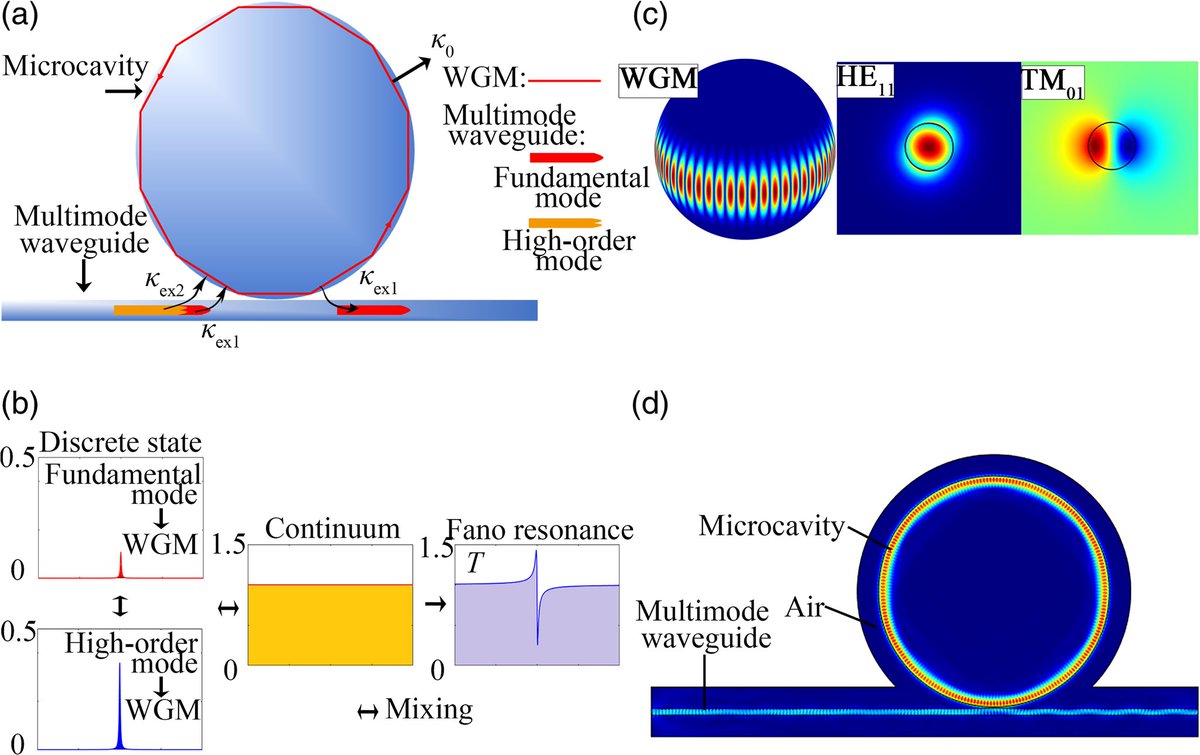
Lens cap
The end is nigh
A huge cover up?
People use plaster for walls because it provides a durable, long-lasting, and versatile finish that is more impact-resistant and can be smoothed or textured in various decorative ways. Plastering also offers practical benefits like improved sound and fire resistance, and it creates a seamless, hard surface ideal for modern homes or those built with solid block or brickwork
Blocking the iris aperture in a camera will make the resulting image darker (underexposed)and increase the depth of field(making more of the scene appear in focus). If the blockage is partial or off-center, it may also introduce image artifacts or vignetting.
A lens cap is a crucial accessory that protects your camera lens from dust, scratches, fingerprints, and physical damage. They are available in various styles, including front caps, rear caps, and body caps, designed for different parts of your gear.
GEARING UP
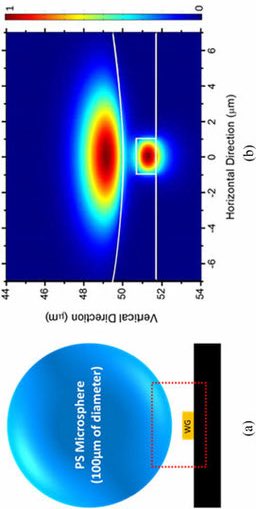
An ultrasound lens, also called an acoustic lens, is a component in an ultrasound transducer that focuses the sound beam to improve image resolution and clarity. It works similarly to an optical lens, but for sound waves, directing them to a specific focal depth. These lenses can be made of various materials, such as silicone or polymer, and some newer designs are even 3D-printed or incorporate liquid to allow for adjustable focus.
•Liquid acoustic lenses: These offer the advantage of being able to adjust the focus depth by changing the liquid volume within the lens.
Liquid acoustic lenses use two immiscible liquids, such as oil and water, to focus sound waves by deforming the interface between them with an acoustic radiation force from a transducer. This makes them tunable variable-focus lenses, unlike fixed-focus solid acoustic lenses. They are useful in applications like photoacoustic microscopy and imaging because of their adjustable focal length, fast response, and low acoustic impedance.
How they work
•Structure: A liquid acoustic lens is typically a cylindrical cell with two liquids that don't mix, like degassed water and silicone oil.
•Interface as a lens: The interface between the two liquids acts as the lens surface.
•Acoustic radiation force: An ultrasound transducer, often piezoelectric, is used to generate acoustic waves. The difference in acoustic energy density between the two liquids causes an acoustic radiation force to push and deform the liquid interface.
•Variable focus: By controlling the voltage to the transducer, the shape of the interface can be changed, which alters the lens's focal length and allows for rapid focusing adjustments.
How they work
•Structure: A liquid acoustic lens is typically a cylindrical cell with two liquids that don't mix, like degassed water and silicone oil.
•Interface as a lens: The interface between the two liquids acts as the lens surface.
•Acoustic radiation force: An ultrasound transducer, often piezoelectric, is used to generate acoustic waves. The difference in acoustic energy density between the two liquids causes an acoustic radiation force to push and deform the liquid interface.
•Variable focus: By controlling the voltage to the transducer, the shape of the interface can be changed, which alters the lens's focal length and allows for rapid focusing adjustments.
An acoustic shockwave lens is a device used to focus acoustic shockwaves, such as those used in extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) for breaking up kidney stones or in some therapeutic applications
A HAMMERING NOISE
It shapes the shockwave to converge at a focal point
The circle of least confusion is the smallest, most focused circular patch of light in an optical system that cannot achieve a perfect point focus due to aberrations like astigmatism or spherical aberration.
Lens prescriptions: The location of the circle of least confusion is equivalent to the spherical equivalent of the prescription, which is calculated as:


•Photography: It is used in photography to describe the smallest blur spot a lens can create, which can be a compromise between different focusing planes to achieve the best possible sharpness.
•Microscopy: In electron microscopy, it's the point where chromatic aberration is minimized, and the image plane is located
•Microscopy: In electron microscopy, it's the point where chromatic aberration is minimized, and the image plane is located
The circle of least confusion(CLC) is the smallest possible cross-sectional area of a conical beam of light (or other radiation) formed by an optical system, occurring at the point of best focus where the effects of aberrations are minimized
Beam Collimation: In systems for beam collimation, the point source is placed at the position of the CLC to achieve the most parallel beam possible
Maser beam collimation refers to the process of focusing the amplified microwave, radio, or infrared radiation into a highly parallel beam. This process and the resulting beam characteristics are relevant in both laboratory maser technology and the study of naturally occurring astrophysical masers
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh