New study indicates that a decrease in nerve cell cholesterol caused by cortisol, inflammation & low SIRT1 activity may be a cause of major depression.
So, do statins exacerbate depression?
And since SIRT1 is NAD⁺-dependent, could NAD⁺ boosters treat or prevent depression? …🧵
So, do statins exacerbate depression?
And since SIRT1 is NAD⁺-dependent, could NAD⁺ boosters treat or prevent depression? …🧵
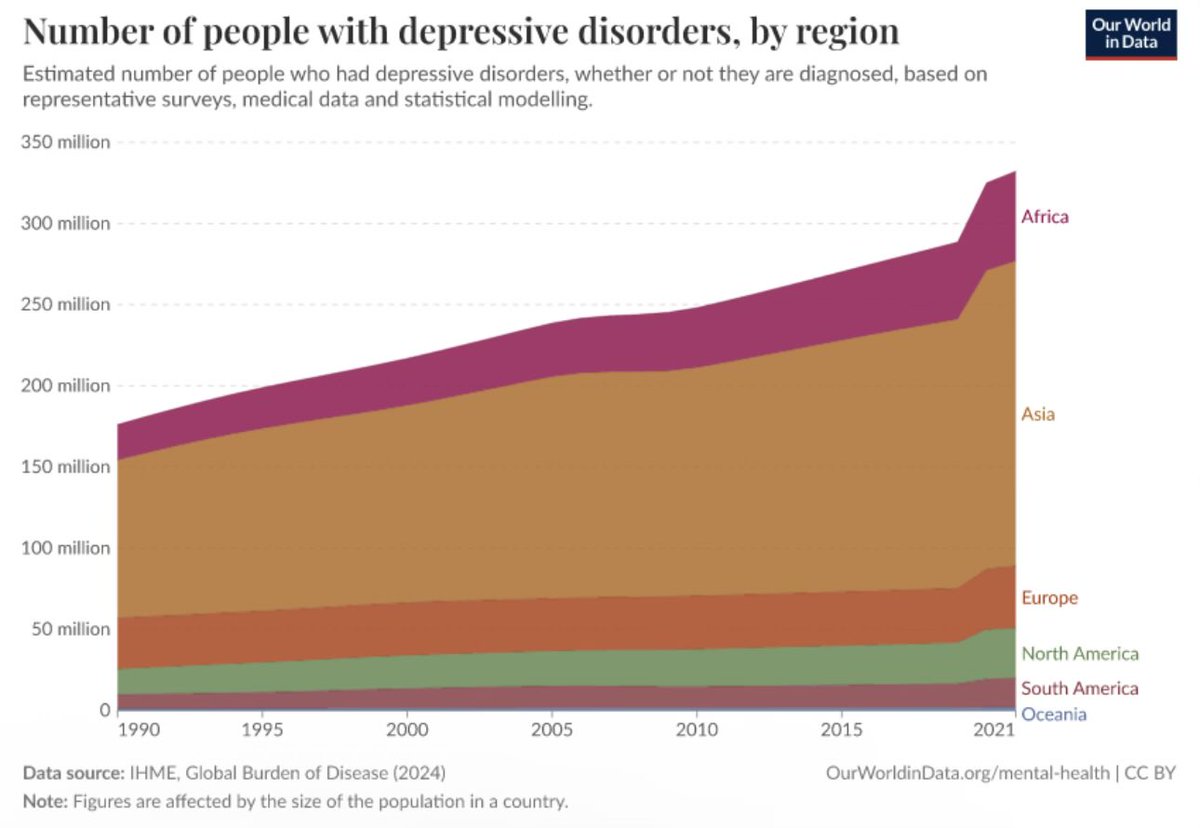
Around 5–5.7% of adults worldwide experience depressive disorders at any given time. >280 million people! 
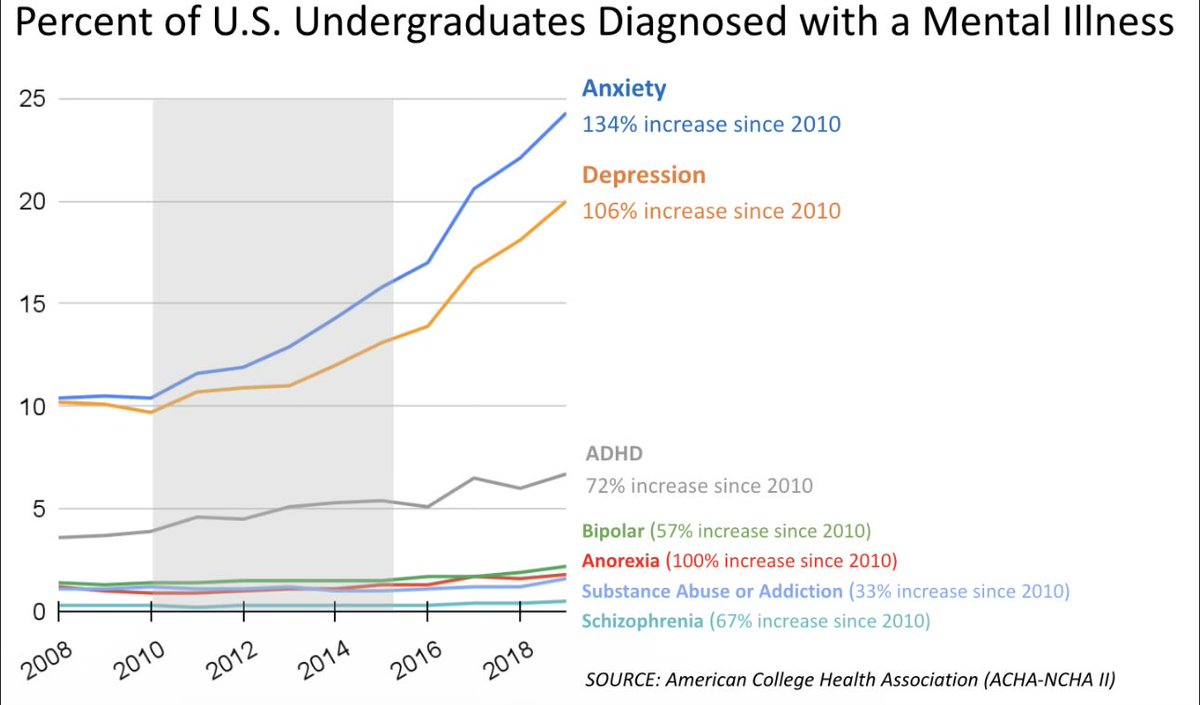
Lifetime depression diagnoses in the U.S. have risen. ~29% report ever being diagnosed, up from ~20% a decade ago 
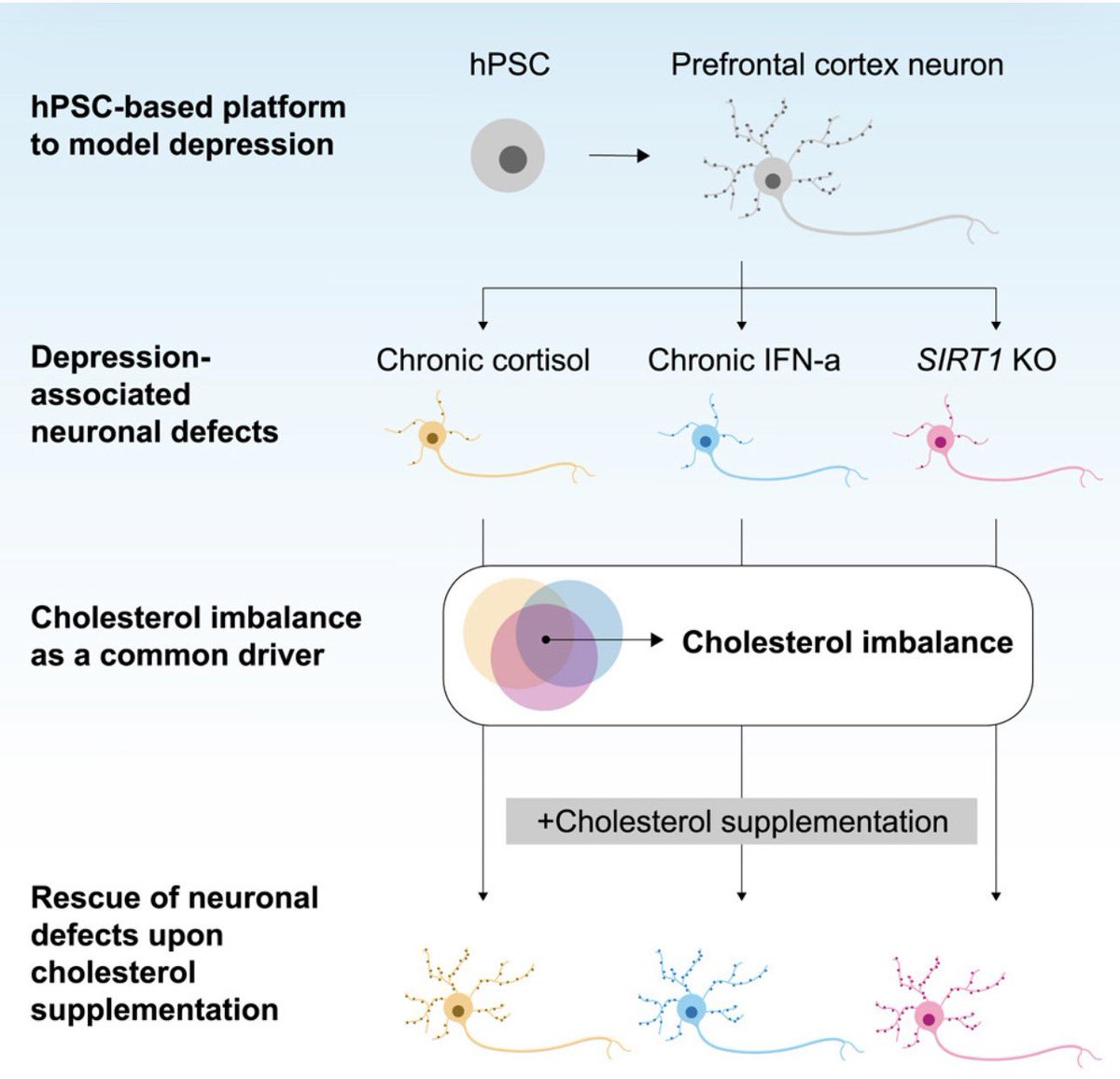
Using human stem cell–derived prefrontal cortex neurons, the authors modeled 3 major risk factors: chronic cortisol (stress), interferon-α (inflammation), and loss of SIRT1, a longevity-linked NAD⁺-dependent deacetylase 
Strikingly, all three caused the same phenotype: dendritic atrophy, synapse loss, reduced glutamate signaling, and neuronal hypoactivity
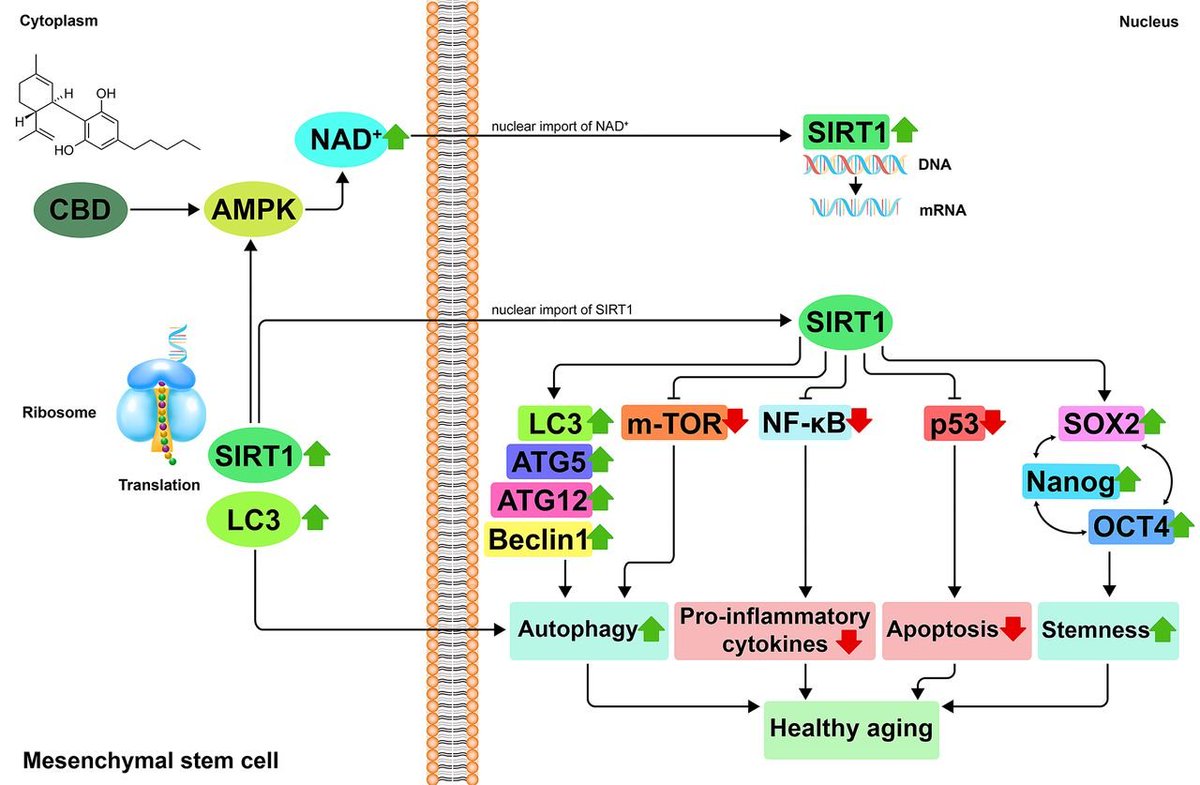
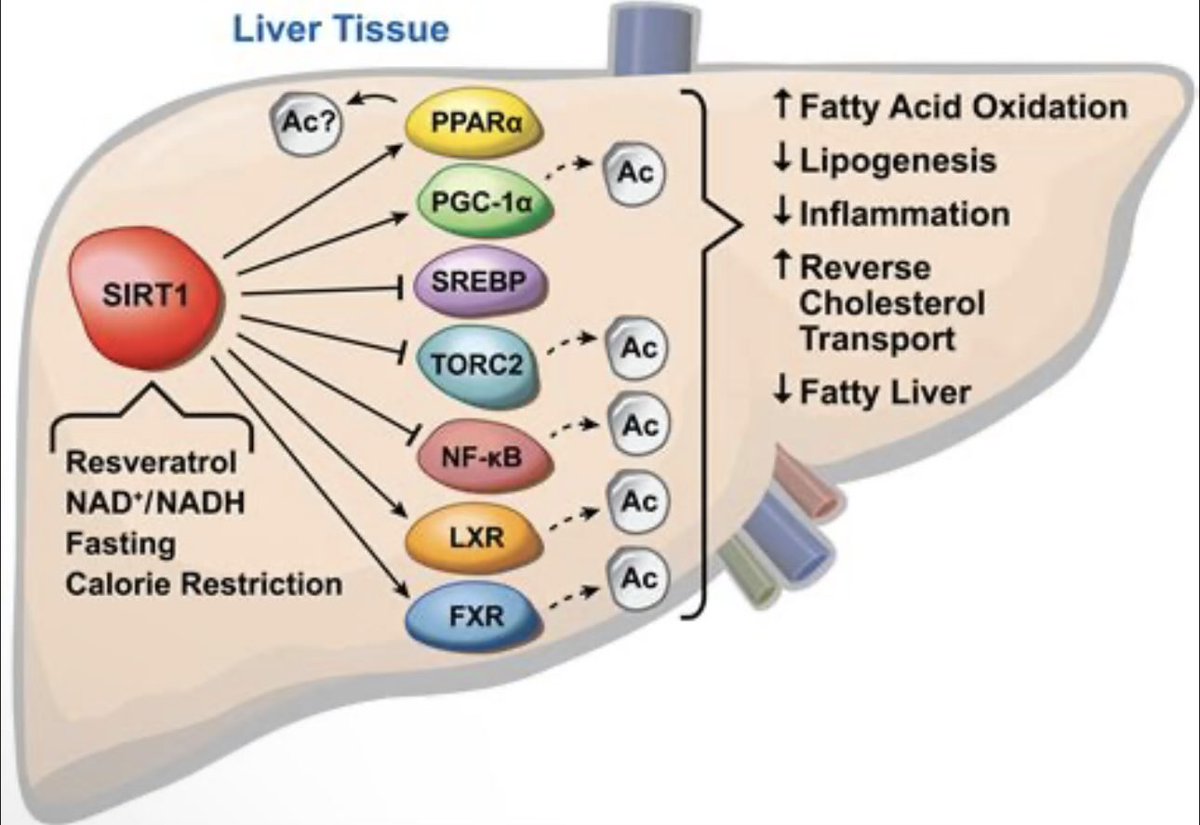
SIRT1 loss alters expression of cholesterol synthesis & transport, reducing membrane cholesterol and impairing synaptic function. This links metabolism, epigenetics, and mood
Lowering cholesterol in healthy neurons reproduced depression-like defects. Conversely, restoring cholesterol rescued synapses and glutamate responses across all models
This study raises a testable idea: could NAD⁺ precursors (NR, NMN, etc.) help restore SIRT1 activity, normalize neuronal cholesterol, and improve synaptic function in subsets of major depressive disorder?
NMN has been reported to improve depression-like behaviors in stress/corticosterone models in mice. Translation to humans is not known
There are mouse studies suggesting another NAD precursor NR can reduce depression-like behaviors in specific contexts
In my experience, NMN has improved my mood over the past 15 years - and clinical trials should be initiated to test it
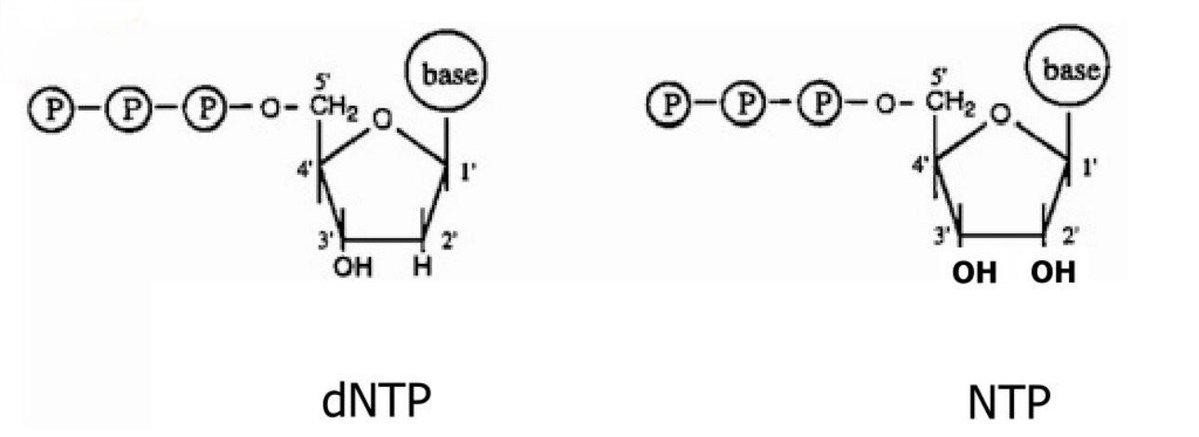
As to whether statins are a risk: possibly. Brain cholesterol is largely synthesized locally (by neurons and especially astrocytes). Peripheral cholesterol does not cross the blood–brain barrier in meaningful amounts
Lipophilic statins (e.g., simvastatin, lovastatin, atorvastatin/Lipitor) can cross the blood brain barrier. Hydrophilic statins (e.g., pravastatin, rosuvastatin/Crestor) cross poorly
Some studies show statins associating with depressive symptoms while others show no effect or even benefit (likely via anti-inflammatory or vascular effects)
A subset of individuals may be vulnerable to cholesterol-lowering drugs, especially if brain cholesterol or SIRT1/NAD⁺ are already altered by genetics, age, or disease
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh