the food preservative appeared to attack Alzheimer’s disease through multiple pathways, unlike current treatments that focus primarily on removing amyloid plaques from the brain.
Sodium benzoate doesn’t fall within existing Alzheimer’s disease treatments but rather sits somewhere in the middle, with its multi-targeted approach.
Unlike the FDA’s product-based cap, the World Health Organization (WHO) sets the acceptable daily intake level for sodium benzoate at zero to 20 milligrams per kilogram of body weight, providing guidance on how much a person can safely take each day over a lifetime.
For context, an adult weighing about 150 pounds could safely ingest up to roughly 1,300 milligrams per day under the WHO standard.
The preservative does have some controversies. When combined with vitamin C, it can form benzene—a known carcinogen—under certain conditions. Some studies have linked it to hyperactivity in children and possible cellular dysfunction.
In the clinical trial, the food preservative appeared to attack Alzheimer’s disease through multiple pathways, unlike current treatments that focus primarily on removing amyloid plaques from the brain.
Sodium benzoate doesn’t fall within existing Alzheimer’s disease treatments but rather sits somewhere in the middle, with its multi-targeted approach.

Hsien-Yuan Lane, a professor and director at the Graduate Institute of Biomedical Sciences at China Medical University, and corresponding author of the study, told The Epoch Times that the possible mechanisms by which sodium benzoate could reduce amyloid beta levels remain unknown, but alternative mechanisms have been suggested.
The preservative may improve communication between brain cells by blocking an enzyme that breaks down D-serine, a chemical messenger needed for learning and memory. D-serine helps switch on special receptors that let brain cells talk to each other. In normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease, both messenger levels and receptor activity drop, making it harder for brain cells to send and receive signals.
Sodium benzoate may also reduce oxidative stress, which is cellular damage caused by harmful molecules and is another driver of Alzheimer’s disease. Previous research shows sodium benzoate can calm inflammation in the brain’s immune cells and protect neurons by boosting proteins that help them survive stress, repair damage, and form new connections.
In patients with mild Alzheimer’s disease, it has been shown to raise levels of two key antioxidants: catalase and glutathione. These antioxidants help protect brain cells from oxidative stress, which damages brain cells and is thought to play a role in Alzheimer’s progression.
The preservative may improve communication between brain cells by blocking an enzyme that breaks down D-serine, a chemical messenger needed for learning and memory. D-serine helps switch on special receptors that let brain cells talk to each other. In normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease, both messenger levels and receptor activity drop, making it harder for brain cells to send and receive signals.
Sodium benzoate may also reduce oxidative stress, which is cellular damage caused by harmful molecules and is another driver of Alzheimer’s disease. Previous research shows sodium benzoate can calm inflammation in the brain’s immune cells and protect neurons by boosting proteins that help them survive stress, repair damage, and form new connections.
In patients with mild Alzheimer’s disease, it has been shown to raise levels of two key antioxidants: catalase and glutathione. These antioxidants help protect brain cells from oxidative stress, which damages brain cells and is thought to play a role in Alzheimer’s progression.

The Pressing Need for Treatment
“Current treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease focus on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression, though there is no cure,” Lane said.
He noted that recent advances in Alzheimer’s disease treatment have shown promise in slowing progression. “However, these therapies can cause adverse effects, including brain swelling and bleeding, and pose practical challenges due to cost and the need for frequent injections and monitoring.”
Holland said that current drugs offer only modest benefits because they target amyloid alone and are approved only for people with mild cognitive impairment—meaning they treat the disease after it has already begun to progress, rather than prevent it.
“The biggest breakthroughs needed are safe, multi-target treatments that address both prevention and treatment of the disease process. Specifically for Alzheimer’s disease, we need treatments that not only target amyloid but also the broader biological changes,” Holland said, adding that it is much like how treating heart disease involves more than just lowering cholesterol.
Holland is a medical adviser and study clinician for the U.S. POINTER trial, a two-year clinical trial testing whether healthy lifestyle changes can protect cognitive function in older adults at risk of decline.
“Current treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease focus on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression, though there is no cure,” Lane said.
He noted that recent advances in Alzheimer’s disease treatment have shown promise in slowing progression. “However, these therapies can cause adverse effects, including brain swelling and bleeding, and pose practical challenges due to cost and the need for frequent injections and monitoring.”
Holland said that current drugs offer only modest benefits because they target amyloid alone and are approved only for people with mild cognitive impairment—meaning they treat the disease after it has already begun to progress, rather than prevent it.
“The biggest breakthroughs needed are safe, multi-target treatments that address both prevention and treatment of the disease process. Specifically for Alzheimer’s disease, we need treatments that not only target amyloid but also the broader biological changes,” Holland said, adding that it is much like how treating heart disease involves more than just lowering cholesterol.
Holland is a medical adviser and study clinician for the U.S. POINTER trial, a two-year clinical trial testing whether healthy lifestyle changes can protect cognitive function in older adults at risk of decline.

Previous Research
In the current trial, researchers used much higher doses of sodium benzoate than what a person may be exposed to by eating processed foods. A previous clinical trial in schizophrenic patients administered doses of up to 2,000 milligrams per day.
“At first glance, hearing ‘food preservative’ may sound alarming. But it’s important to separate trace amounts in processed foods from carefully studied medical doses,” Holland said.
Still, he noted that the long-term effect of using these doses isn’t yet known, especially since preservatives in the diet can interact with other compounds.
In the current trial, researchers used much higher doses of sodium benzoate than what a person may be exposed to by eating processed foods. A previous clinical trial in schizophrenic patients administered doses of up to 2,000 milligrams per day.
“At first glance, hearing ‘food preservative’ may sound alarming. But it’s important to separate trace amounts in processed foods from carefully studied medical doses,” Holland said.
Still, he noted that the long-term effect of using these doses isn’t yet known, especially since preservatives in the diet can interact with other compounds.

This isn’t the first time researchers have tested sodium benzoate against Alzheimer’s disease.
Small human trials in Taiwan have shown promise. In a 2014 24-week trial of 60 patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment or mild Alzheimer’s disease, those taking sodium benzoate had greater gains in skills such as remembering instructions, word recall, comprehension, and orientation than those taking a placebo, with no notable side effects.
A smaller trial found similar improvements in skills such as word recall, orientation, and ability to pick up and retain words with repetition, plus changes in brain activity on MRI scans.
Holland said that sodium benzoate is intriguing because it works differently. “It doesn’t just address the ‘debris’ in the brain, amyloid, but also the oxidative stress that damages brain cells. From a patient perspective, taking a pill safely at home would be far more practical than repeated hospital infusions.”
He added that although larger studies are needed to confirm these benefits, the compound has the potential to complement existing therapies or even serve as a safer first-line option.
Small human trials in Taiwan have shown promise. In a 2014 24-week trial of 60 patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment or mild Alzheimer’s disease, those taking sodium benzoate had greater gains in skills such as remembering instructions, word recall, comprehension, and orientation than those taking a placebo, with no notable side effects.
A smaller trial found similar improvements in skills such as word recall, orientation, and ability to pick up and retain words with repetition, plus changes in brain activity on MRI scans.
Holland said that sodium benzoate is intriguing because it works differently. “It doesn’t just address the ‘debris’ in the brain, amyloid, but also the oxidative stress that damages brain cells. From a patient perspective, taking a pill safely at home would be far more practical than repeated hospital infusions.”
He added that although larger studies are needed to confirm these benefits, the compound has the potential to complement existing therapies or even serve as a safer first-line option.

Experts caution that several key questions remain unanswered. The study measured amyloid proteins in blood, not in the brain itself.
“This is an important nuance. Blood amyloid levels do not perfectly mirror brain amyloid, but trends can be informative,” Holland said.
He compared measuring blood amyloid levels to checking for pollution downstream in a river—lower levels might suggest cleaner conditions upstream, but the connection isn’t exact.
The researchers acknowledged that it’s unclear whether changes in blood amyloid levels reflect actual changes in the brain or spinal fluid. Lane also noted that it’s unknown whether sodium benzoate eaten through diet affects Alzheimer’s risk or progression.
“While encouraging, these findings need to be paired with brain imaging or spinal fluid studies to be conclusive,” Holland said.
“This is an important nuance. Blood amyloid levels do not perfectly mirror brain amyloid, but trends can be informative,” Holland said.
He compared measuring blood amyloid levels to checking for pollution downstream in a river—lower levels might suggest cleaner conditions upstream, but the connection isn’t exact.
The researchers acknowledged that it’s unclear whether changes in blood amyloid levels reflect actual changes in the brain or spinal fluid. Lane also noted that it’s unknown whether sodium benzoate eaten through diet affects Alzheimer’s risk or progression.
“While encouraging, these findings need to be paired with brain imaging or spinal fluid studies to be conclusive,” Holland said.

Thanks for reading! If you found this valuable, here's a special deal:
Unlock our ENTIRE library of @EpochHealth articles for just $1/week—plus unlimited access to everything else on our site.
Claim it here: on.theepochtimes.com/vfox/health?ut…
Unlock our ENTIRE library of @EpochHealth articles for just $1/week—plus unlimited access to everything else on our site.
Claim it here: on.theepochtimes.com/vfox/health?ut…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh