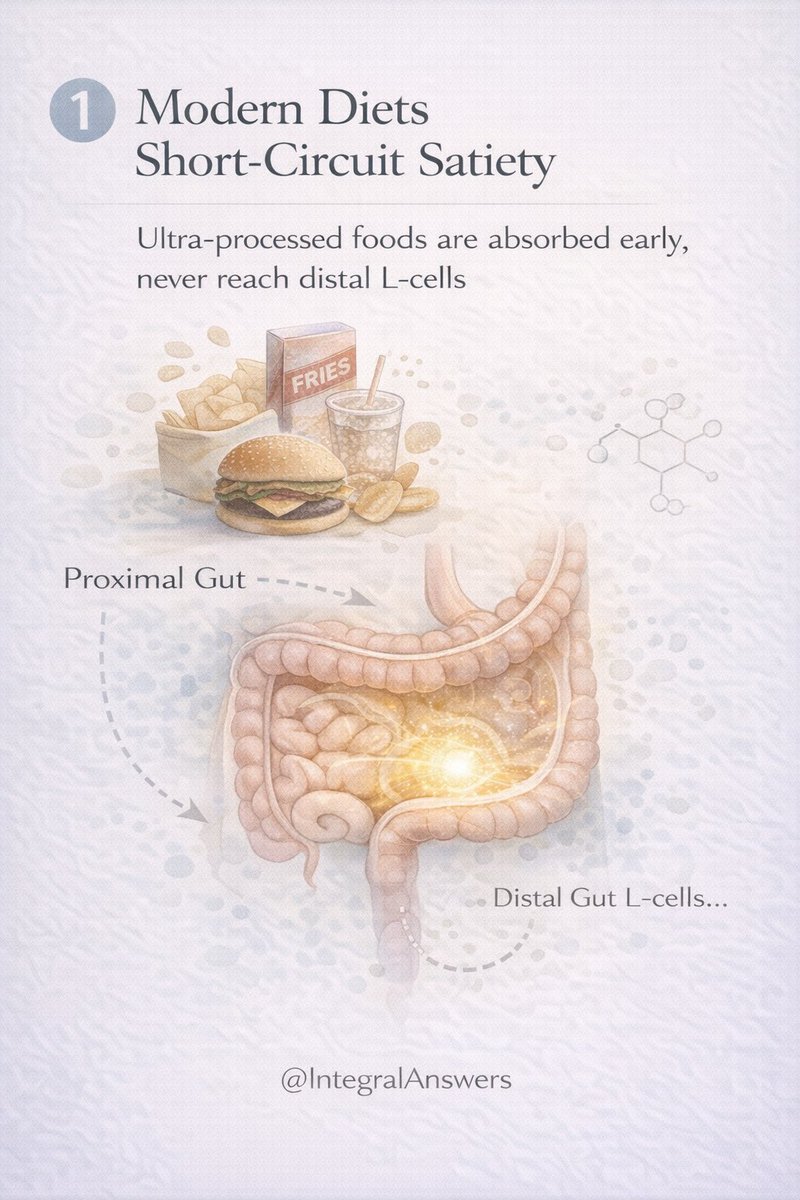
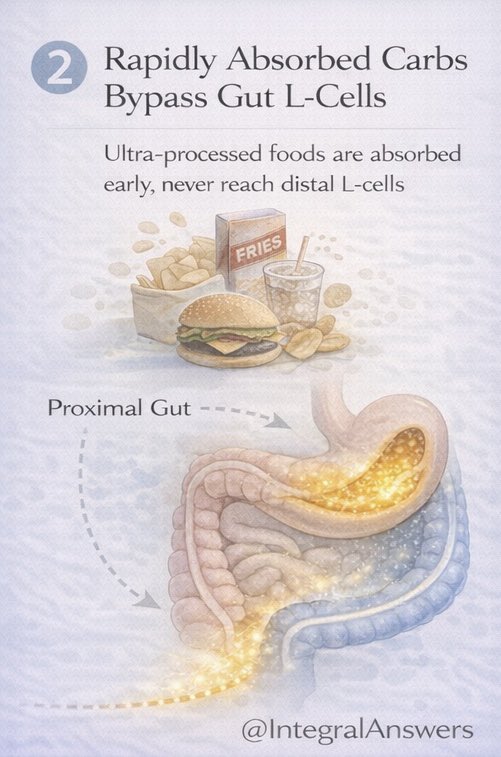
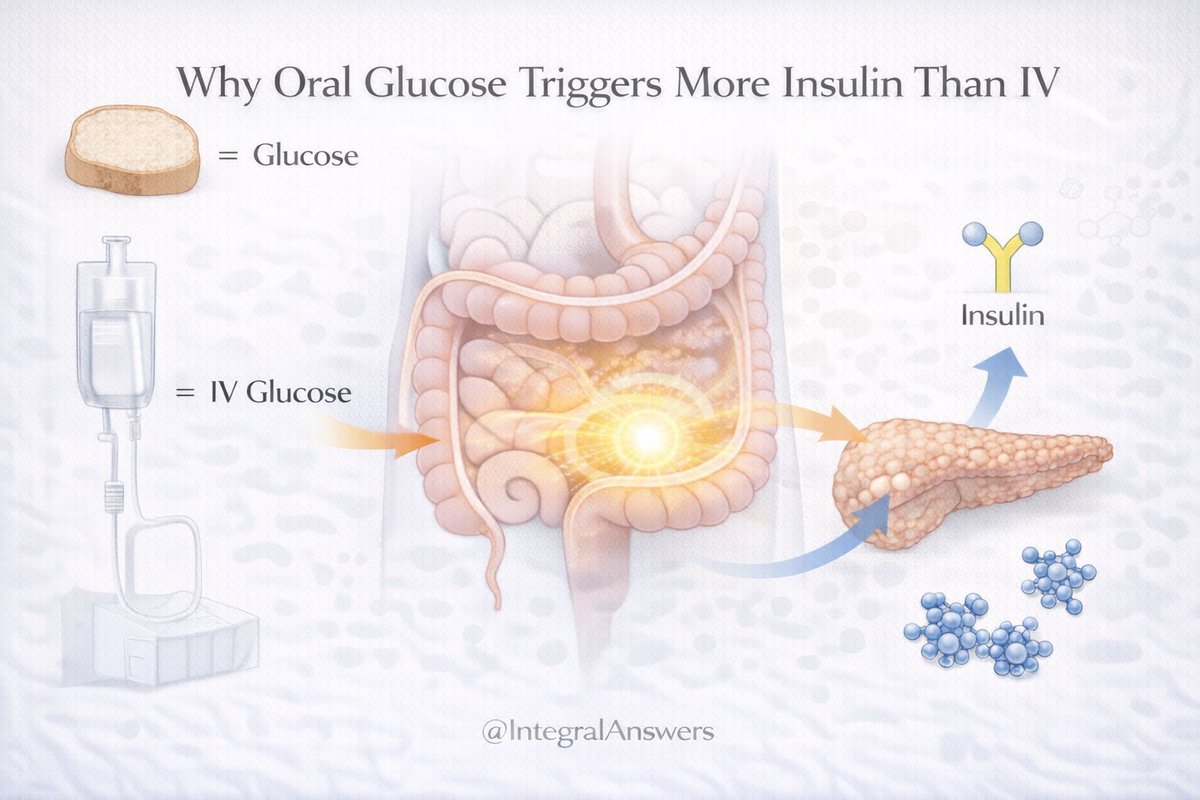
1/ How did life begin?
Abiogenesis is the idea that life arose from non-living chemistry on early Earth — step by step, not all at once.
Understanding these steps helps explain why life is the expected outcome of the right conditions.
Abiogenesis is the idea that life arose from non-living chemistry on early Earth — step by step, not all at once.
Understanding these steps helps explain why life is the expected outcome of the right conditions.
2/ Early Earth Context
Earth 4 billion years ago wasn’t a calm blue world. It was a high-energy chemical laboratory — lightning, volcanoes, intense UV, and oceans full of reactive molecules. The environment constantly pushed chemistry forward.
Earth 4 billion years ago wasn’t a calm blue world. It was a high-energy chemical laboratory — lightning, volcanoes, intense UV, and oceans full of reactive molecules. The environment constantly pushed chemistry forward.

3/ Formation of Simple Organics
When energy hits the right ingredients, simple organic molecules form easily.
We’ve replicated this in labs: spark discharges, UV light, and mineral surfaces all drive the creation of amino acids and basic carbon compounds.
When energy hits the right ingredients, simple organic molecules form easily.
We’ve replicated this in labs: spark discharges, UV light, and mineral surfaces all drive the creation of amino acids and basic carbon compounds.

4/ Increasing Molecular Complexity
Once simple molecules exist, they start interacting. Wet–dry cycles, mineral surfaces, and heat all promote bonding.
Over countless cycles, chemistry naturally drifts toward more complex, information-rich molecules.
Once simple molecules exist, they start interacting. Wet–dry cycles, mineral surfaces, and heat all promote bonding.
Over countless cycles, chemistry naturally drifts toward more complex, information-rich molecules.
5/ Why RNA Matters
Before DNA and proteins, early life likely relied on molecules that could both store information and catalyze reactions. RNA fits that role beautifully — and in modern cells, it still carries out ancient catalytic tasks.
Before DNA and proteins, early life likely relied on molecules that could both store information and catalyze reactions. RNA fits that role beautifully — and in modern cells, it still carries out ancient catalytic tasks.
6/ The Breakthrough: Replication
Life requires replication, but it doesn’t need perfection at first. Early replicators probably copied themselves poorly, but “good enough” to let variation creep in — and variation is the fuel of natural selection.
Life requires replication, but it doesn’t need perfection at first. Early replicators probably copied themselves poorly, but “good enough” to let variation creep in — and variation is the fuel of natural selection.

7/ Chemical Natural Selection
Even before cells existed, chemical systems competed. Some used energy more effectively, persisted longer, or copied with fewer errors. Chemistry doesn’t need intent — natural selection emerges anywhere replication + variation exist.
Even before cells existed, chemical systems competed. Some used energy more effectively, persisted longer, or copied with fewer errors. Chemistry doesn’t need intent — natural selection emerges anywhere replication + variation exist.

8/ Replication + variation = competition.
Systems that were better at surviving and making copies outcompeted others.
Natural selection began long before the first cell existed.
Systems that were better at surviving and making copies outcompeted others.
Natural selection began long before the first cell existed.

9/ Do scientists have every step solved? No. But we’ve recreated many ingredients in the lab: amino acids, nucleotides, lipid bubbles, simple replicators. Nothing requires magic — just chemistry, energy, and deep time. 

10/ Abiogenesis doesn’t compete with evolution — it precedes it.
Chemistry → self-replication → selection → cells.
Once the first cell existed, evolution reshaped life endlessly.
Want to explore more? See the reference card below.
Chemistry → self-replication → selection → cells.
Once the first cell existed, evolution reshaped life endlessly.
Want to explore more? See the reference card below.

@LyingWrongAgain let me know how I did in creating a simple overview?
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh